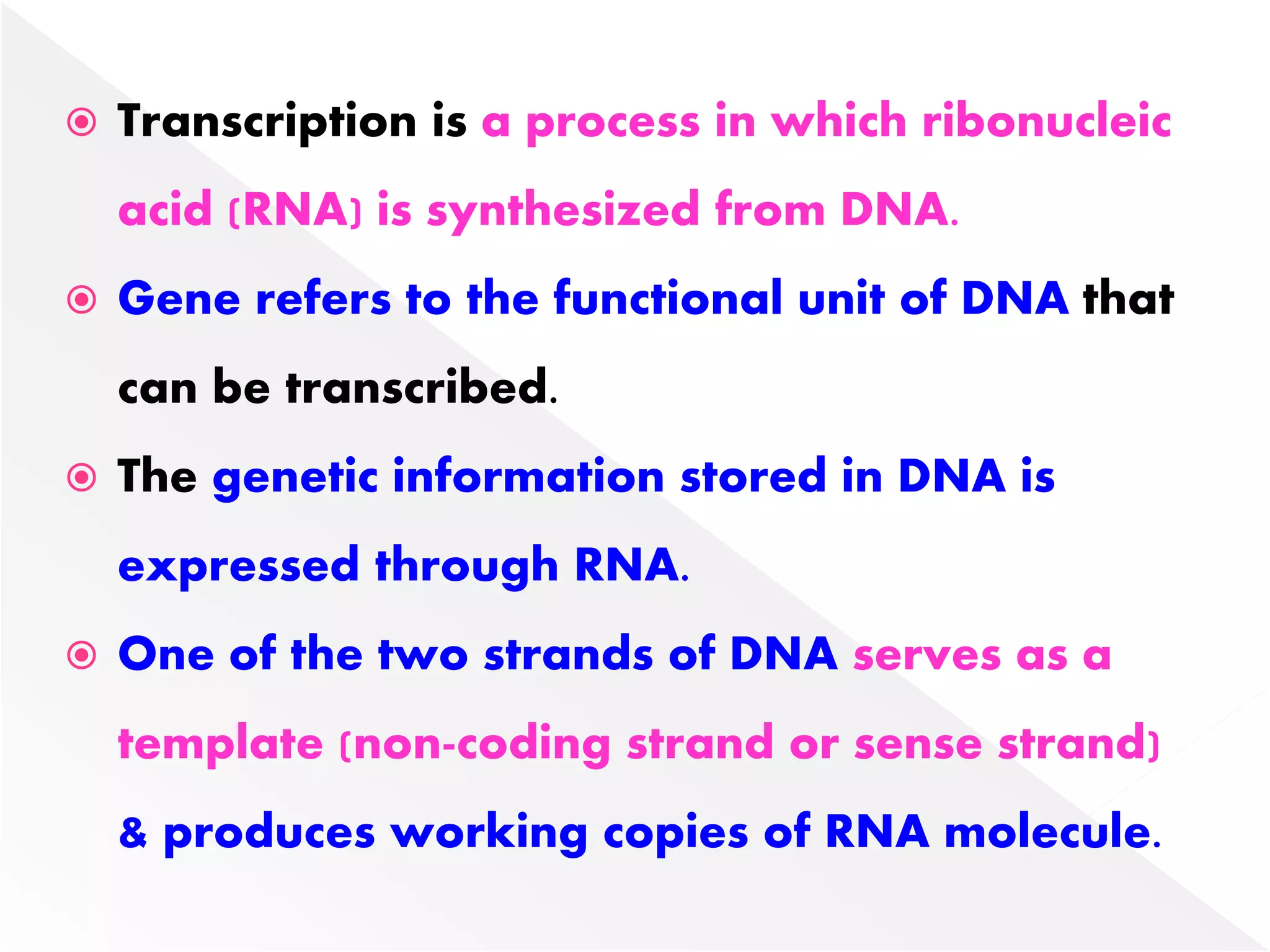
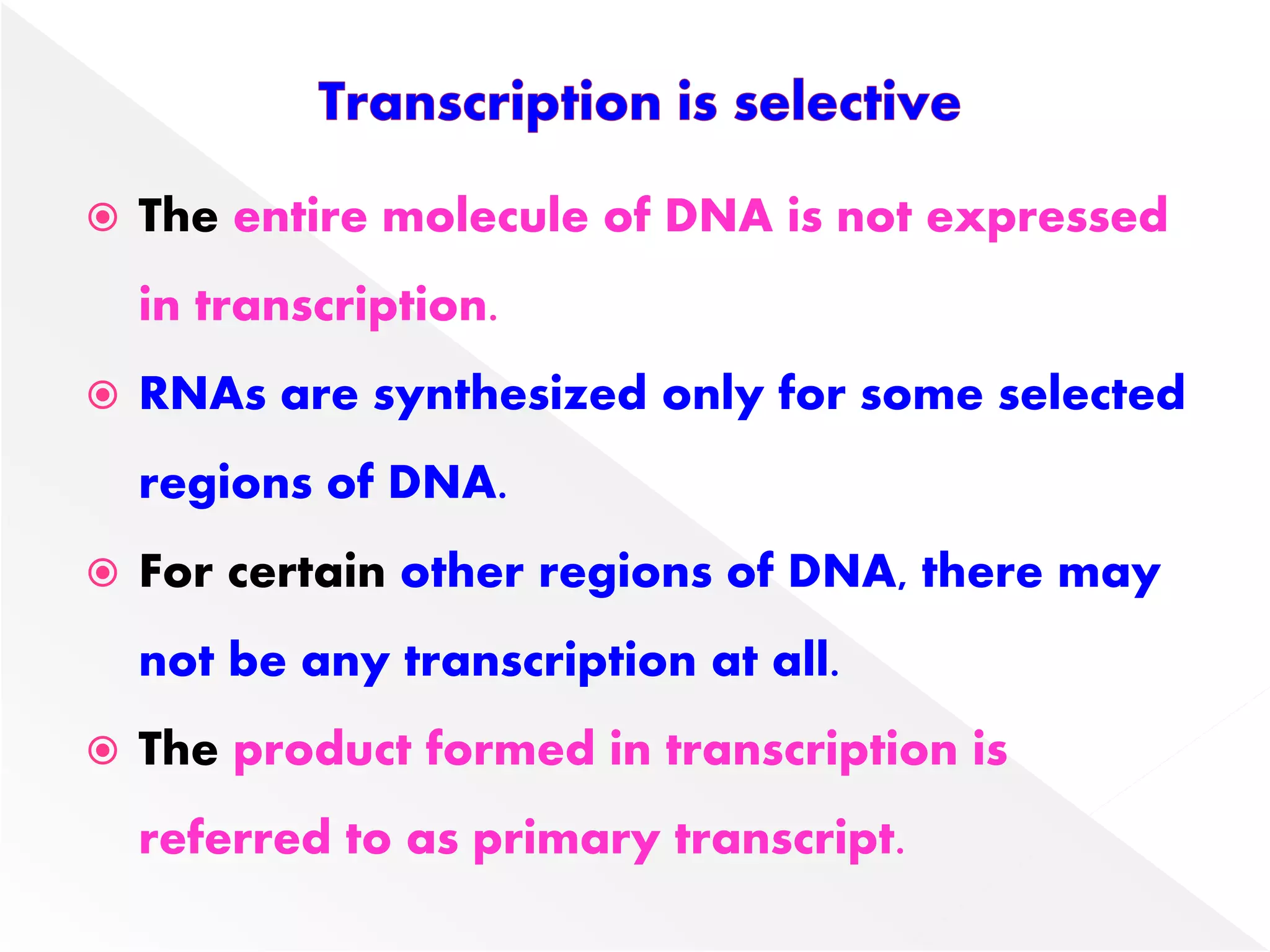
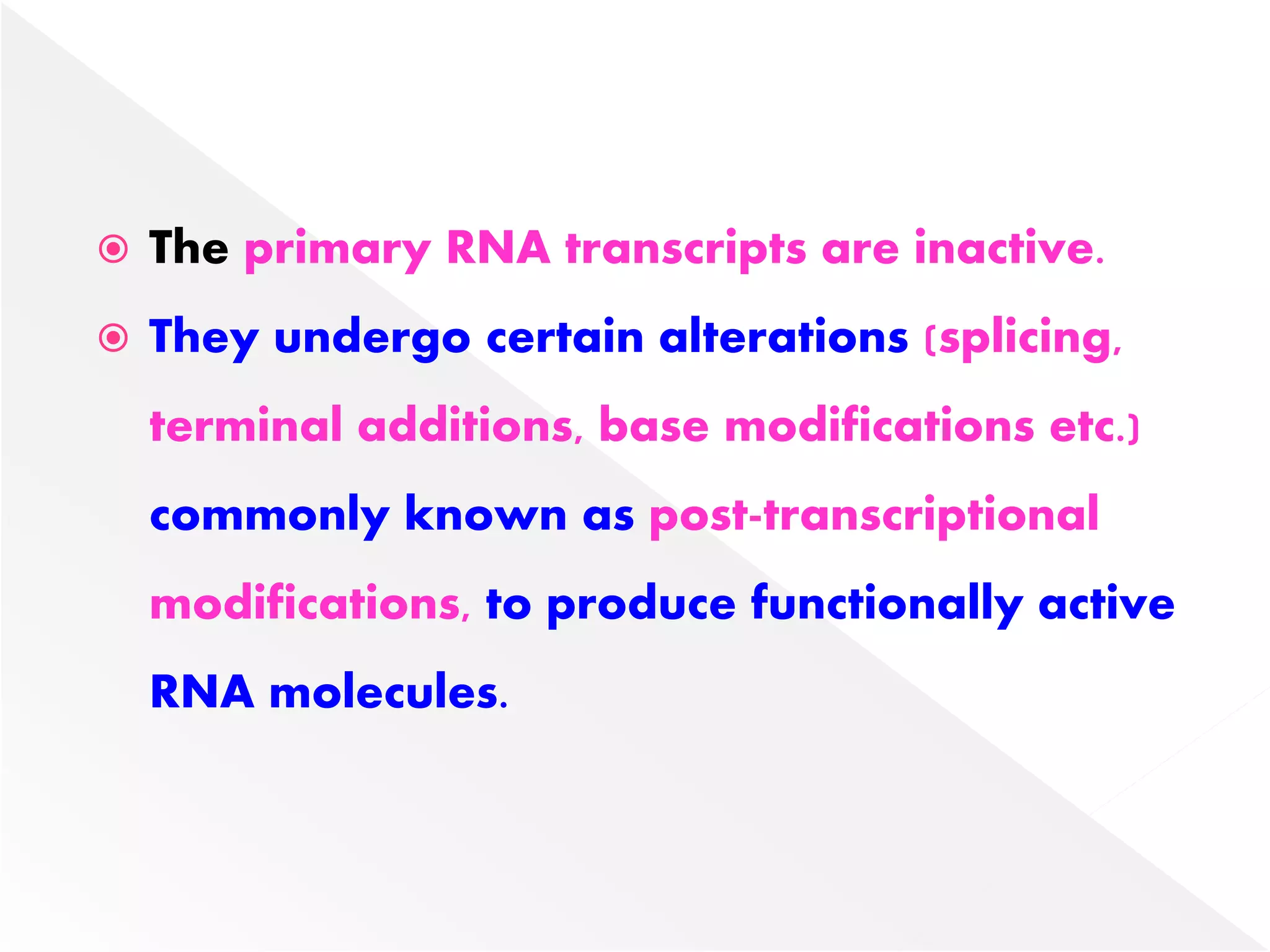
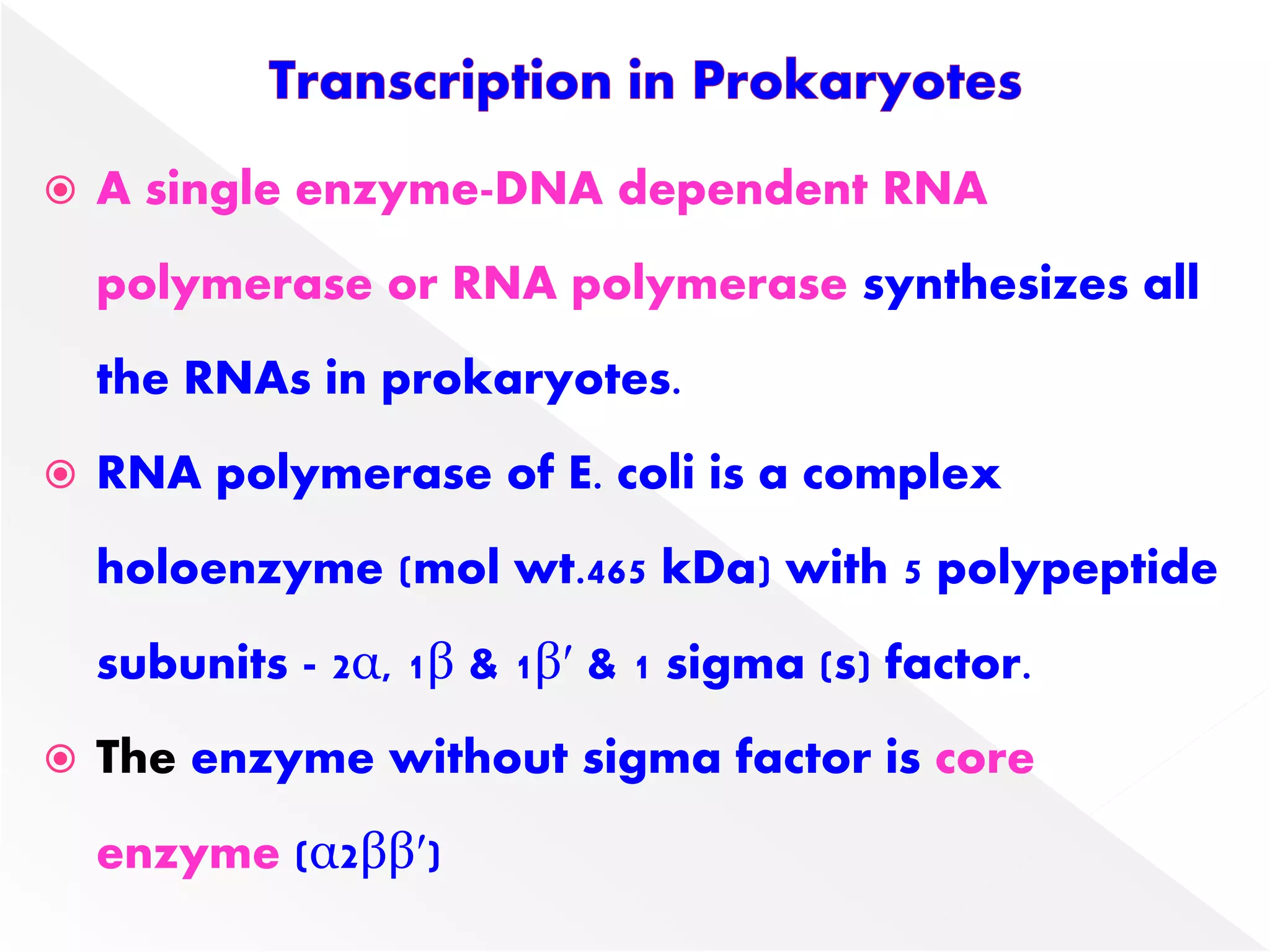
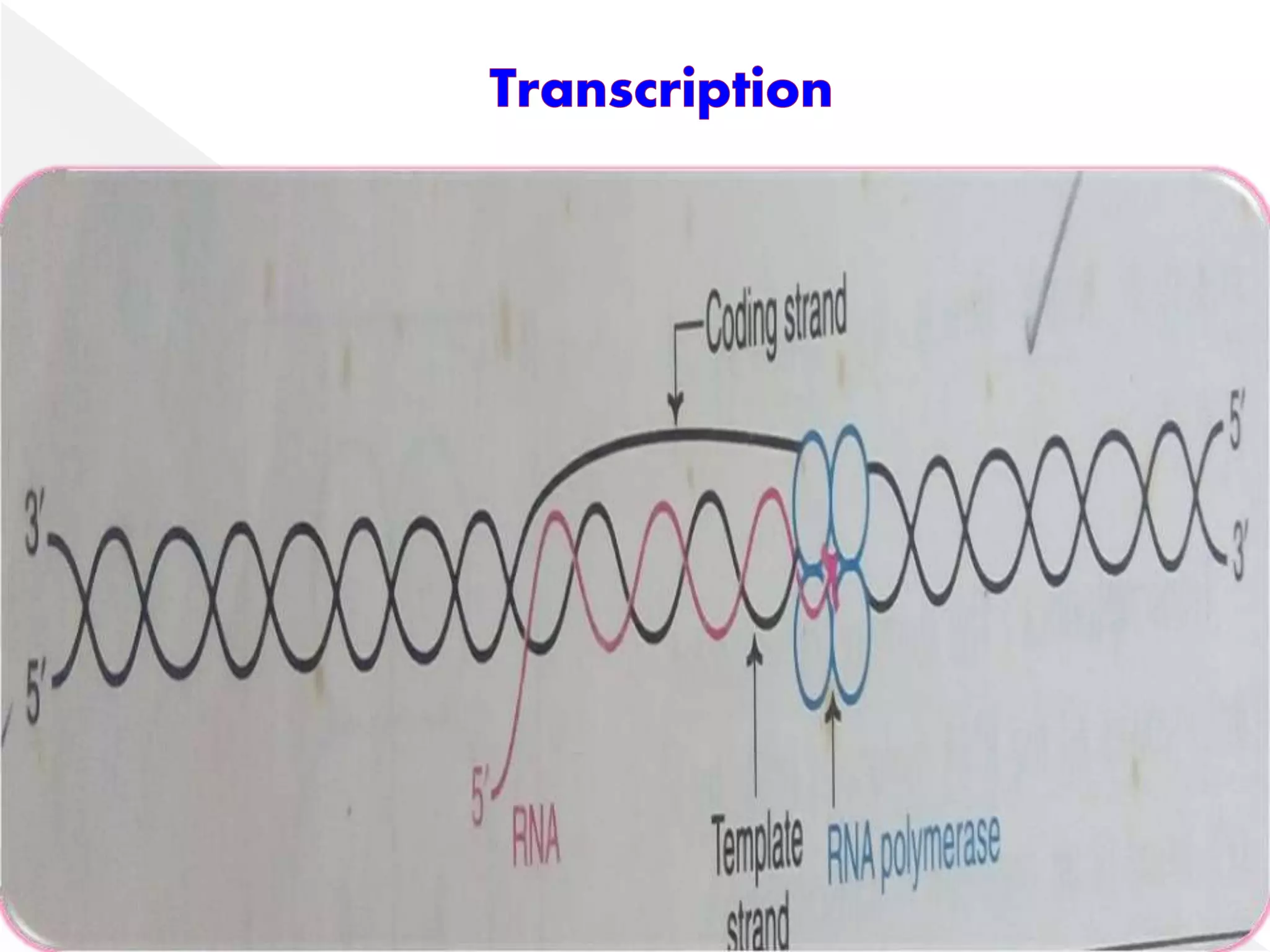
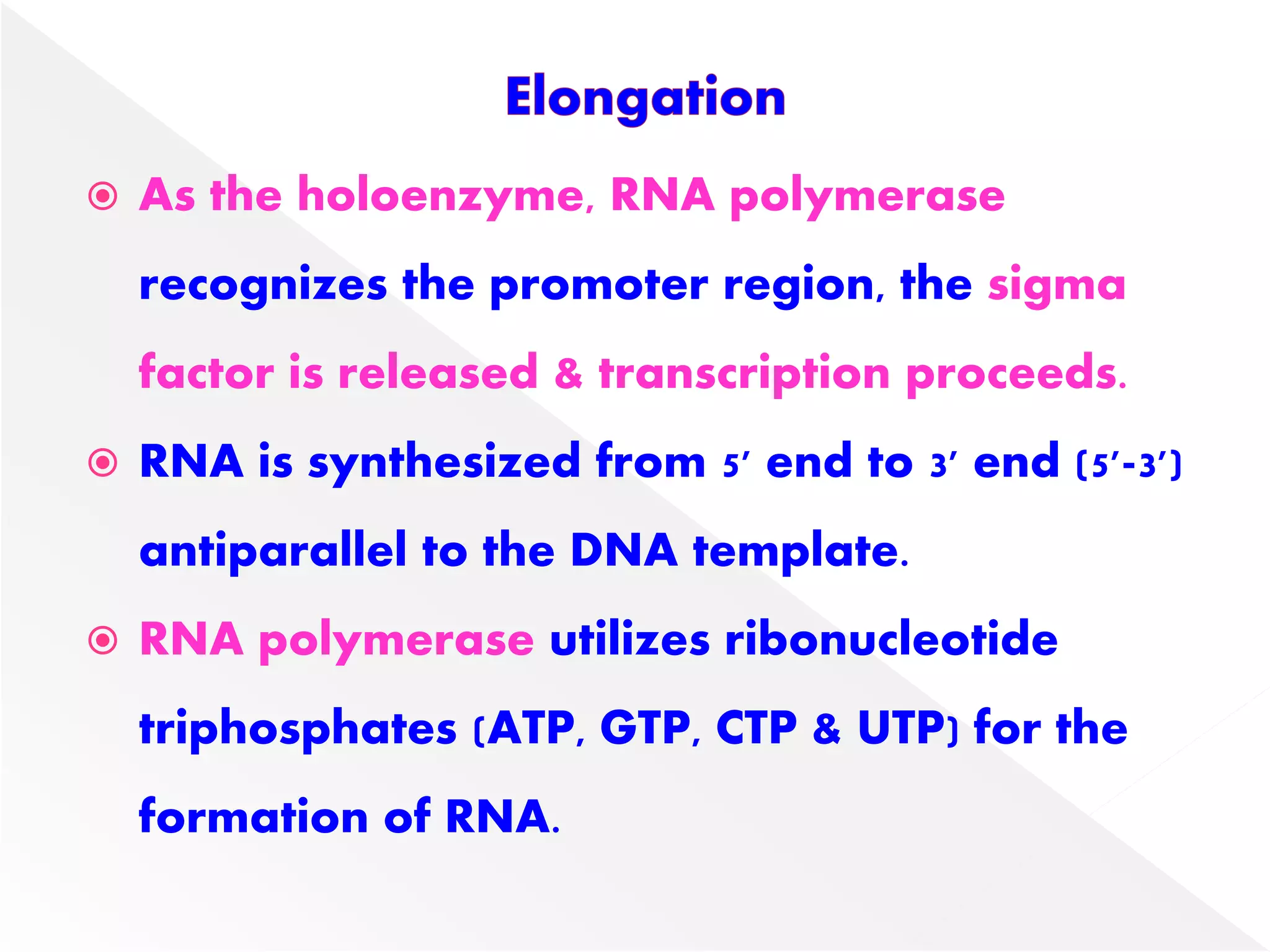
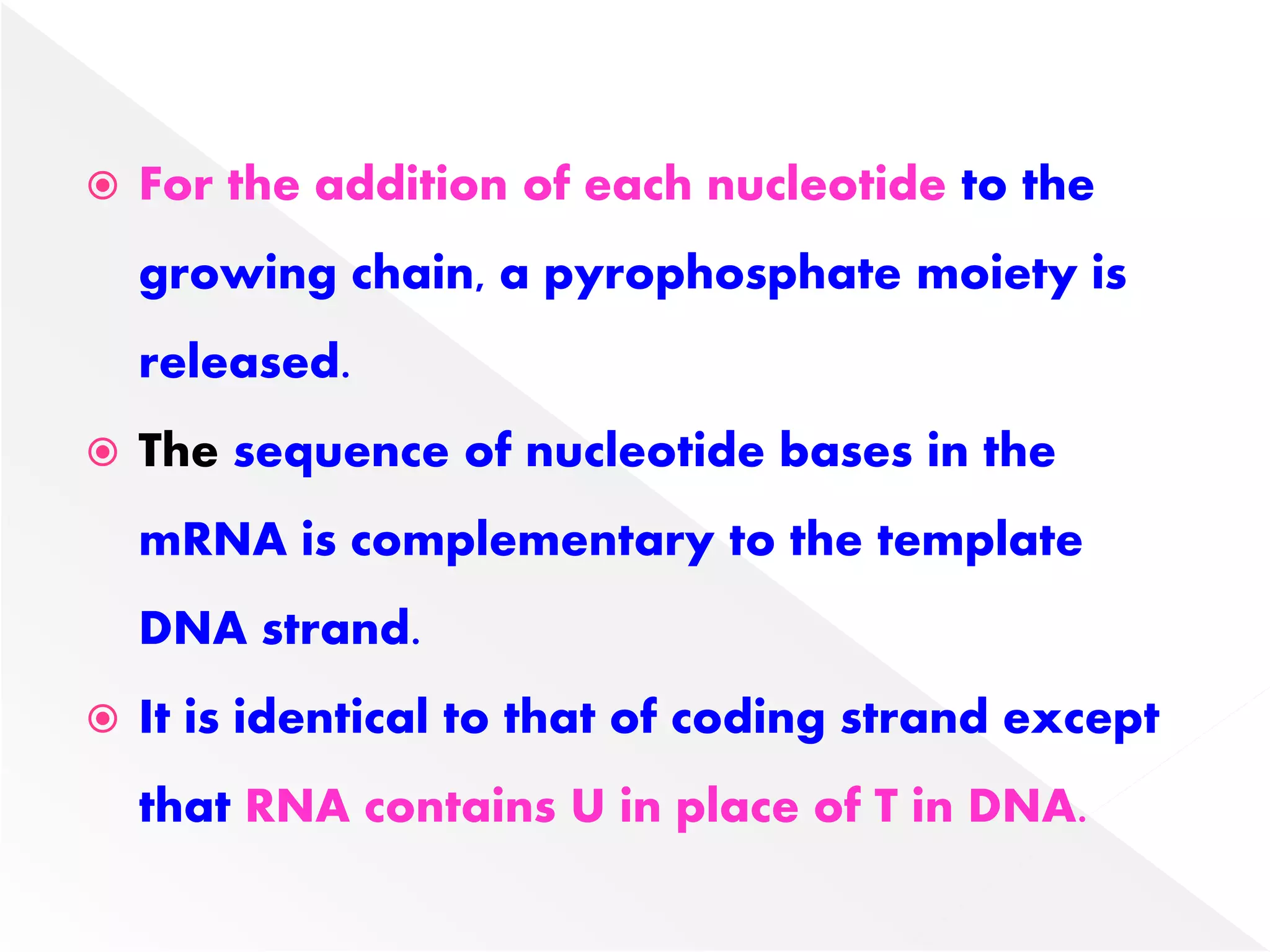
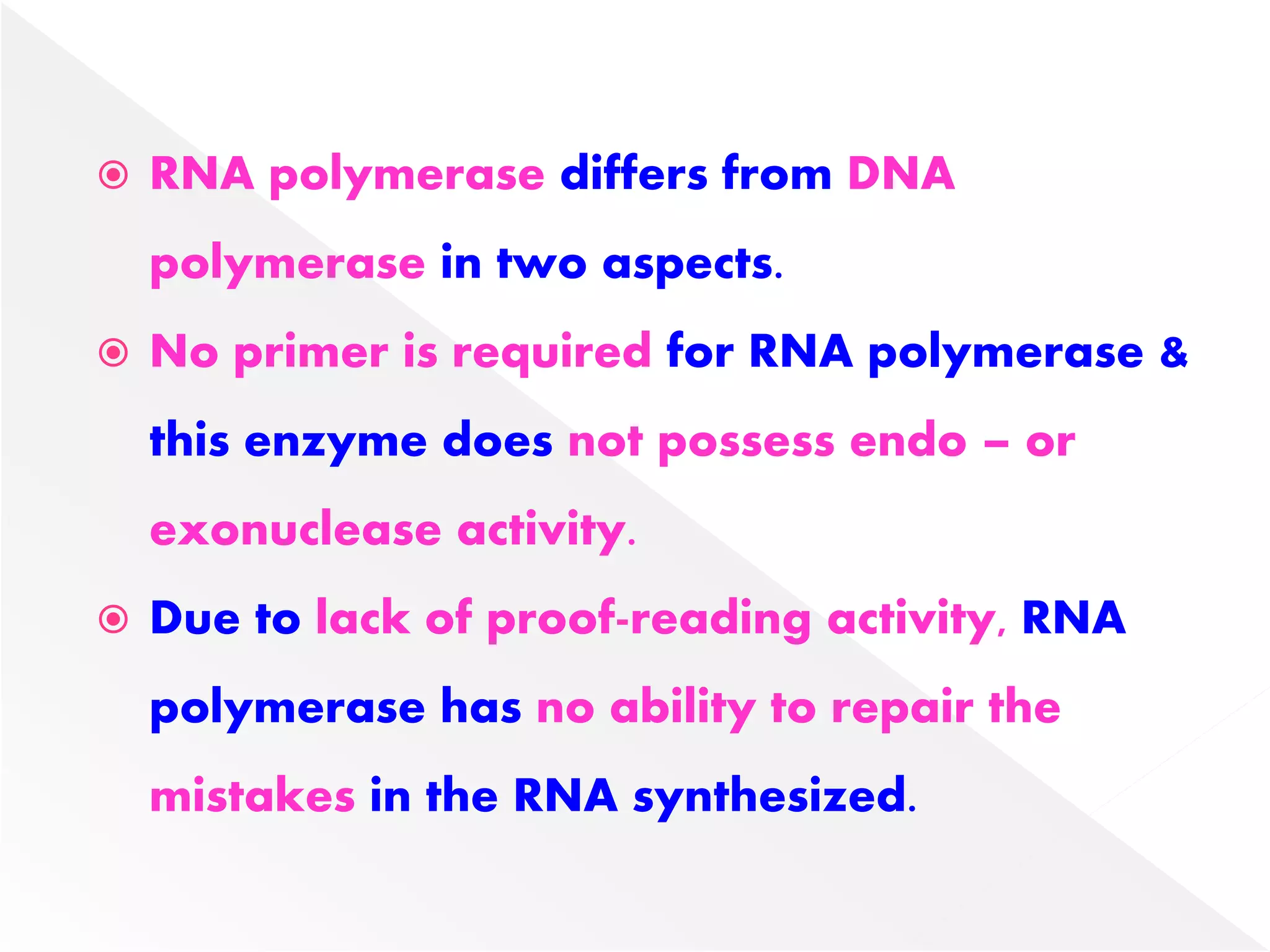
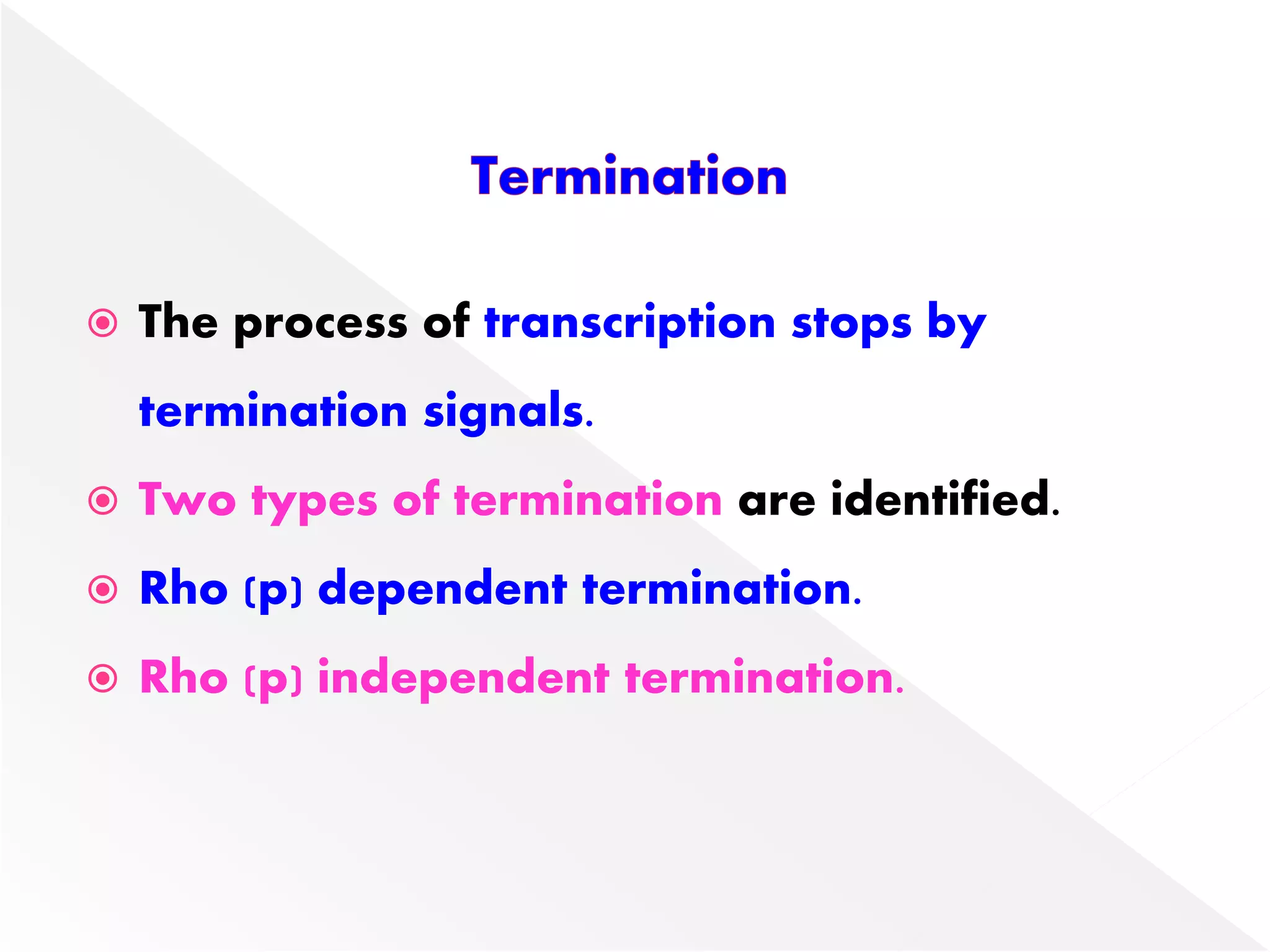
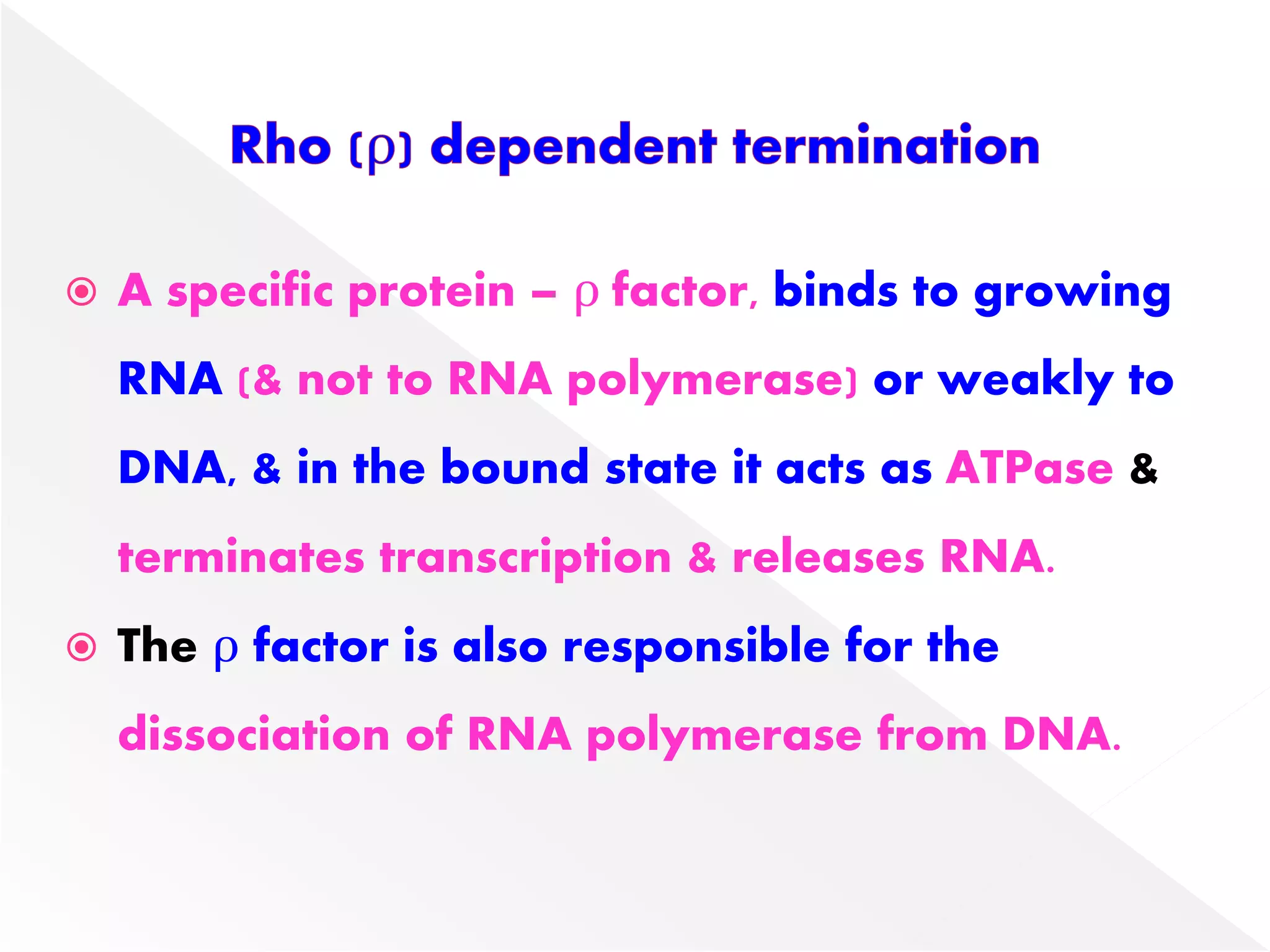
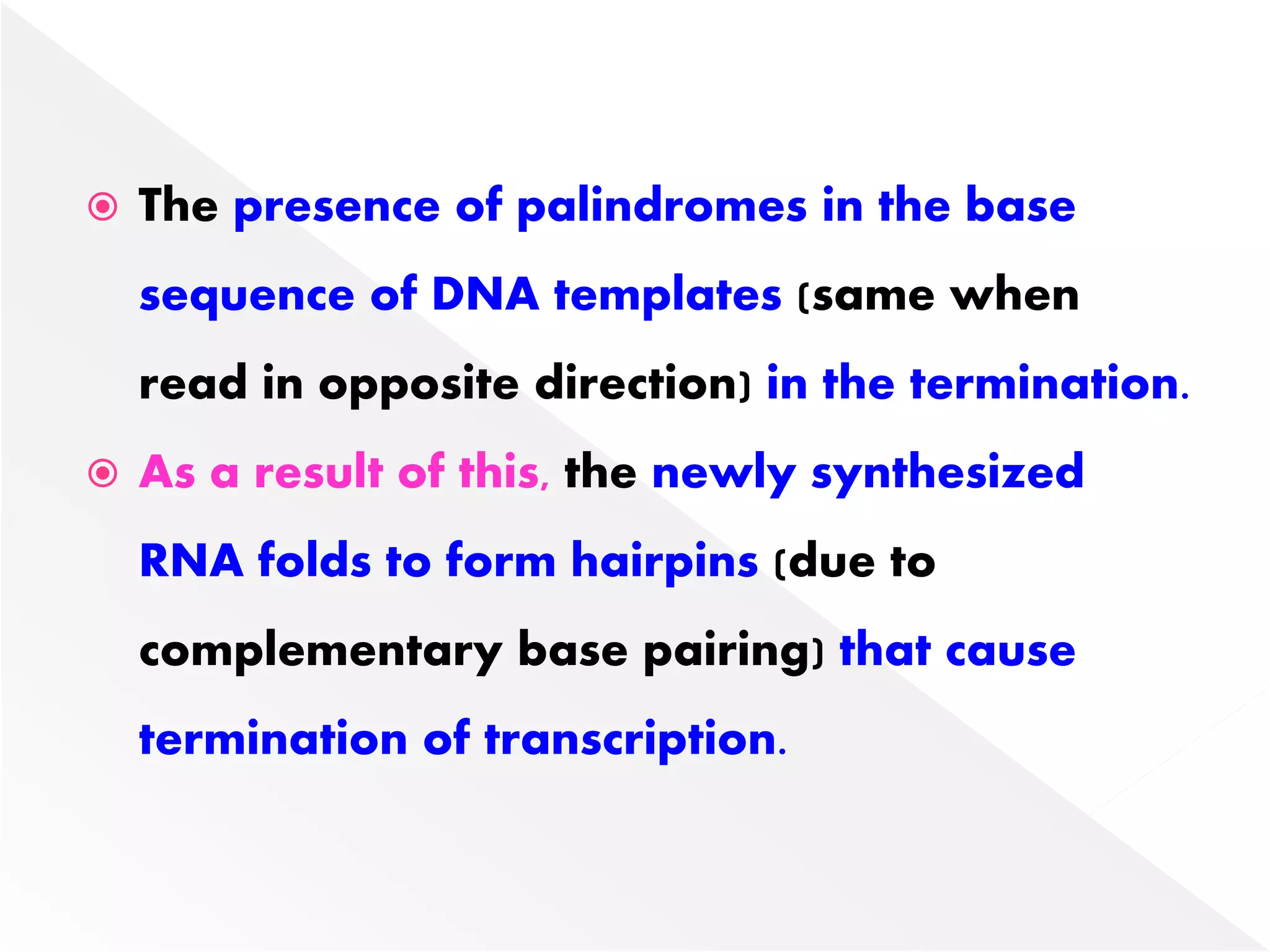
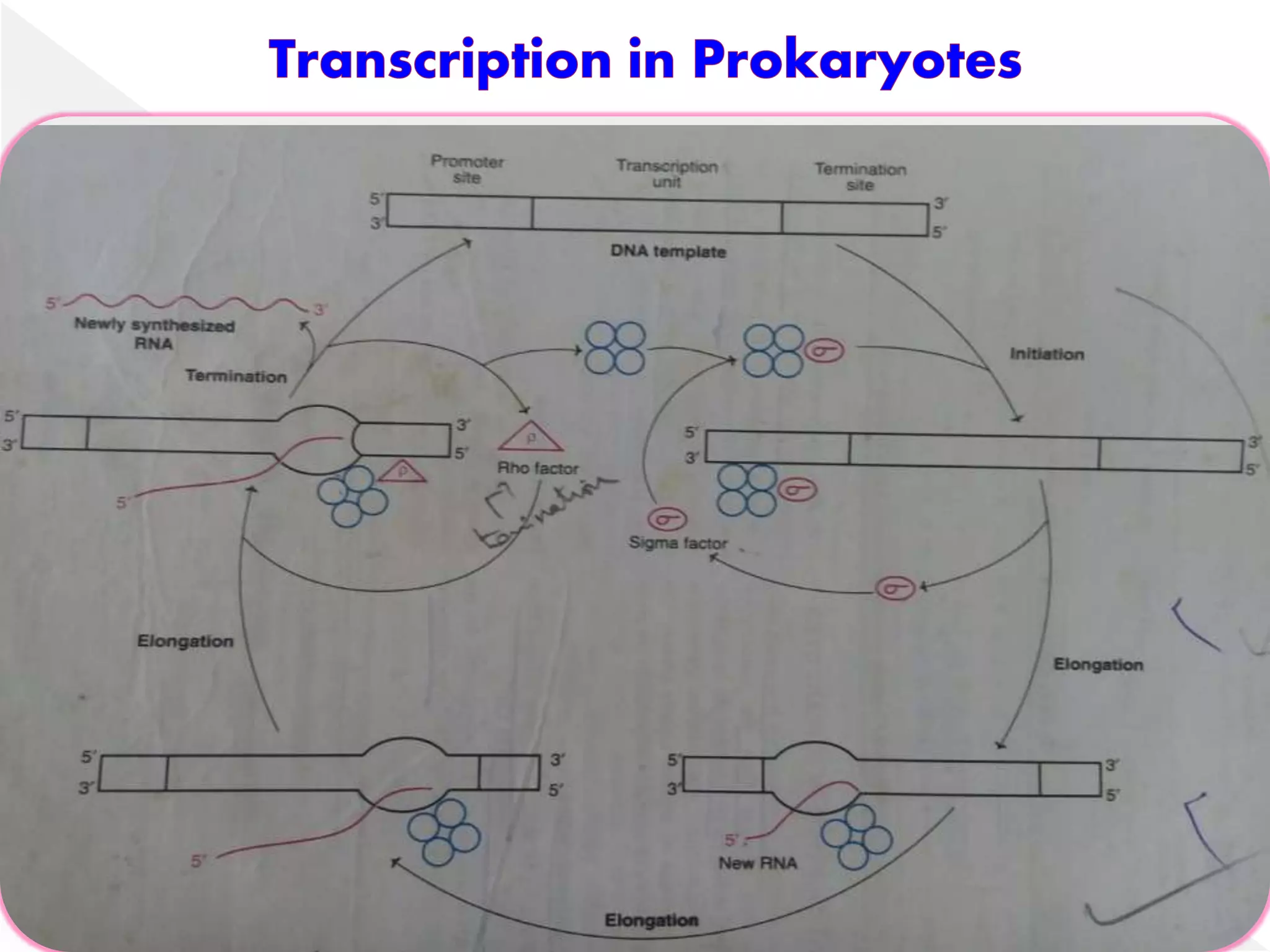
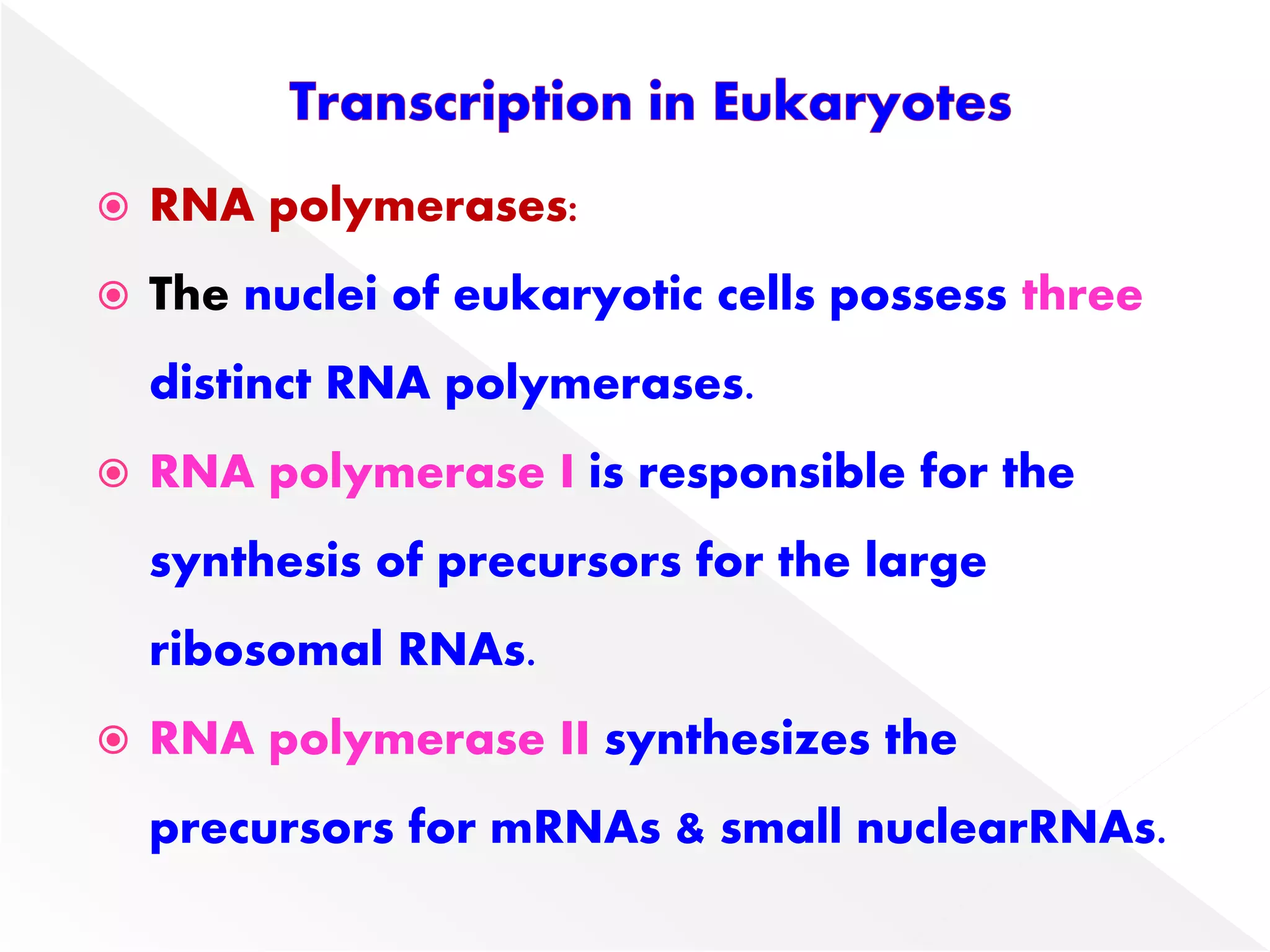
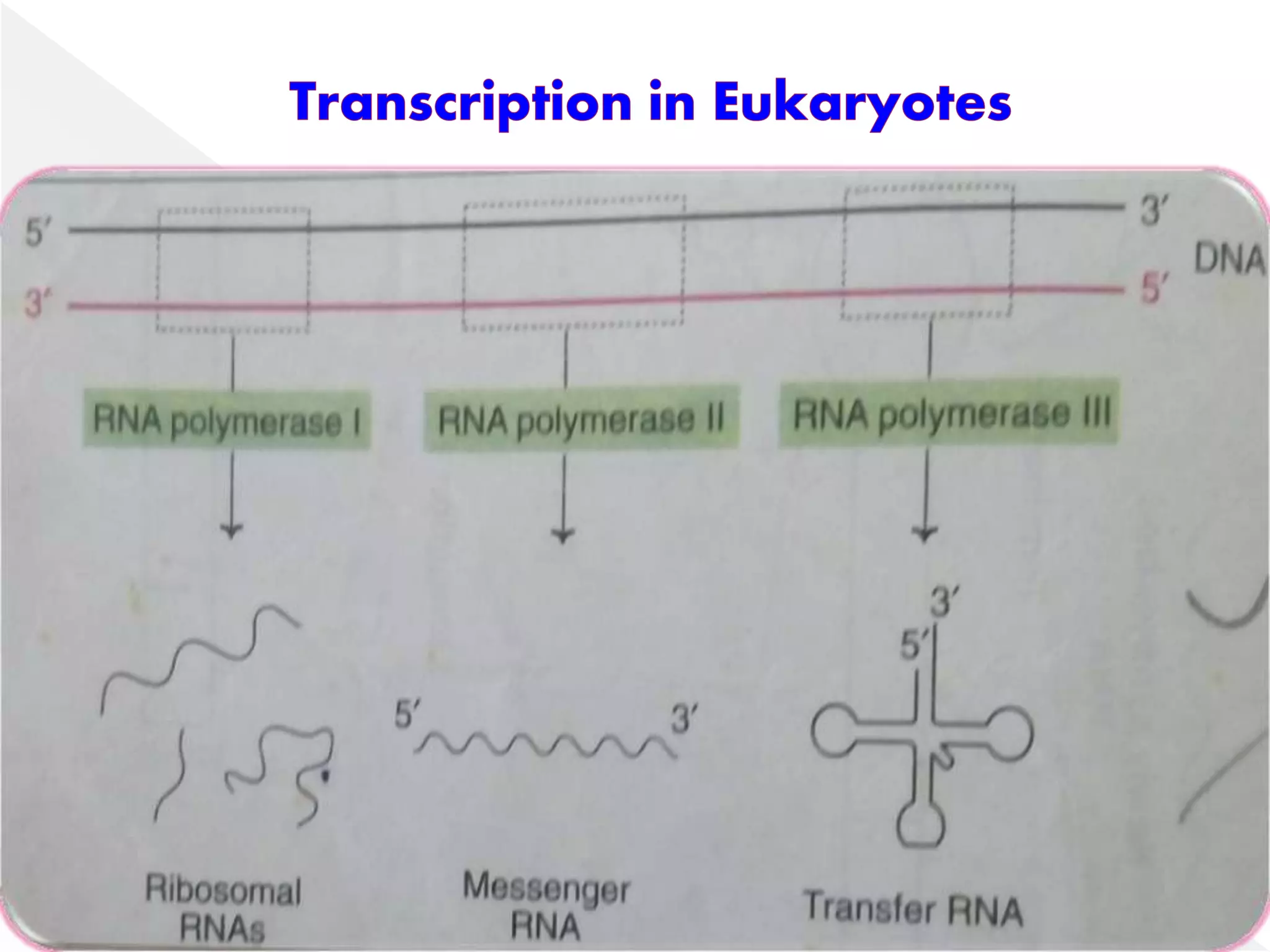
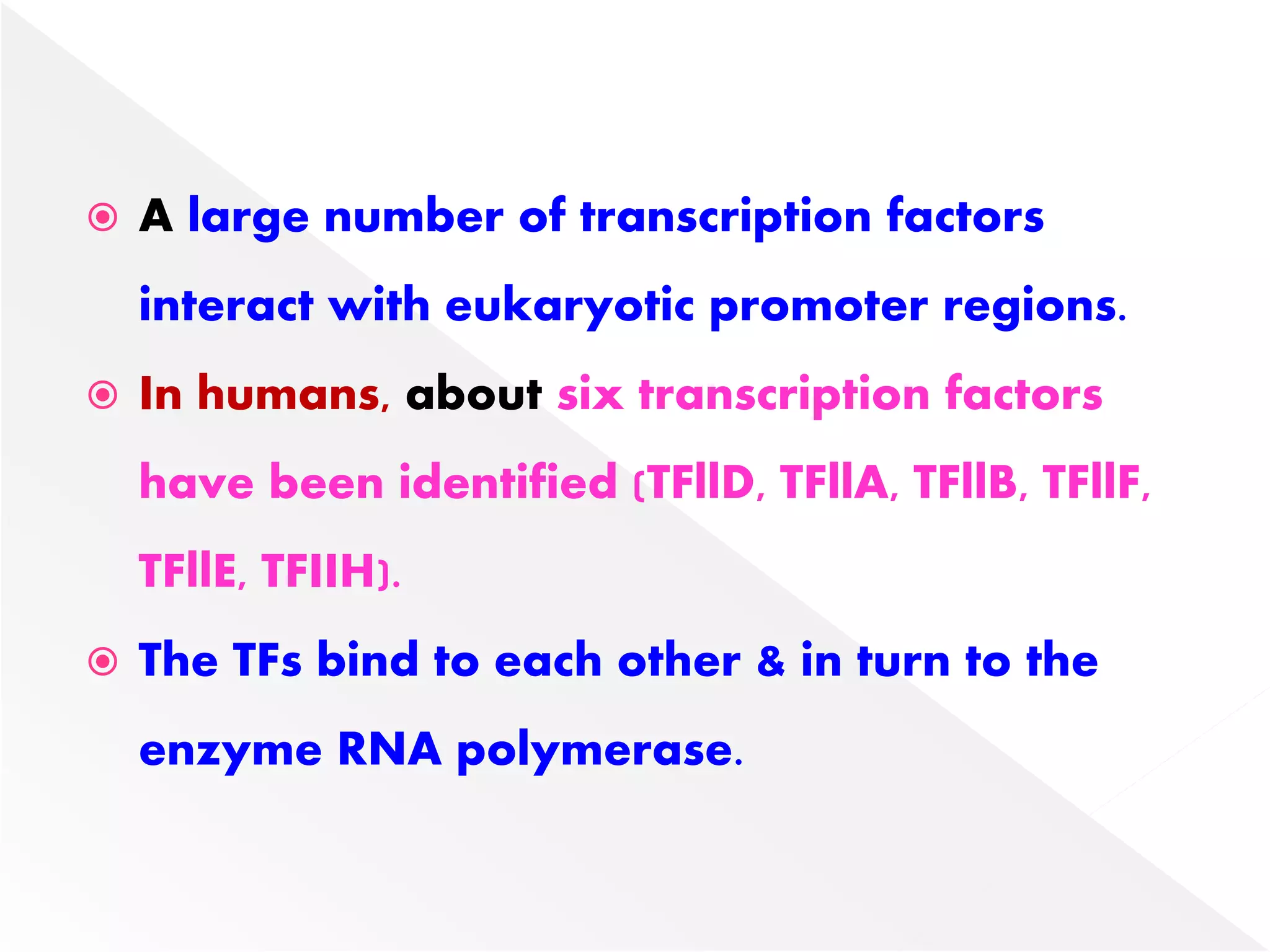
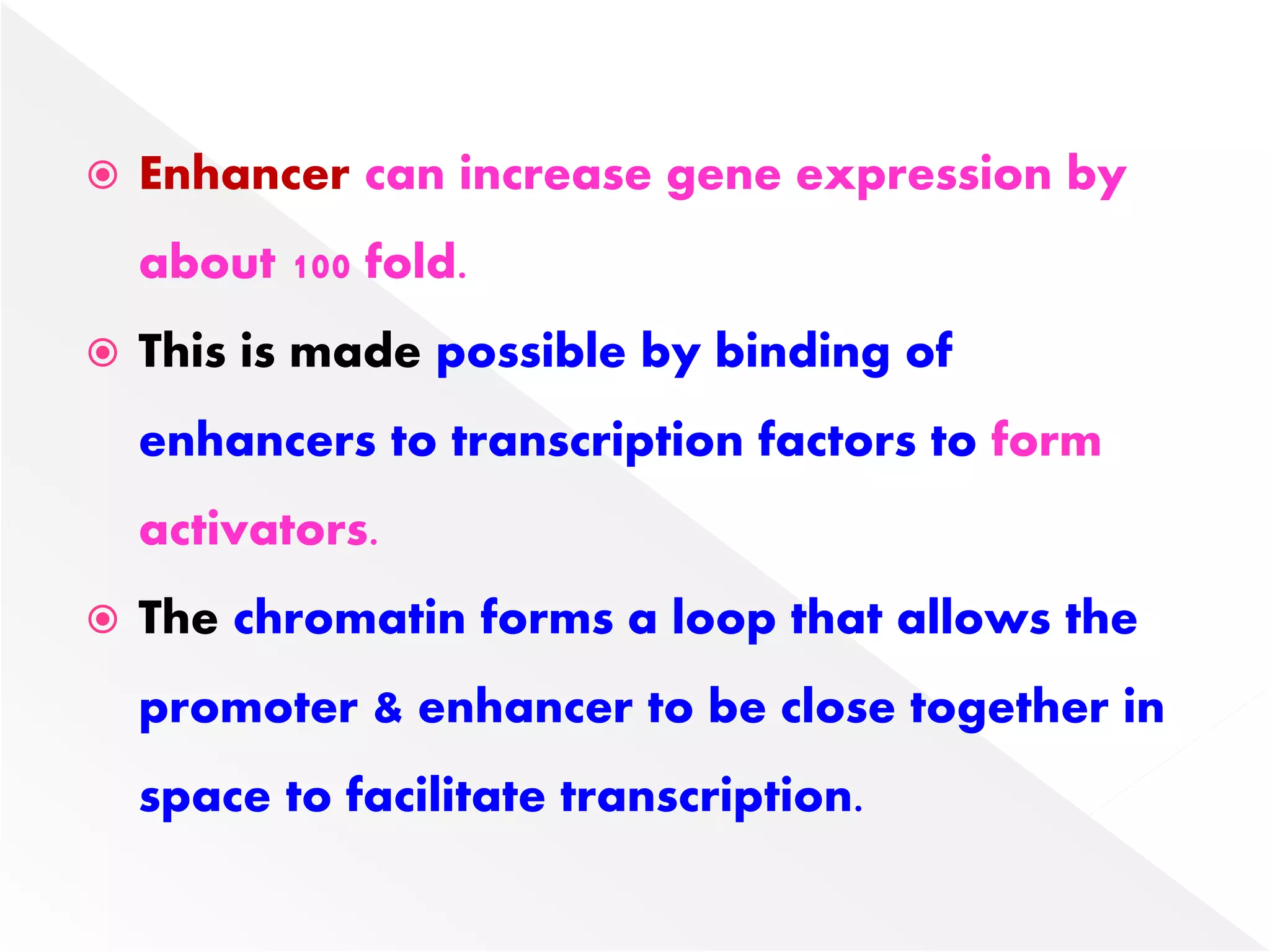
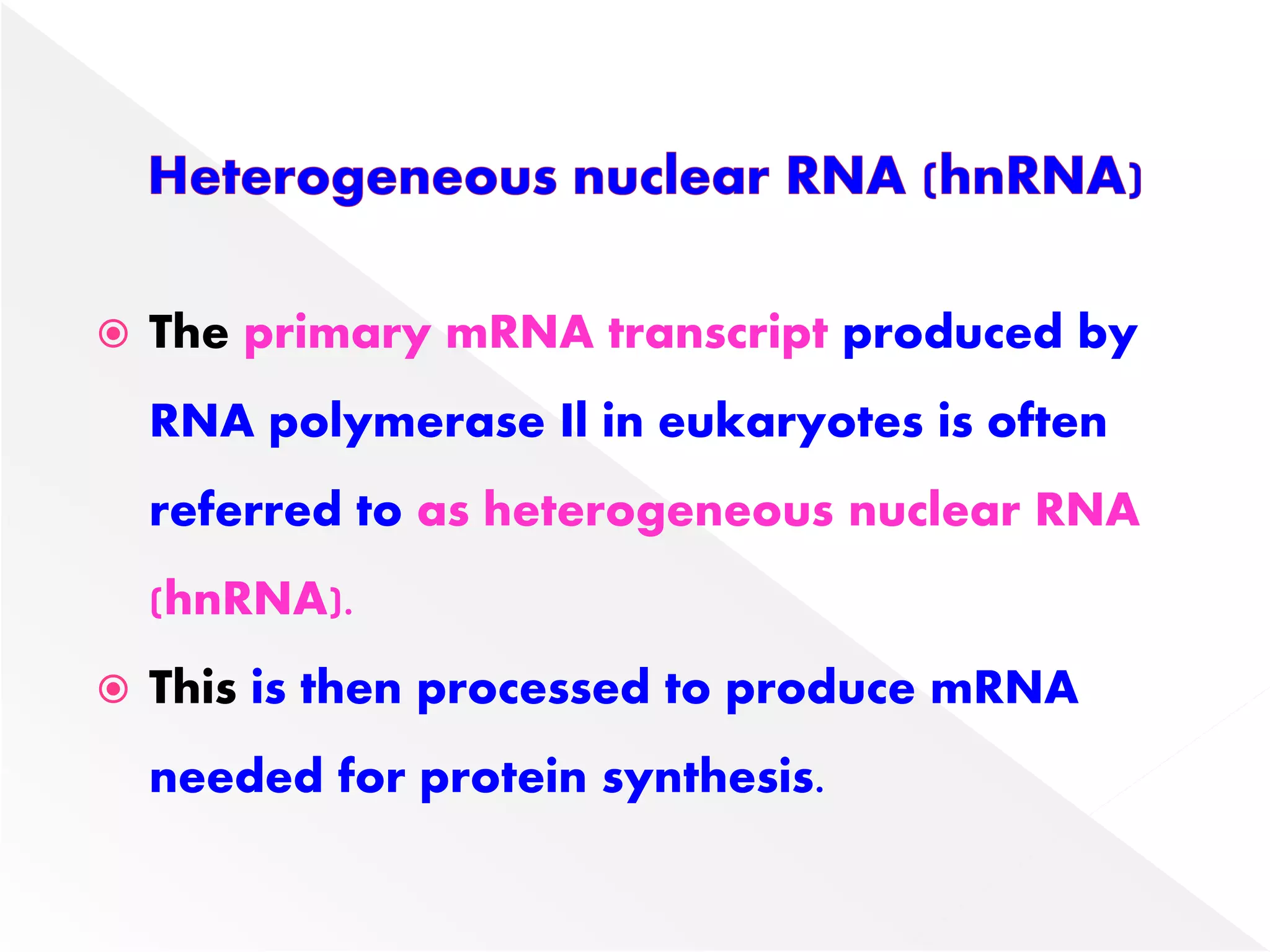
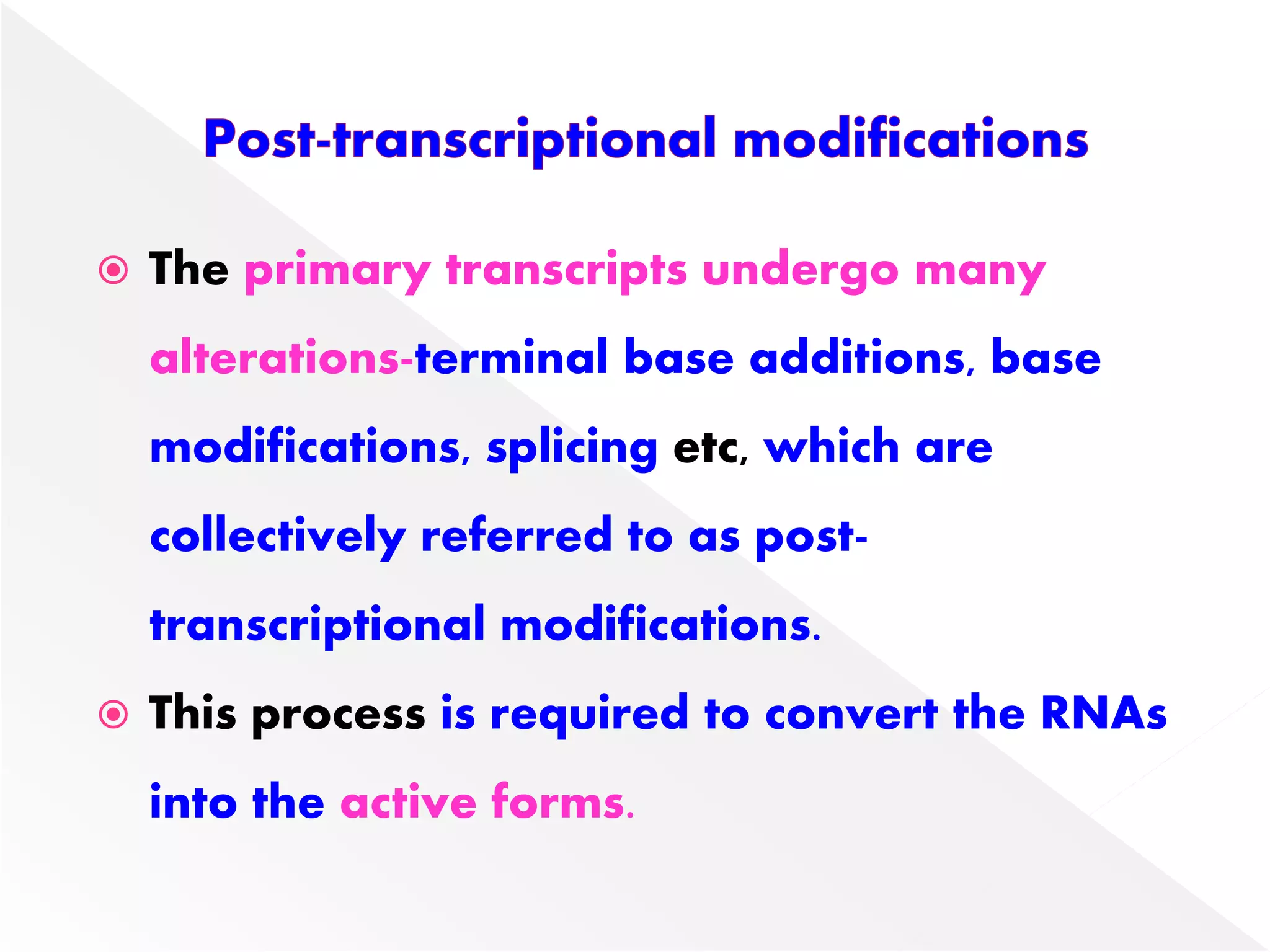
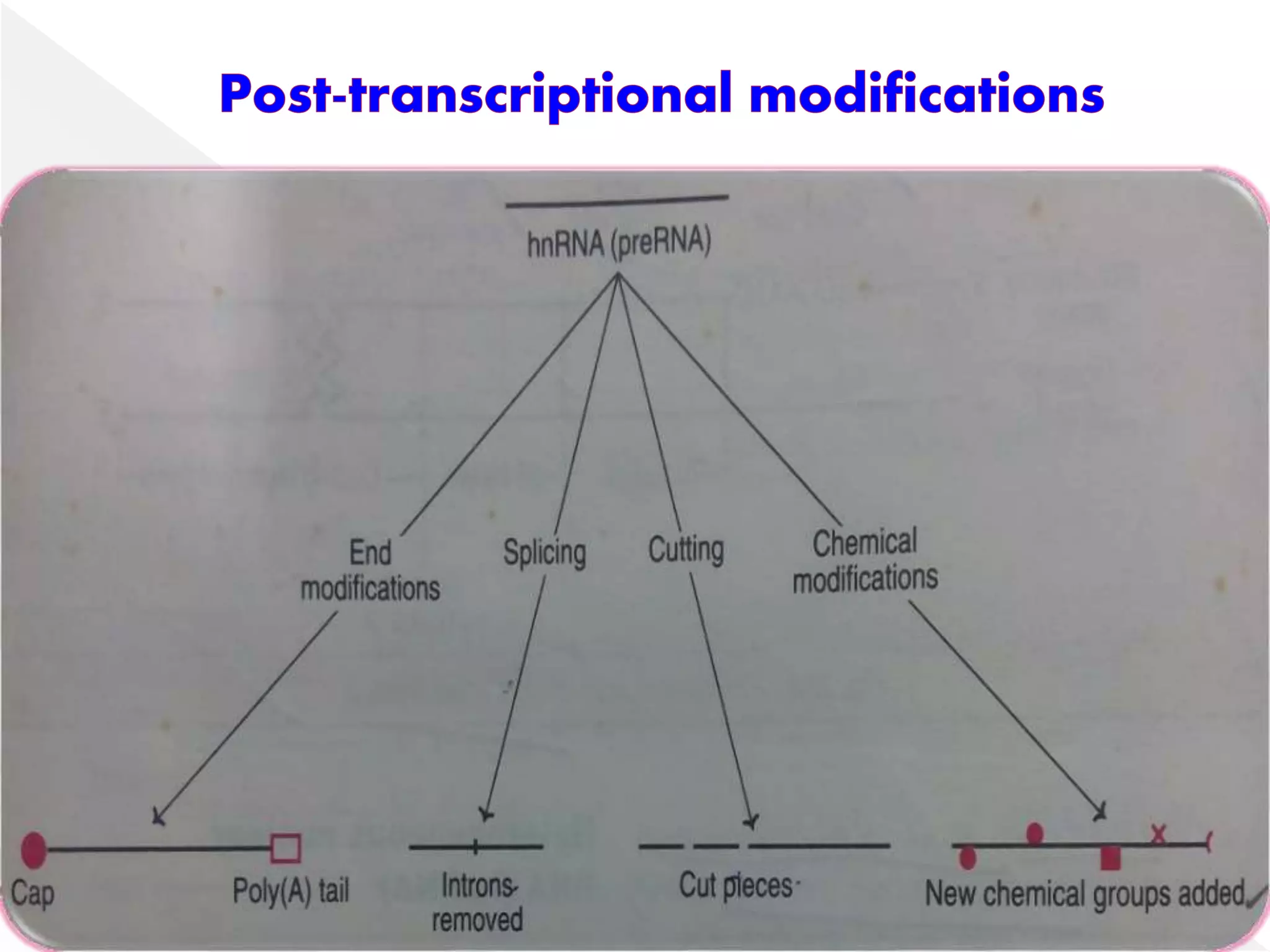
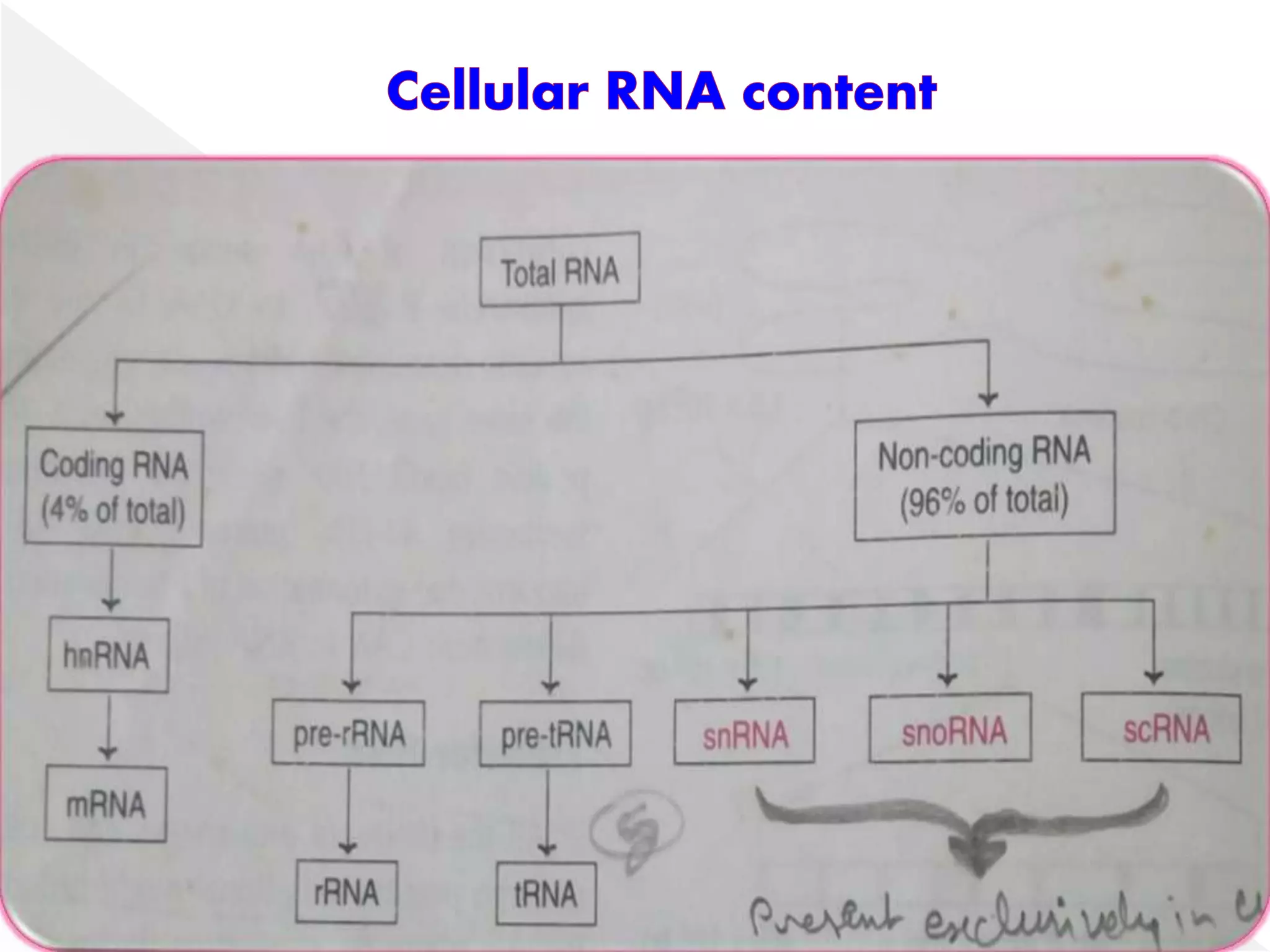
Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. In prokaryotes, a single RNA polymerase synthesizes all RNA, while eukaryotes have multiple RNA polymerases. The enzyme binds to promoter regions on DNA and uses one strand as a template to make complementary RNA. Primary transcripts in eukaryotes undergo processing like capping, polyadenylation, and splicing to produce mature, functional RNAs that can be translated or act as non-coding RNAs. Transcription involves initiation, elongation, and termination and can be inhibited by various antibiotics that target bacterial or eukaryotic RNA polymerases.