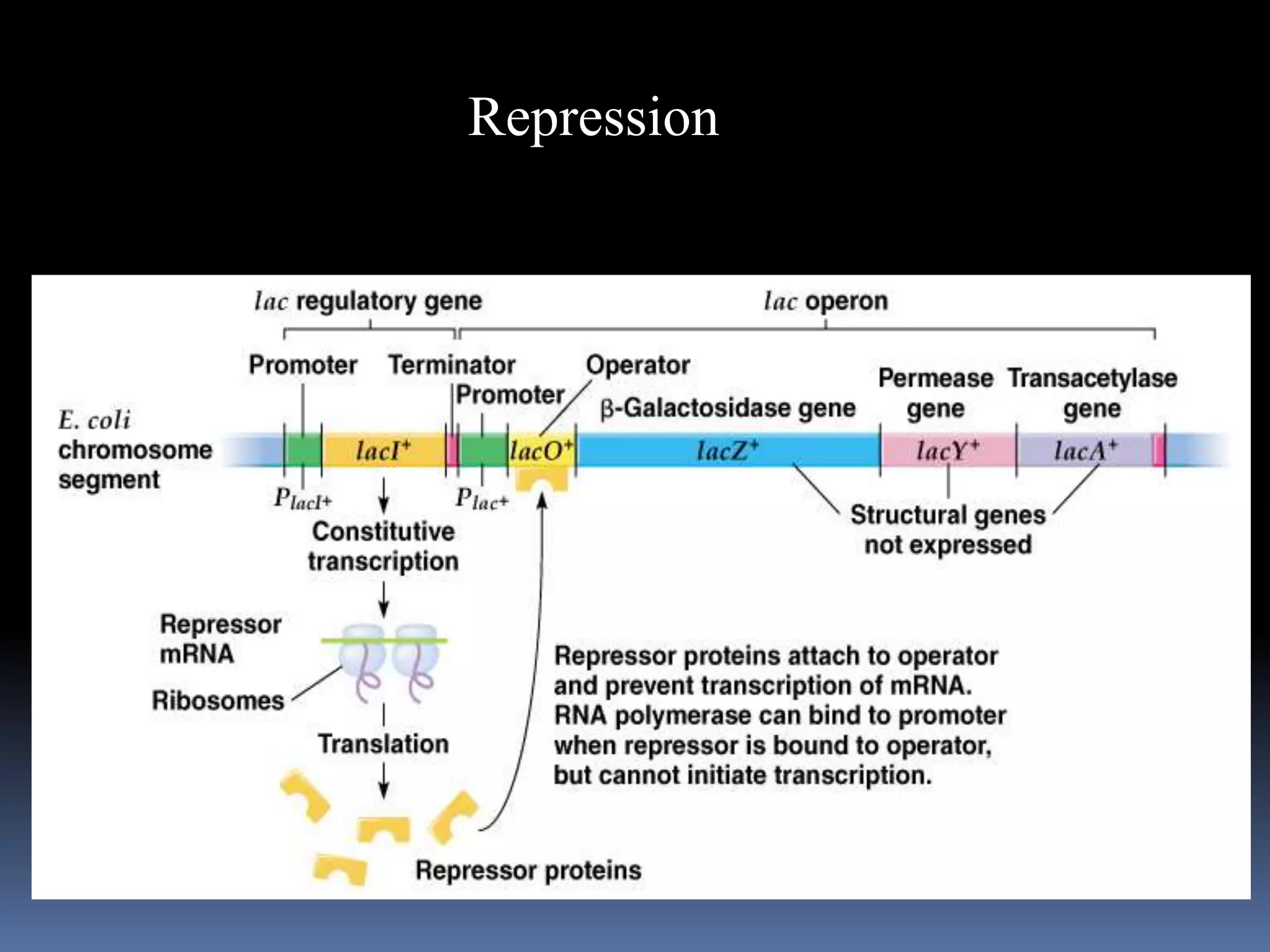
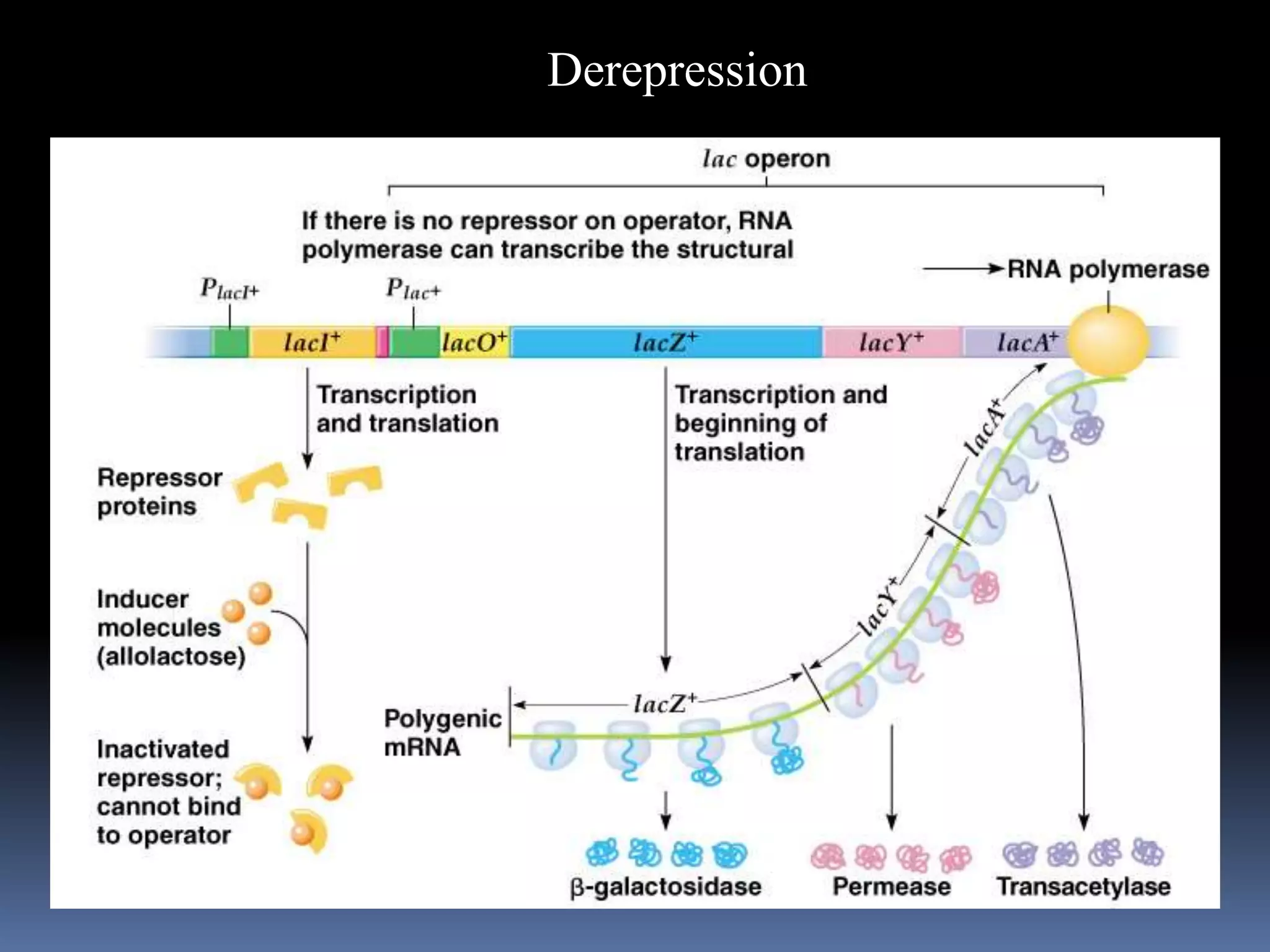
The document summarizes regulation of gene expression through the lac operon in E. coli. It describes how Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod discovered the lac operon in the 1960s and were awarded the Nobel Prize. The lac operon is a cluster of genes whose expression is regulated by an operator and repressor protein. In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds the operator to prevent transcription. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor and causes derepression, allowing transcription of genes encoding beta-galactosidase, lactose permease, and transacetylase which break down lactose. Positive control involves cAMP and CAP activating transcription when glucose levels are low.