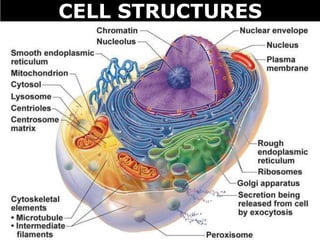
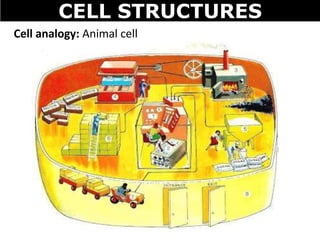
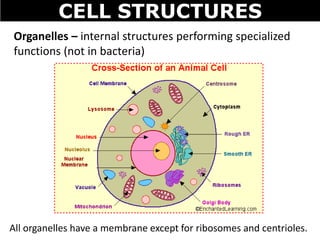
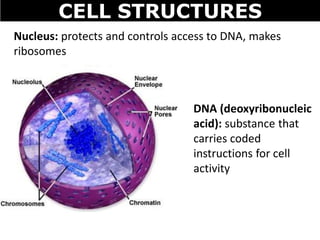
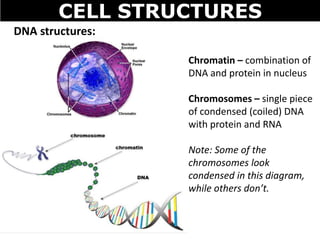
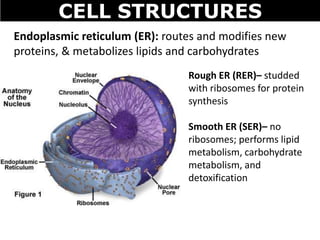
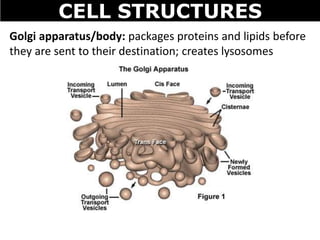
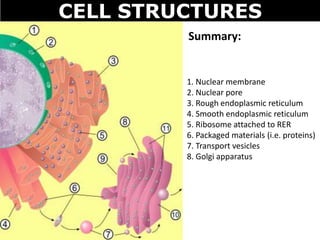
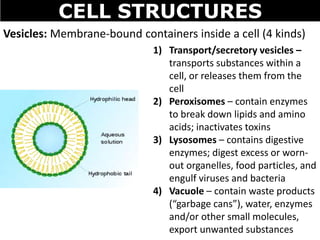
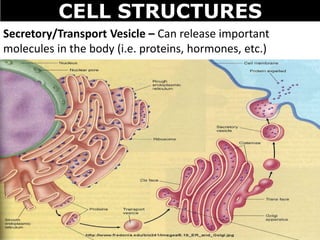
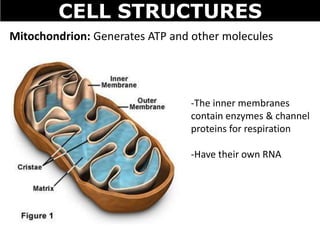
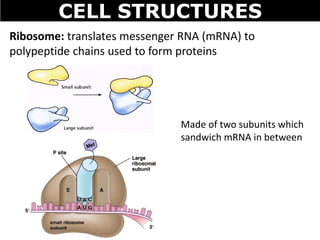
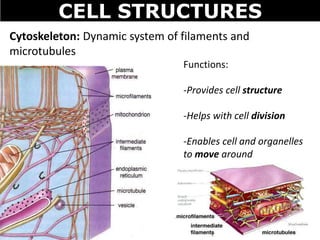
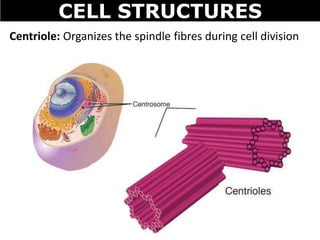
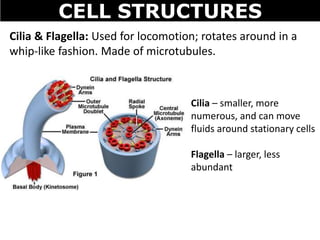
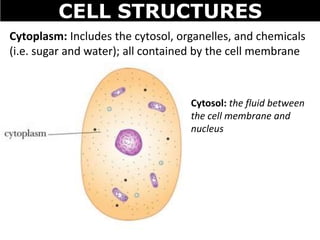
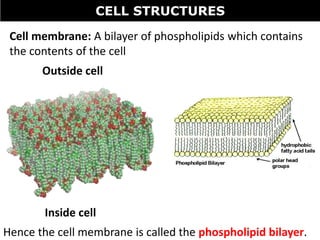
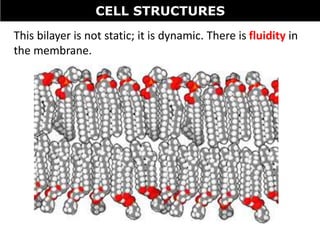
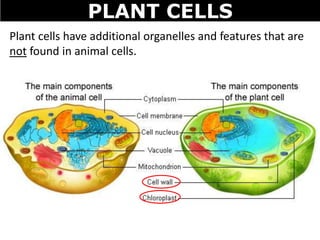
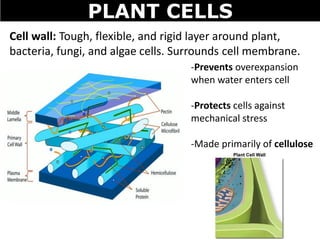
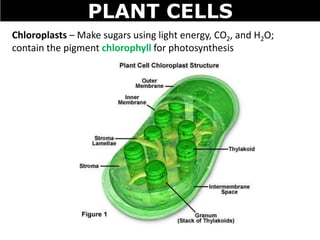
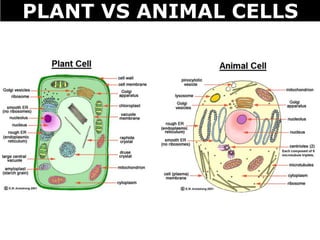
The document discusses the structures and components of animal and plant cells. It describes the cell theory that all living things are made of cells, which are the basic unit of life that come from pre-existing cells. It then explains key organelles in animal cells like the nucleus that controls the cell, endoplasmic reticulum that modifies proteins, Golgi apparatus that packages cell components, mitochondria that generate energy, and ribosomes that produce proteins. Additional structures in plant cells include a cell wall for protection and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.