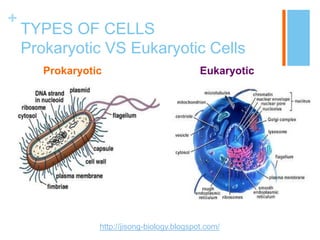
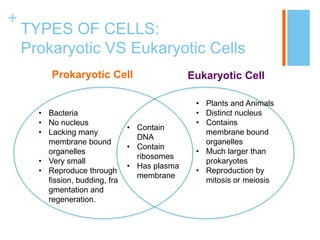
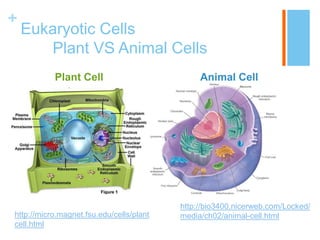
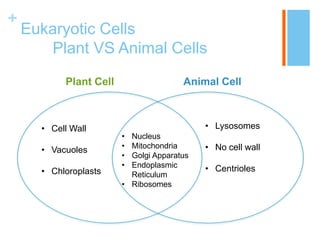
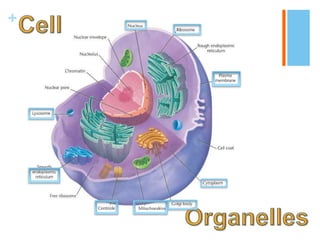
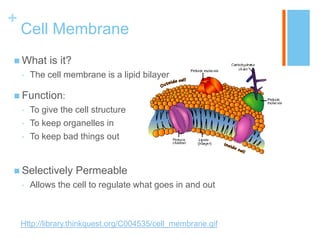
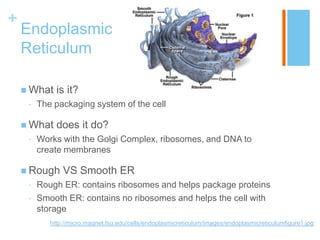
This document provides information about the structures and organelles found within plant and animal cells. It compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells. The main organelles of the animal cell are then described in more detail, including their structure and function. These organelles include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, centrioles, ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Pictures and citations are provided to support the information presented.