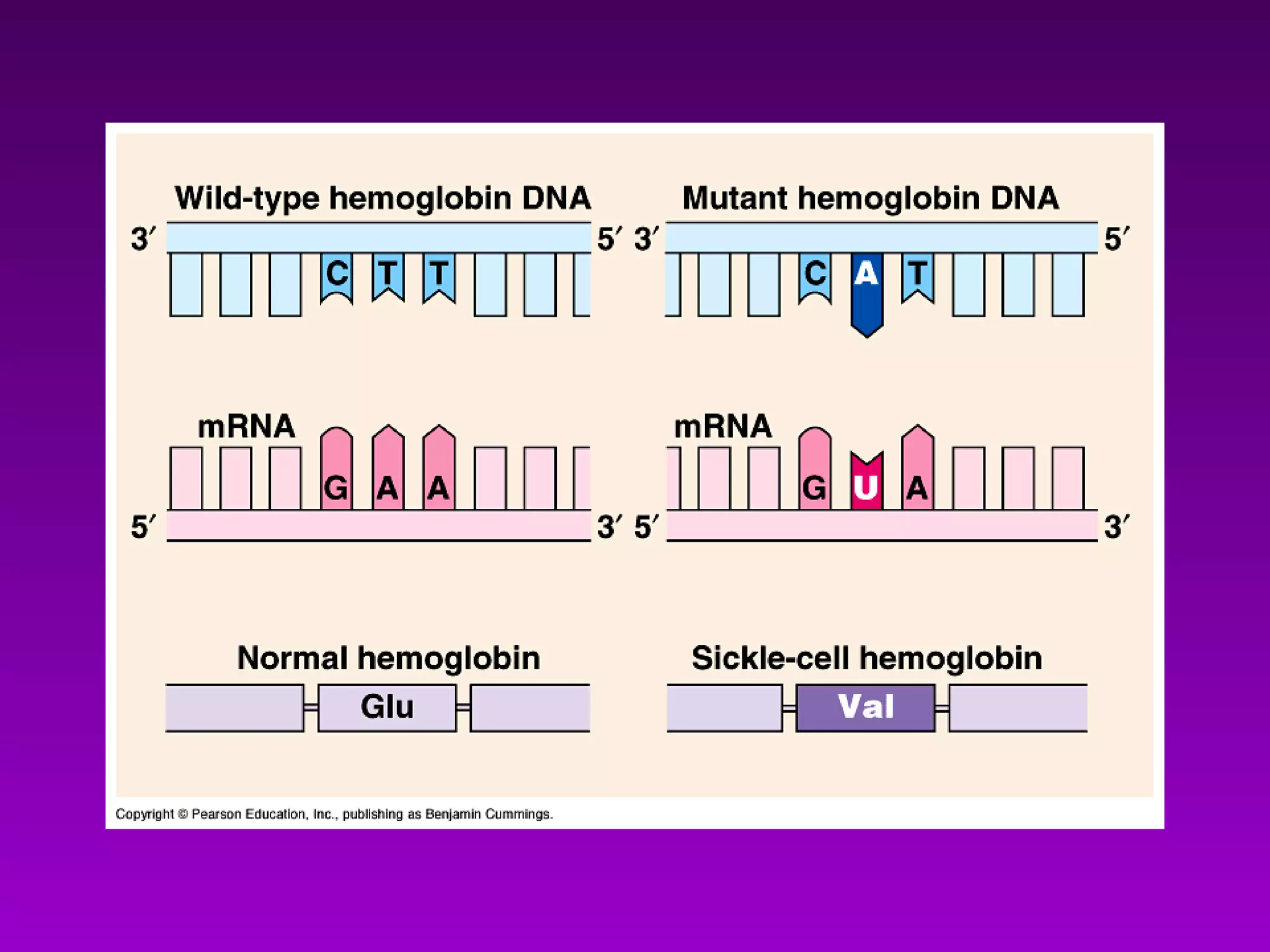
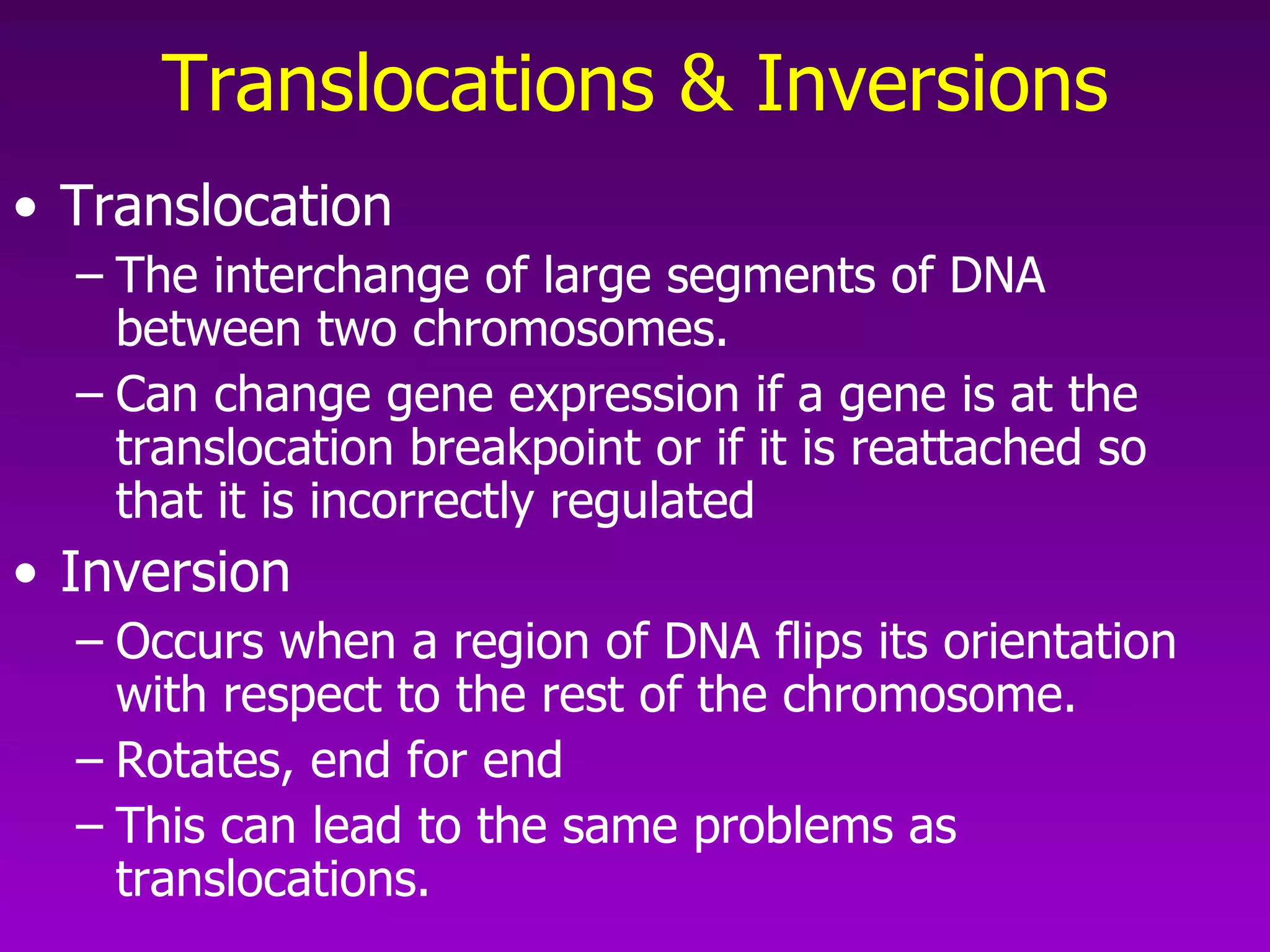
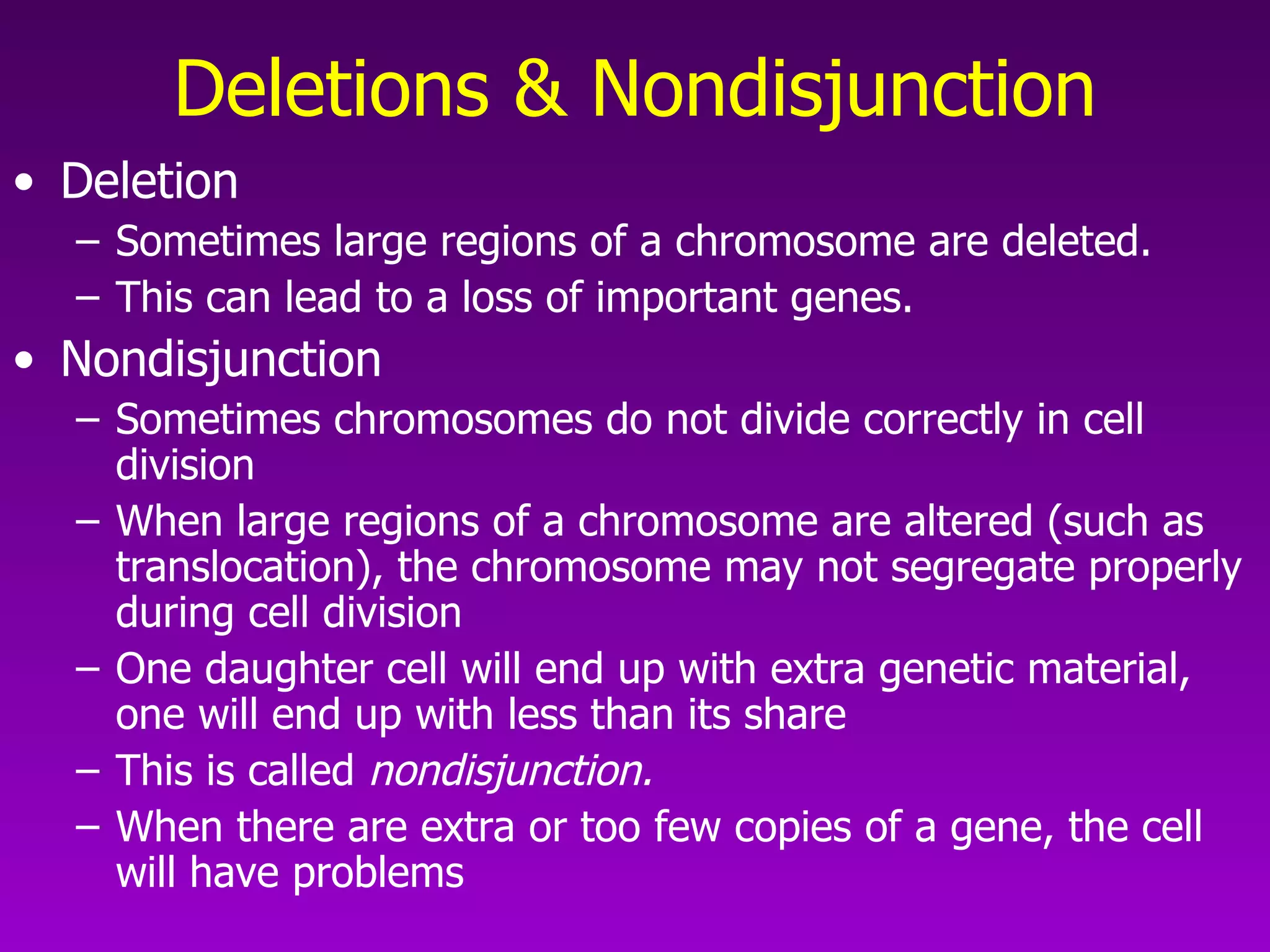
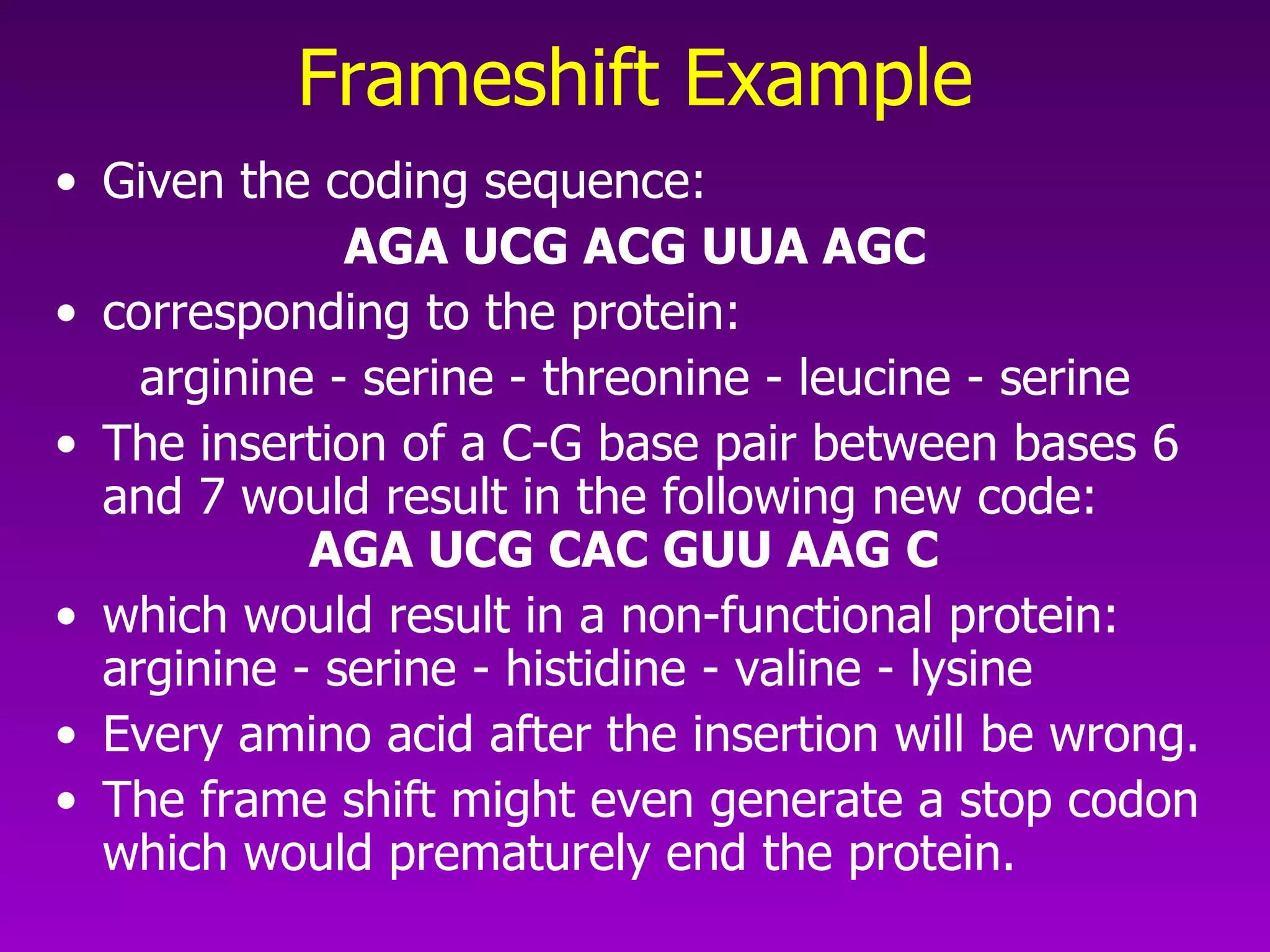
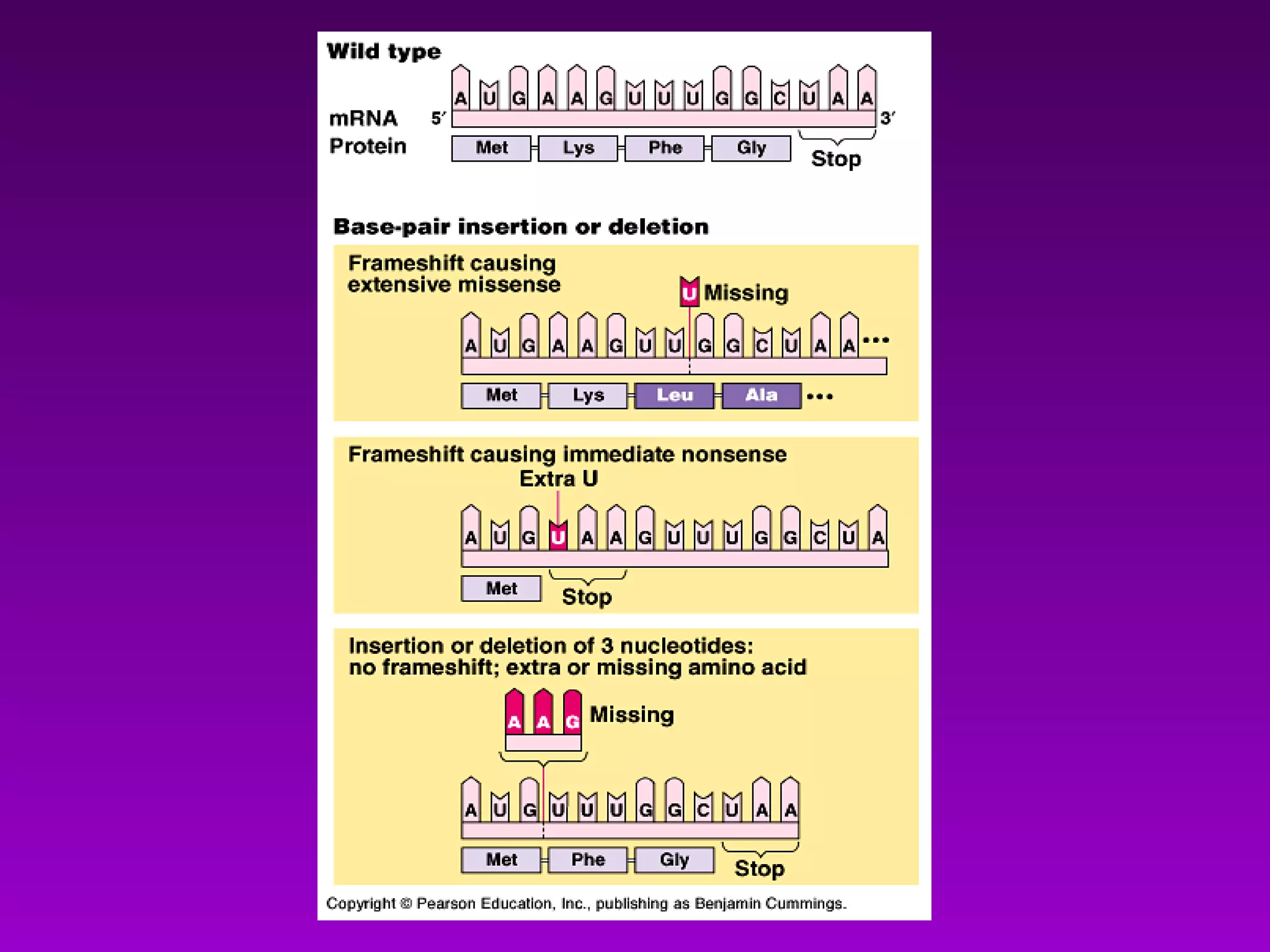
This document summarizes the process of gene expression from DNA to protein. It discusses:
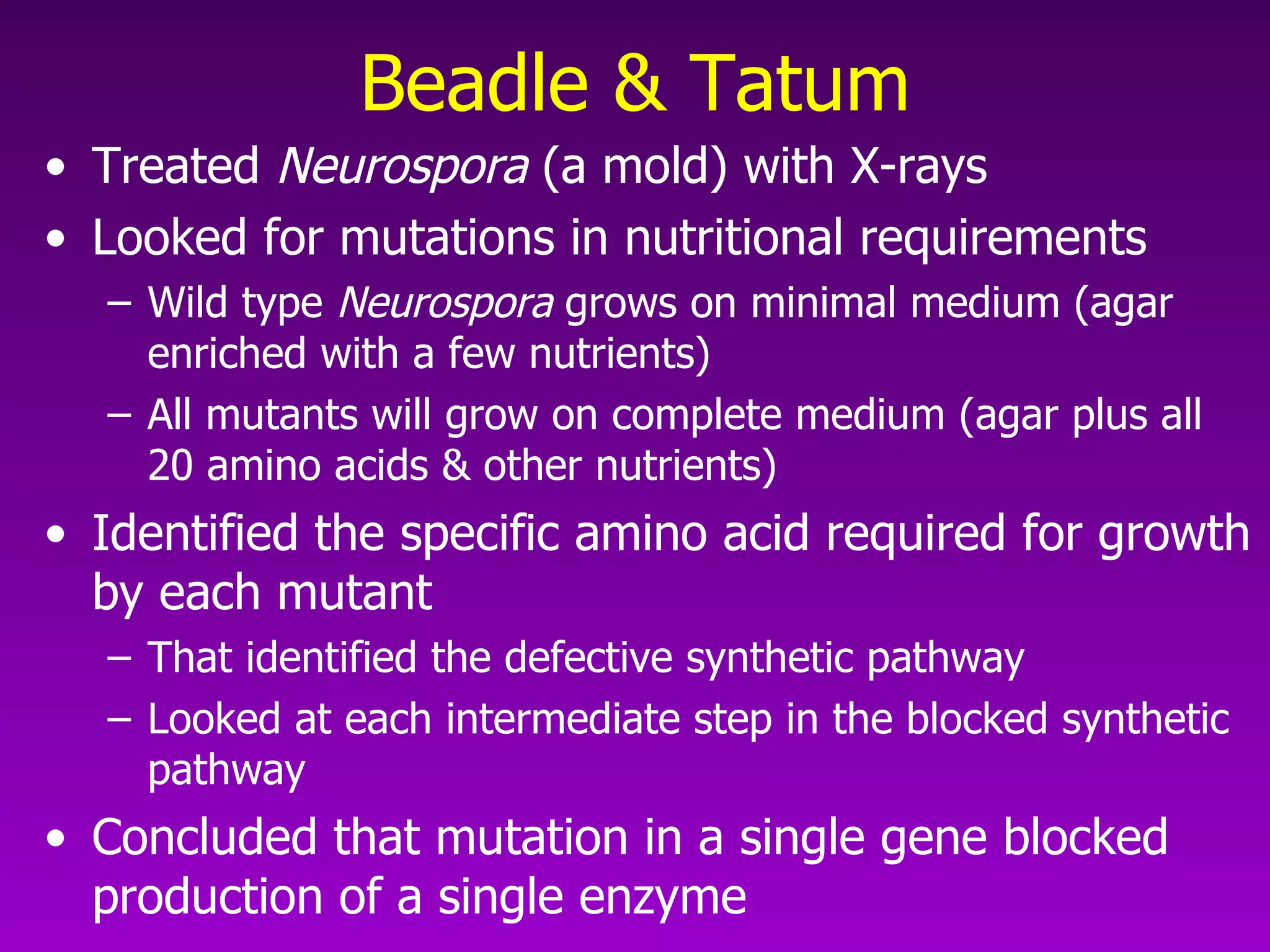
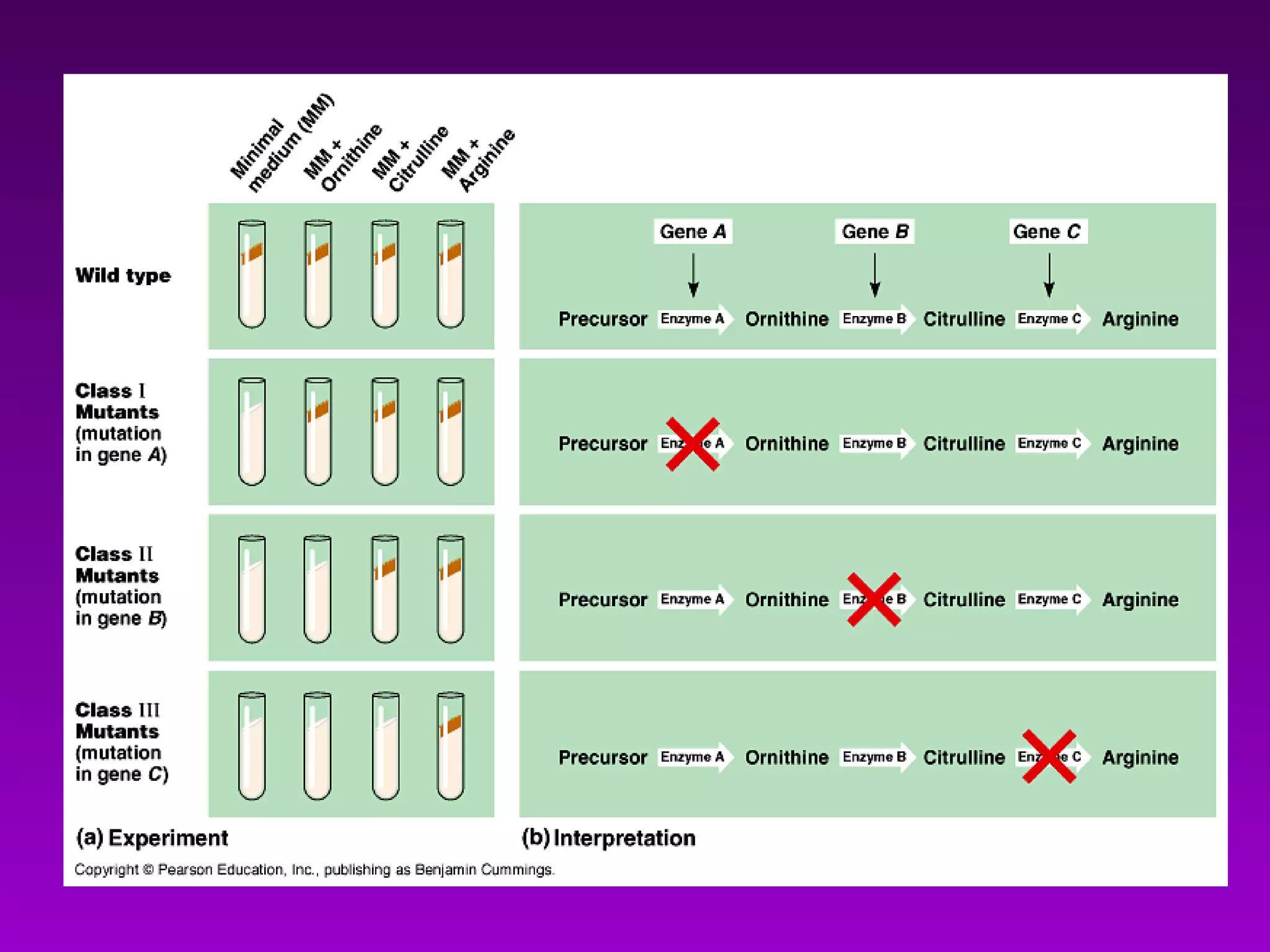
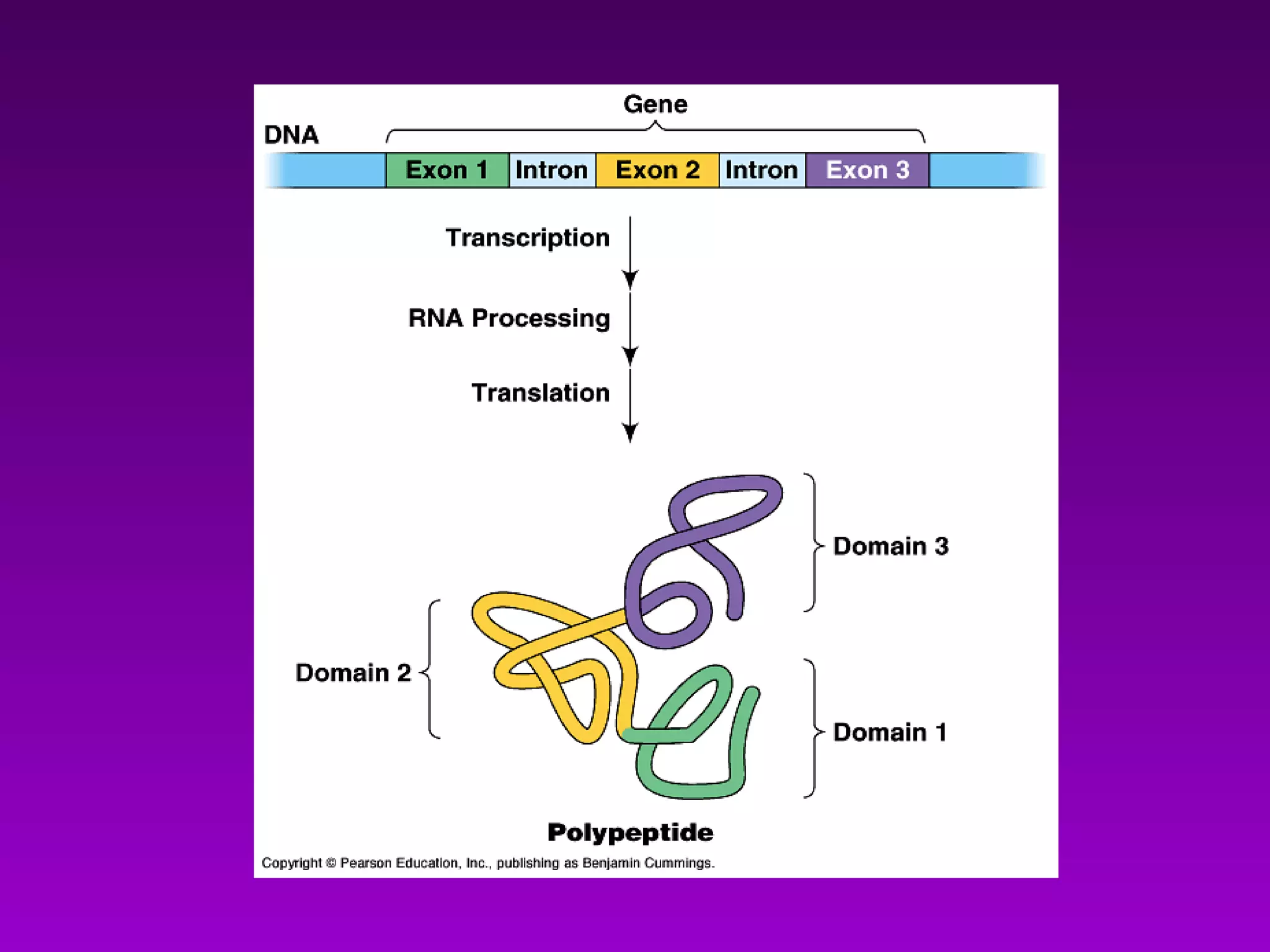
1) How early experiments established that genes encode proteins through RNA intermediates. One gene encodes one polypeptide.
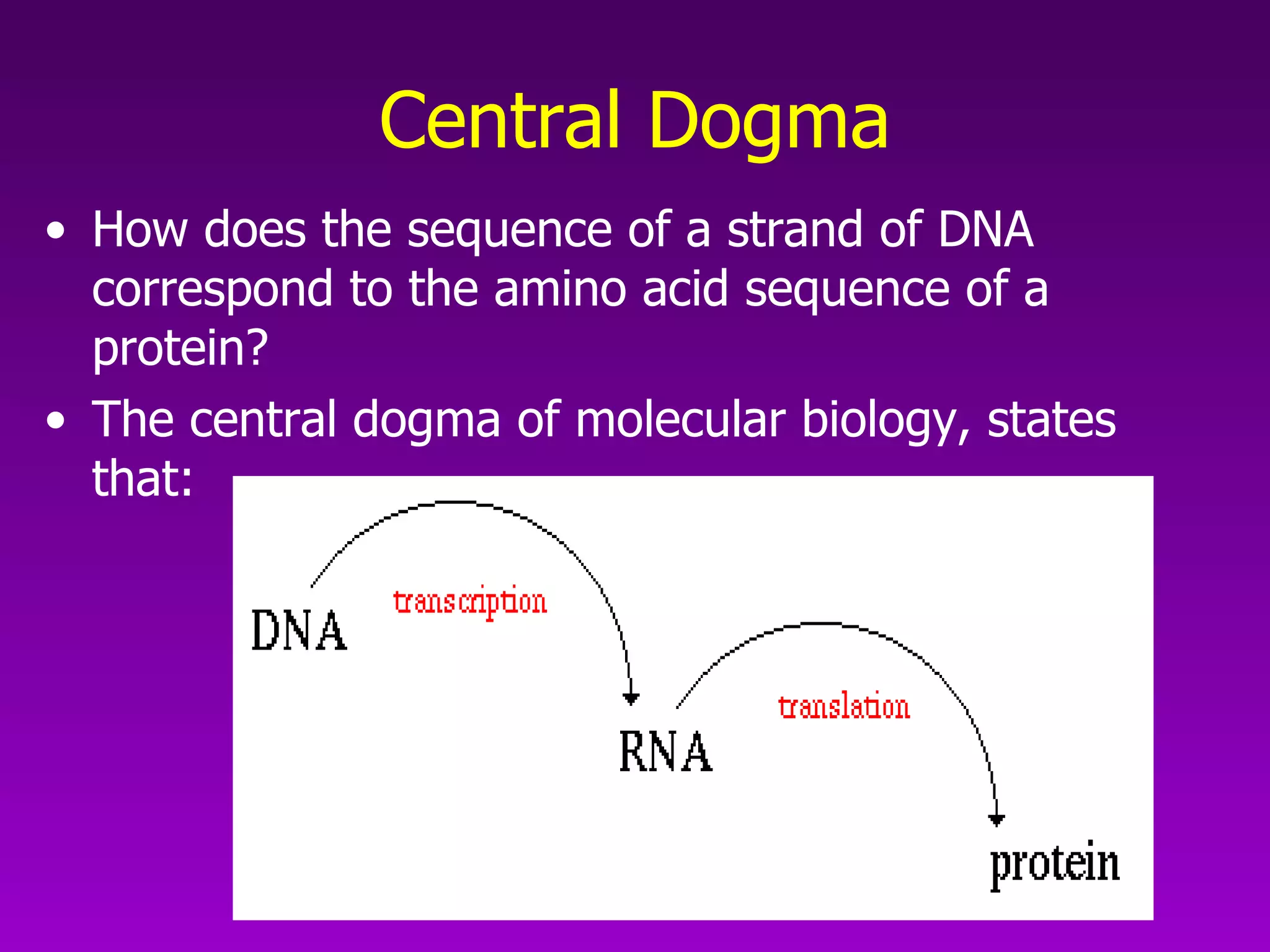
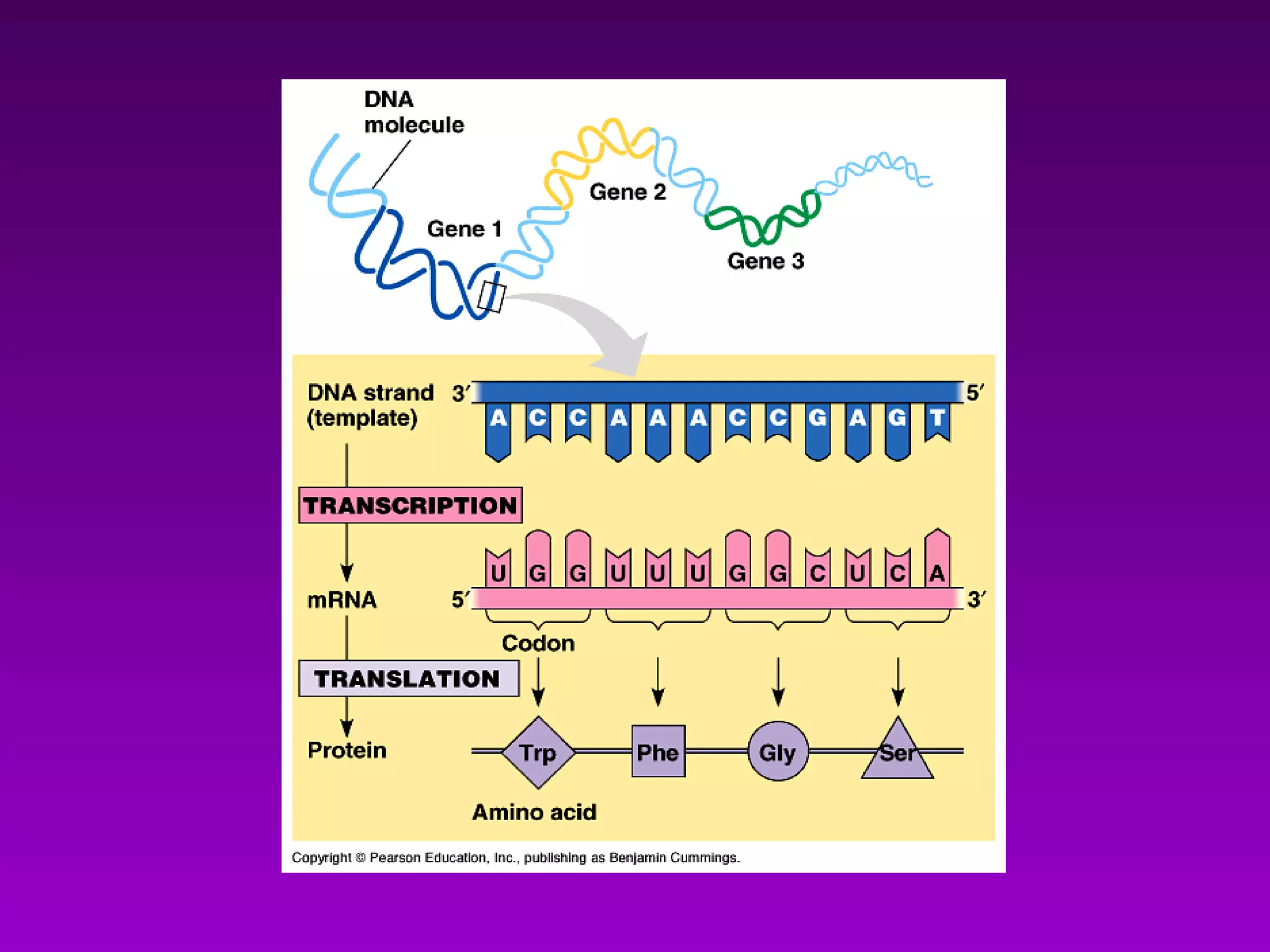
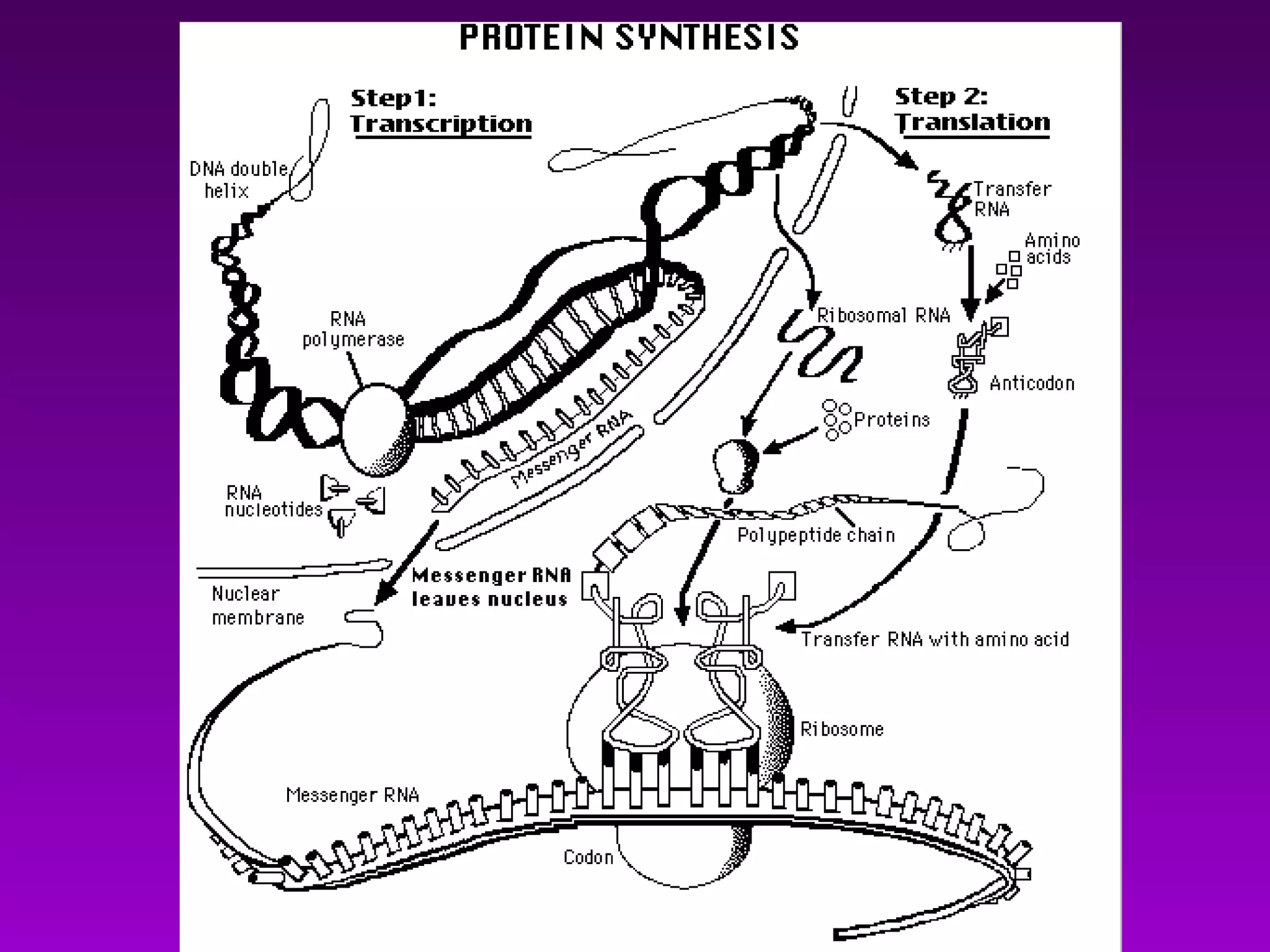
2) The "central dogma" of molecular biology - that DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into protein. RNA acts as an intermediate to protect DNA and allow for gene regulation.
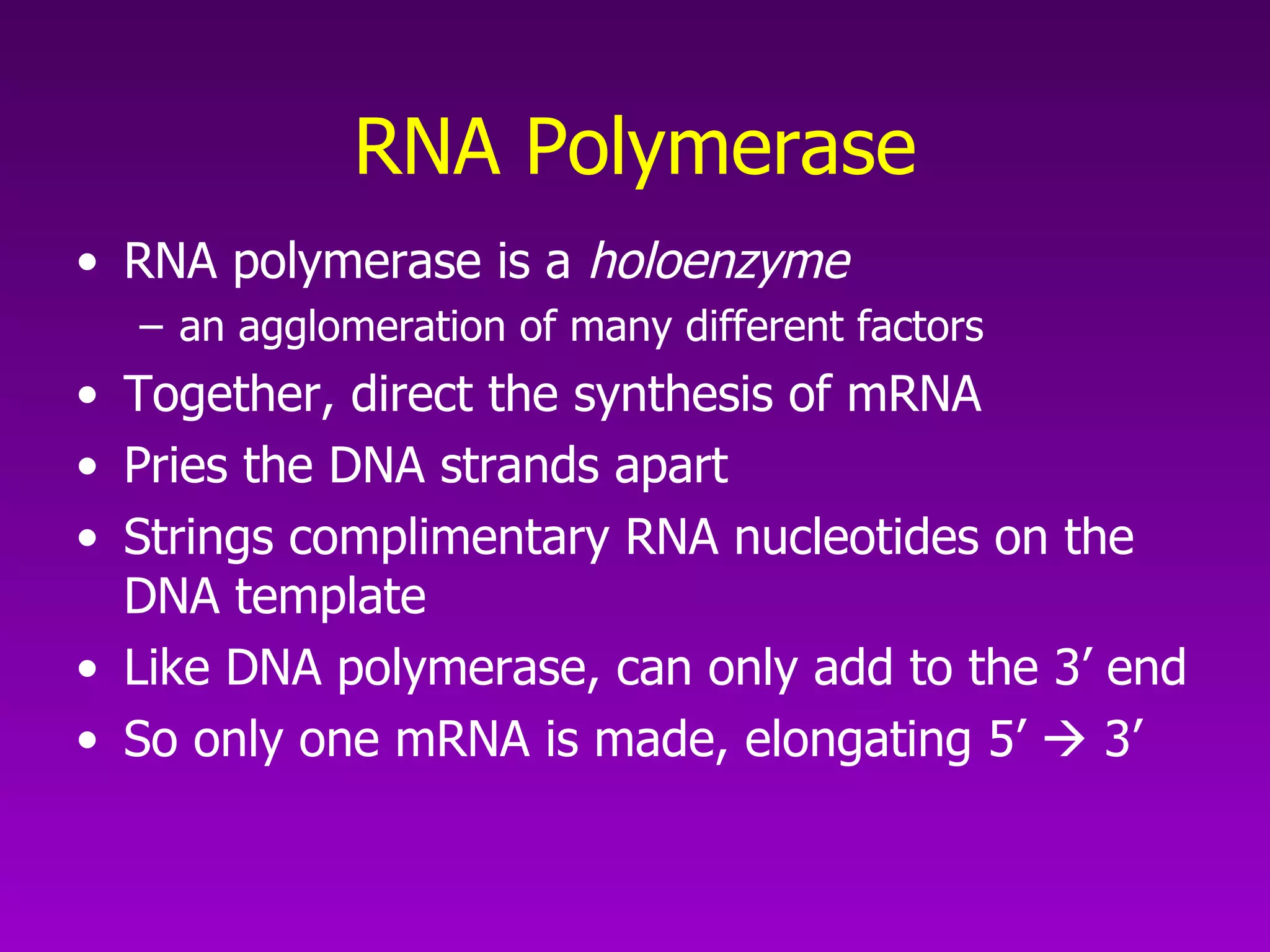
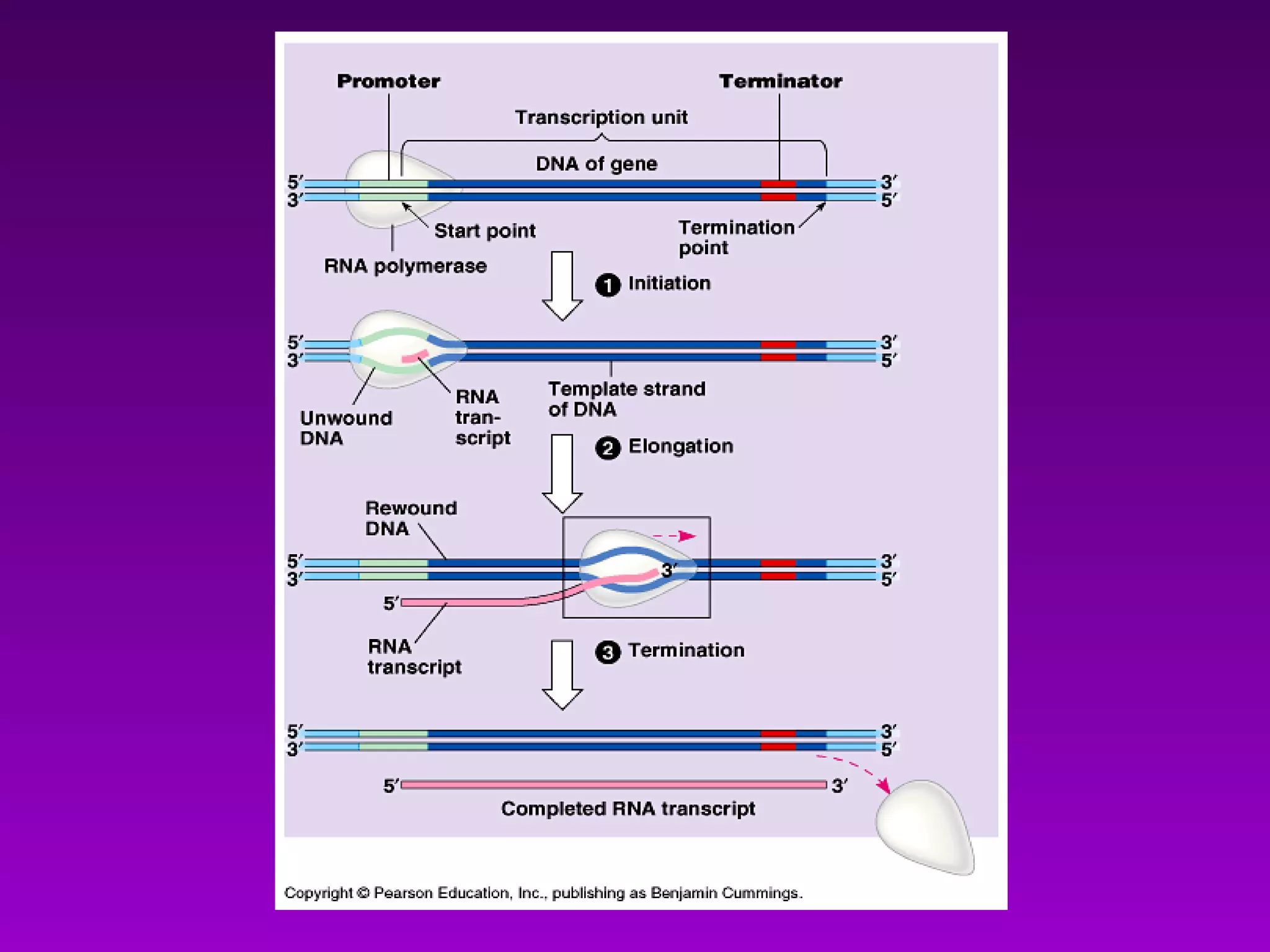
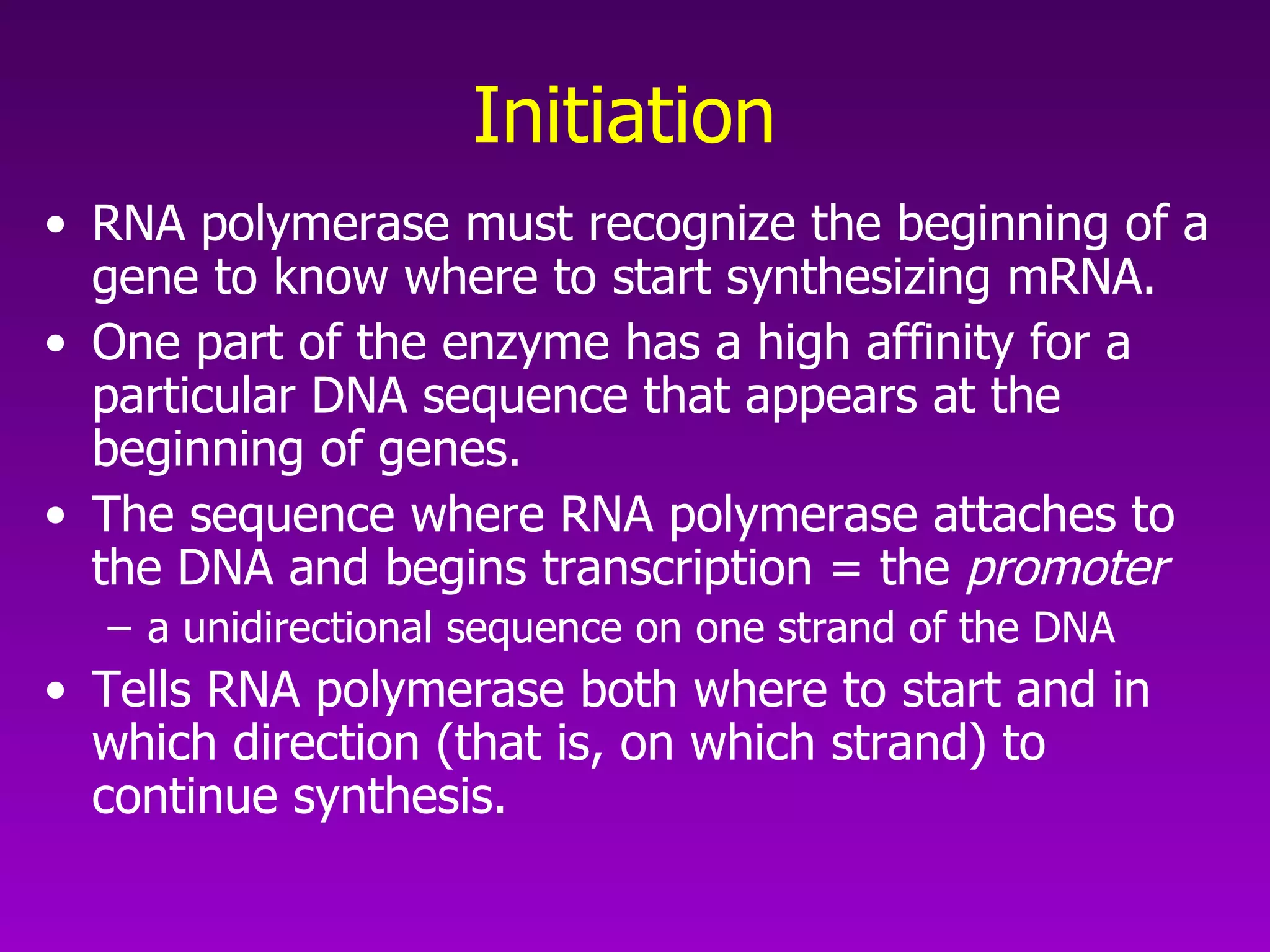
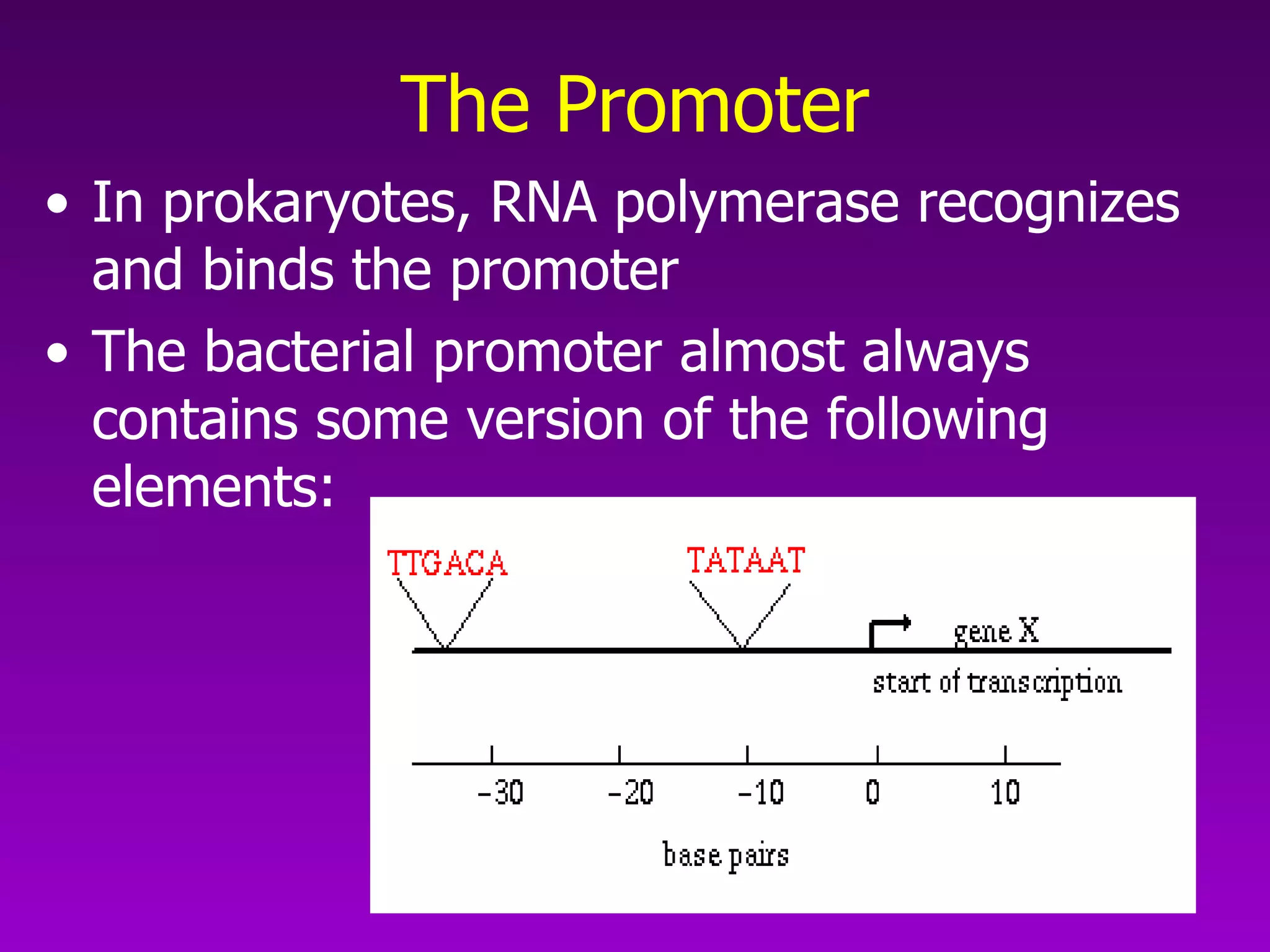
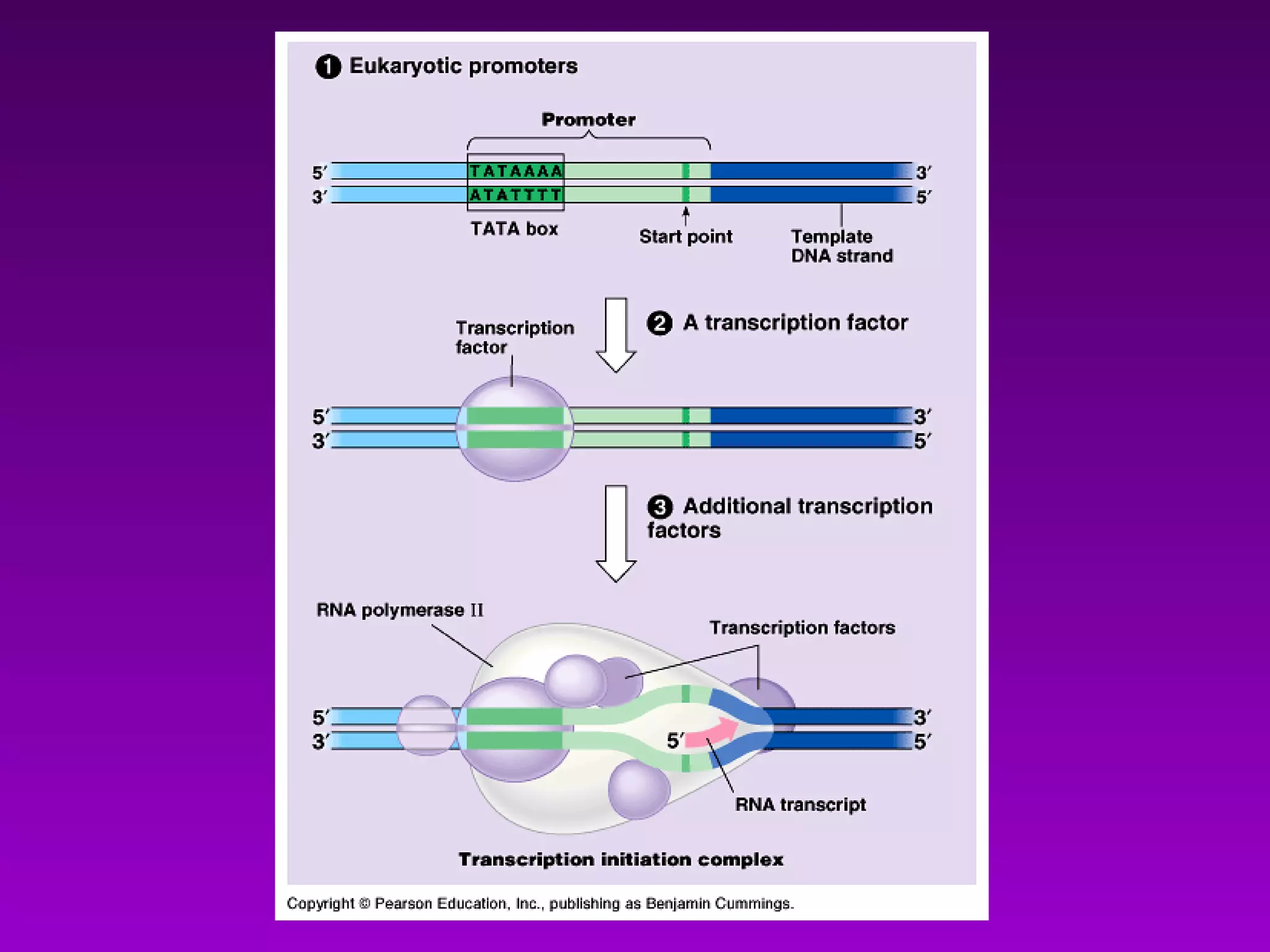
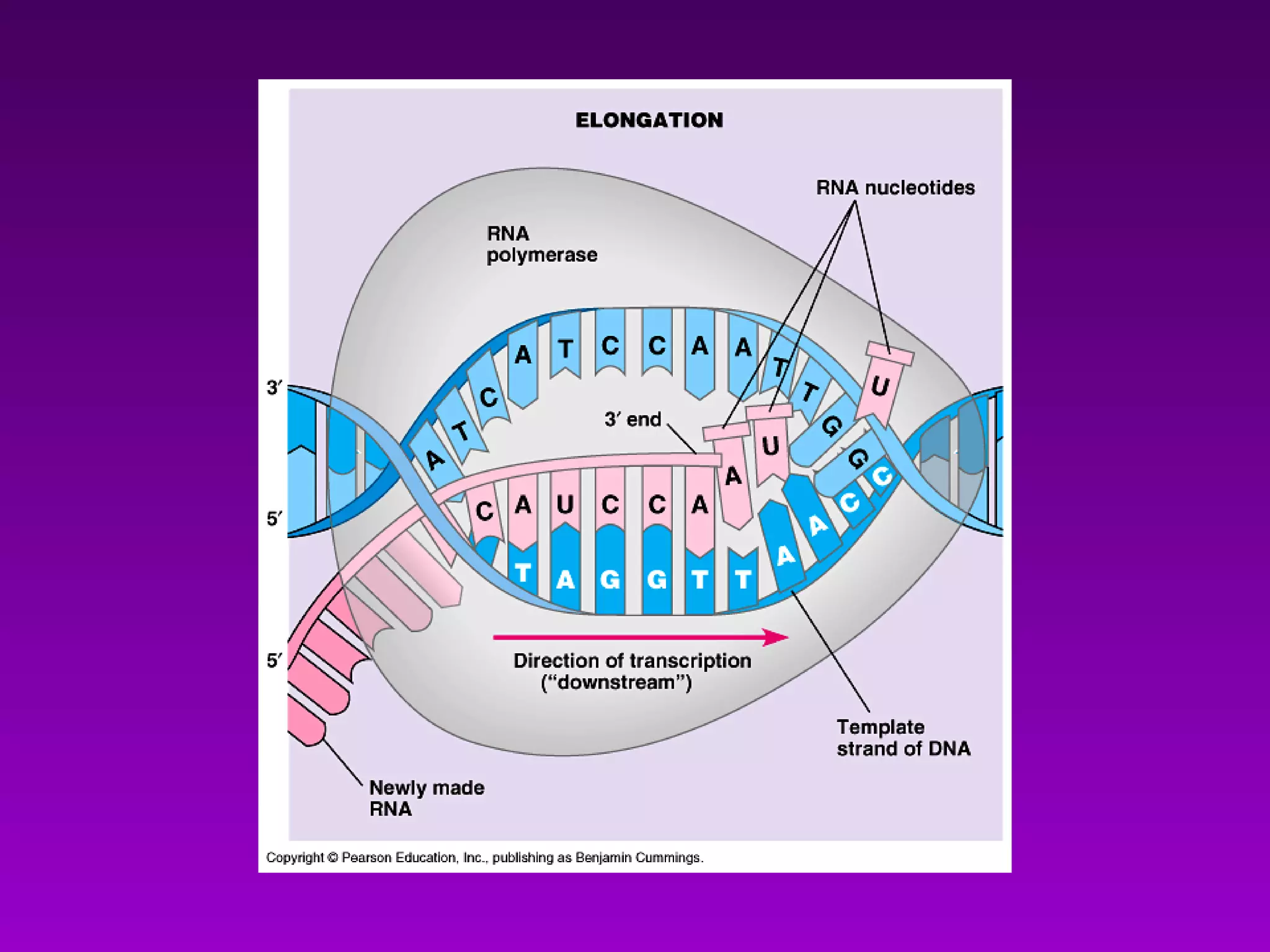
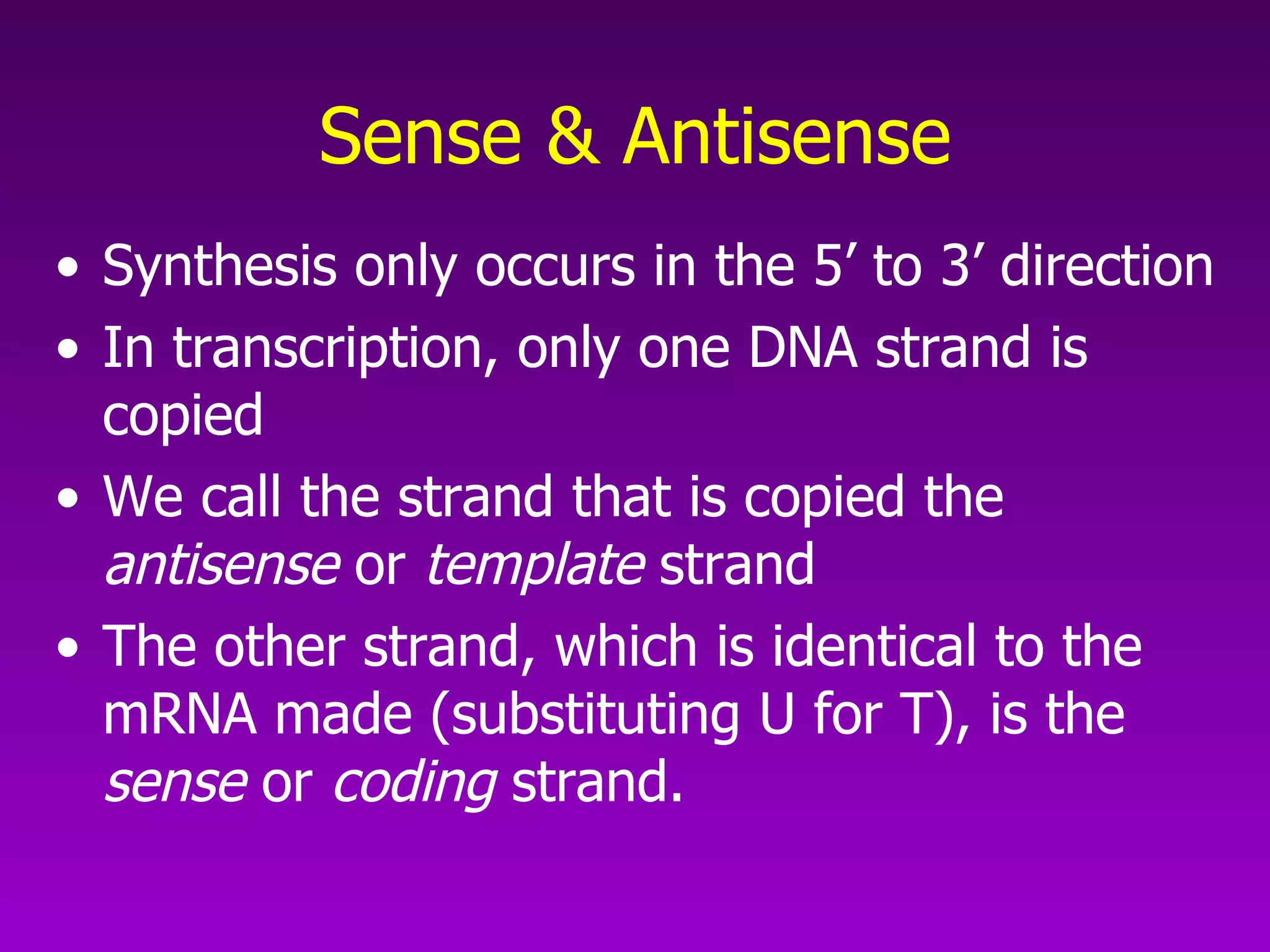
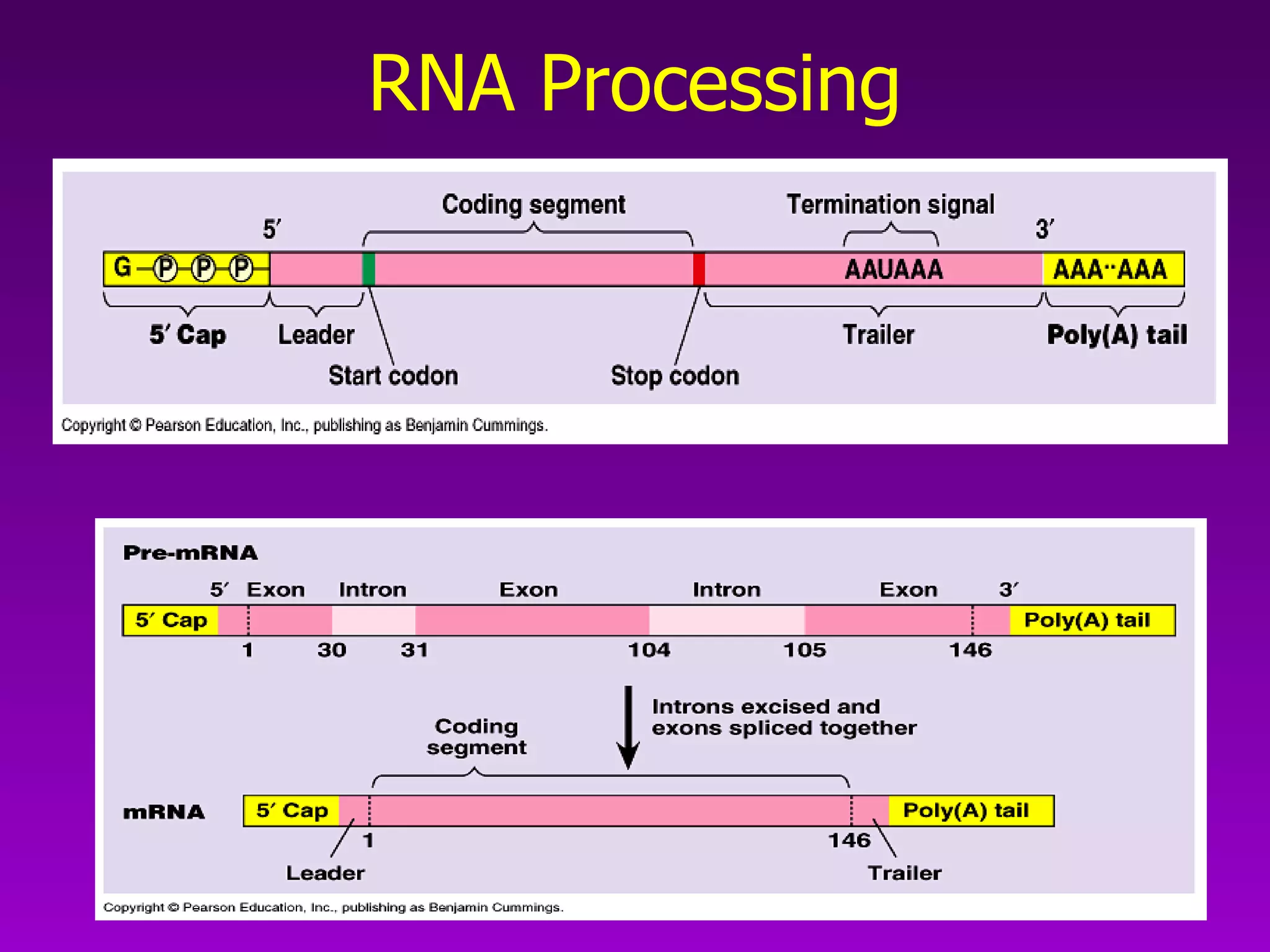
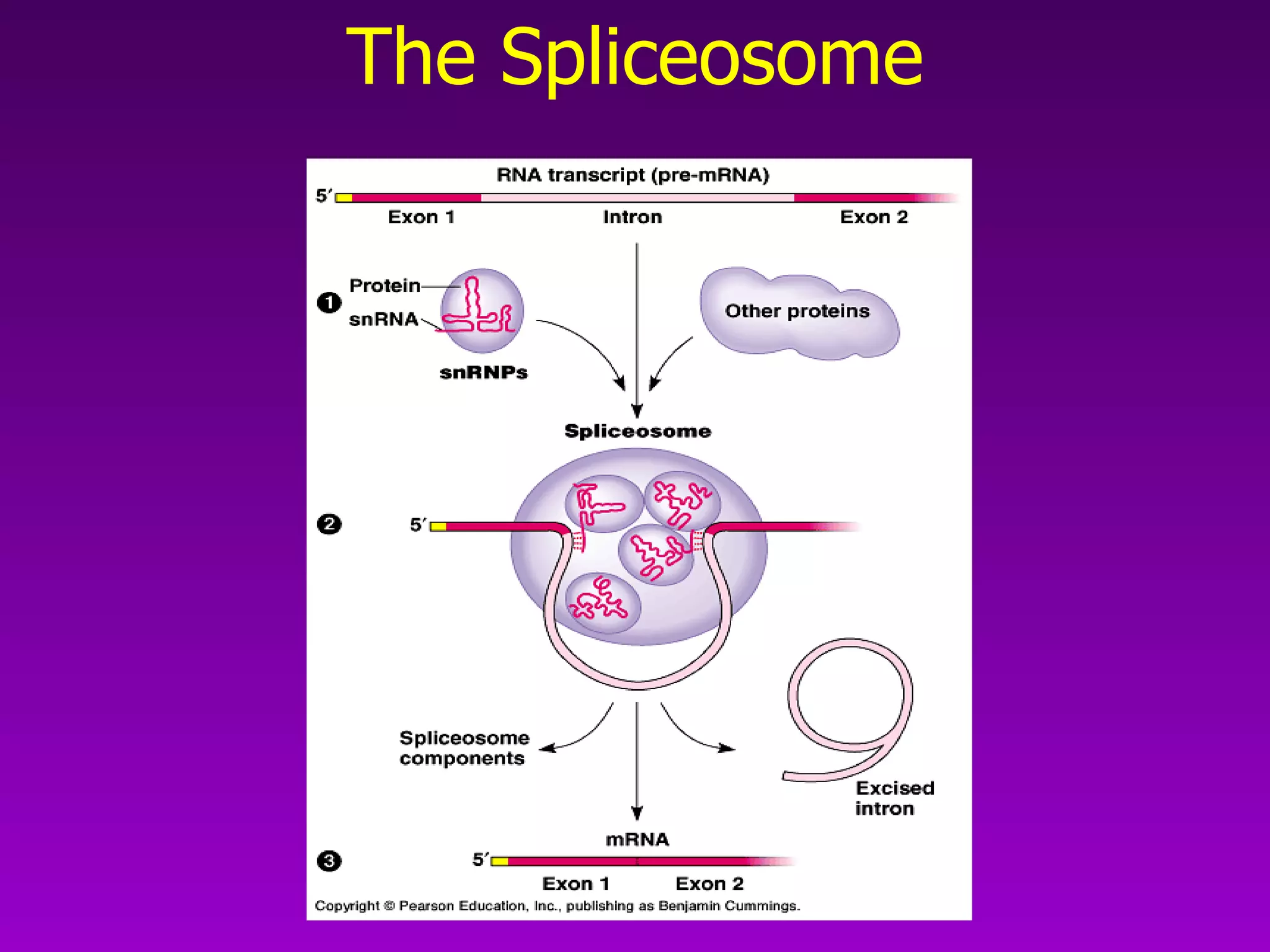
3) The process of transcription, including initiation, elongation, termination, and post-transcriptional modification of pre-mRNA in eukaryotes.
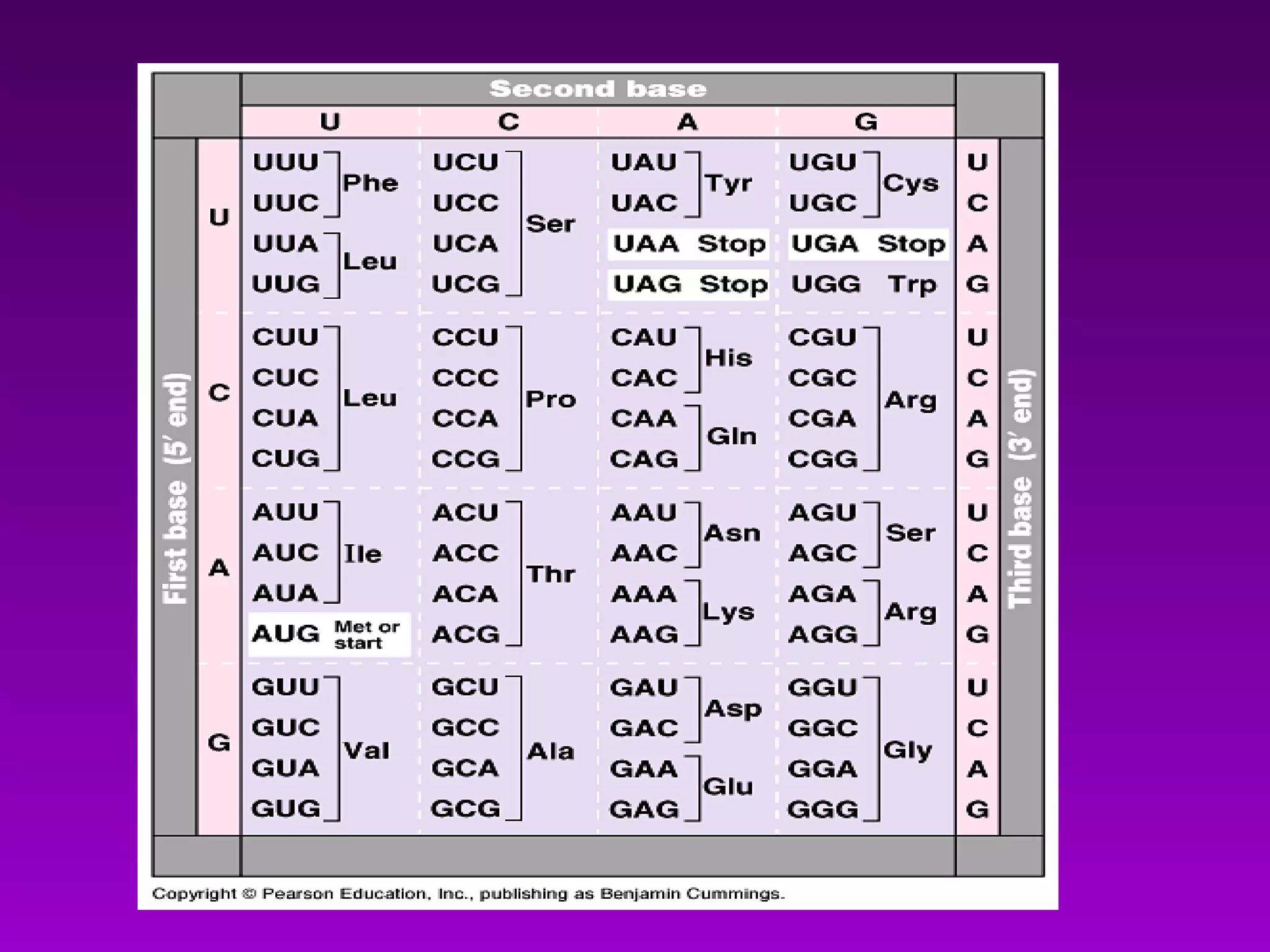
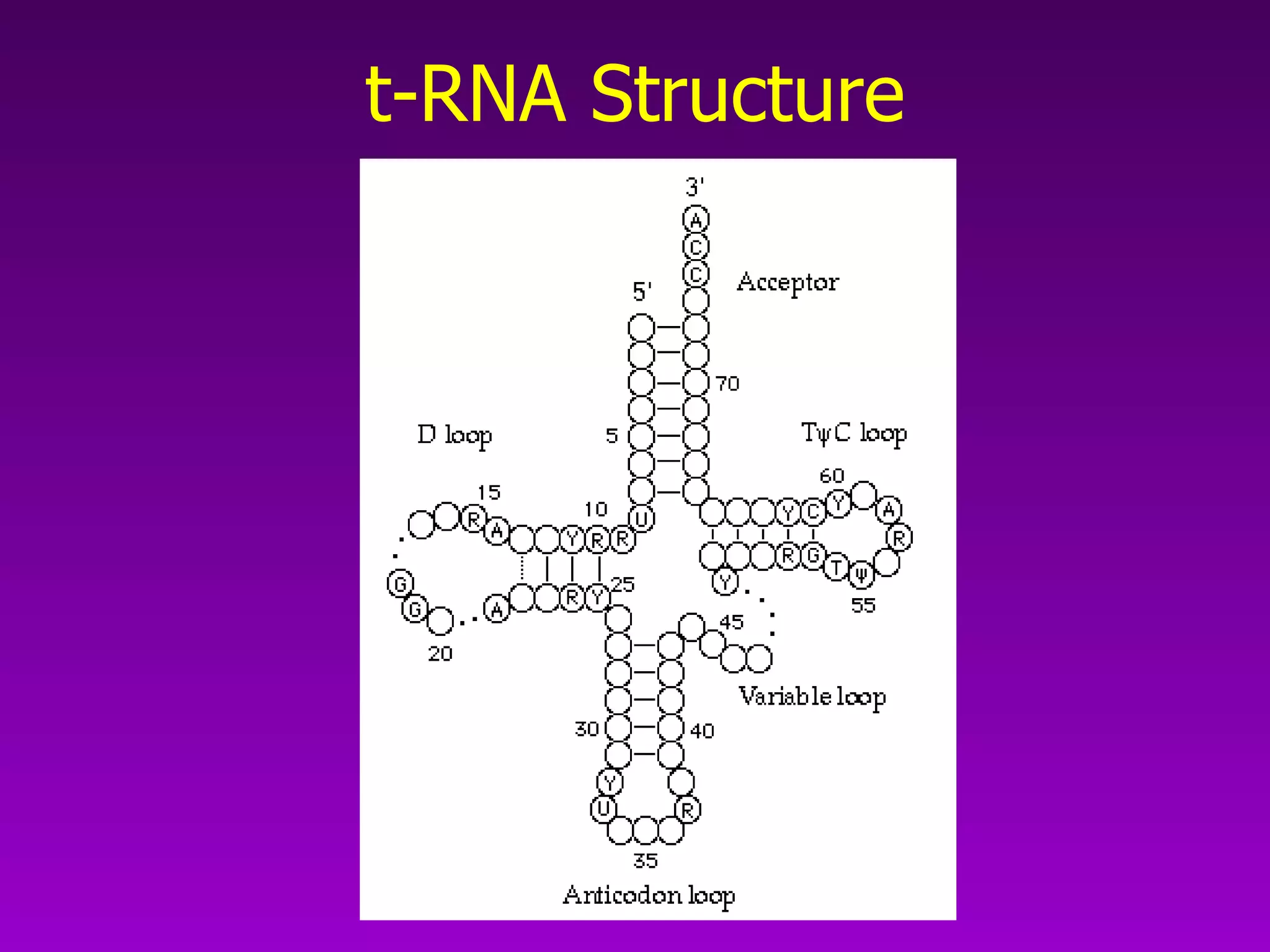
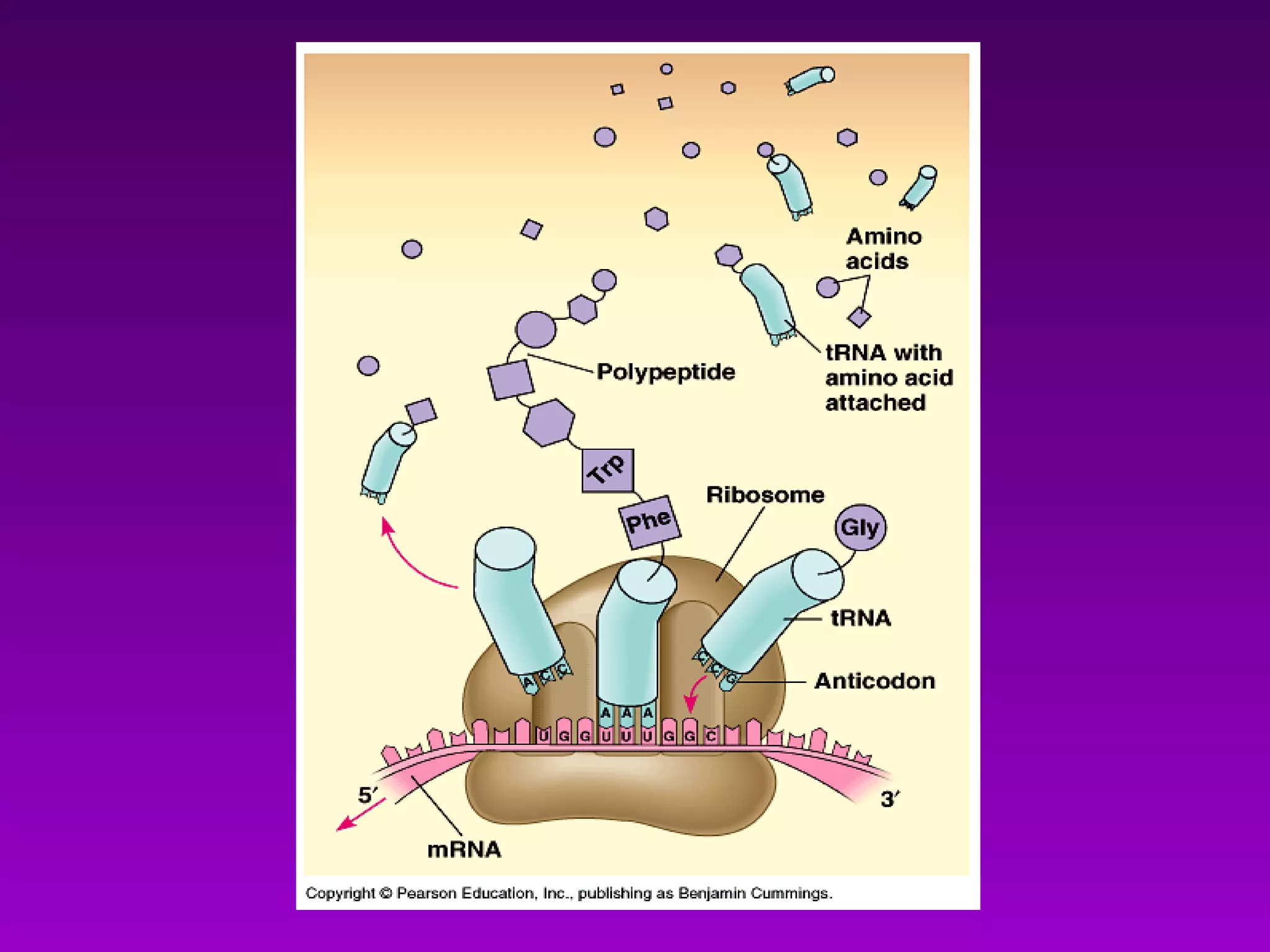
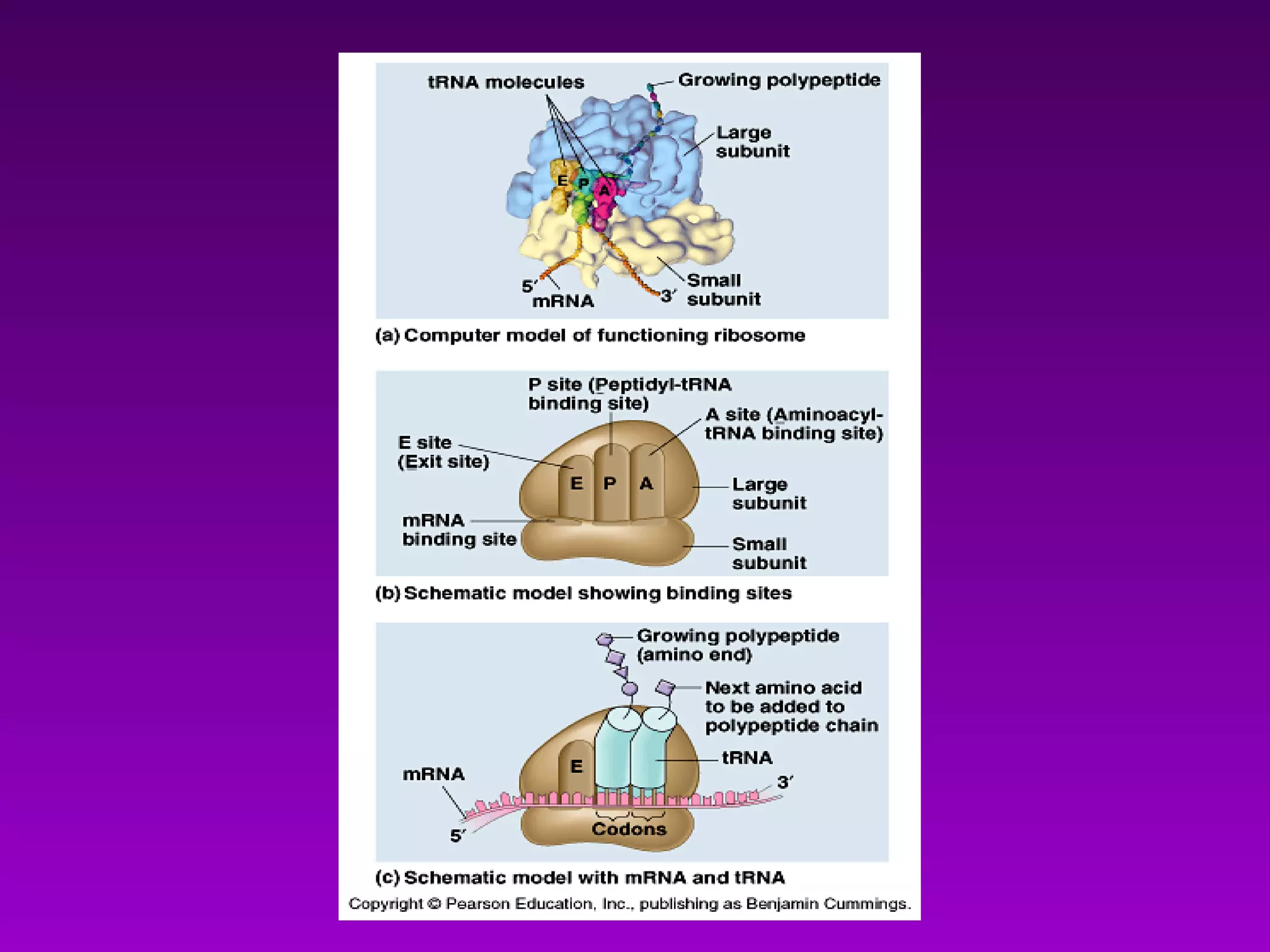
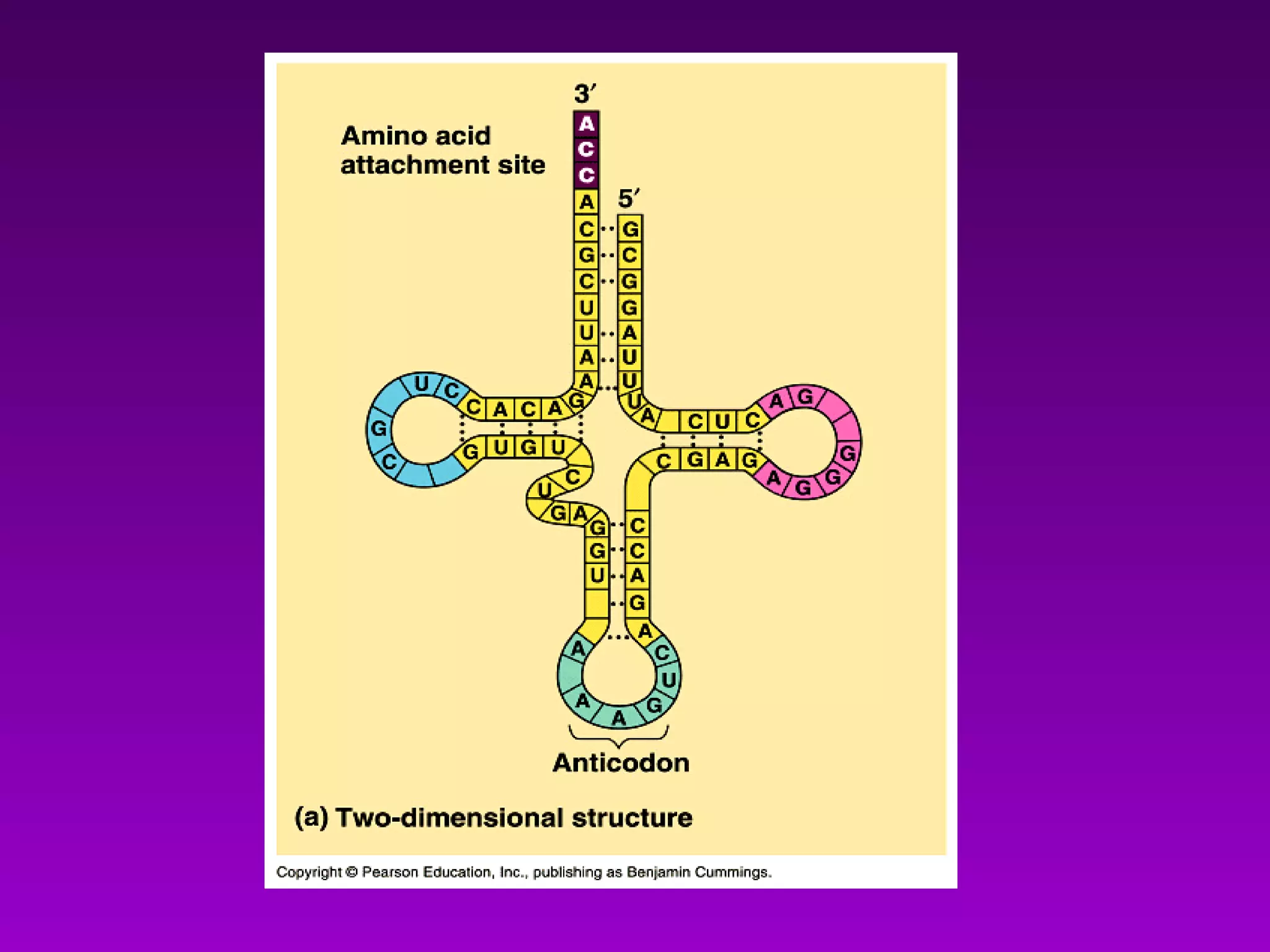
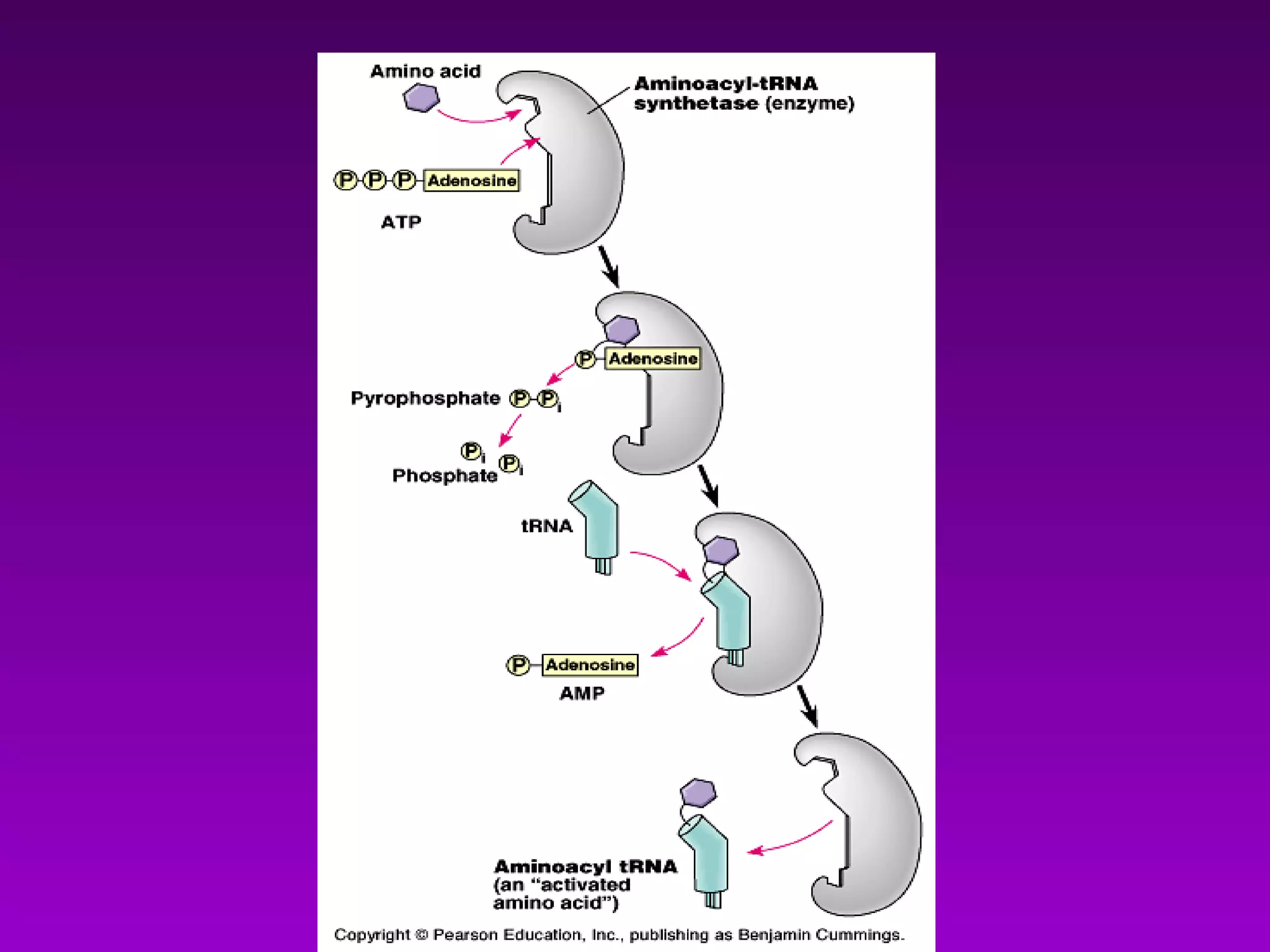
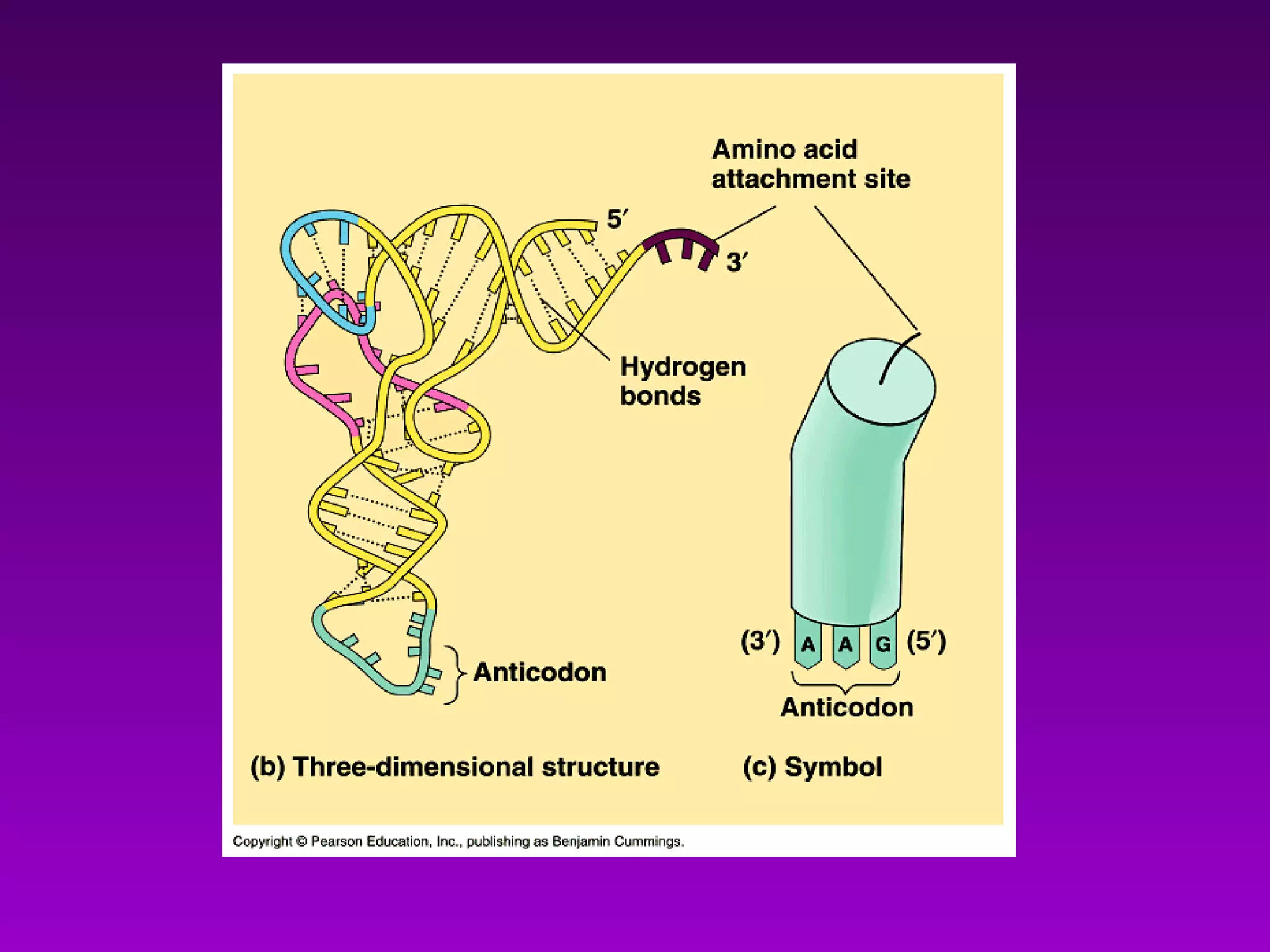
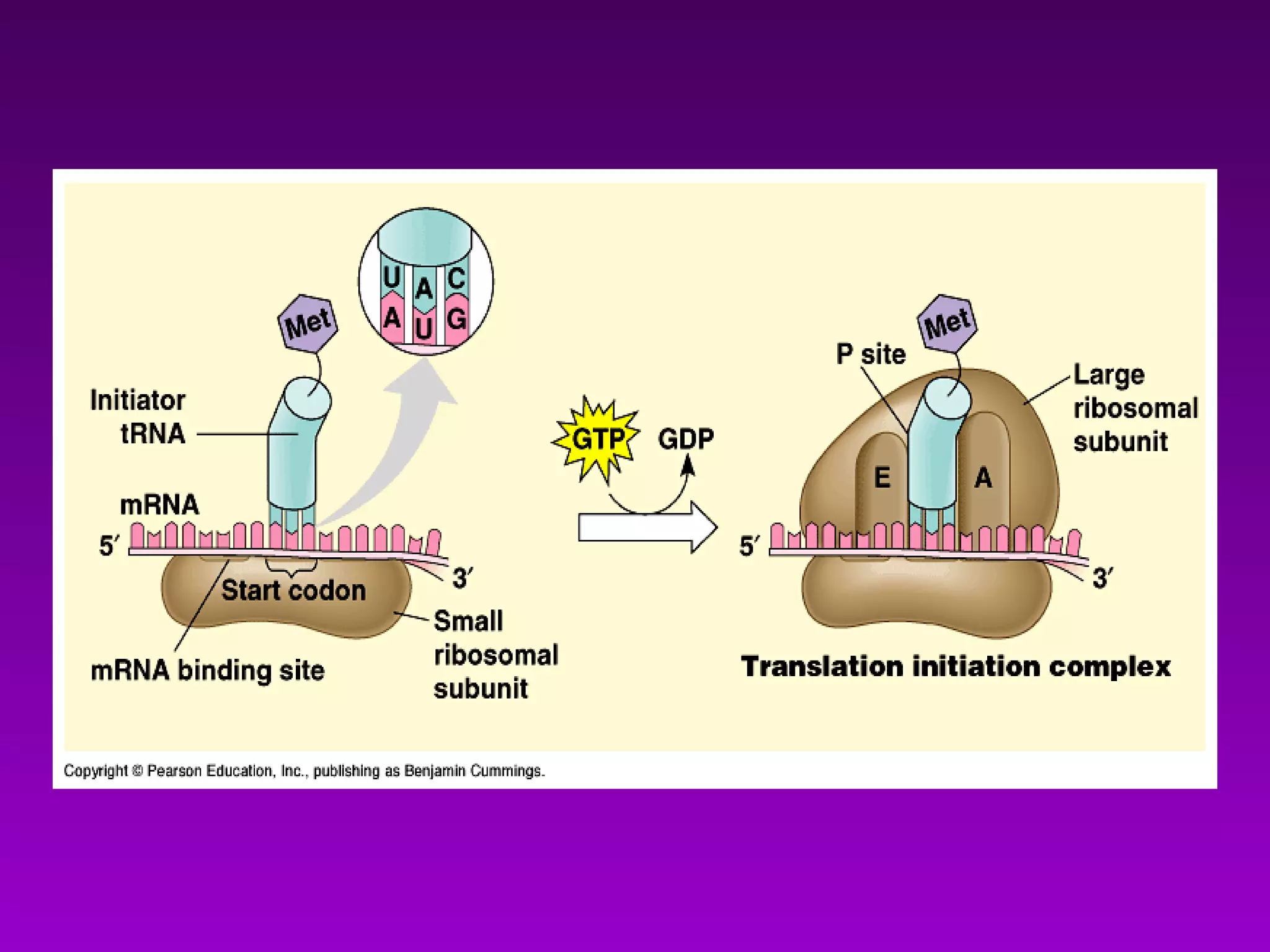
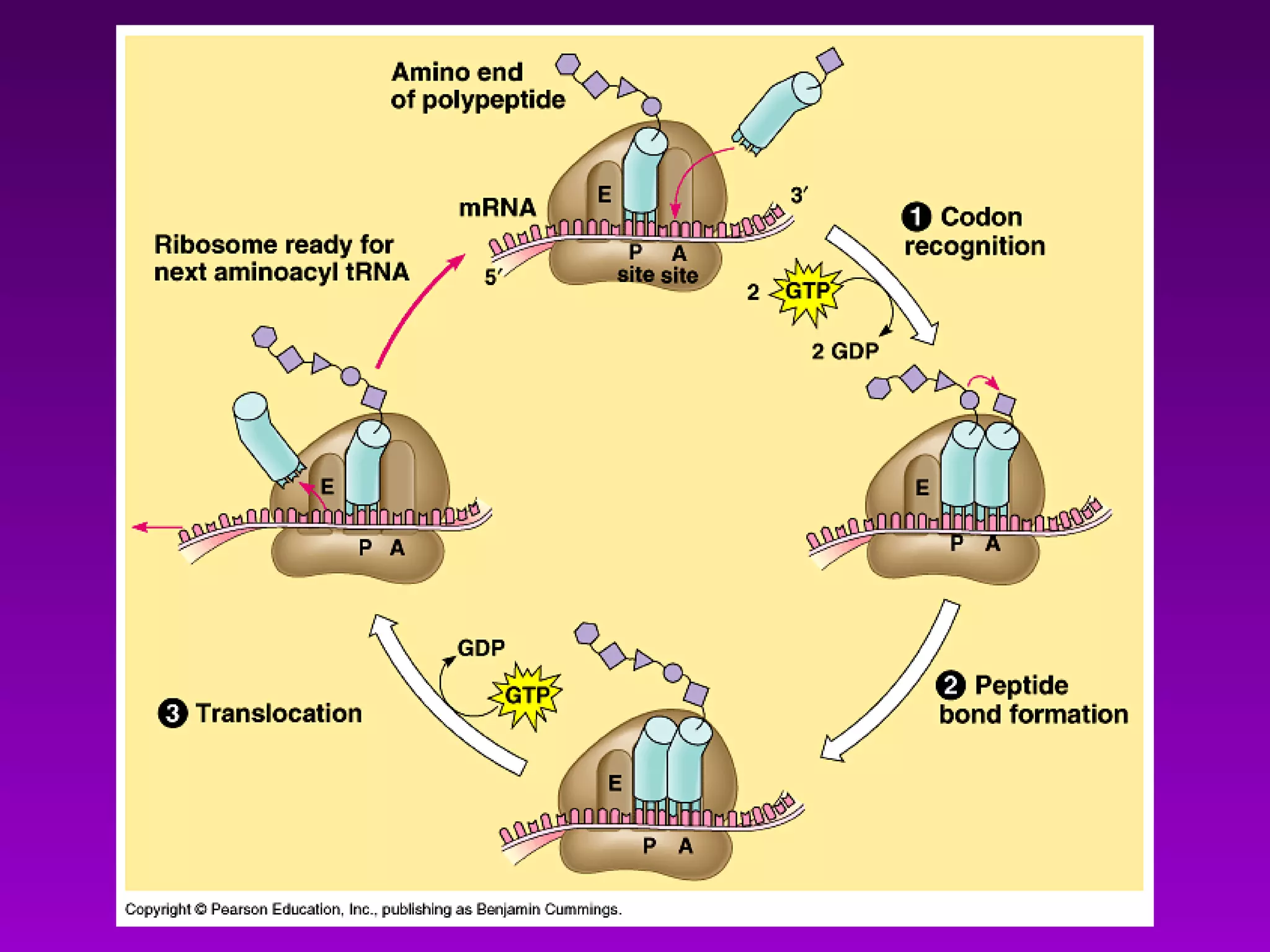
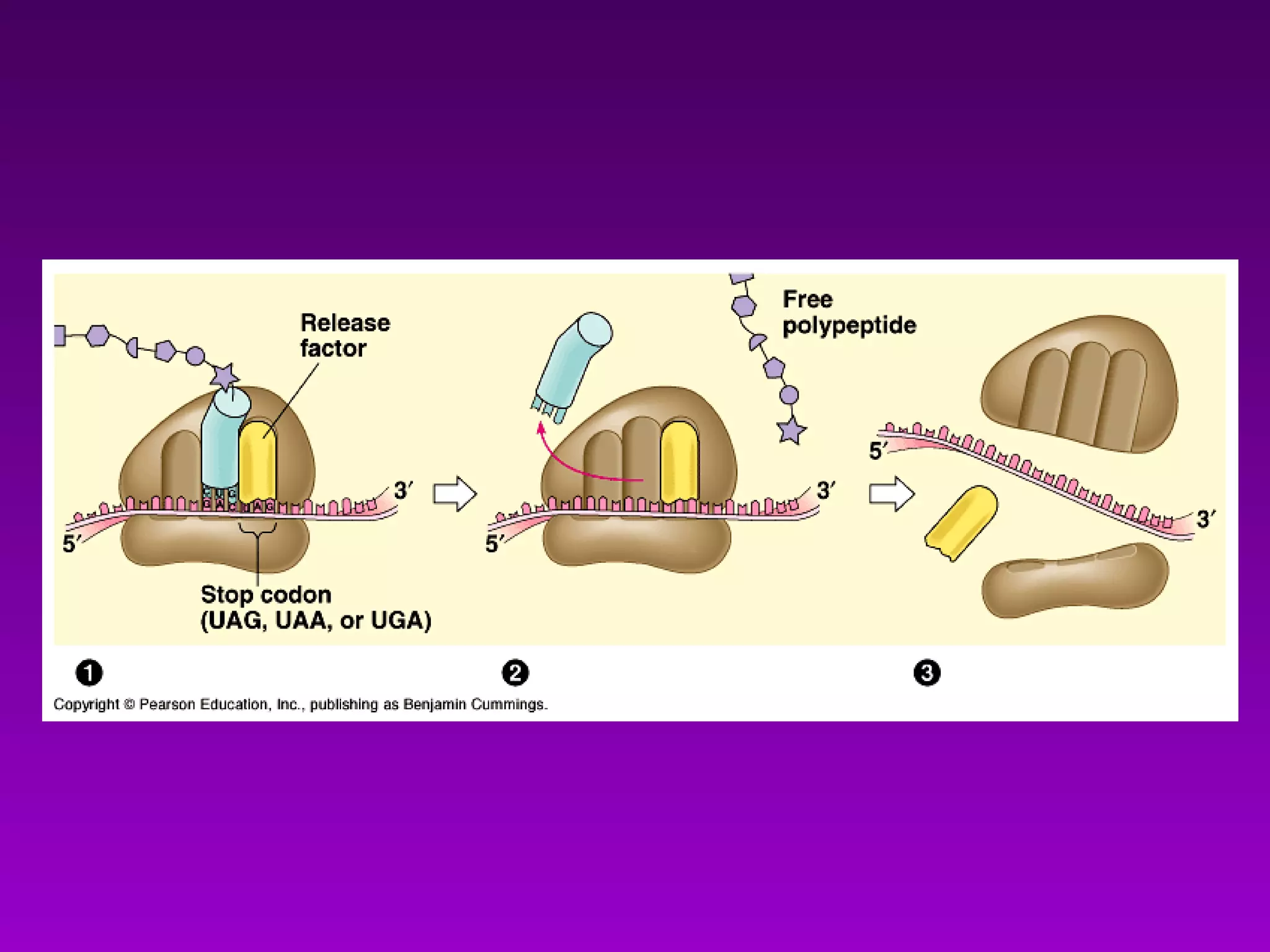
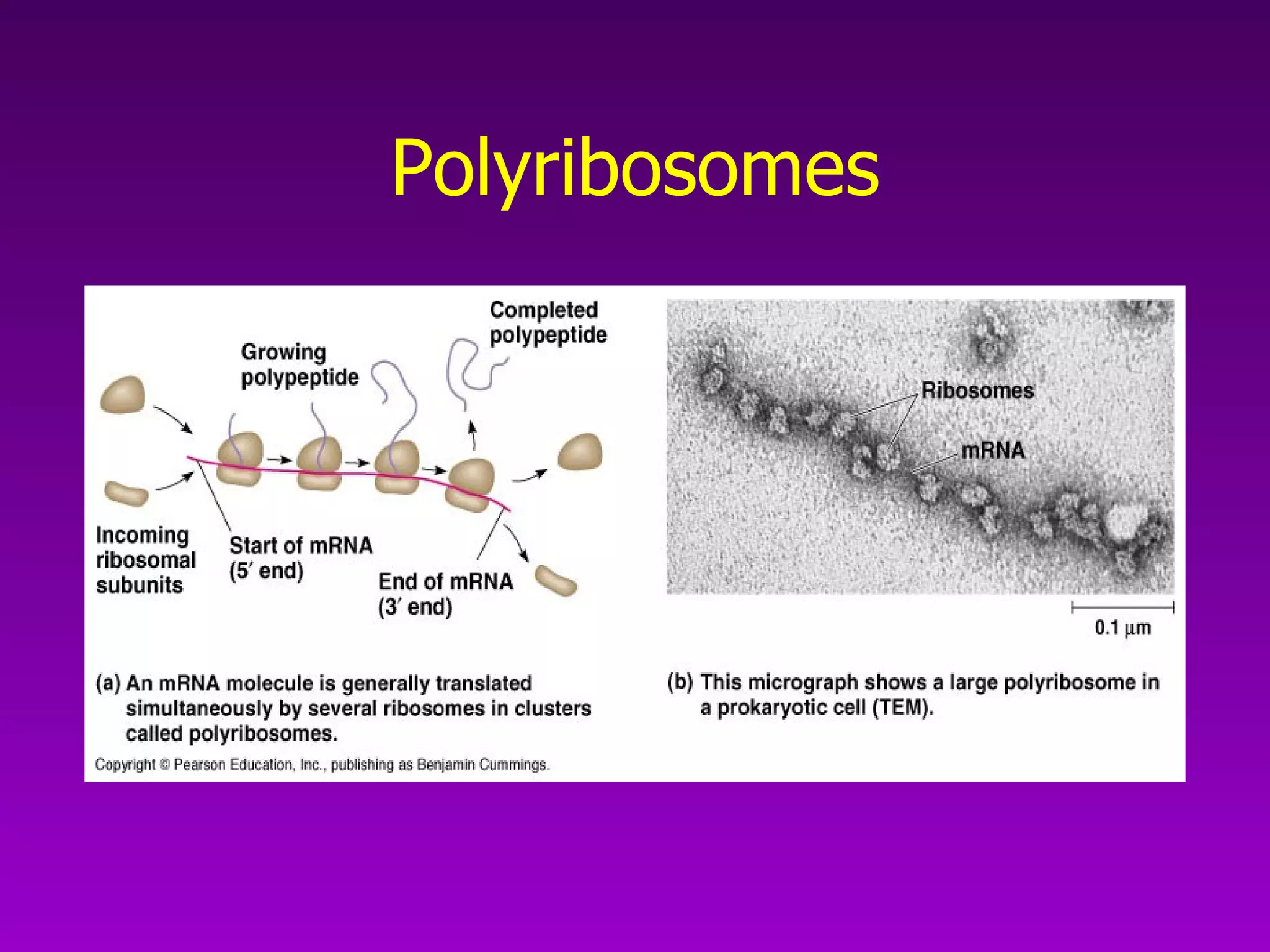
4) Translation occurs on ribosomes, where mRNA directs the assembly of amino acids into polypeptides according to the genetic code