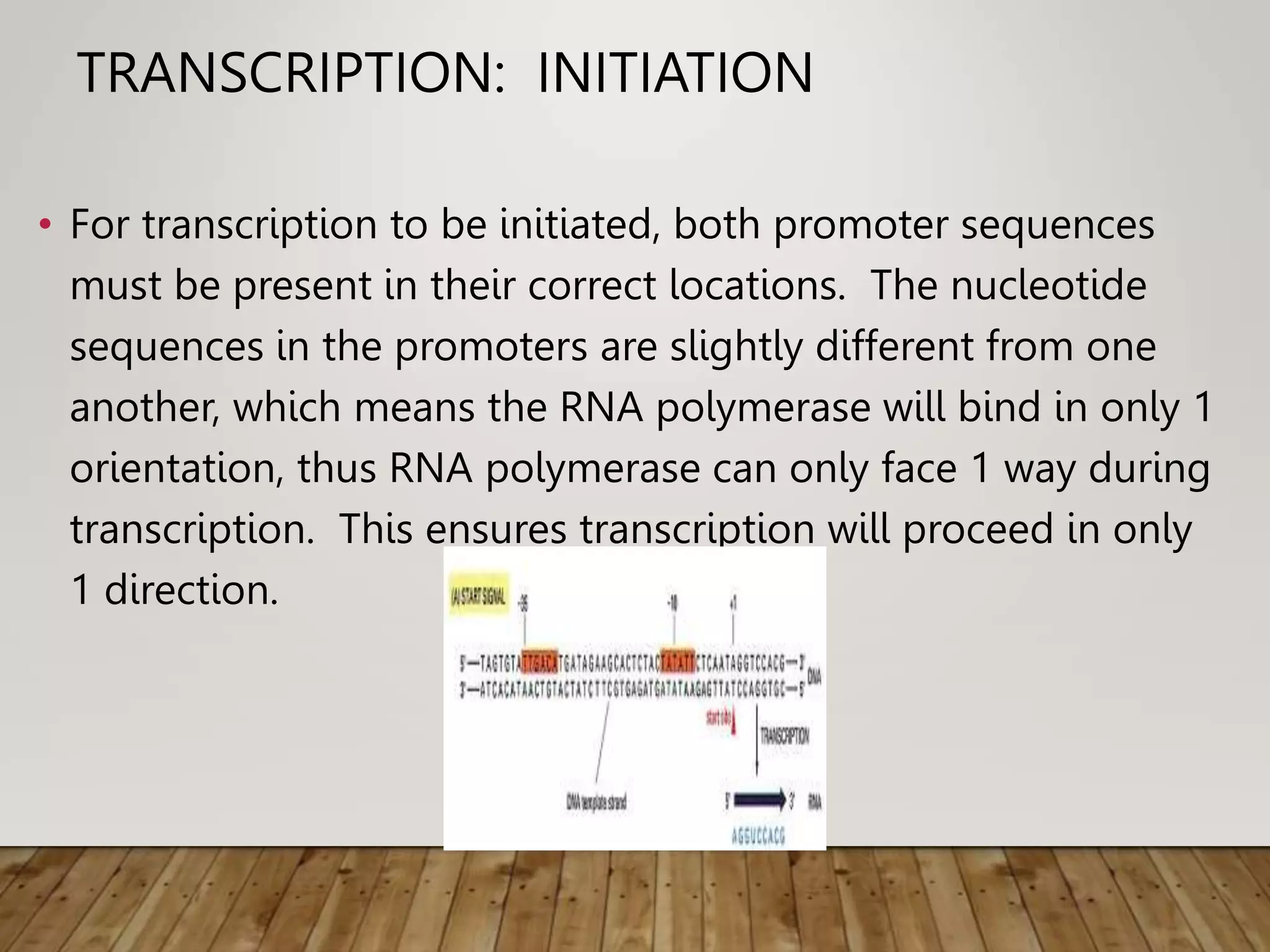
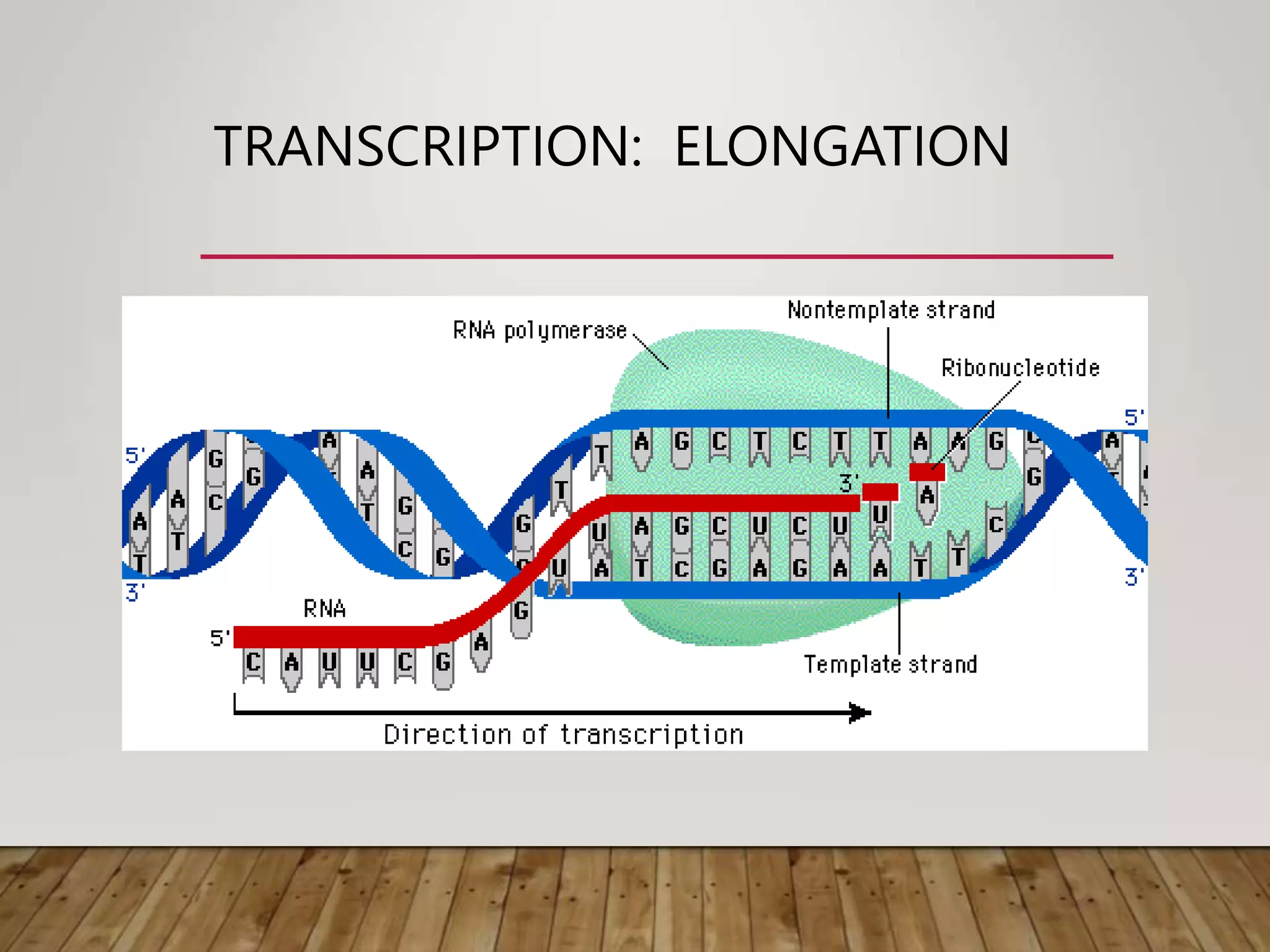
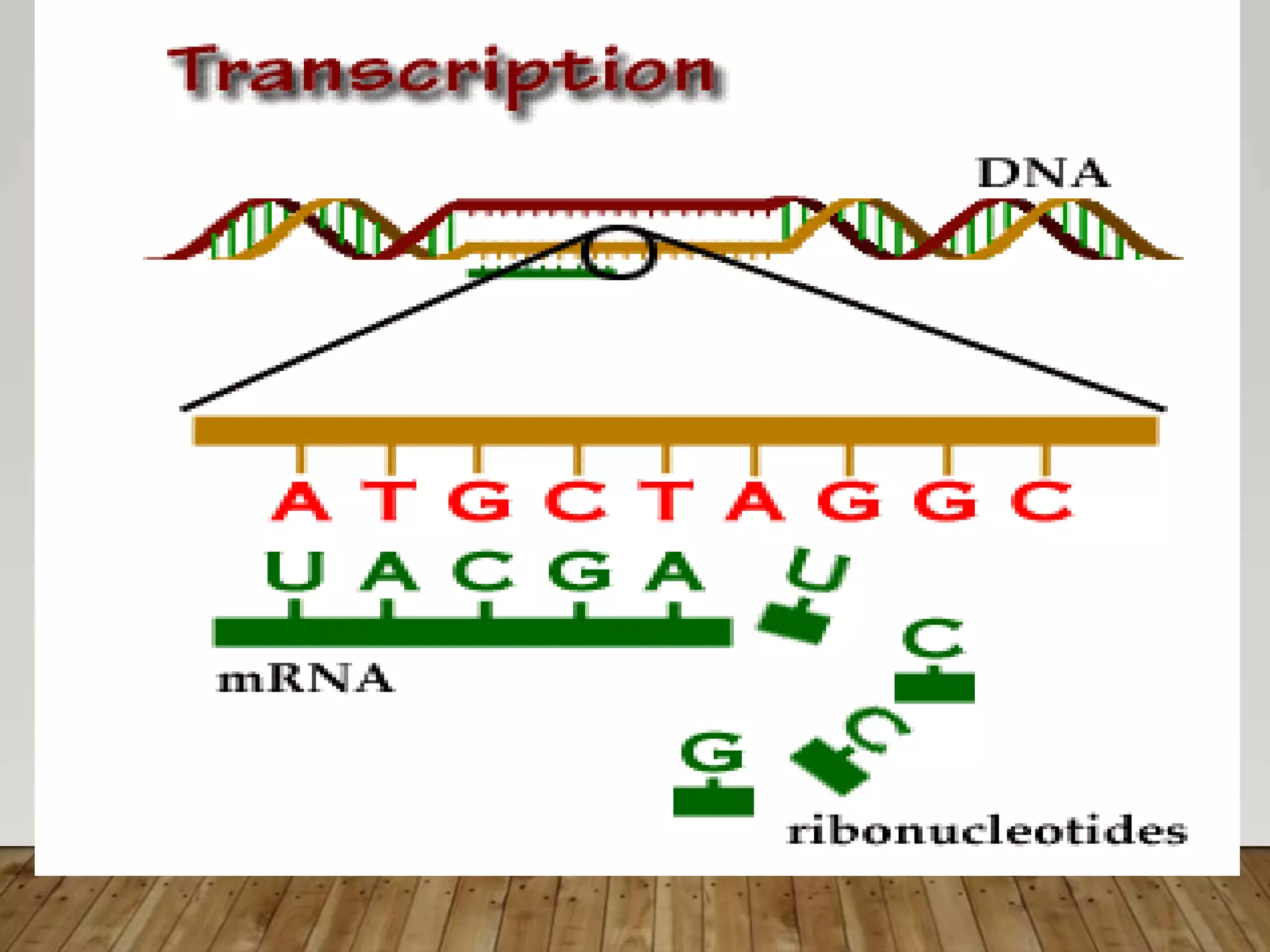
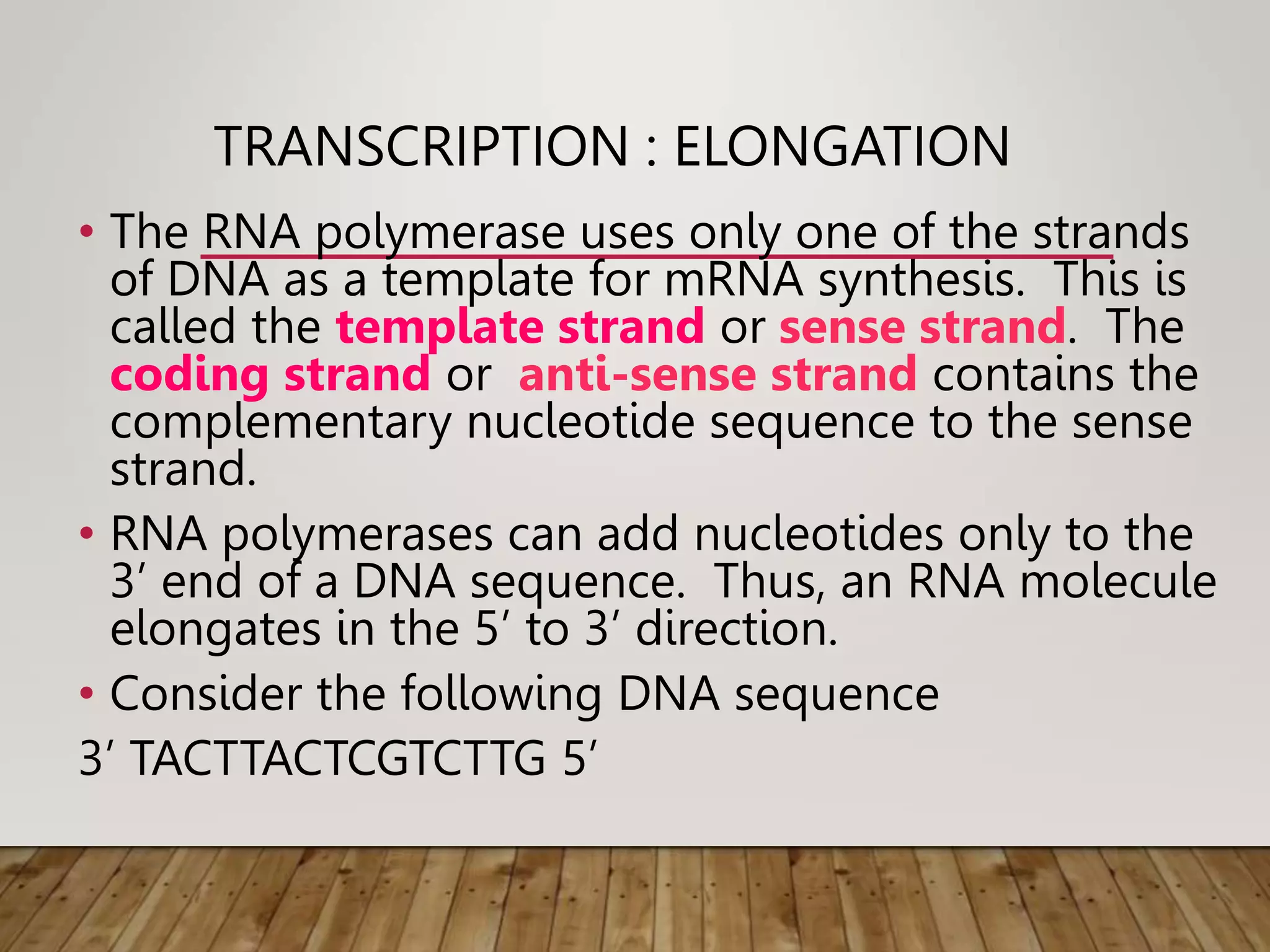
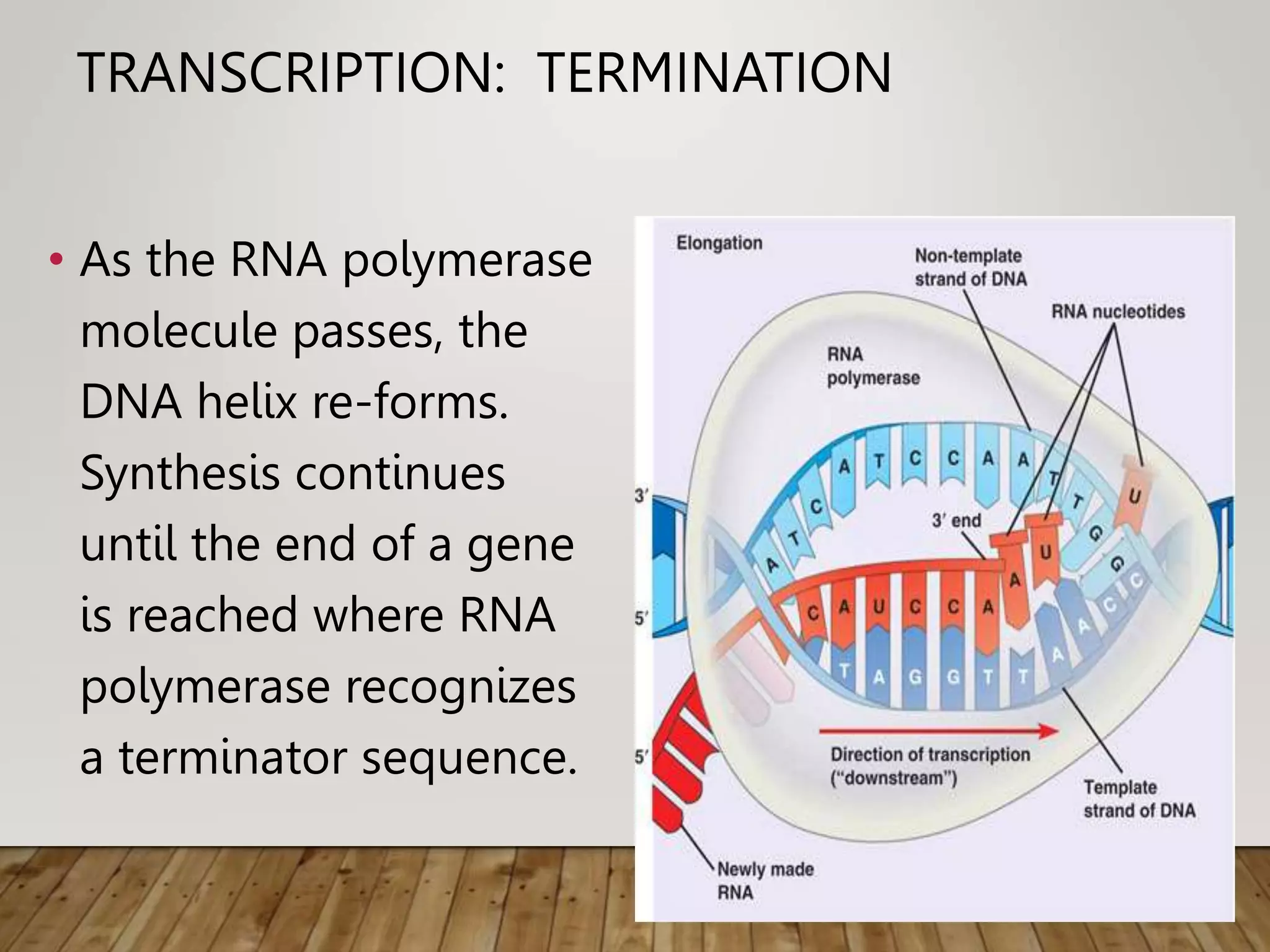
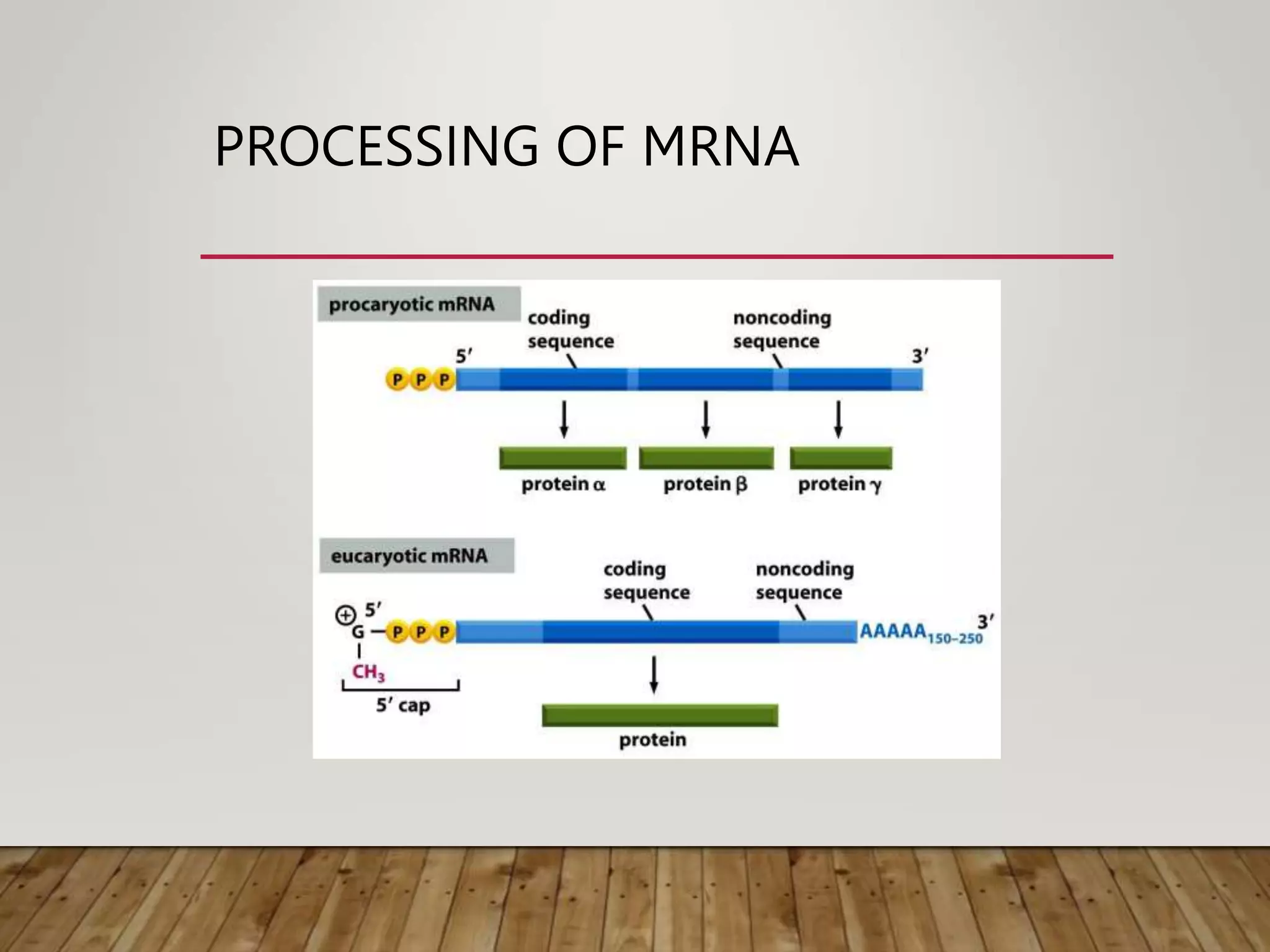
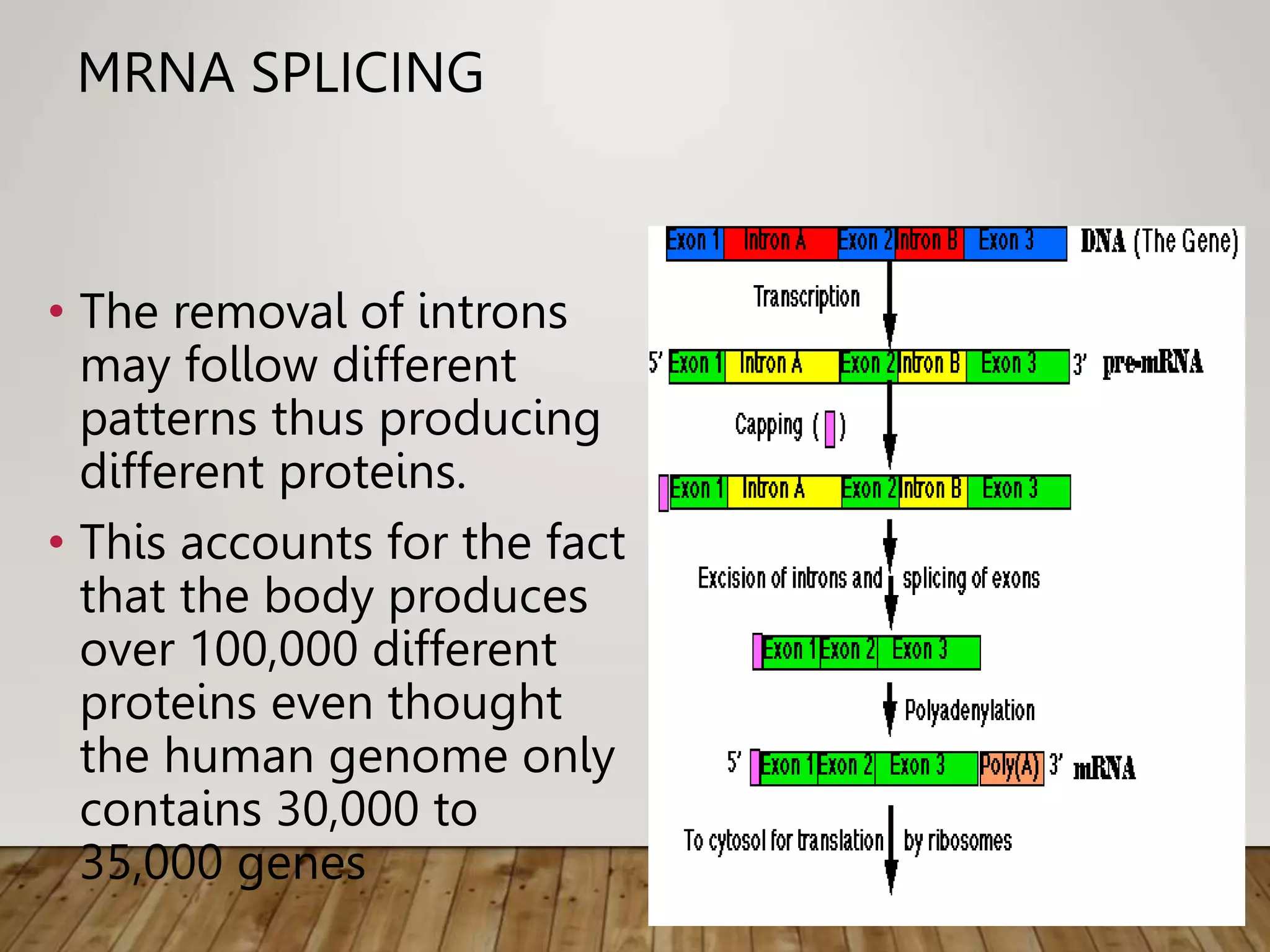
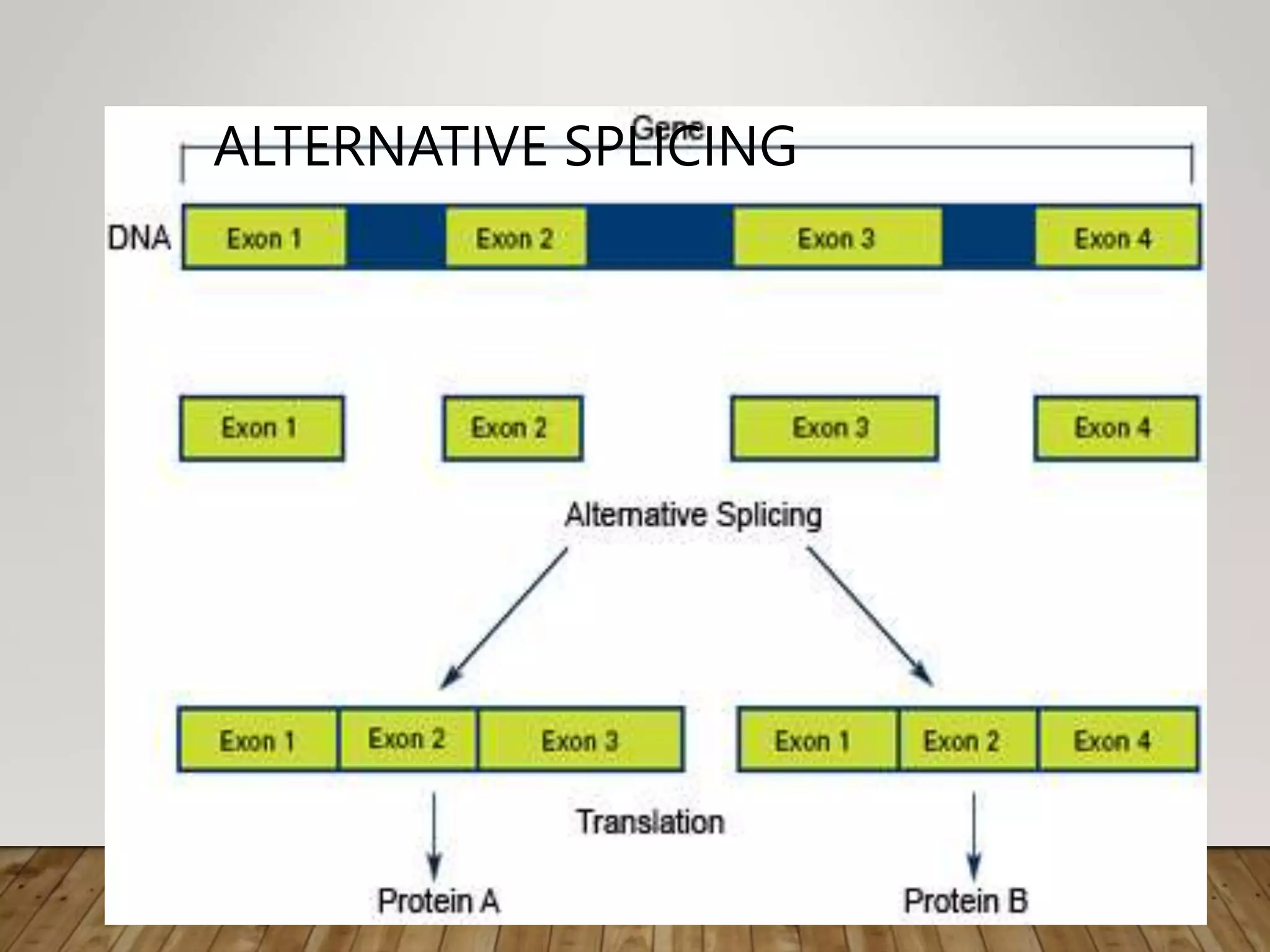
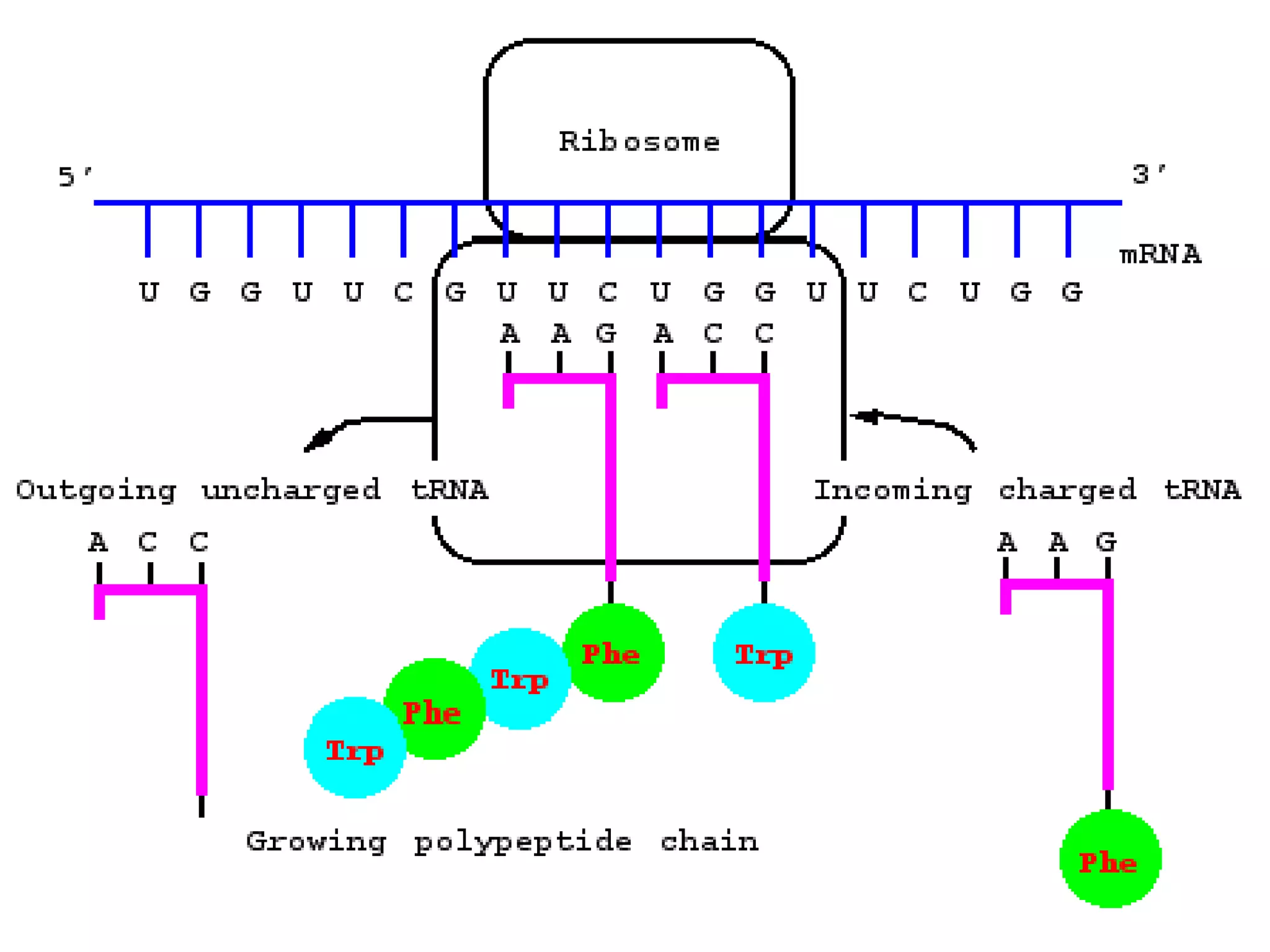
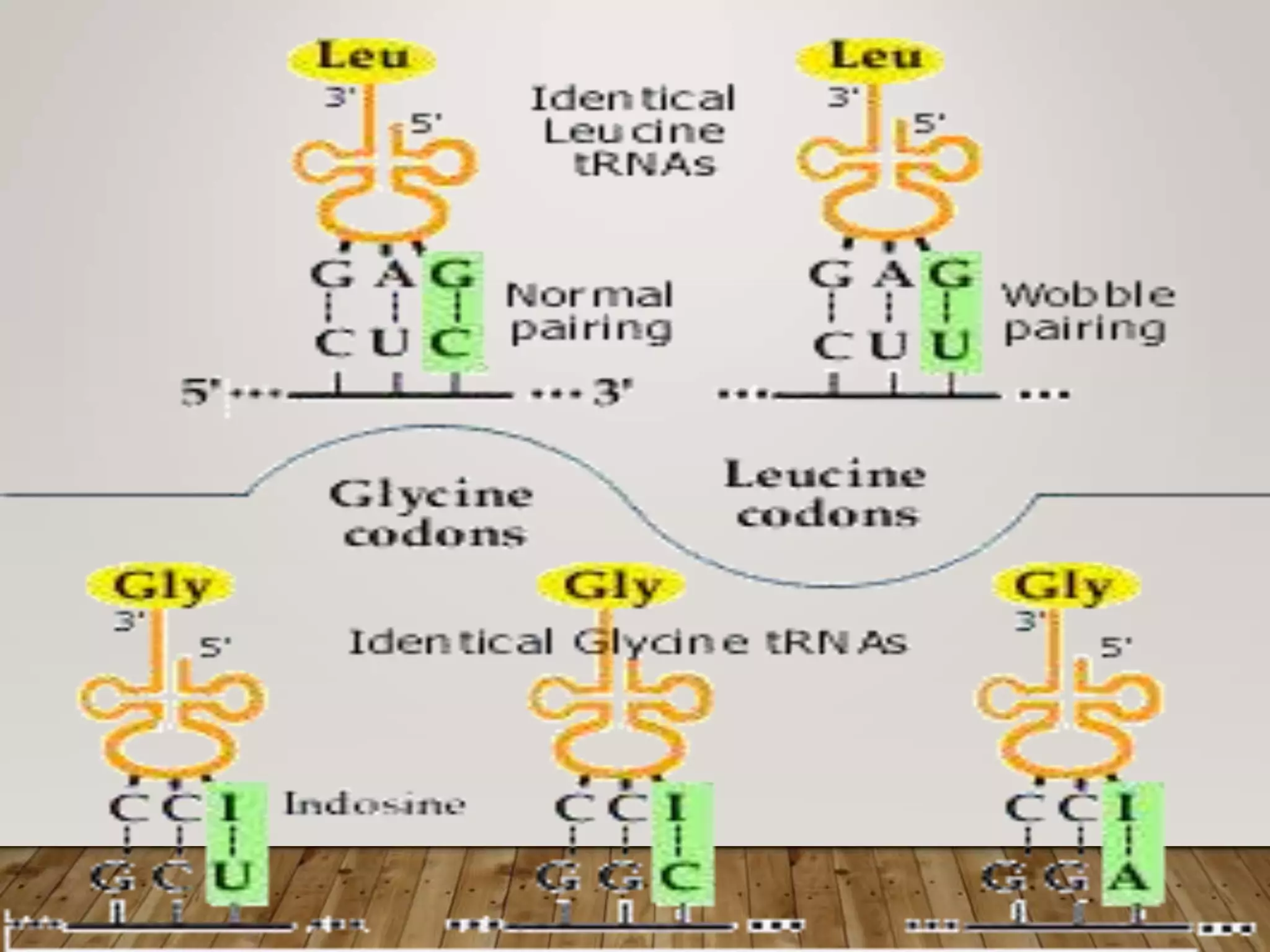
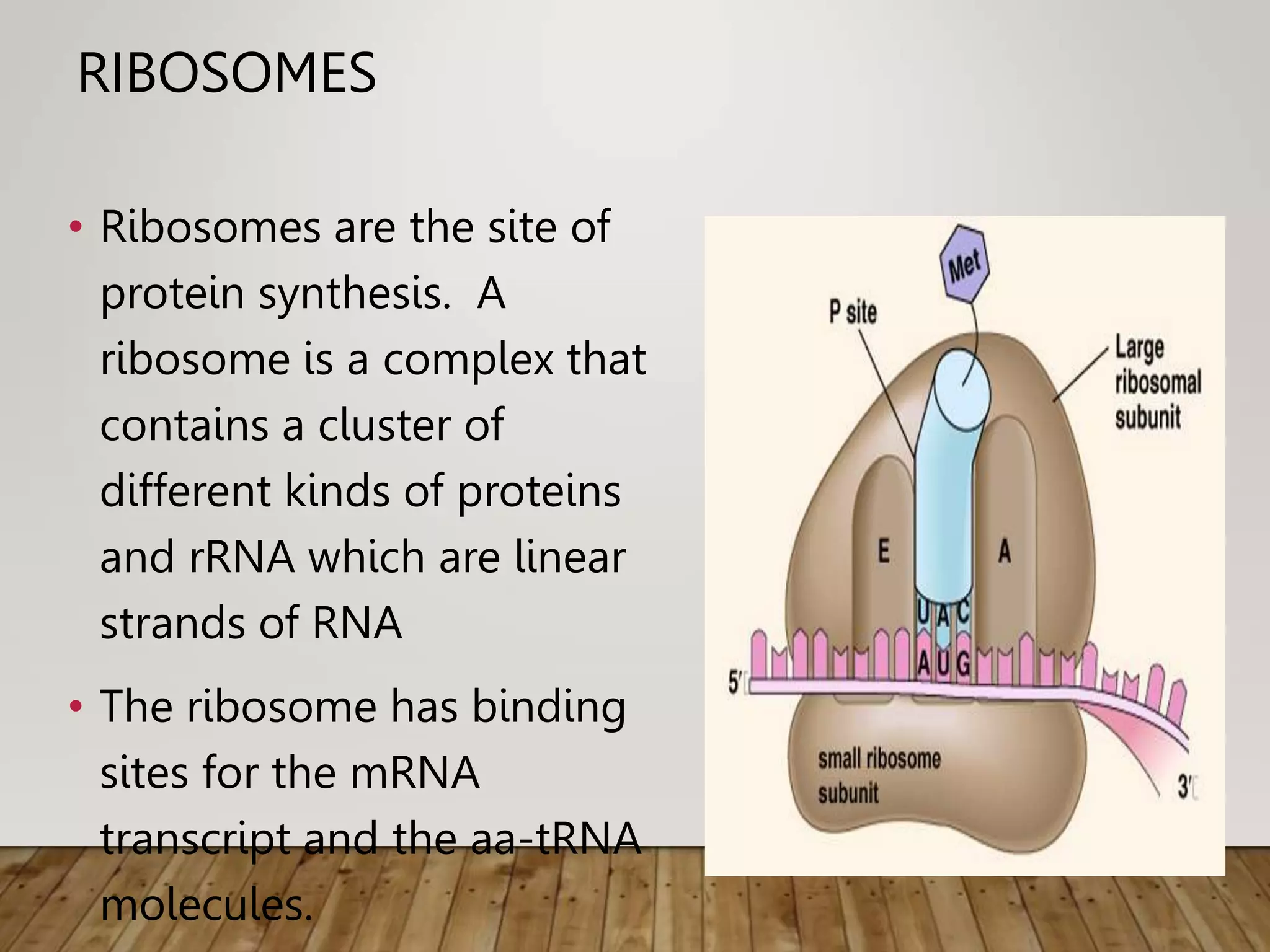
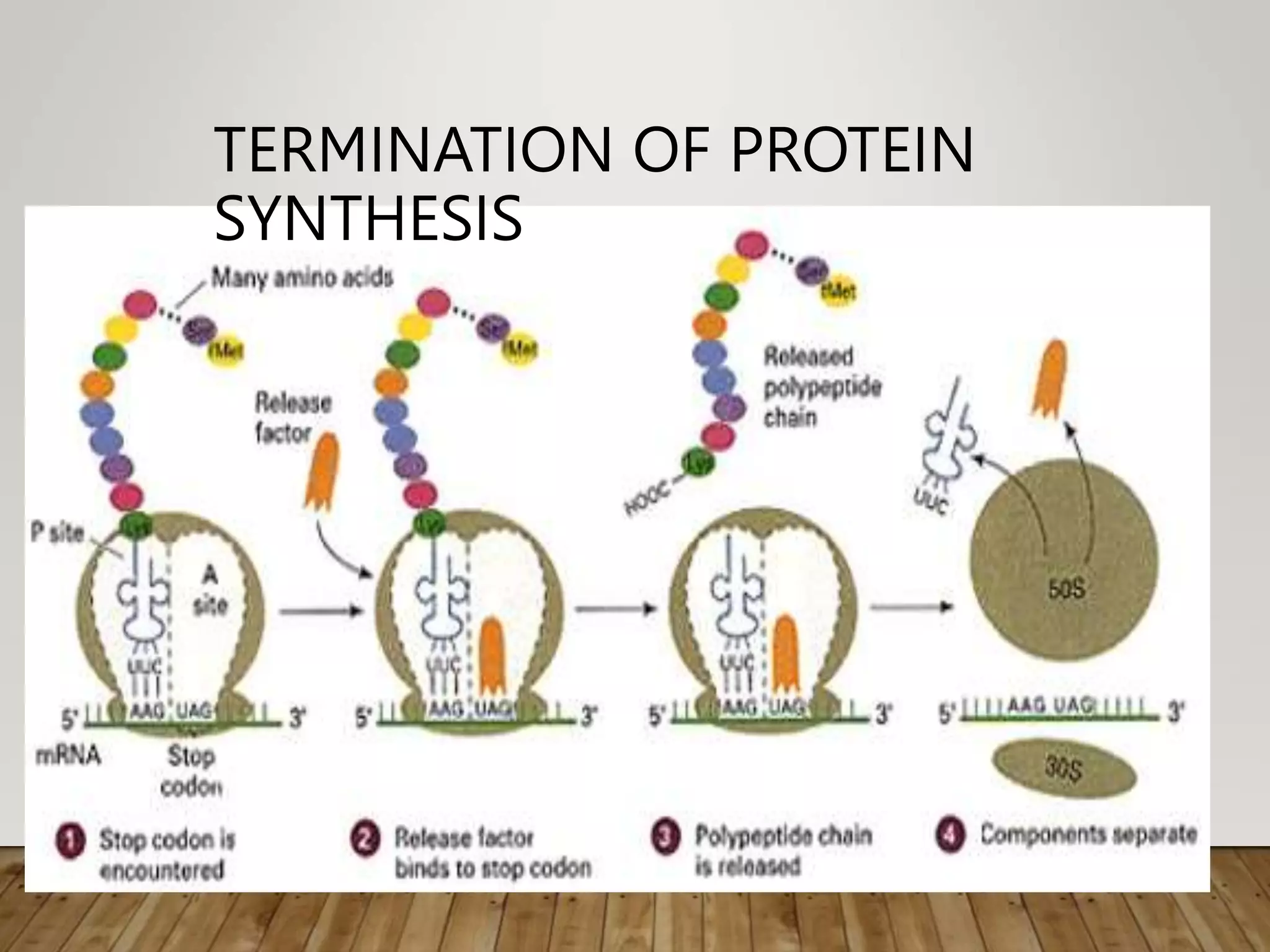
Protein synthesis involves two main processes - transcription and translation. In transcription, the DNA code is copied into mRNA by RNA polymerase. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm during translation, where the mRNA code is read to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the genetic code. There are 64 possible codons that make up the genetic code.