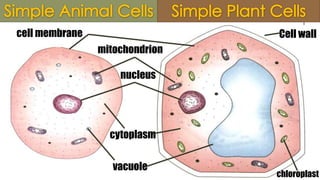
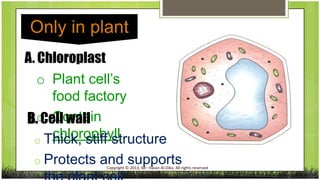
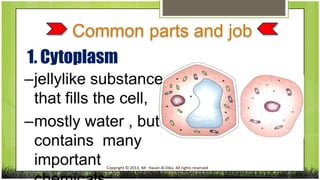
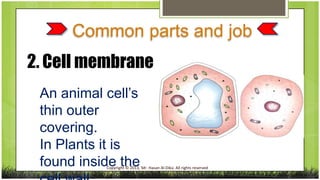
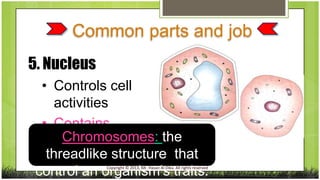
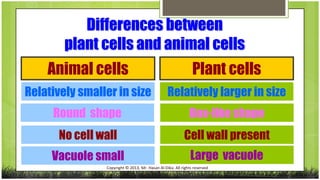
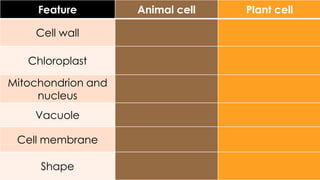
The document compares plant and animal cells, highlighting their similarities and differences in structure and function. Key components such as the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles are discussed, alongside their specific roles within the cells. Both types of cells share common features like the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria, but differ in size, shape, and presence of certain structures.