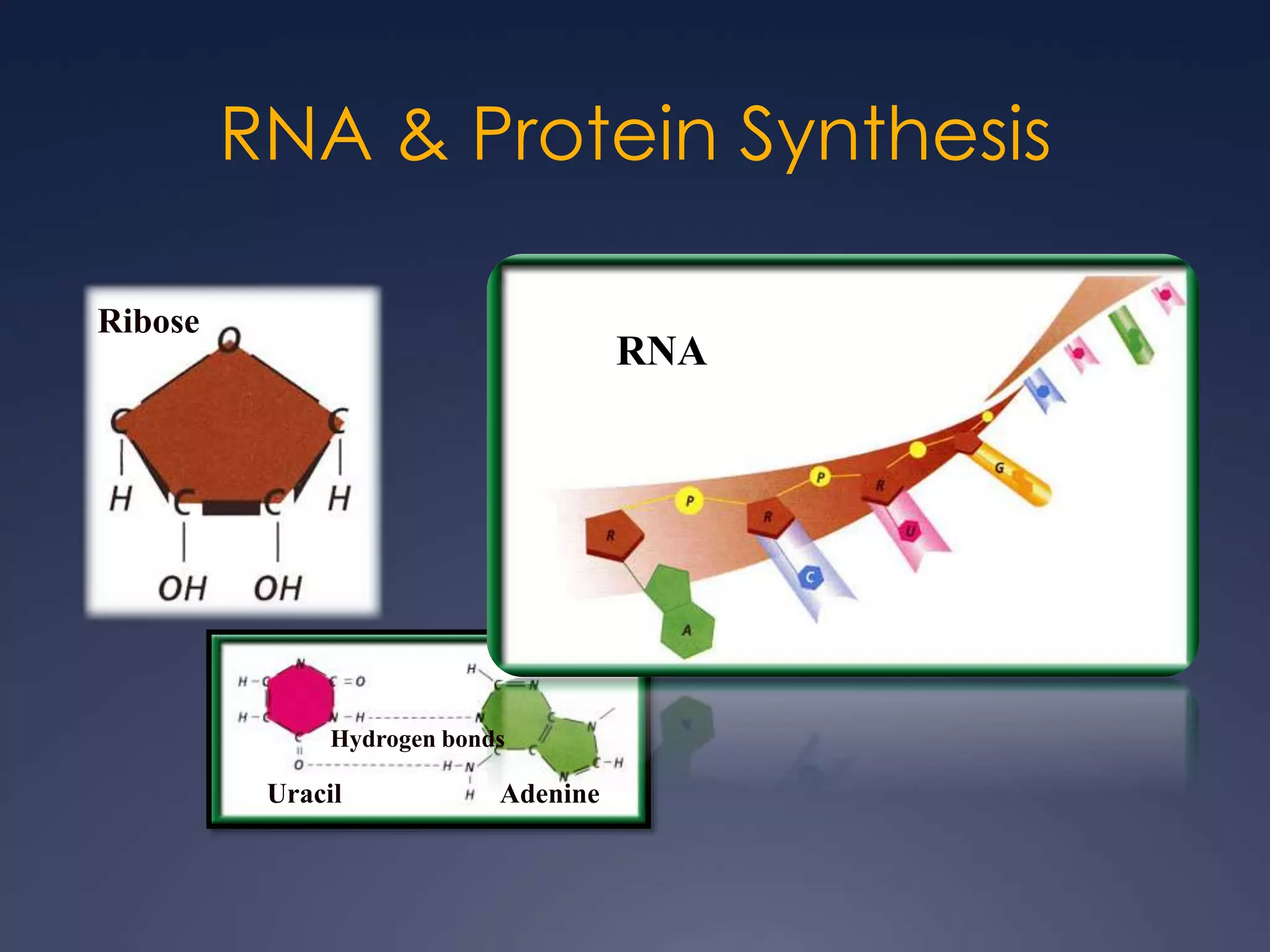
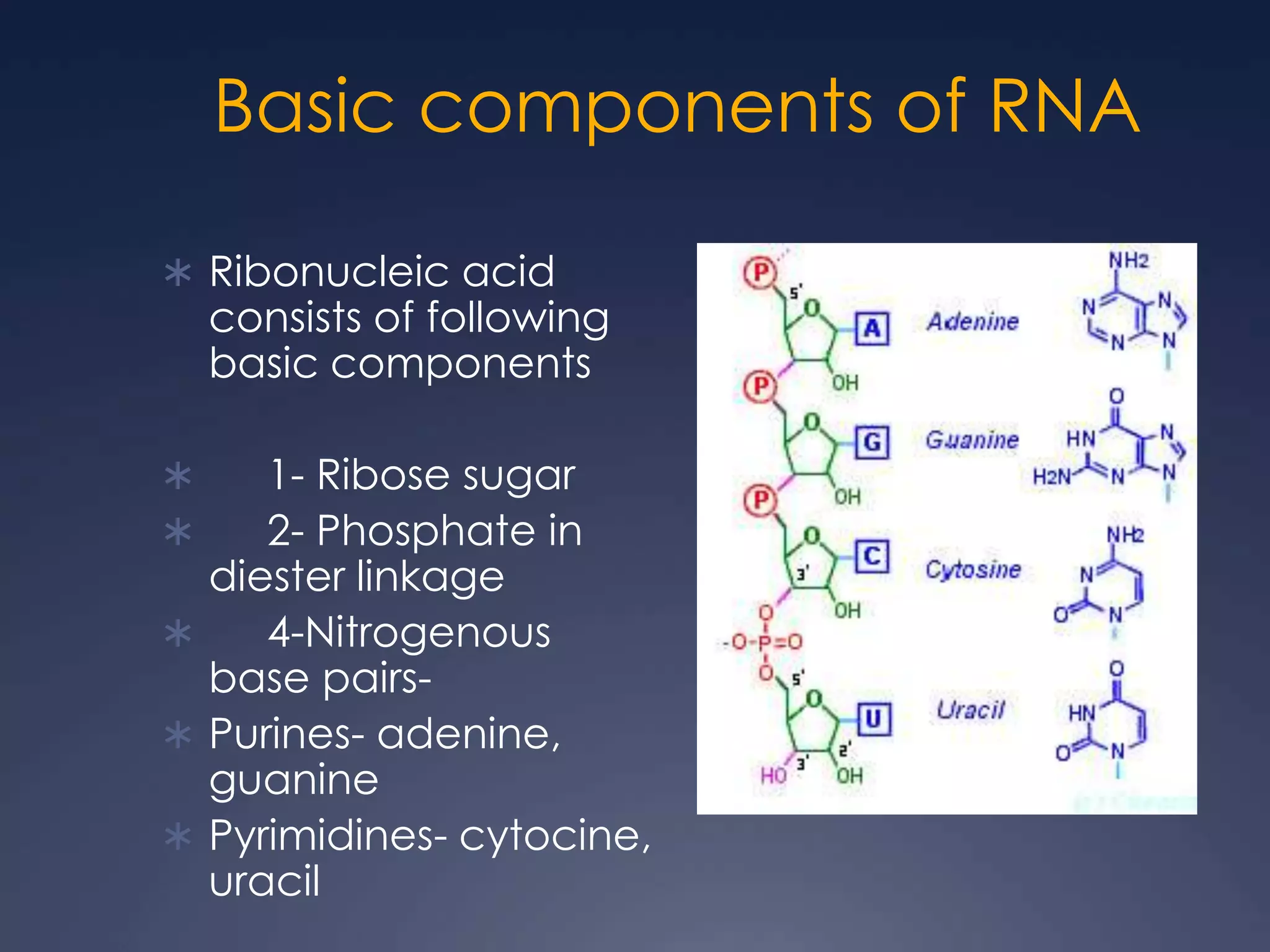
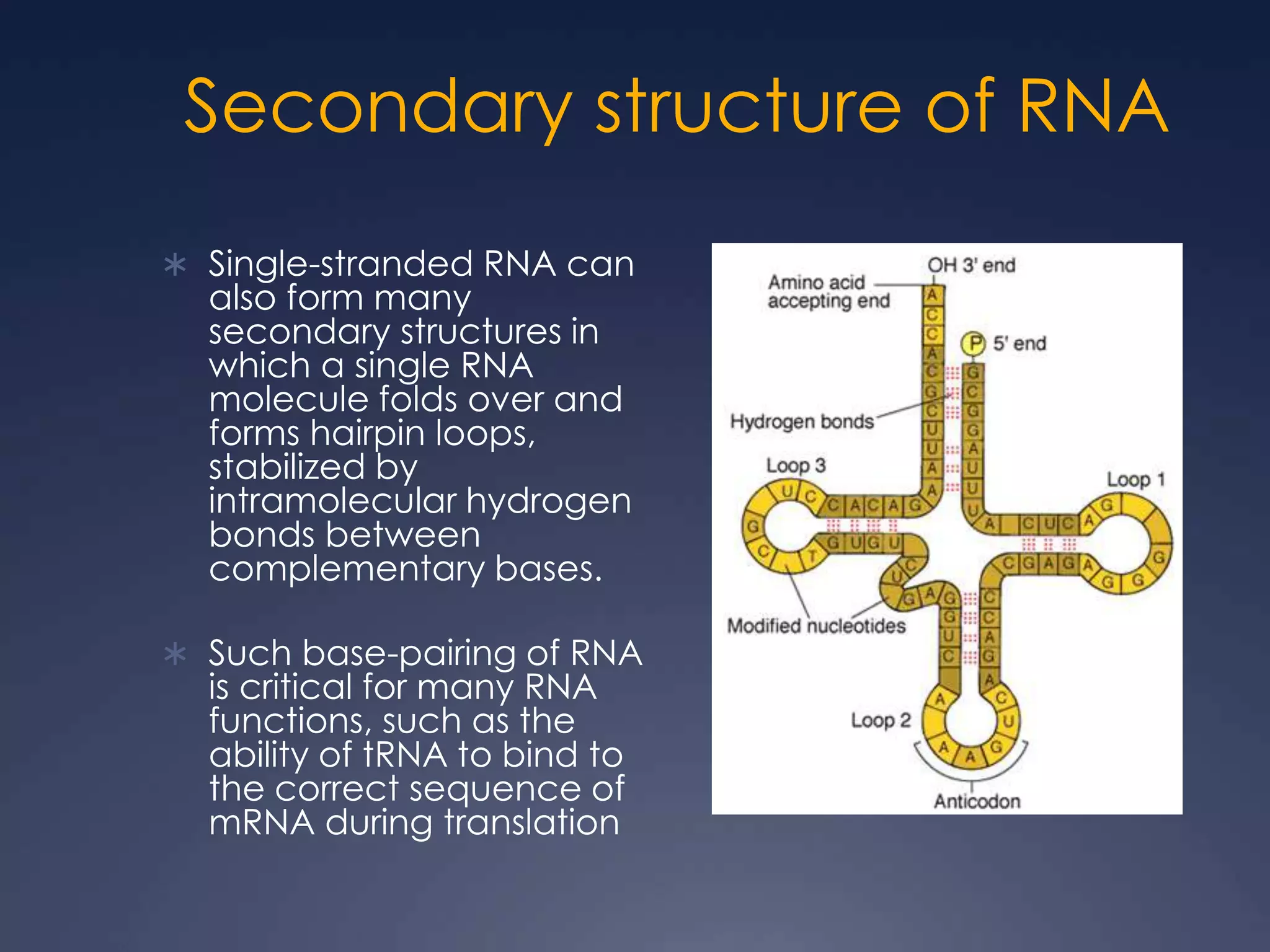
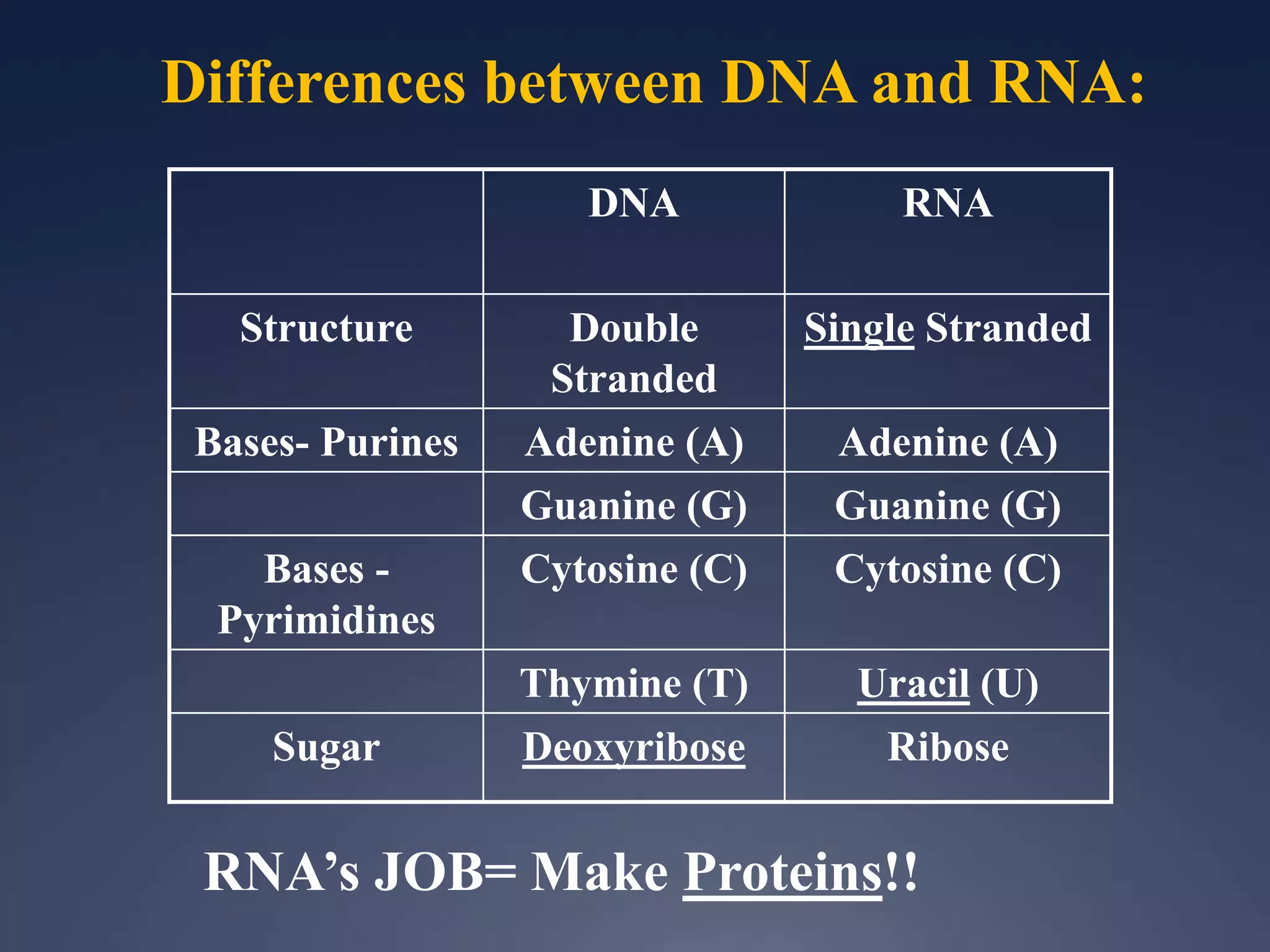
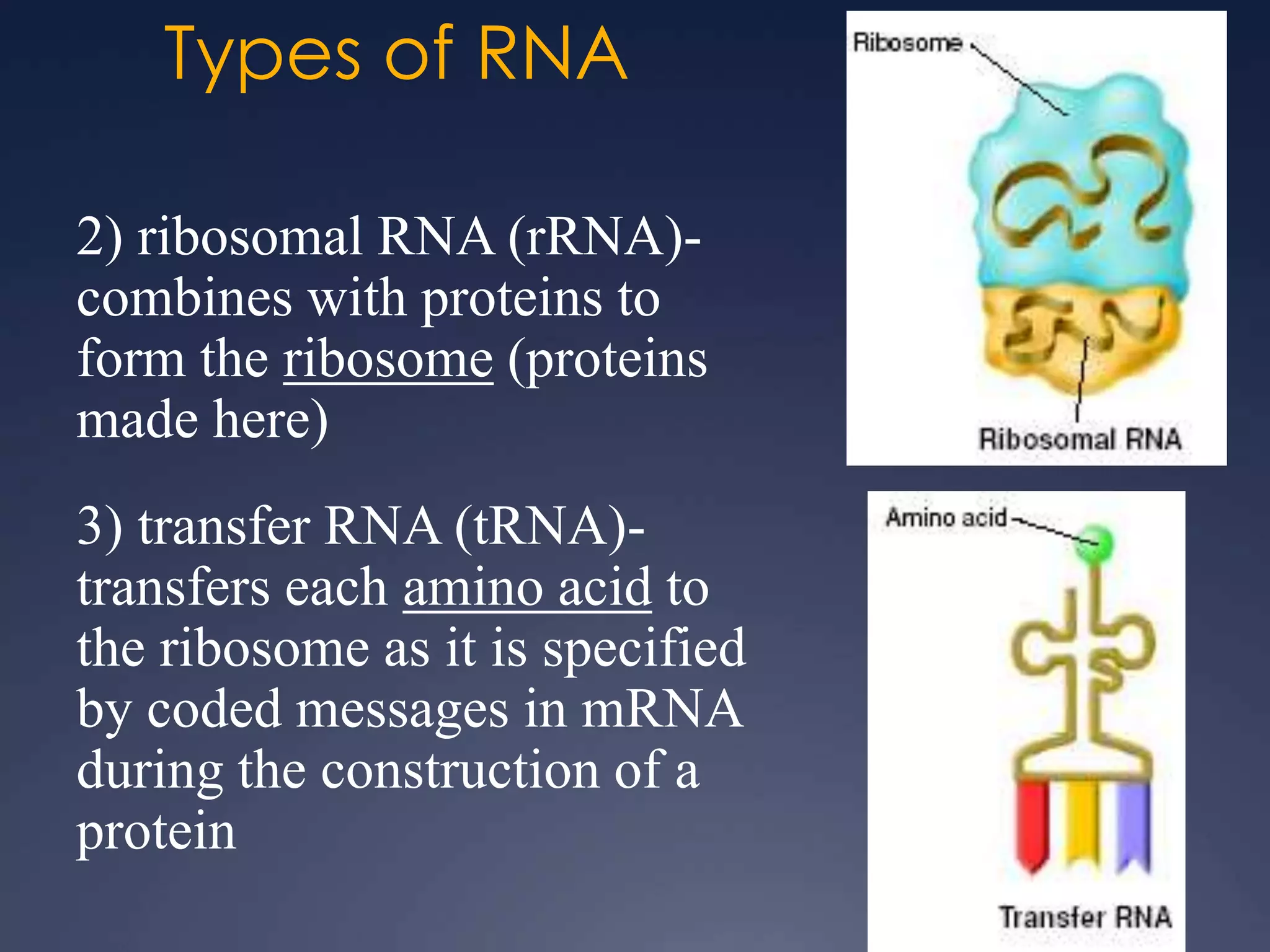
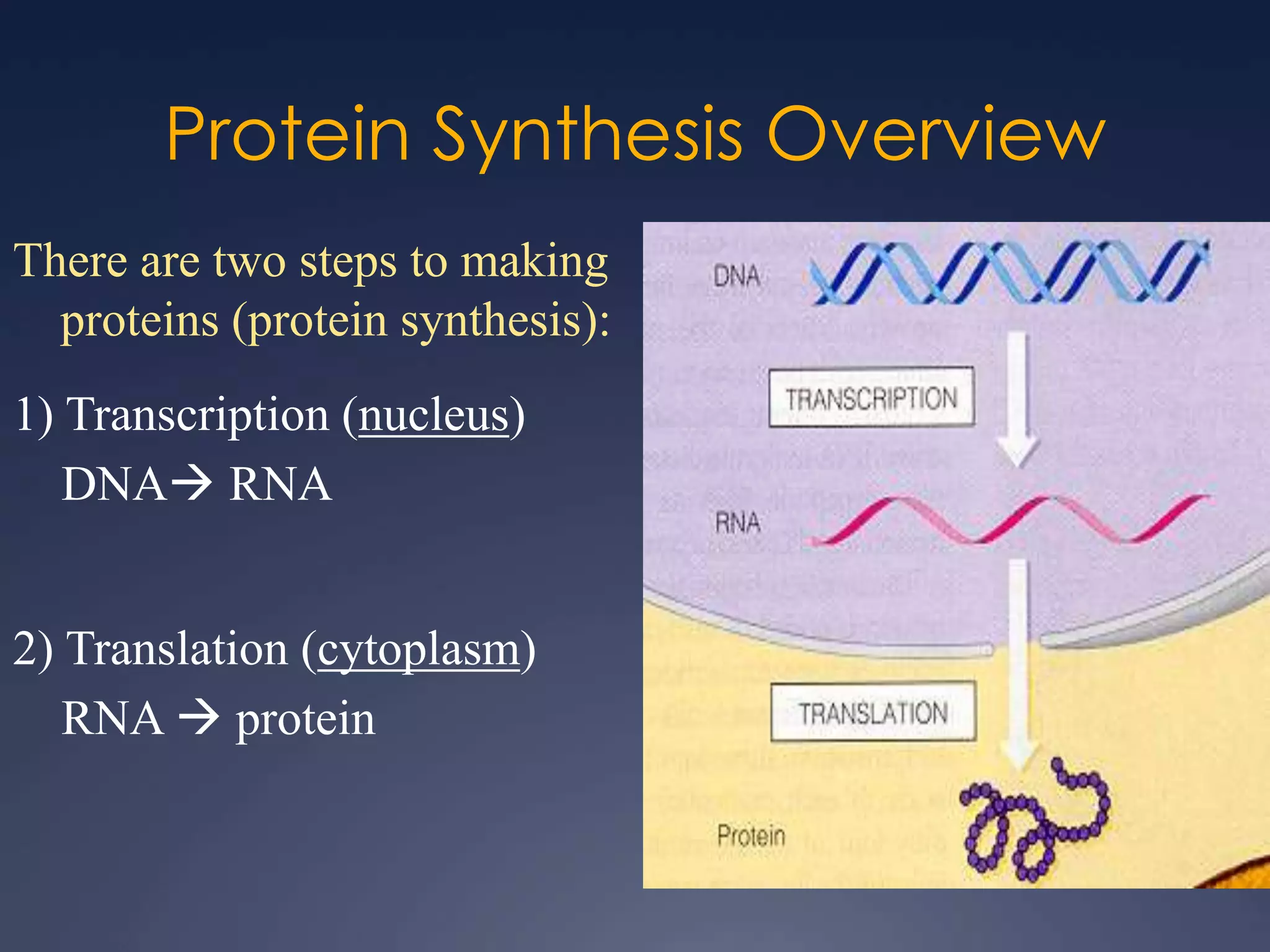
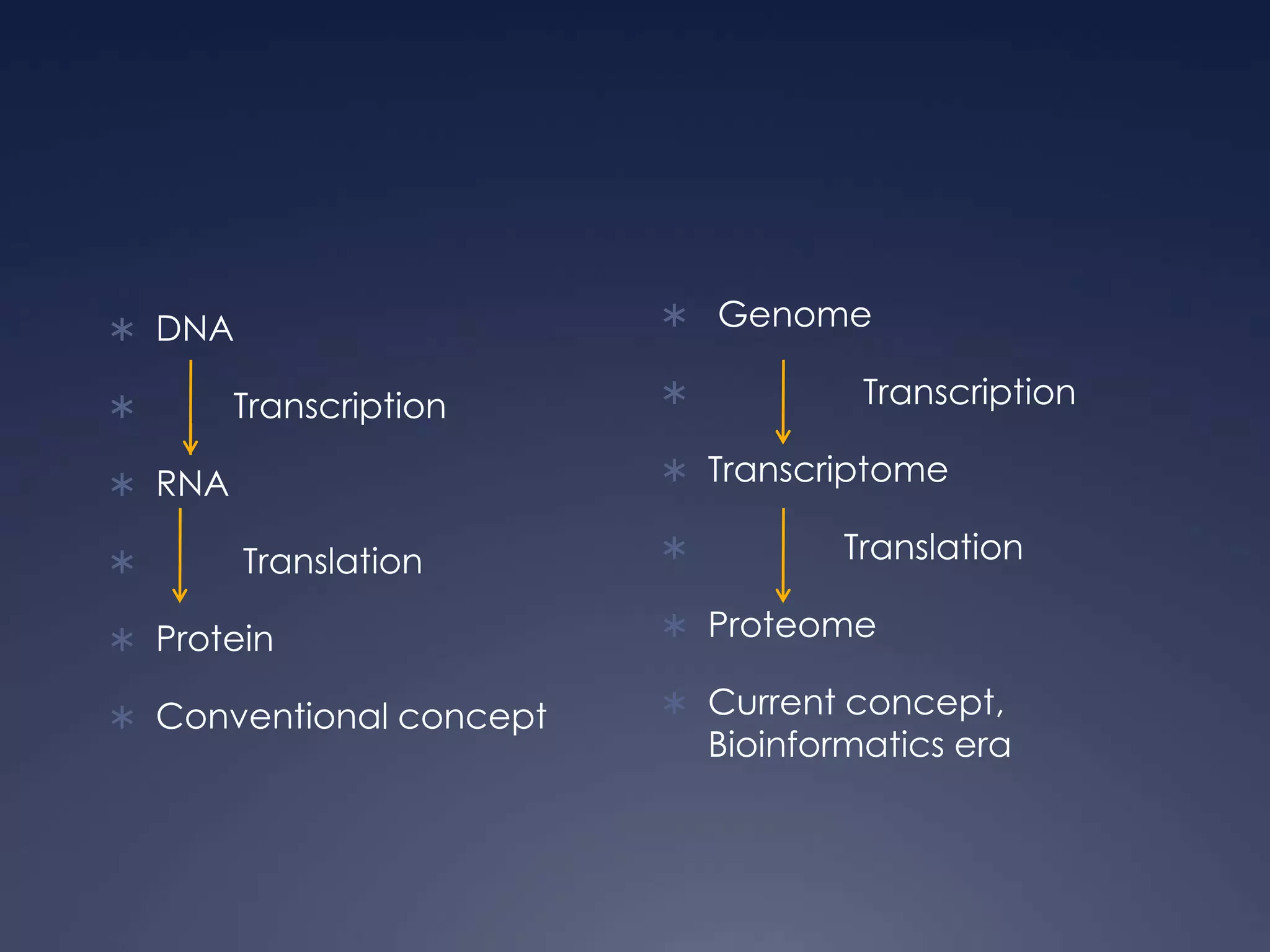
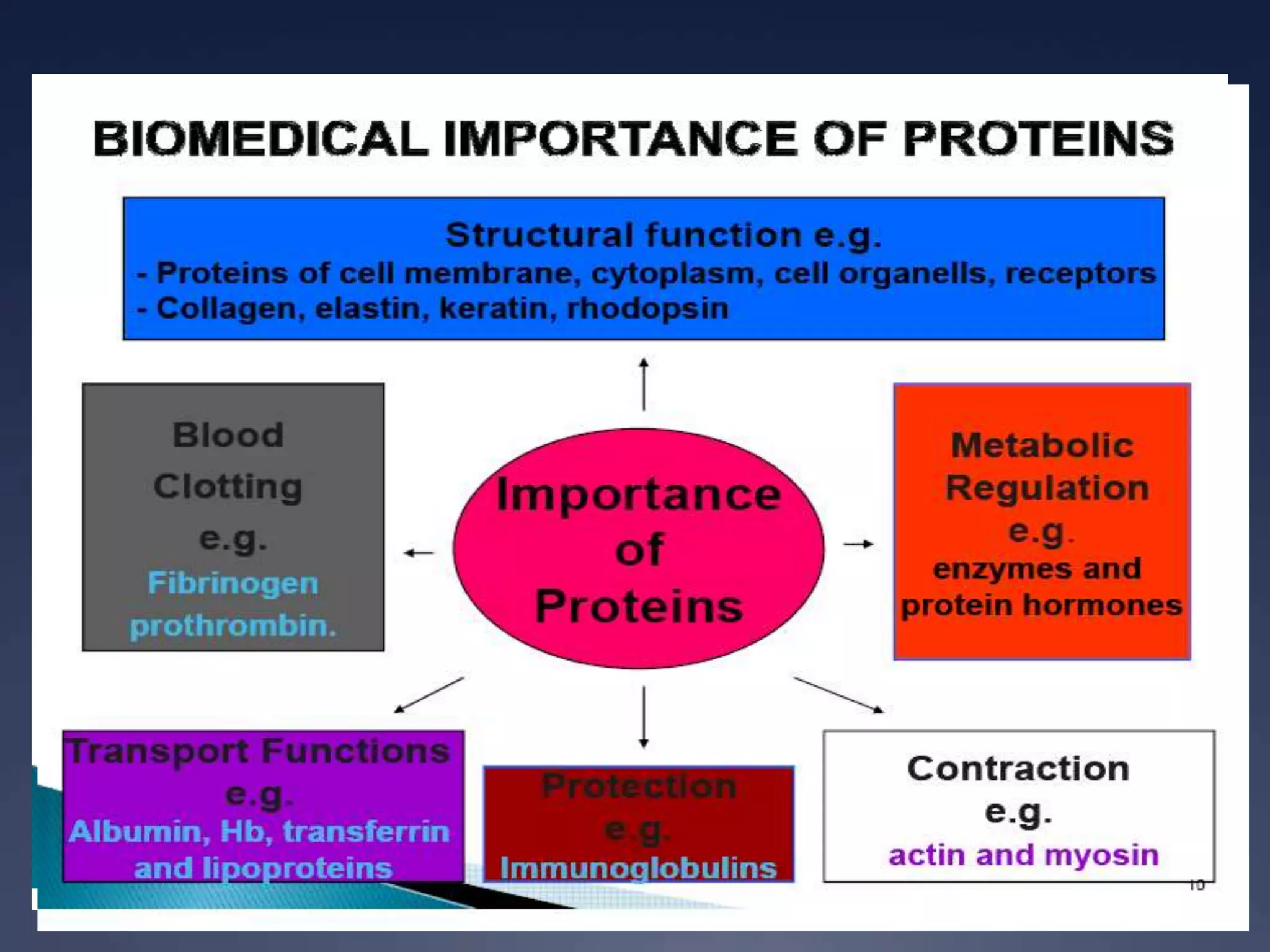
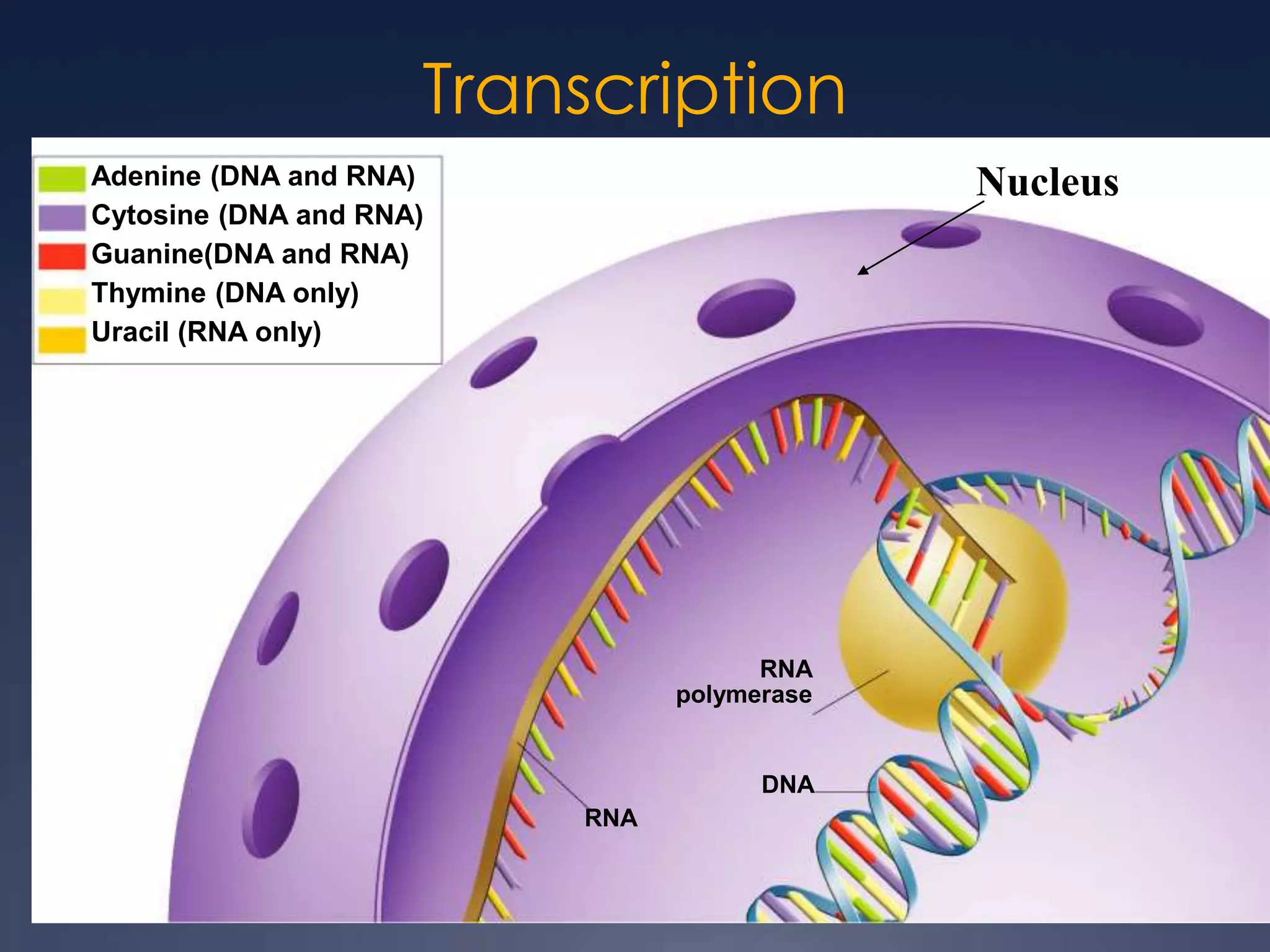
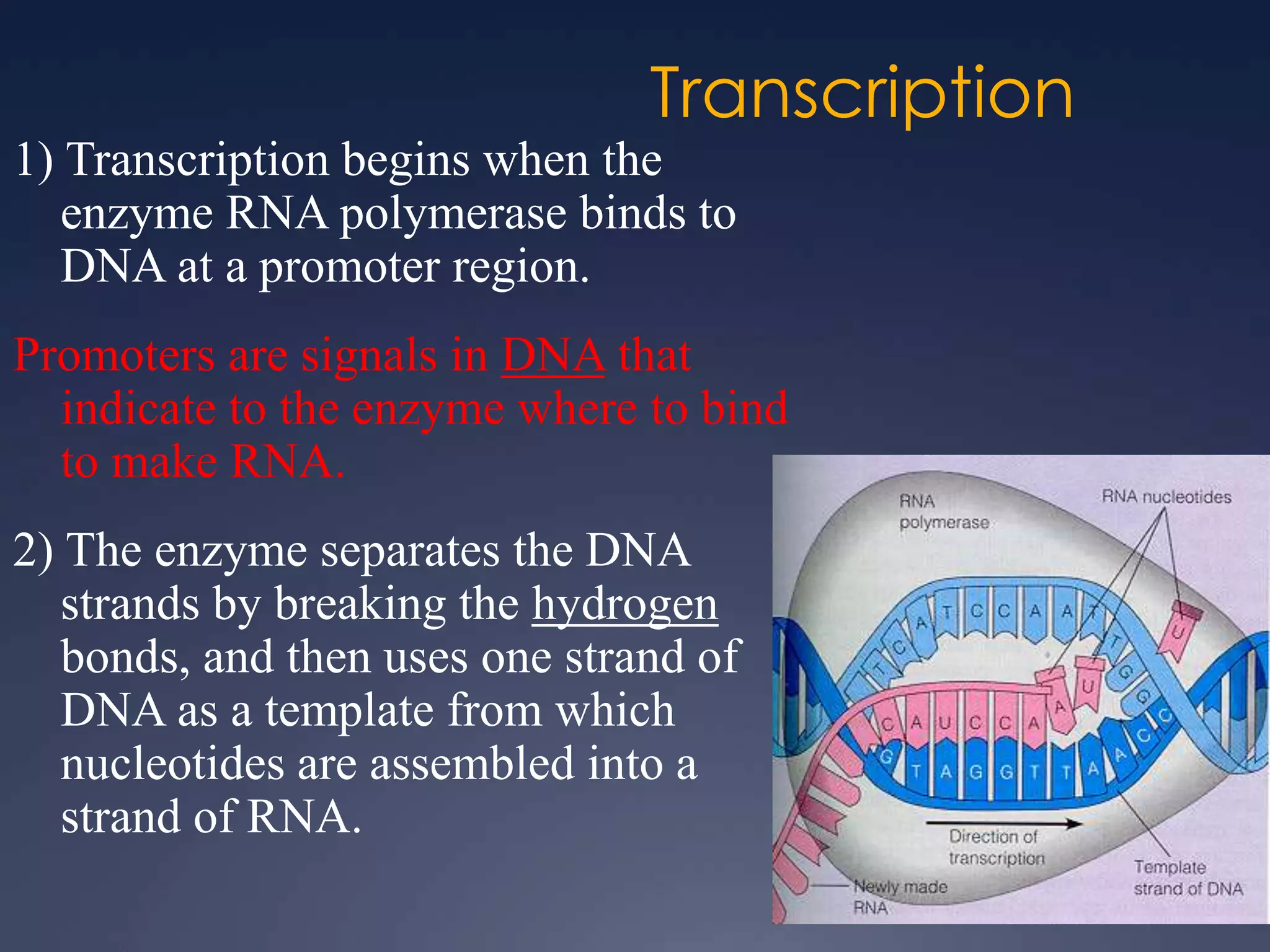
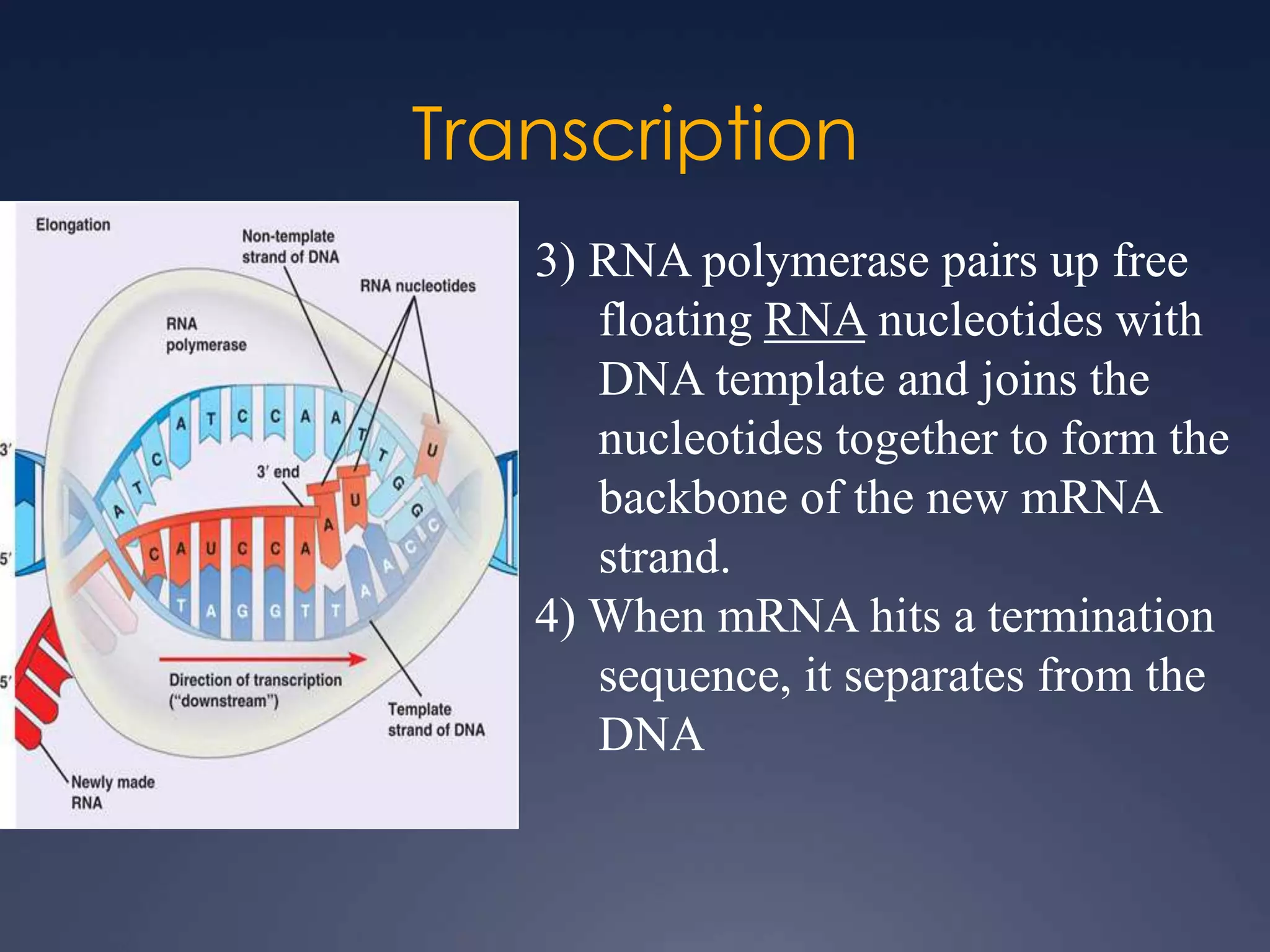
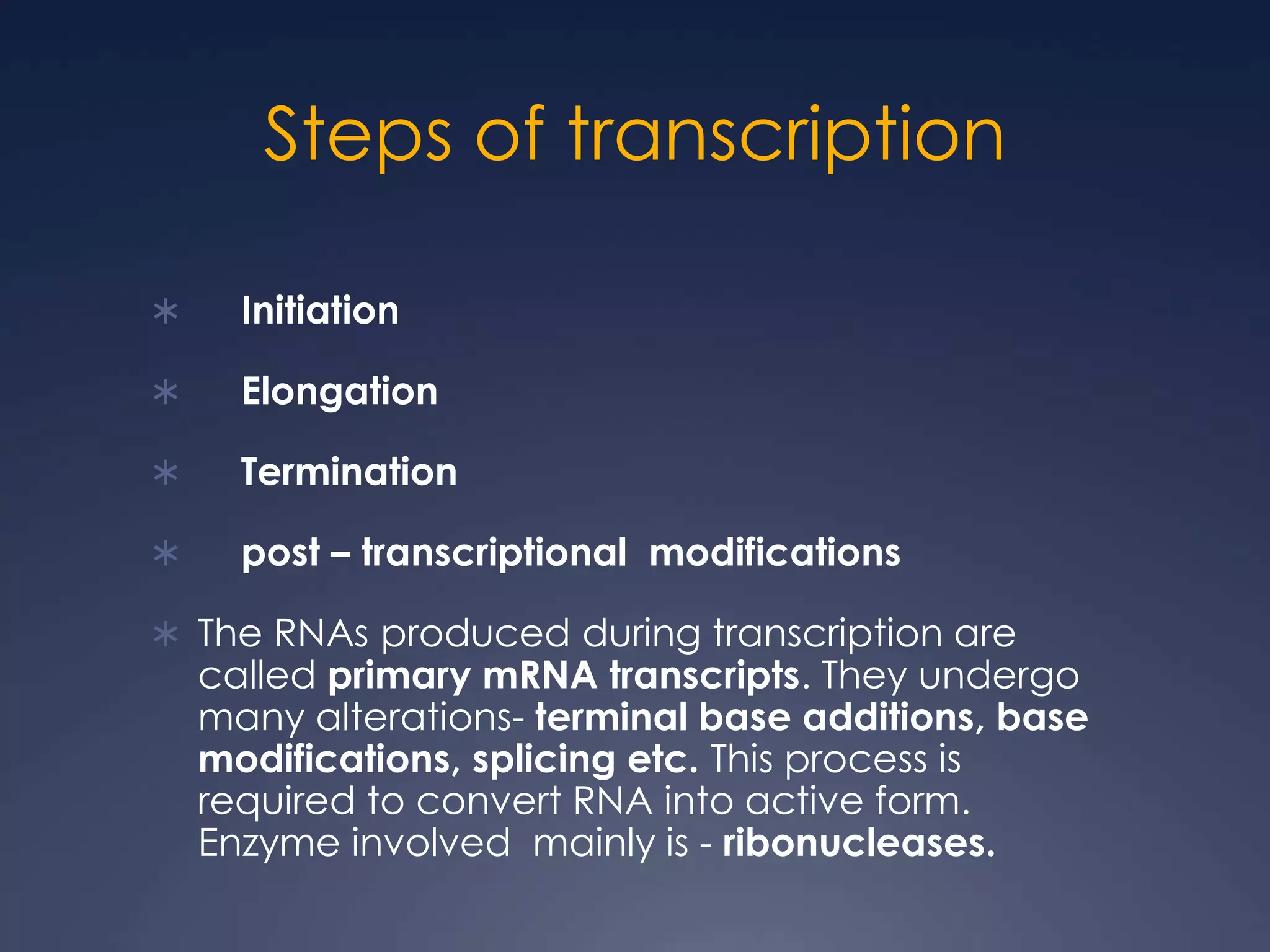
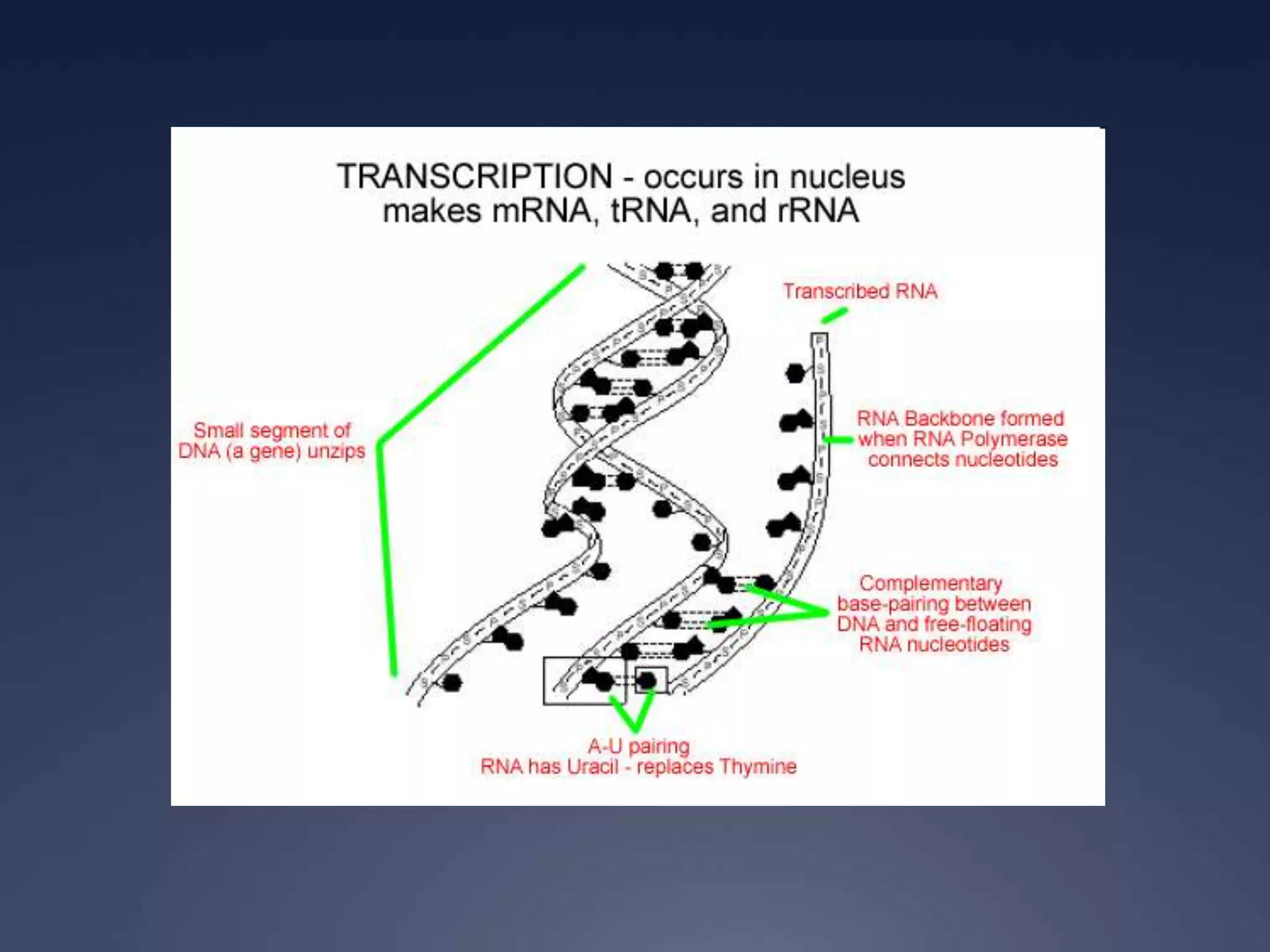
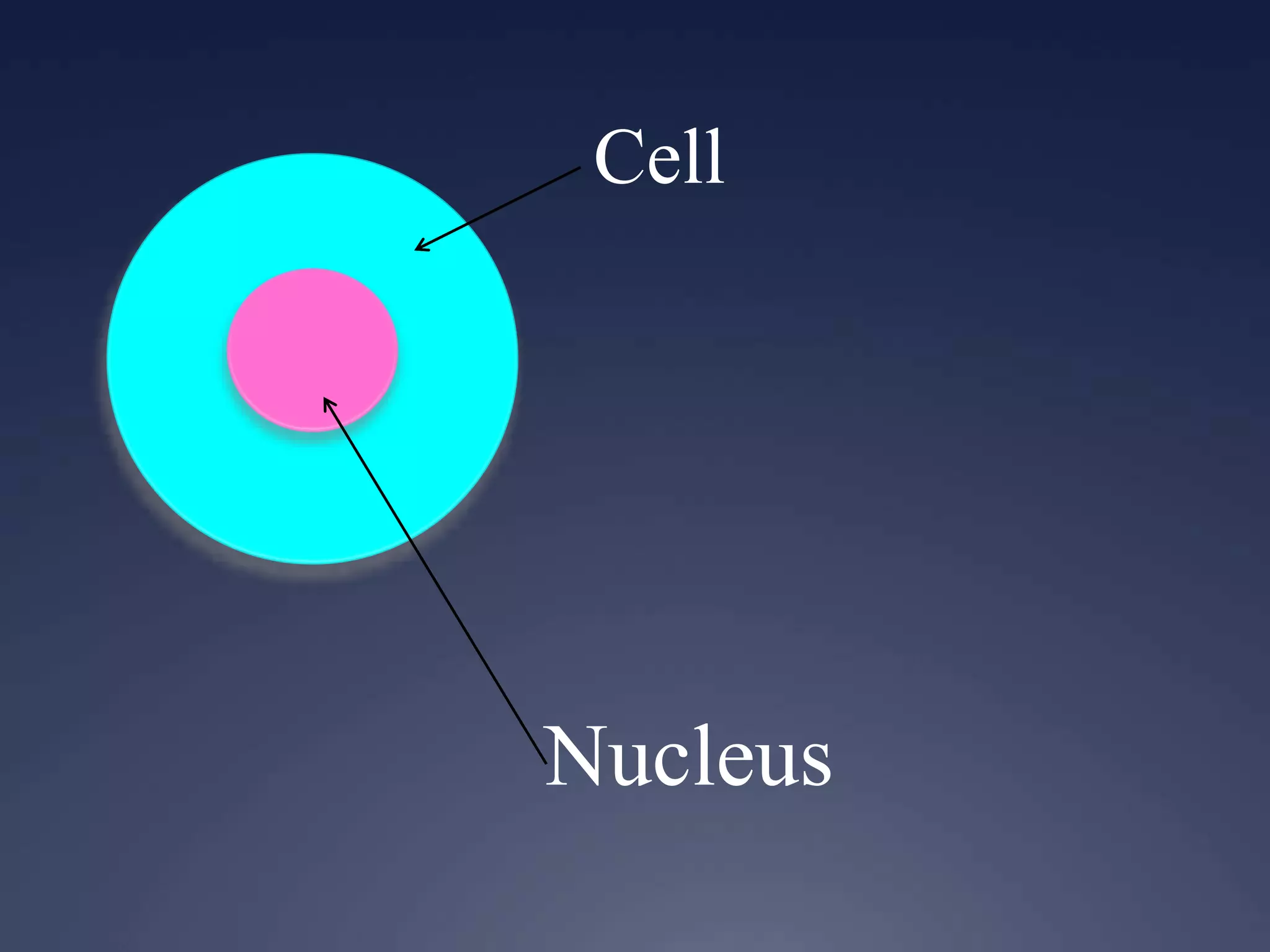
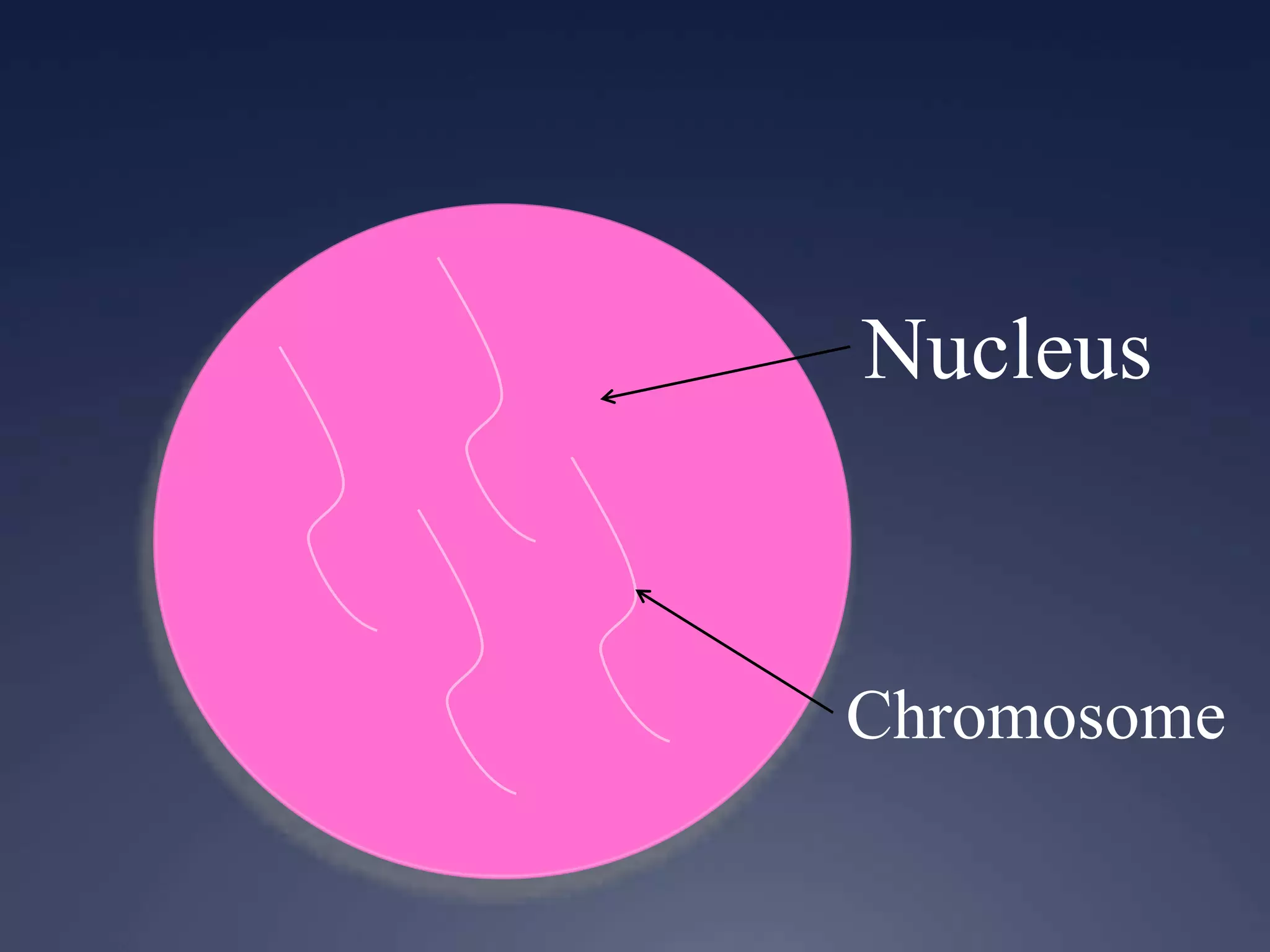
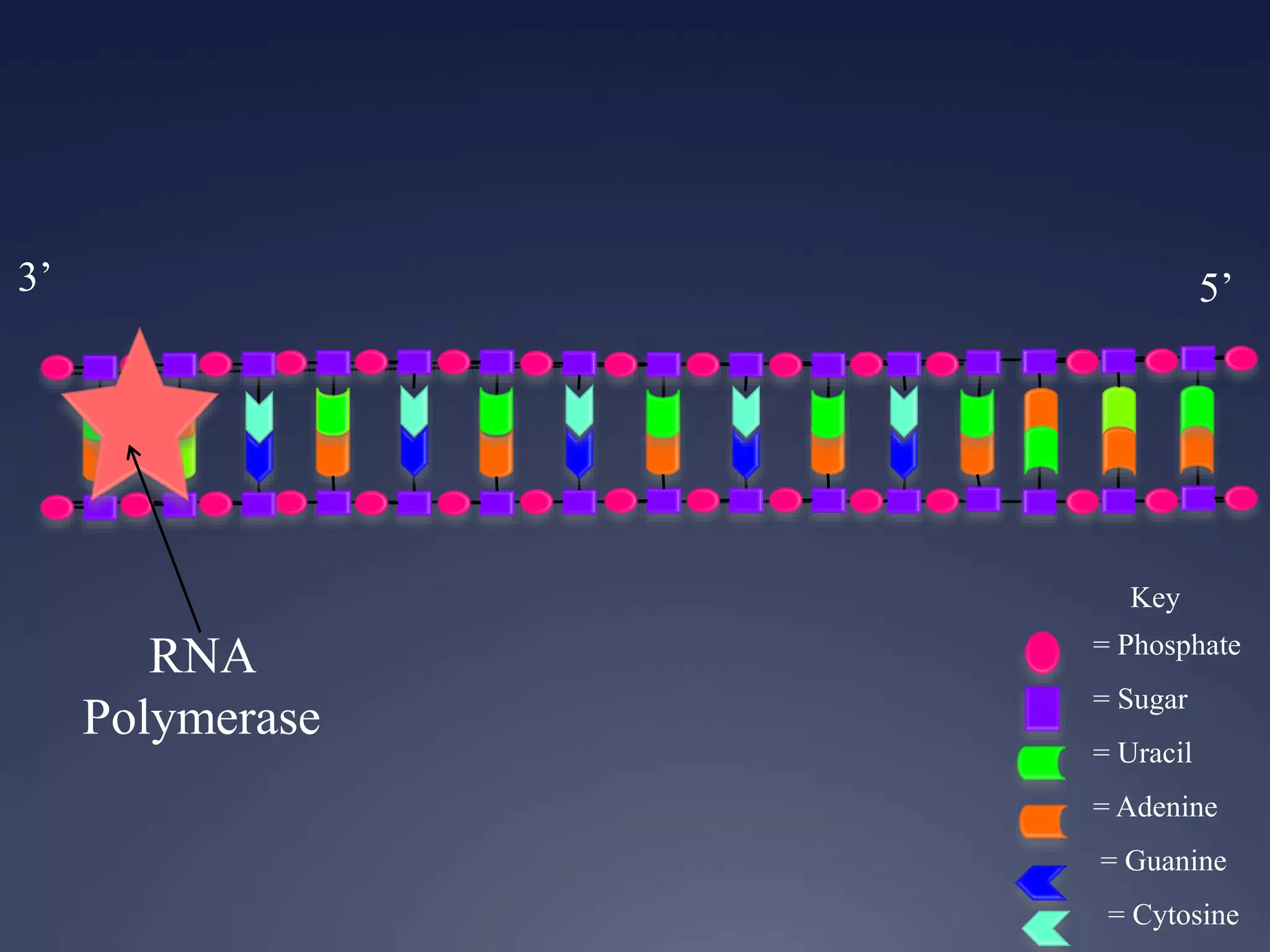
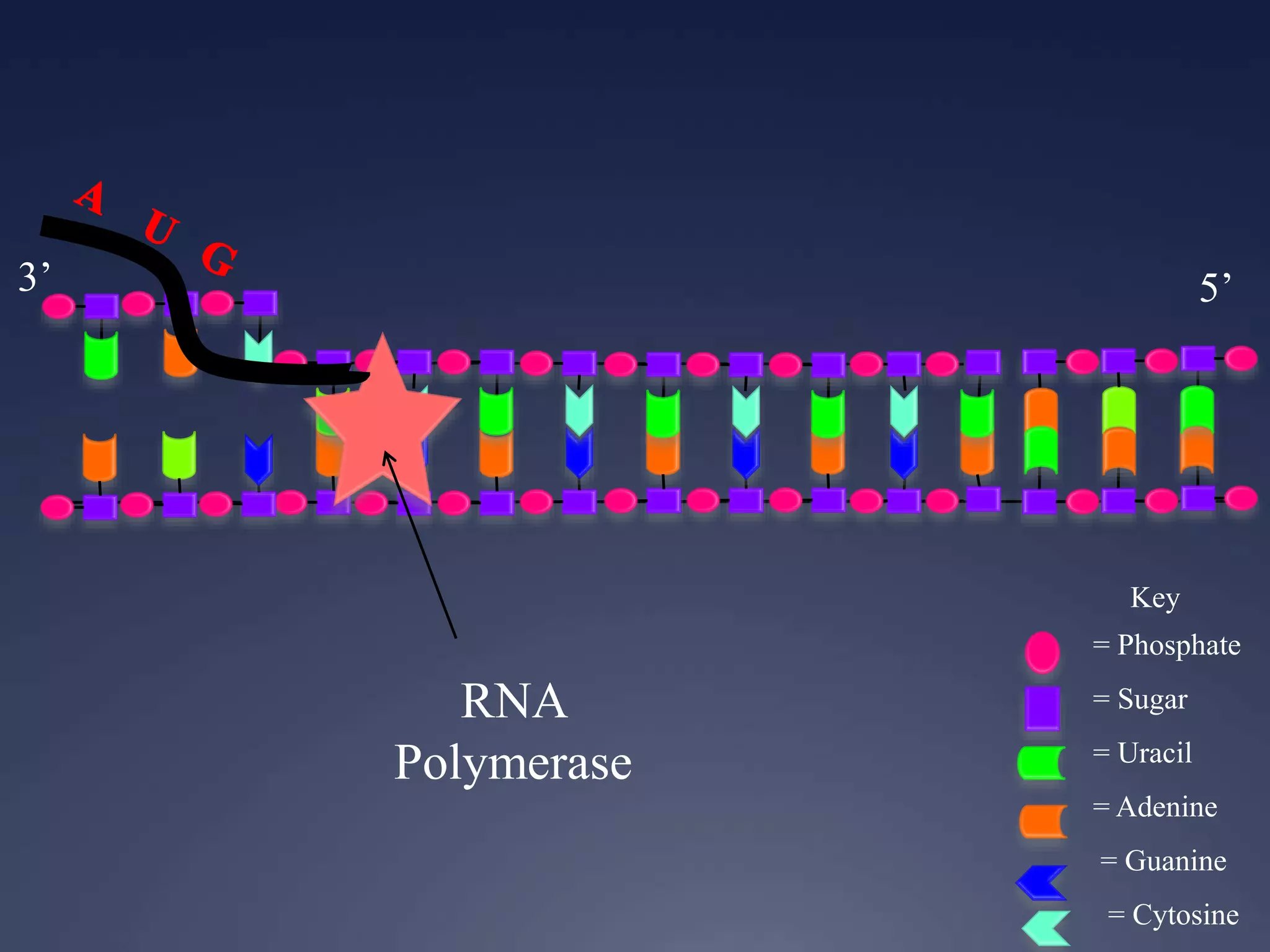
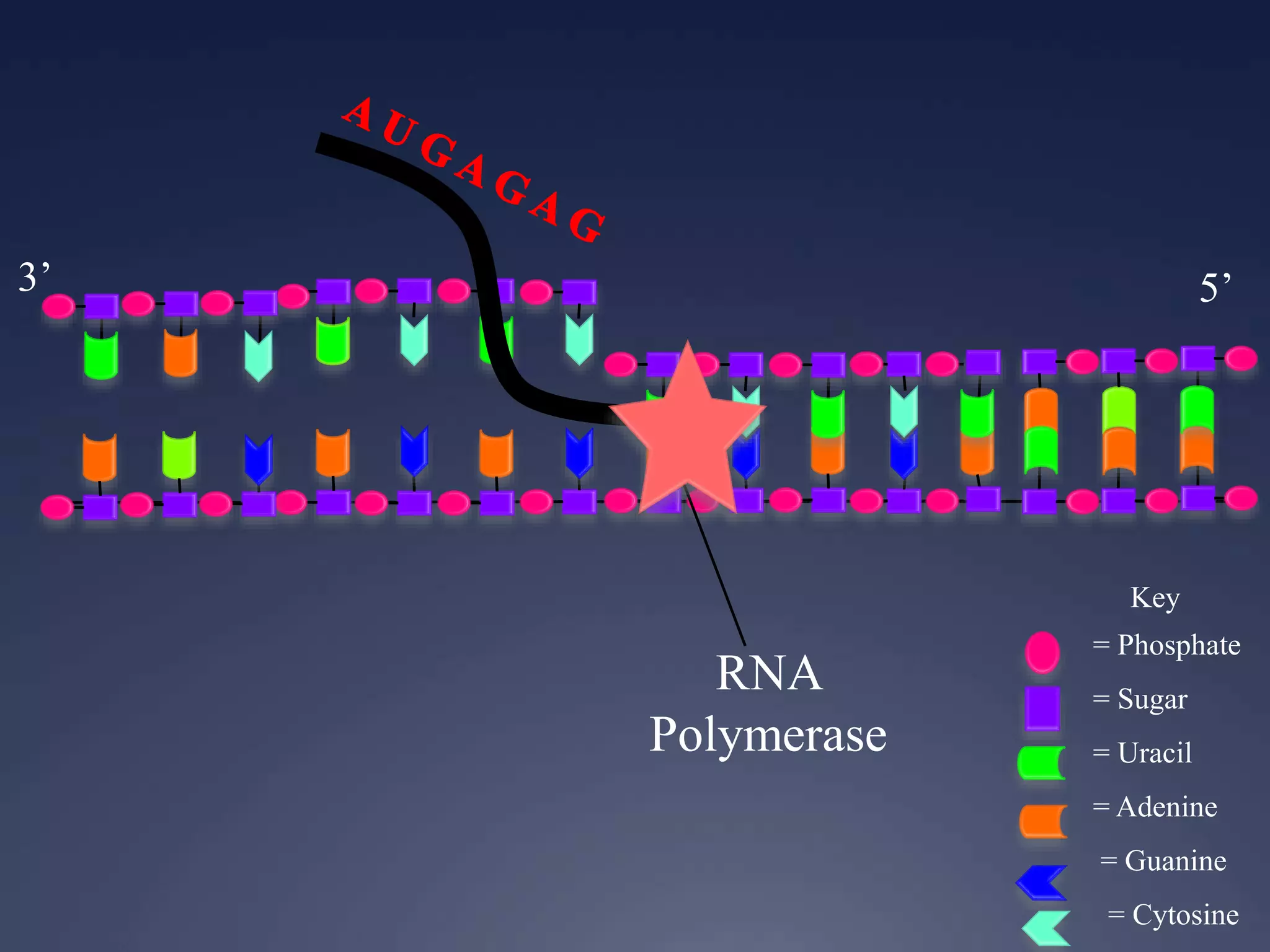
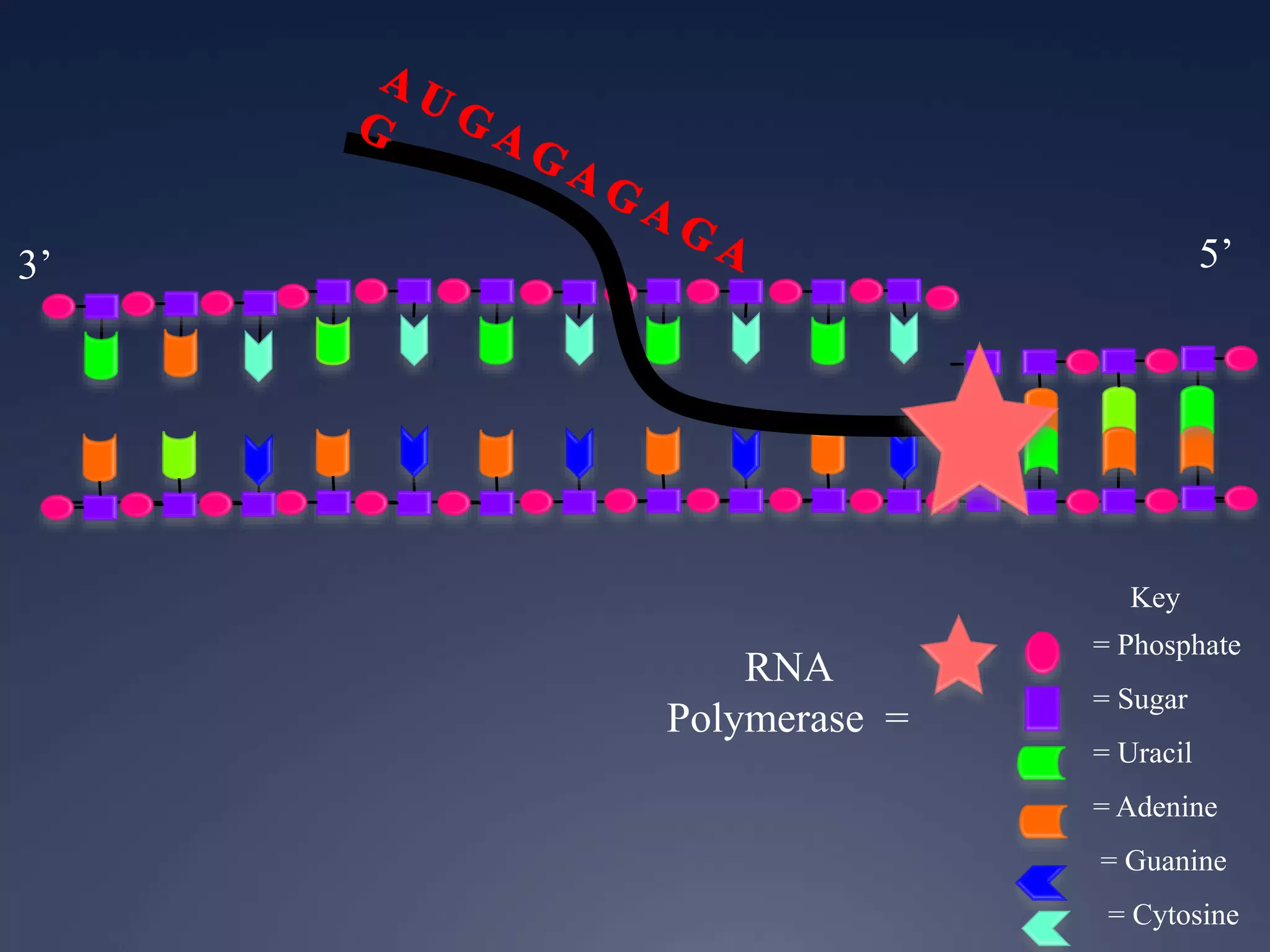
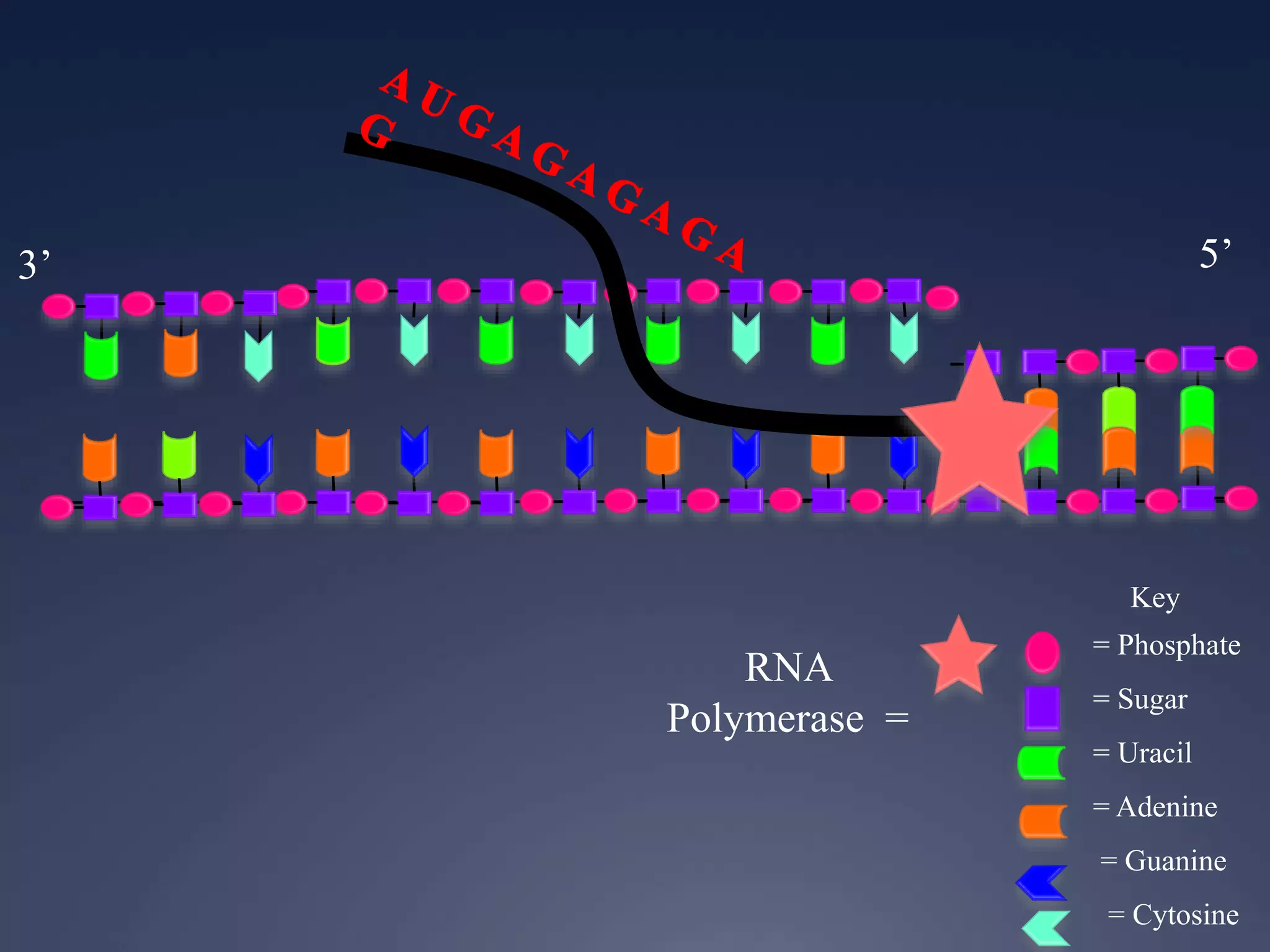
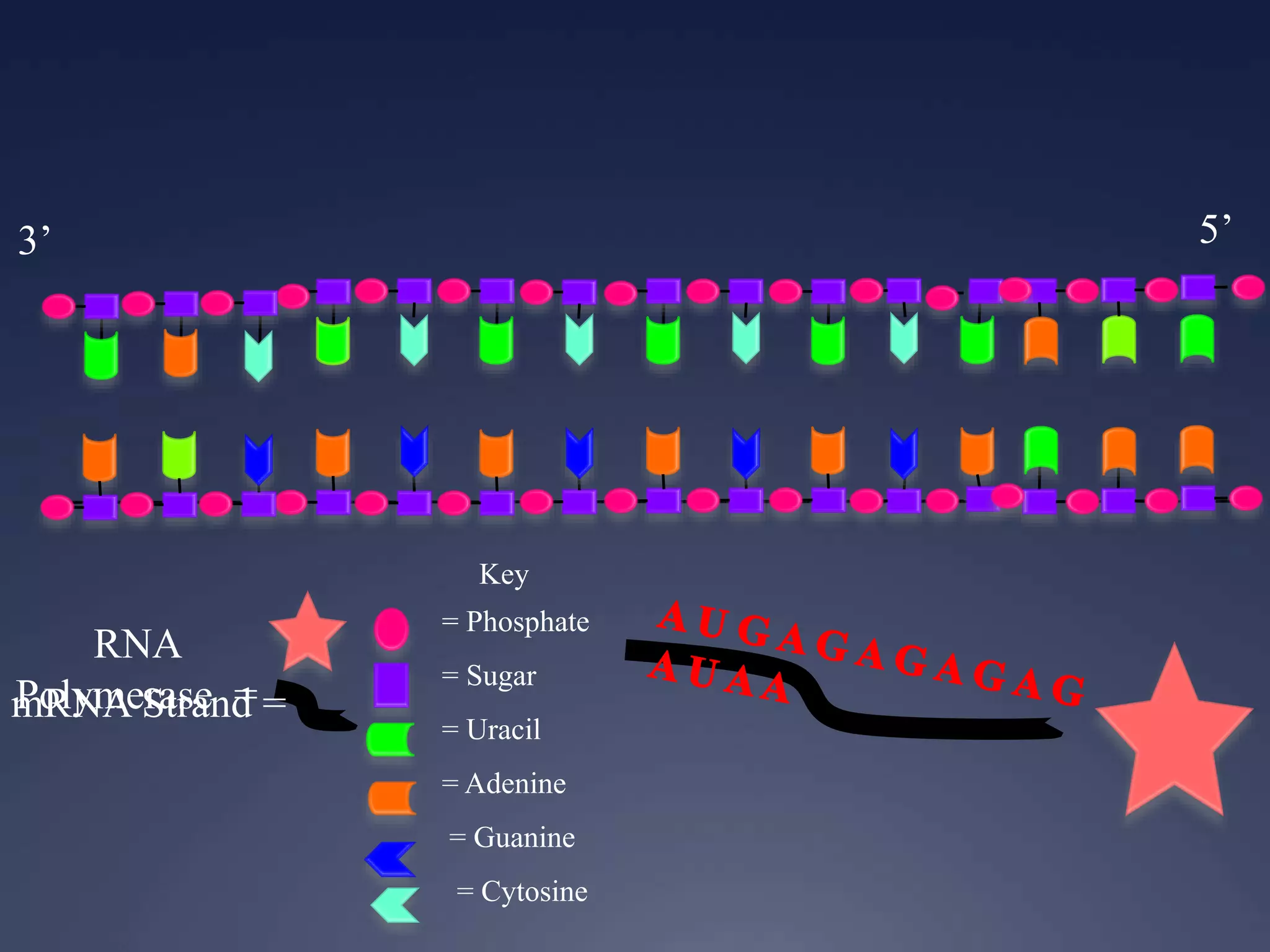
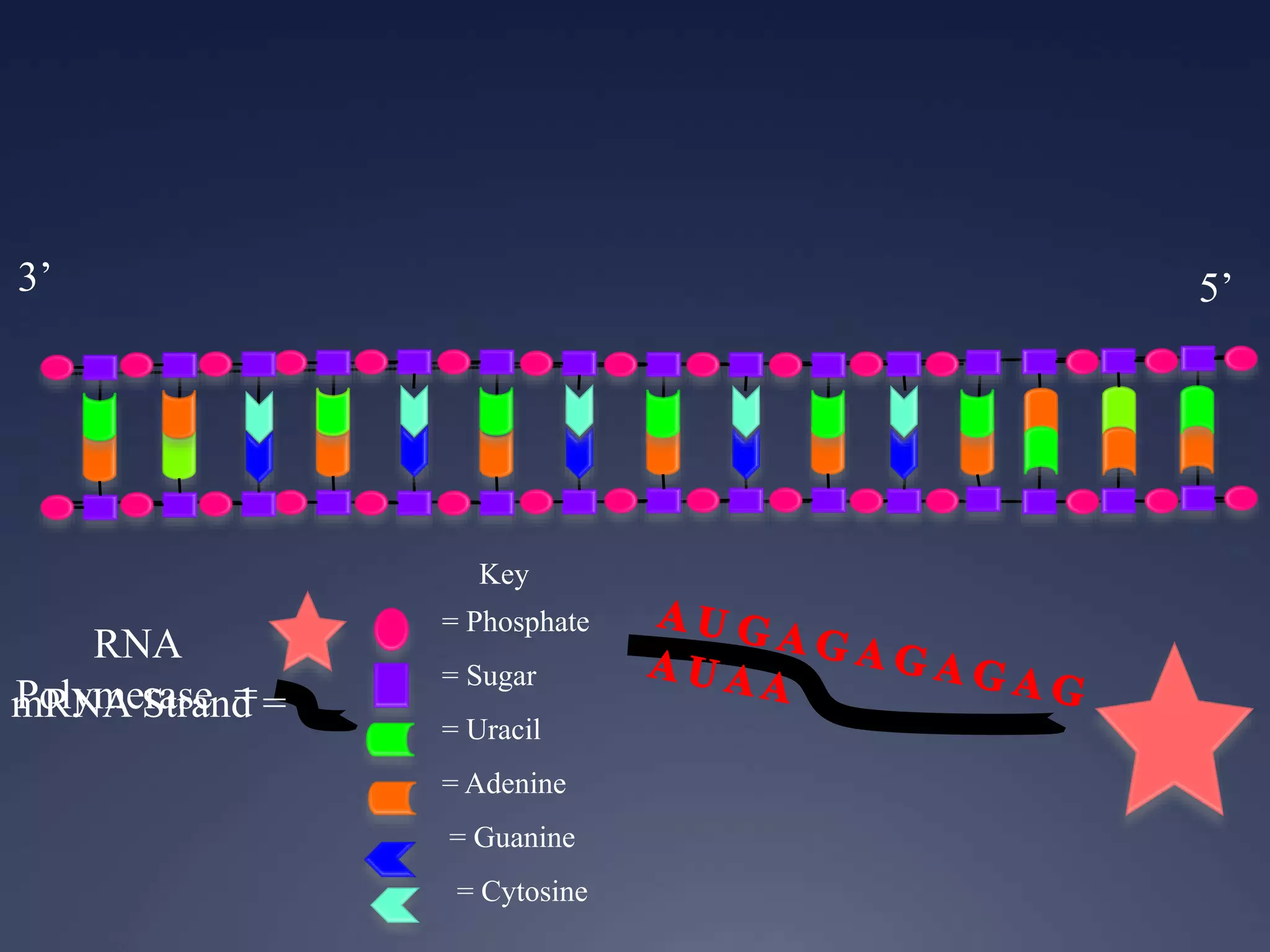
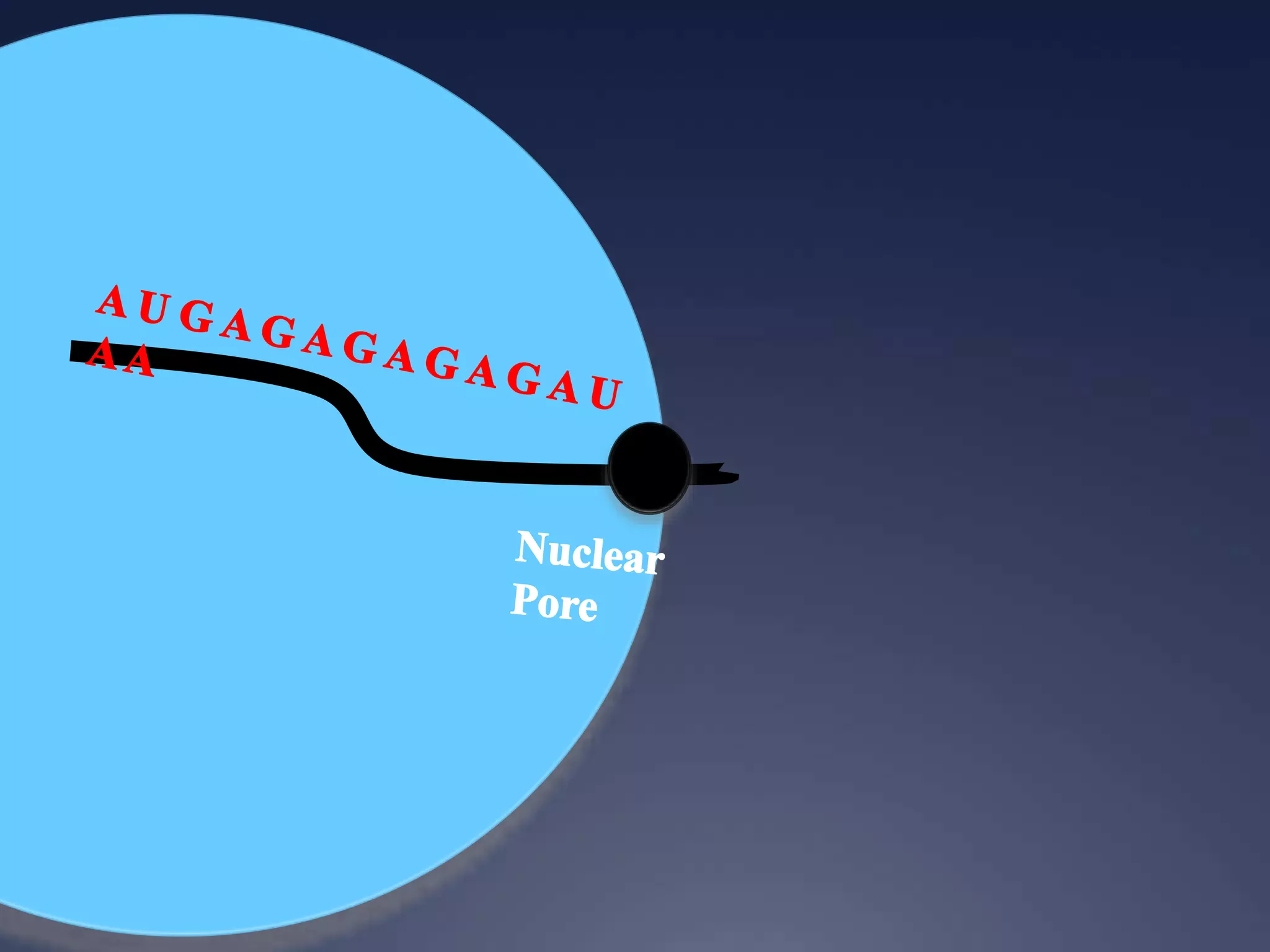
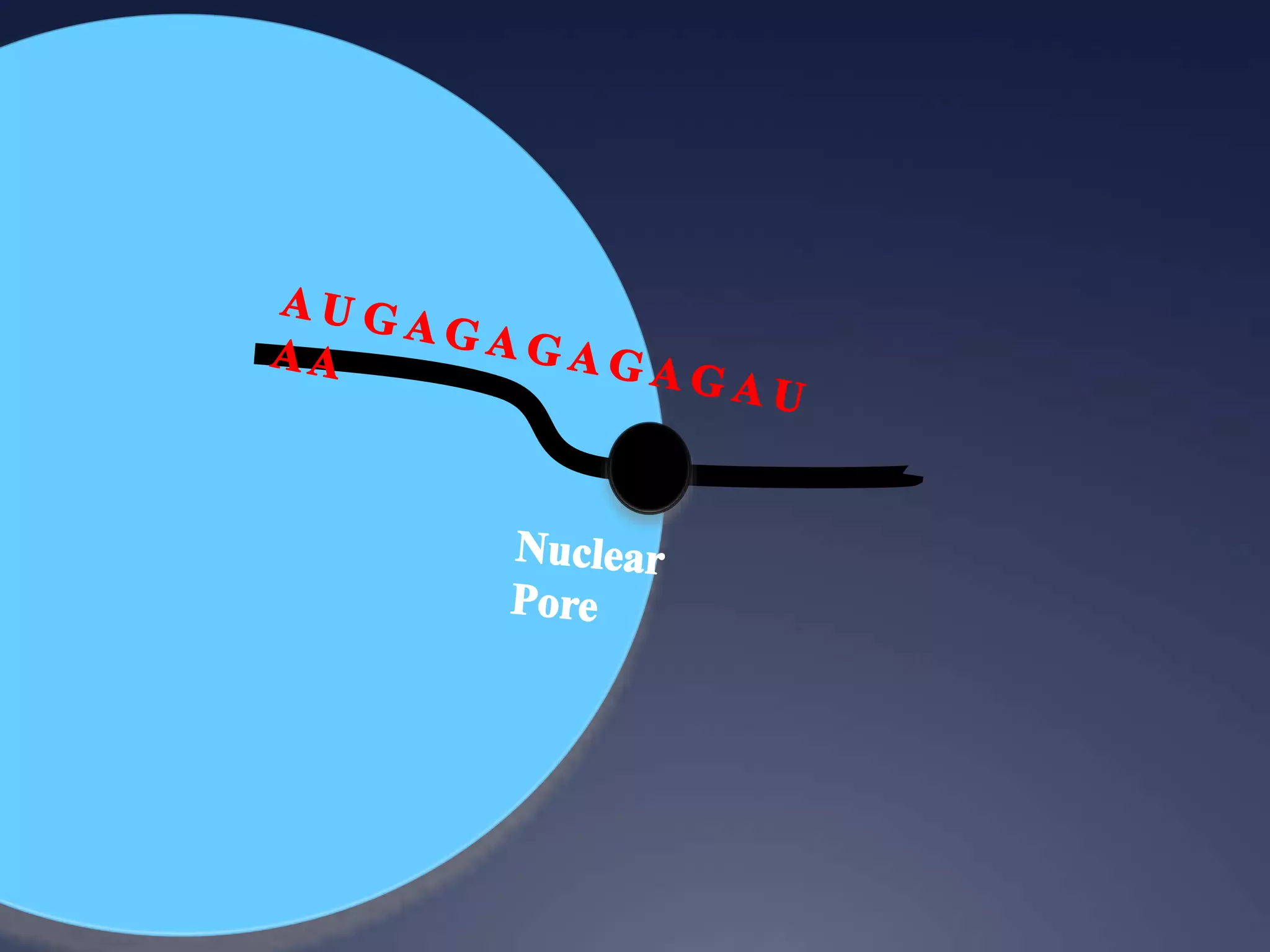
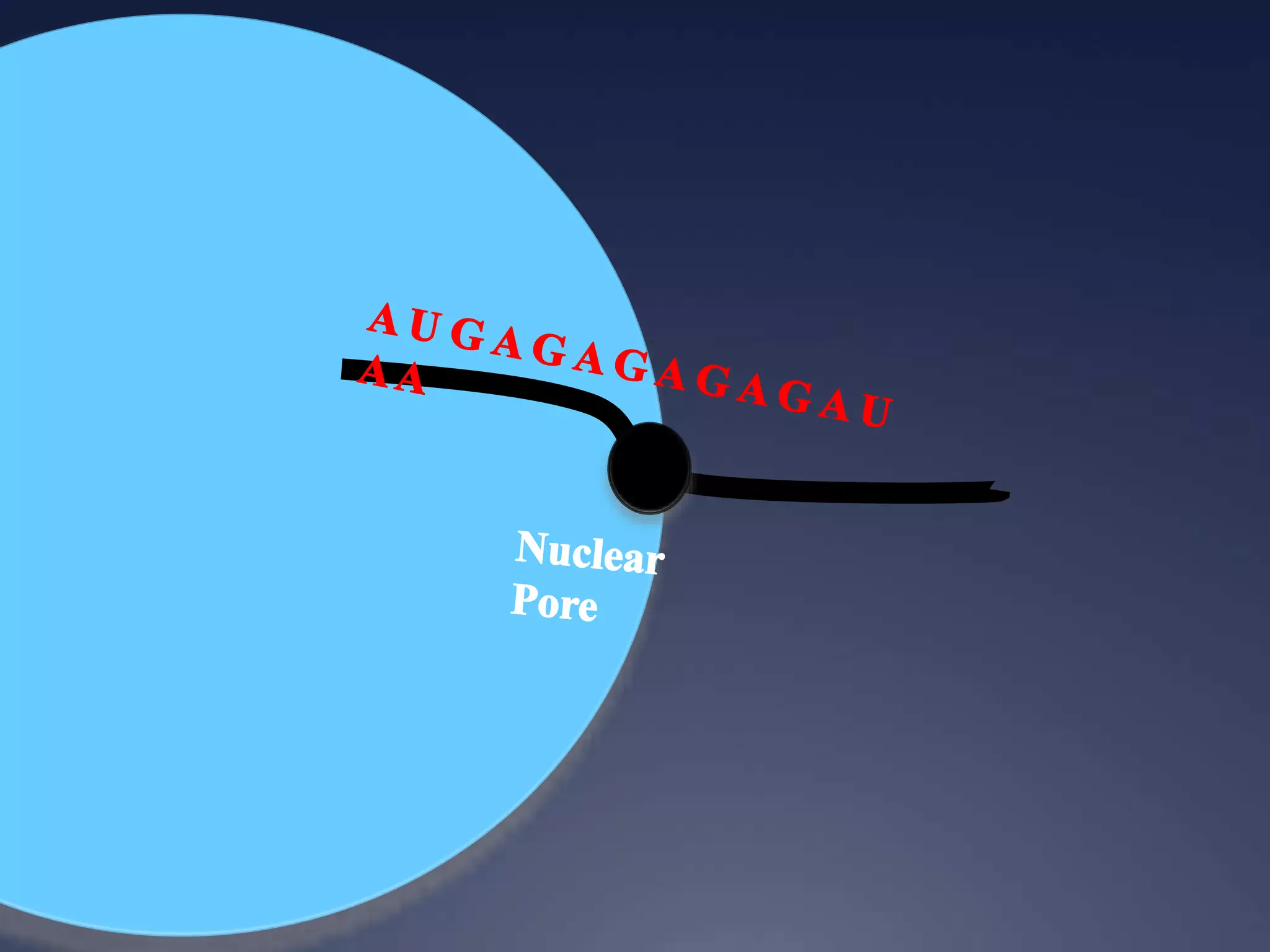
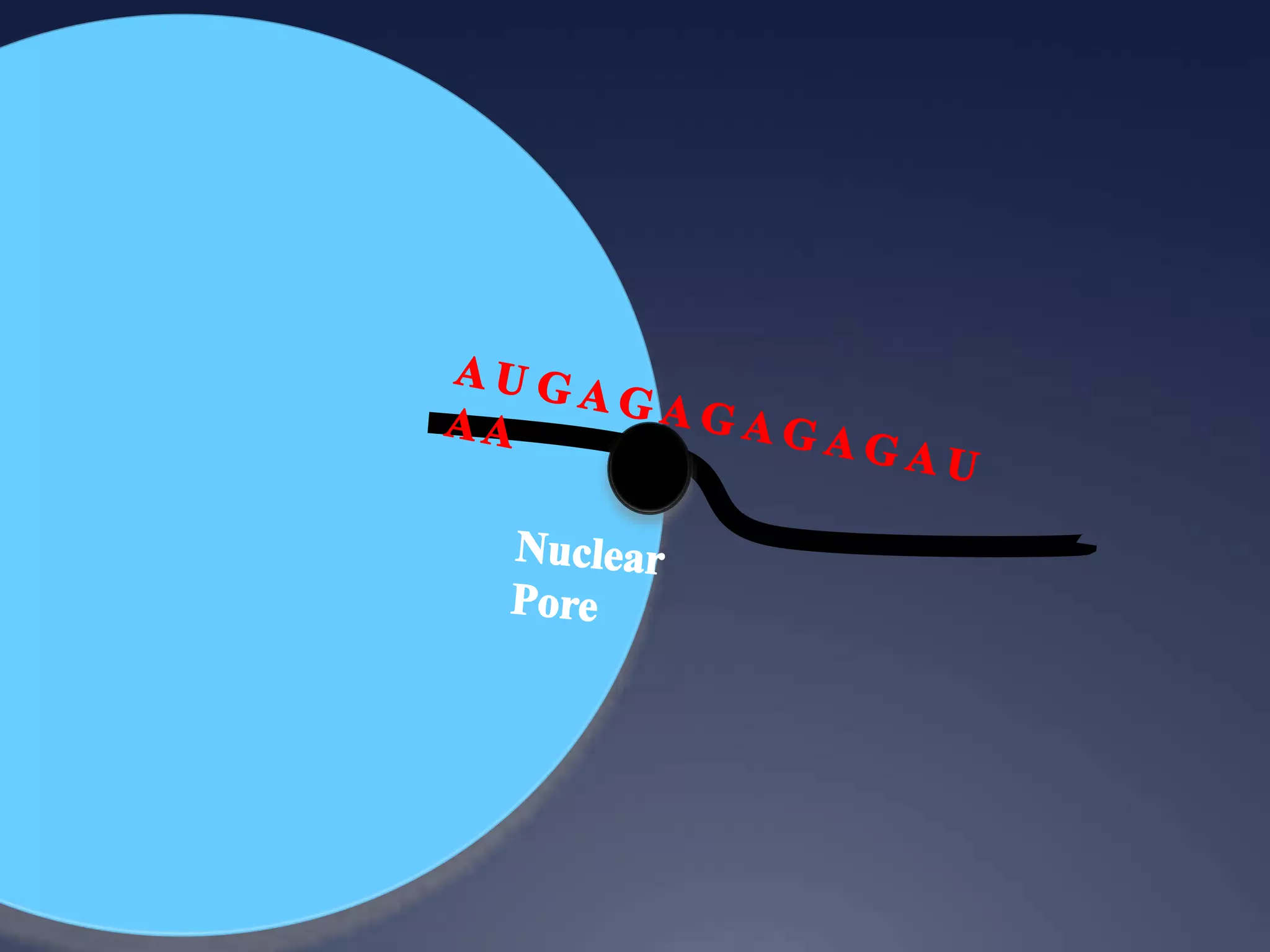
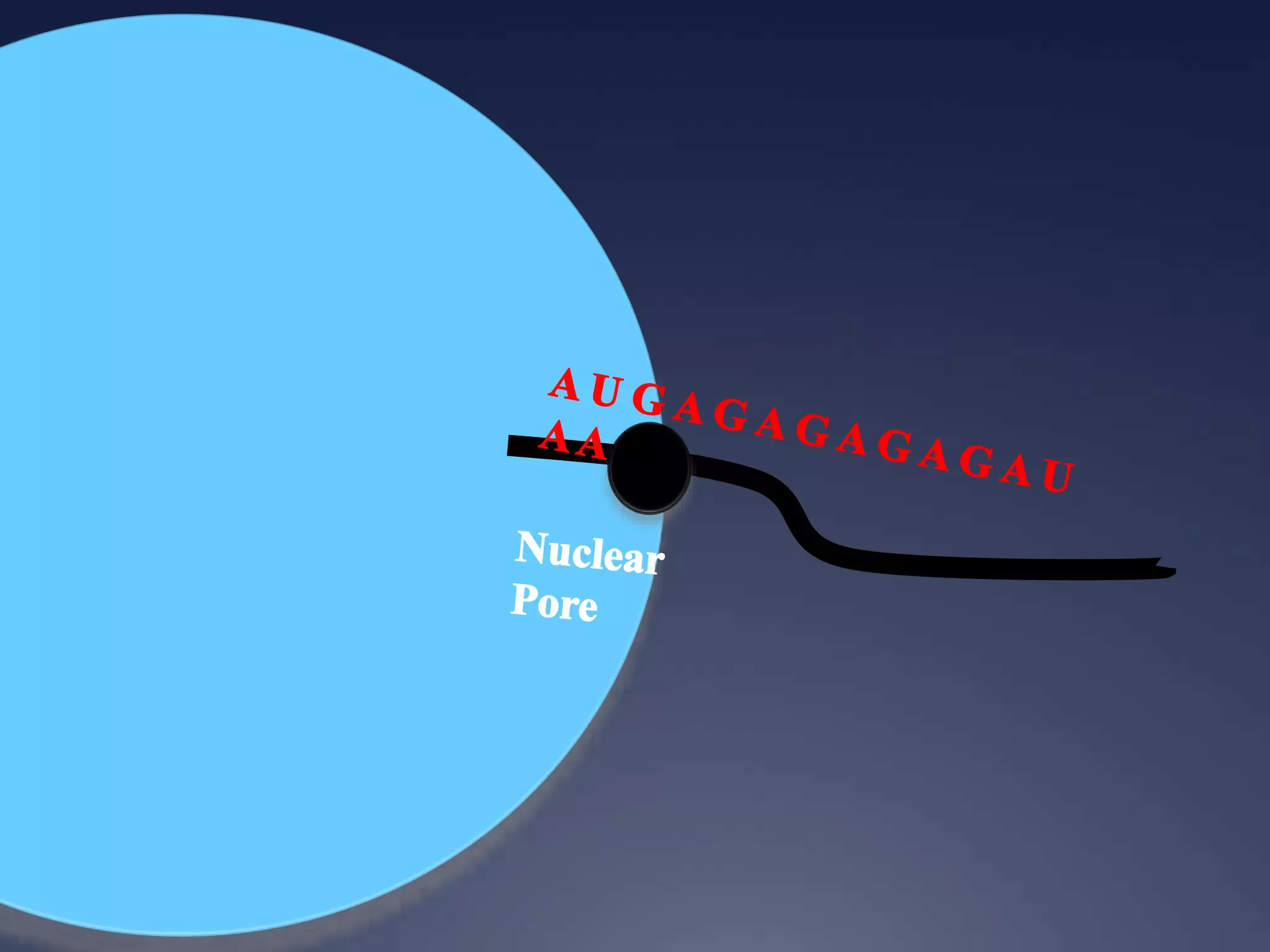
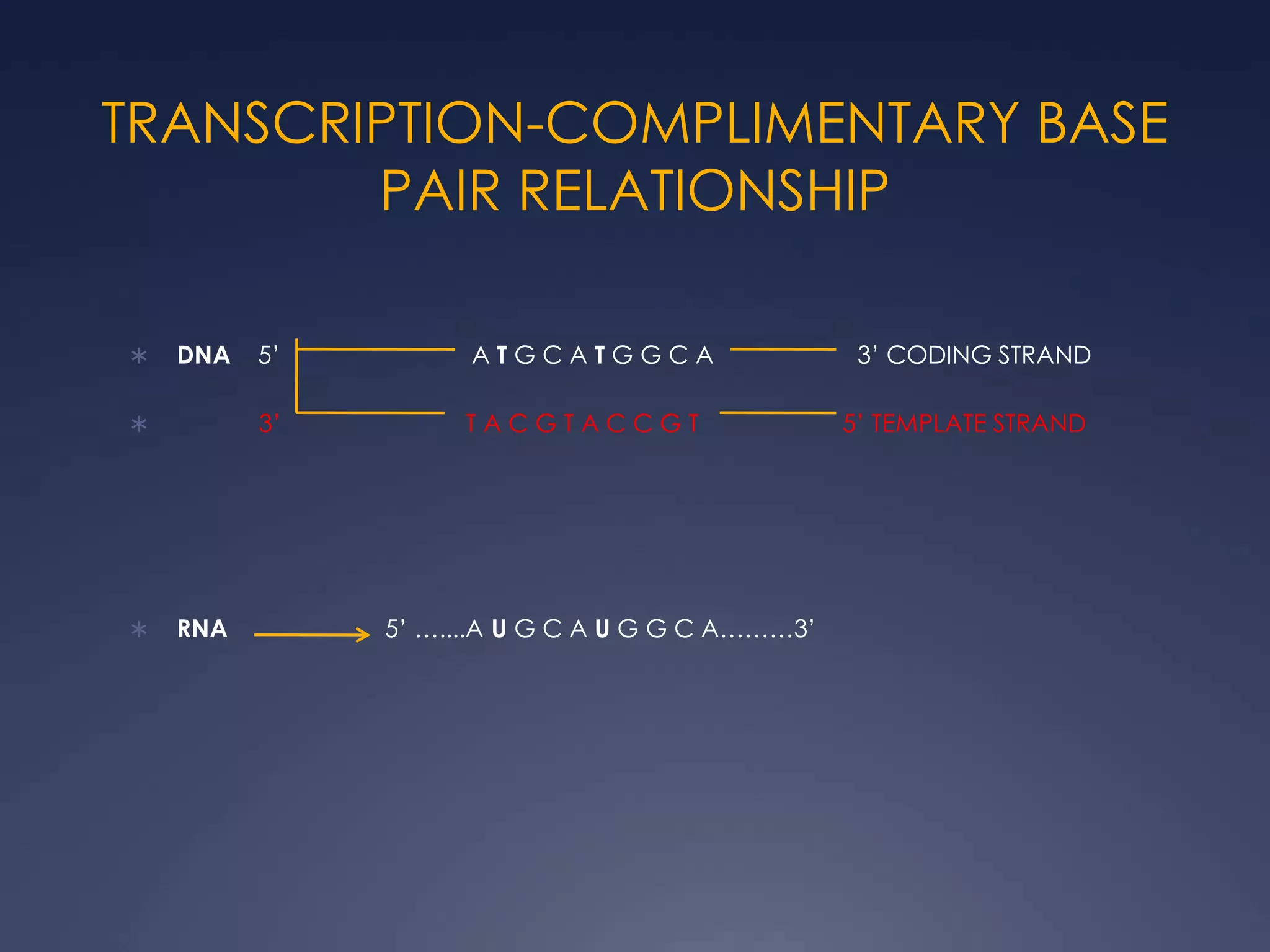
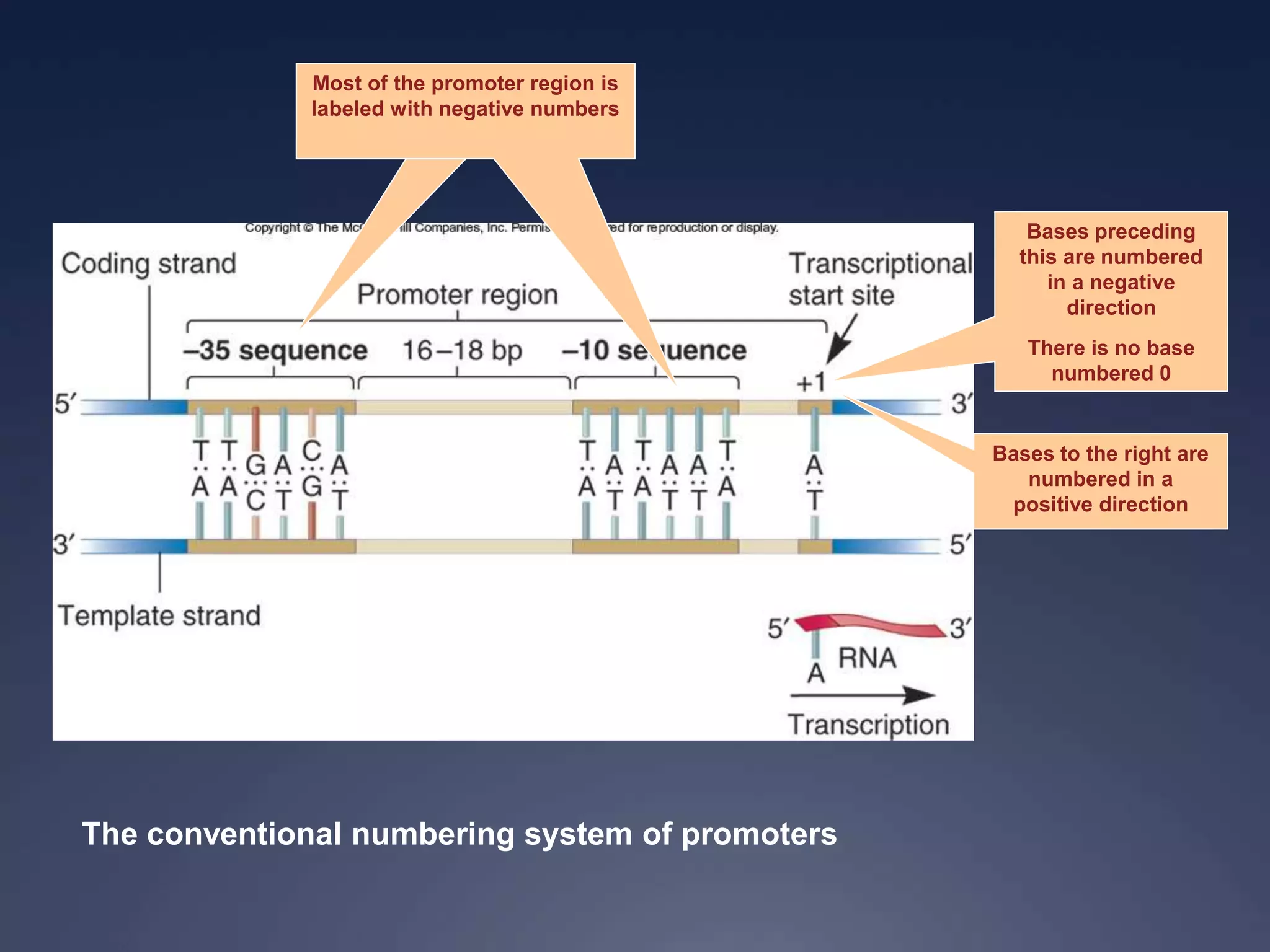
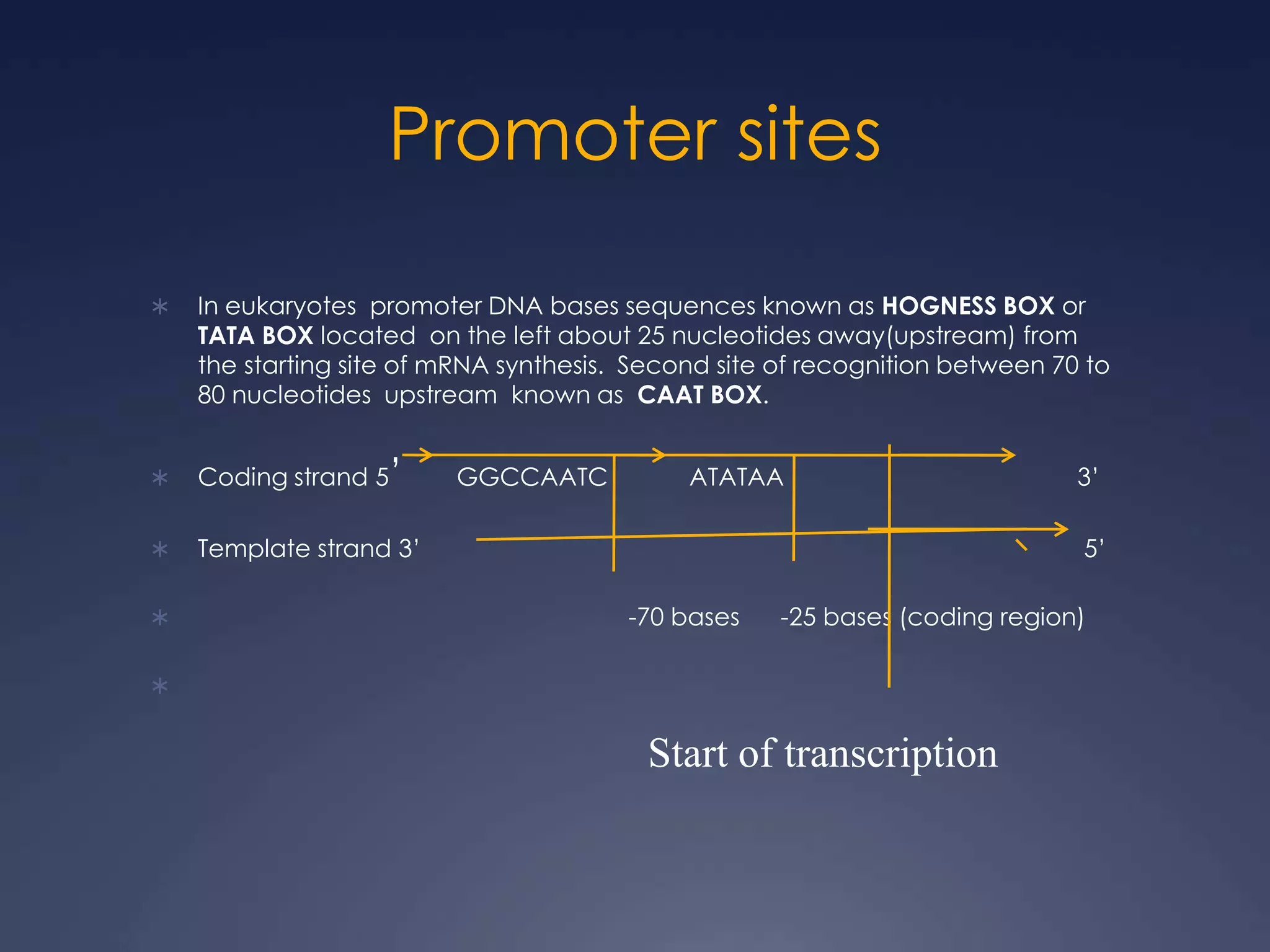
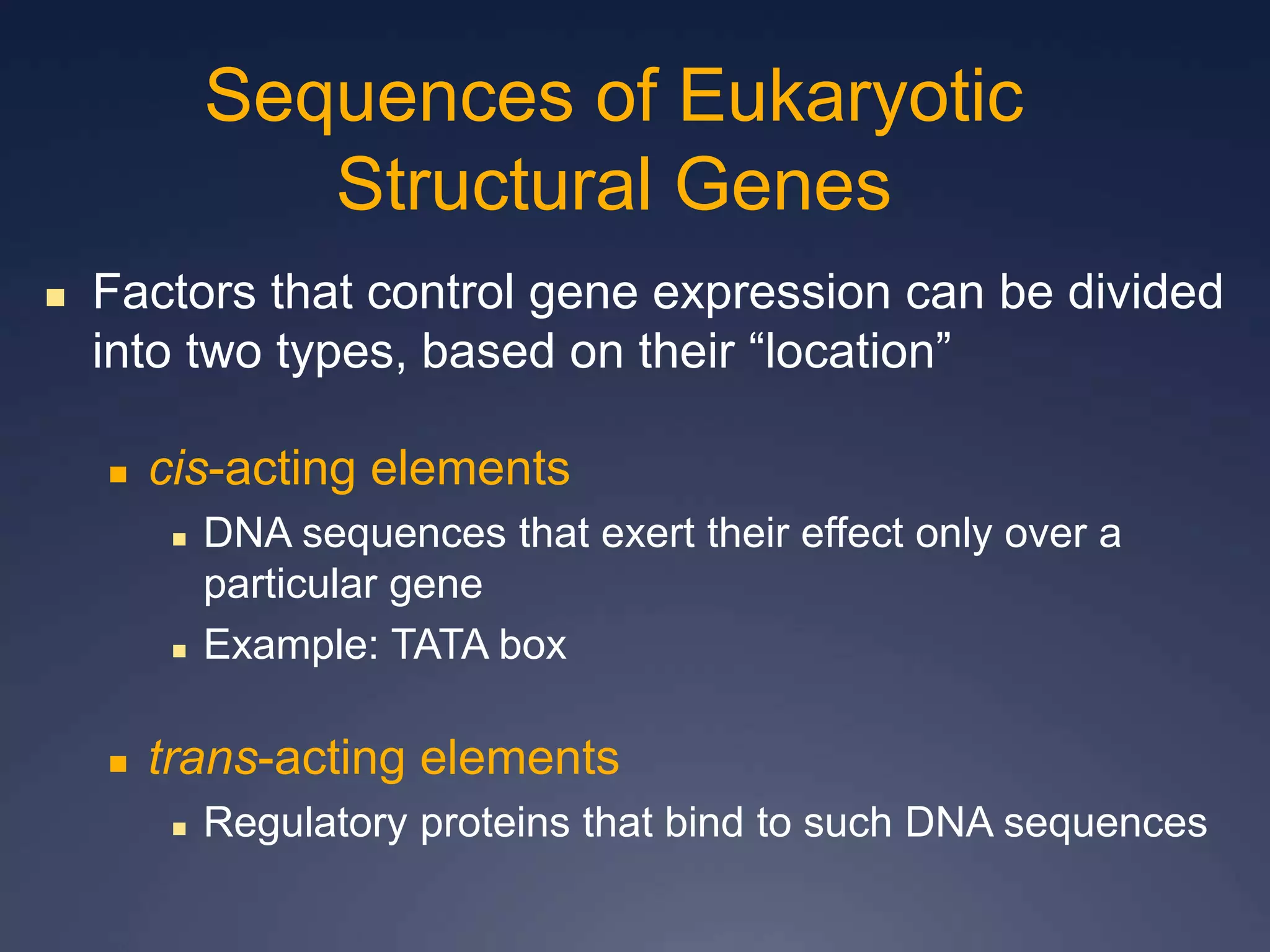
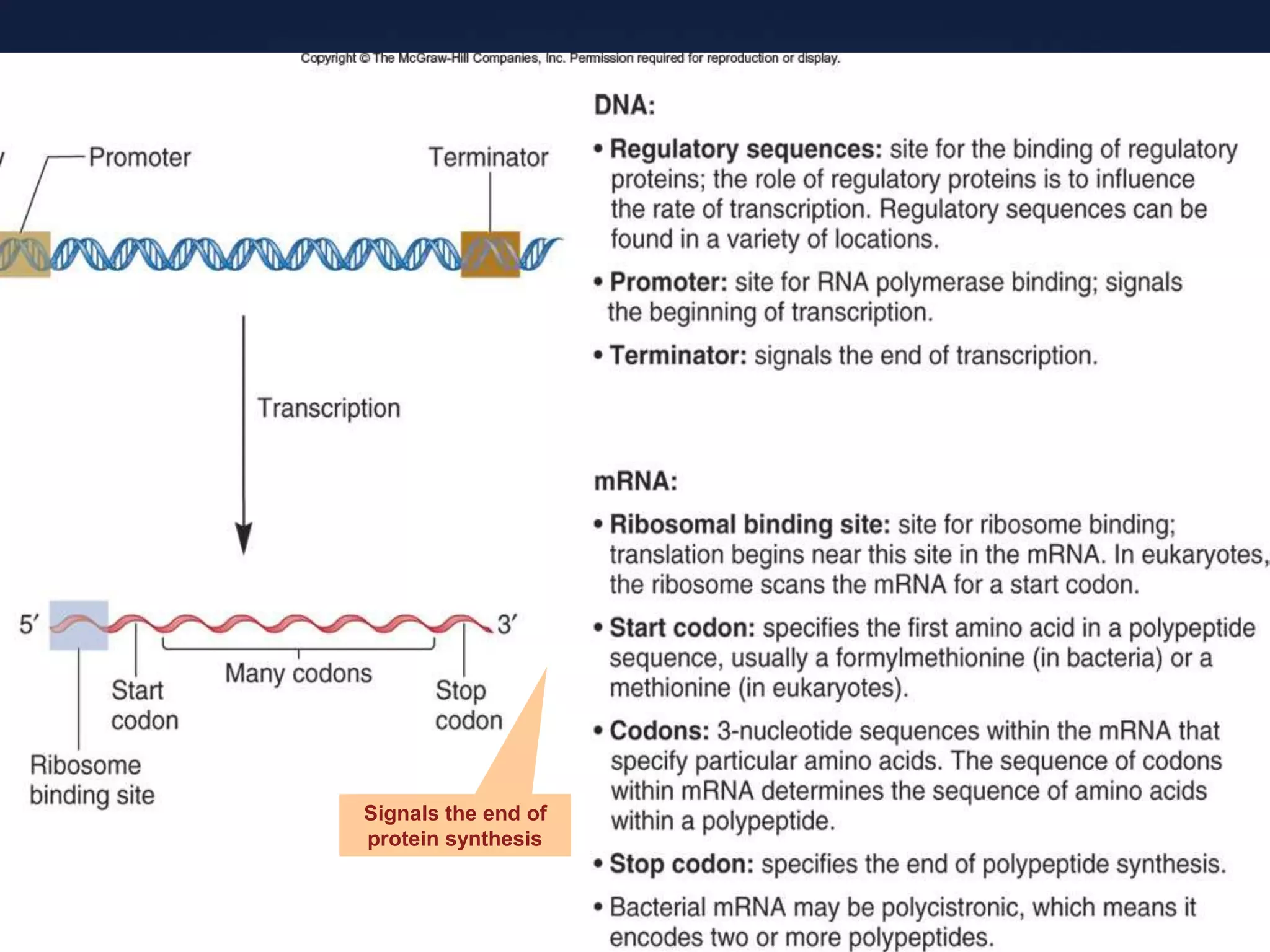
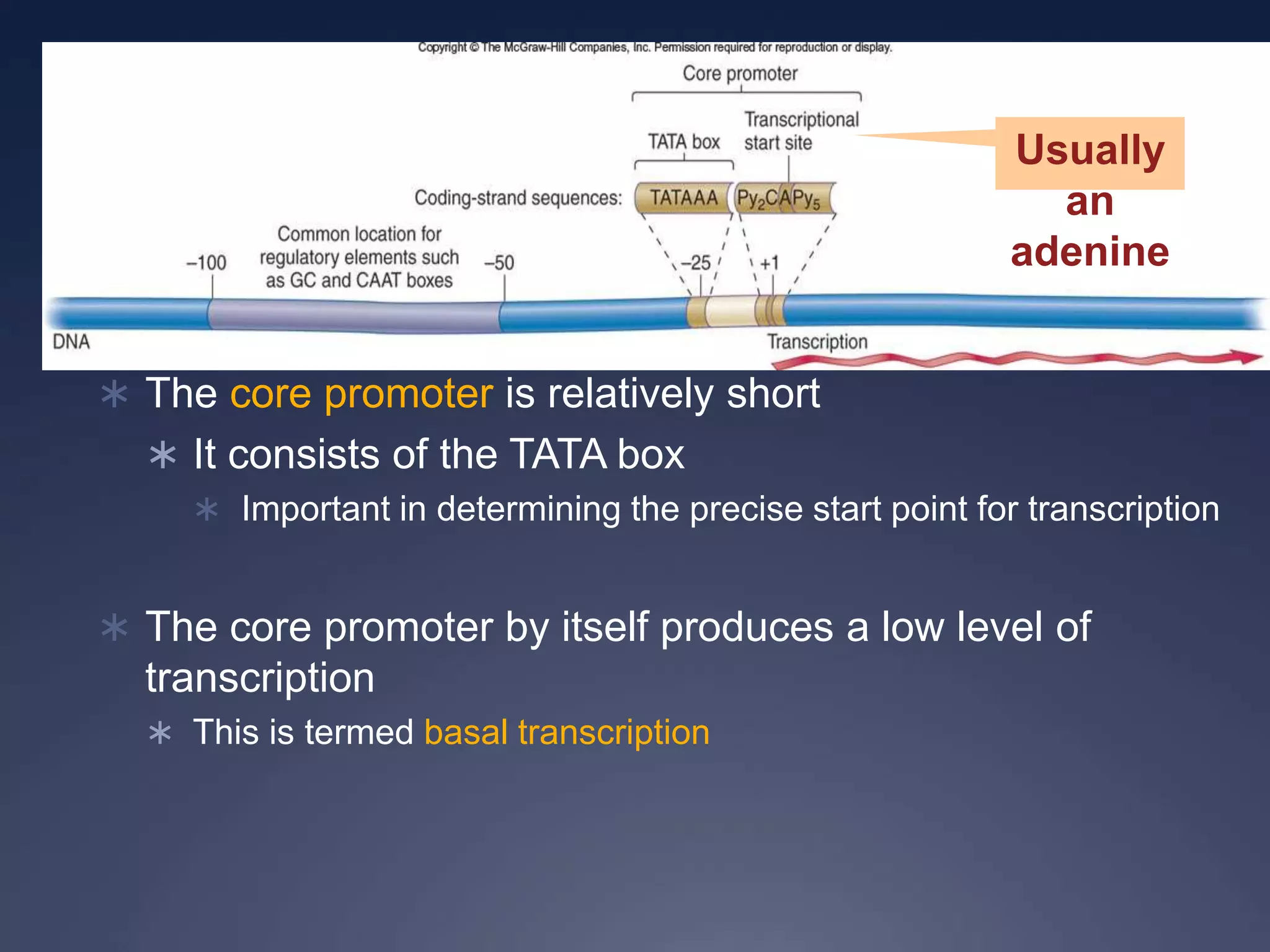
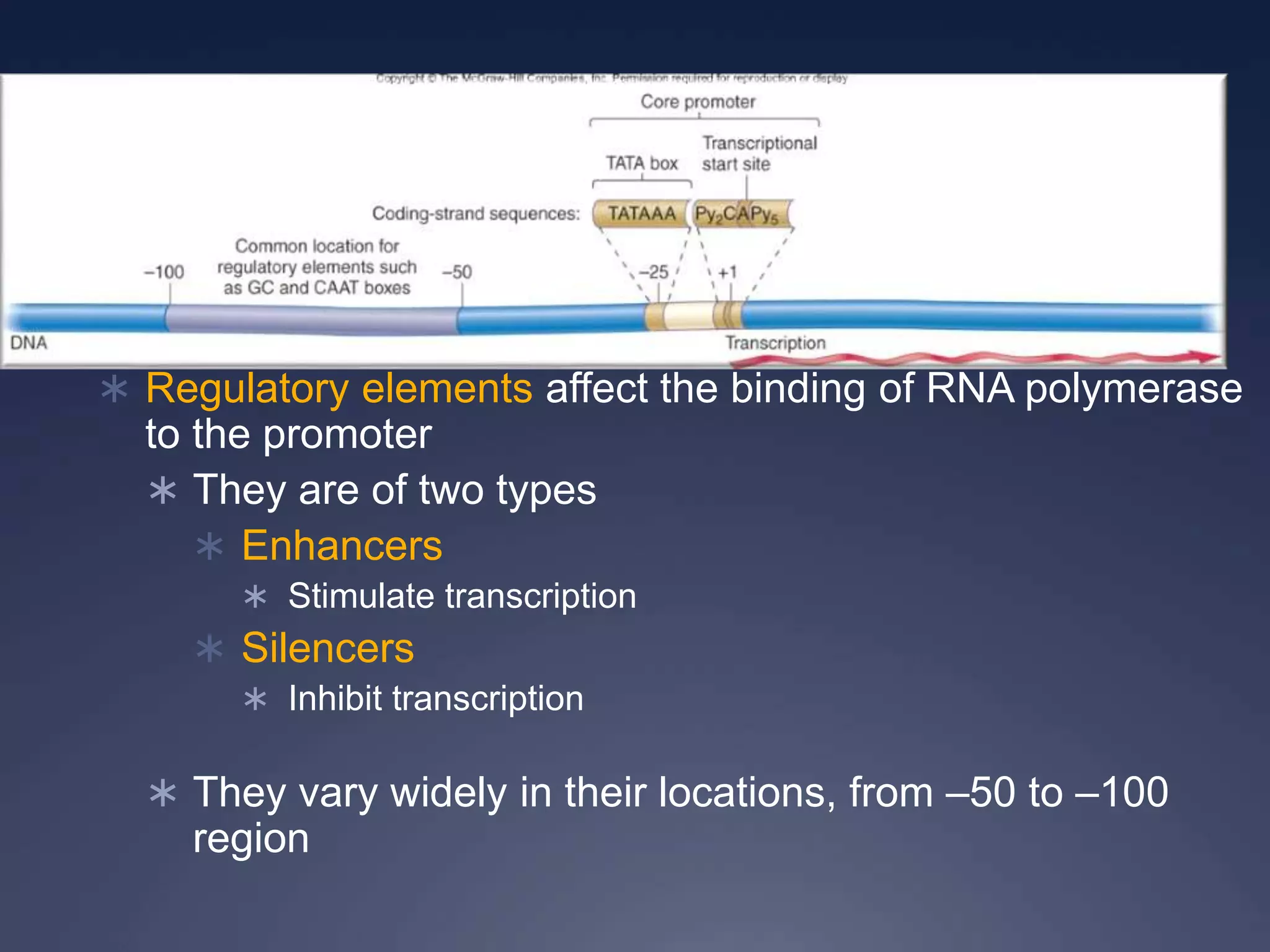
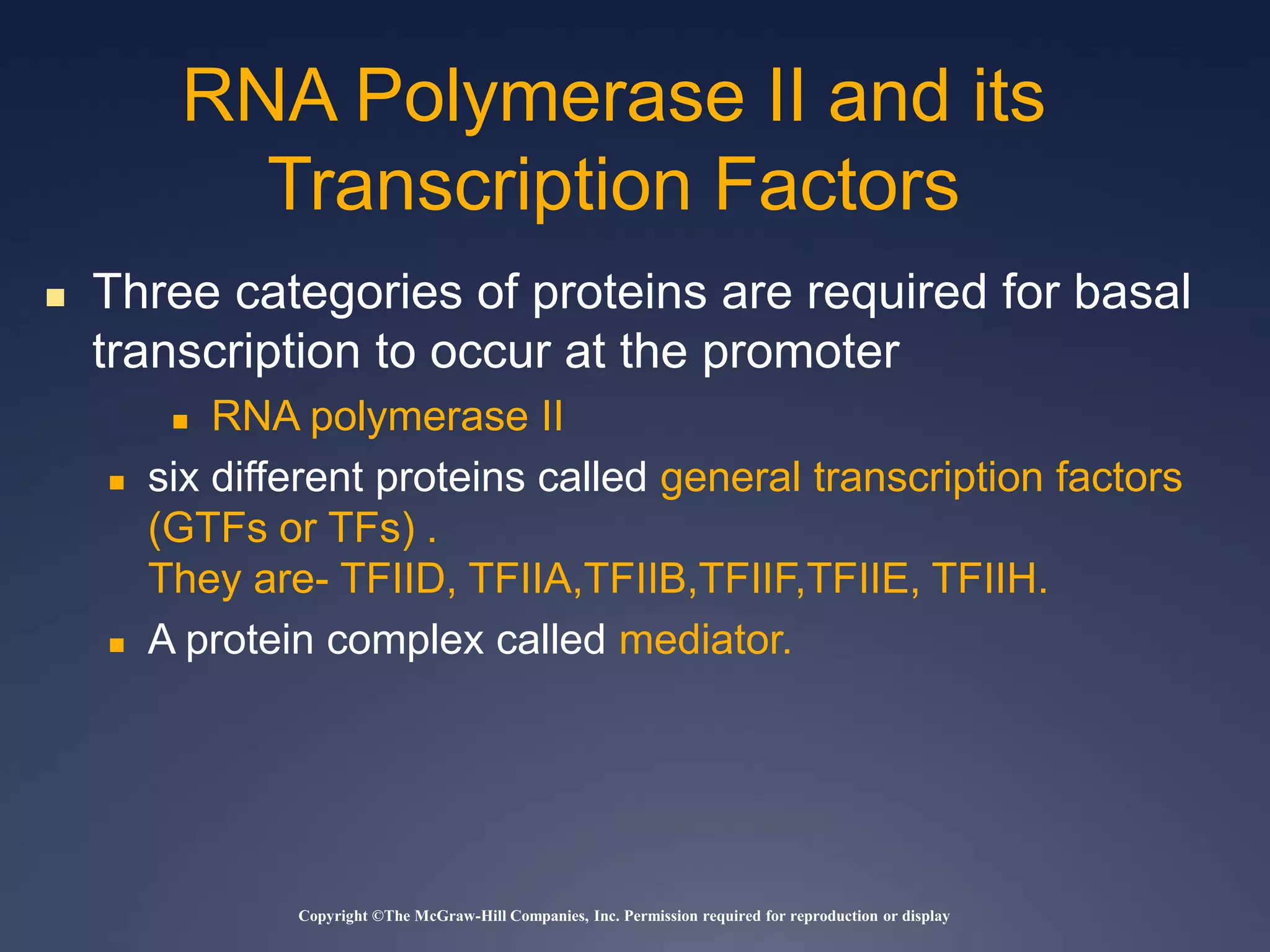
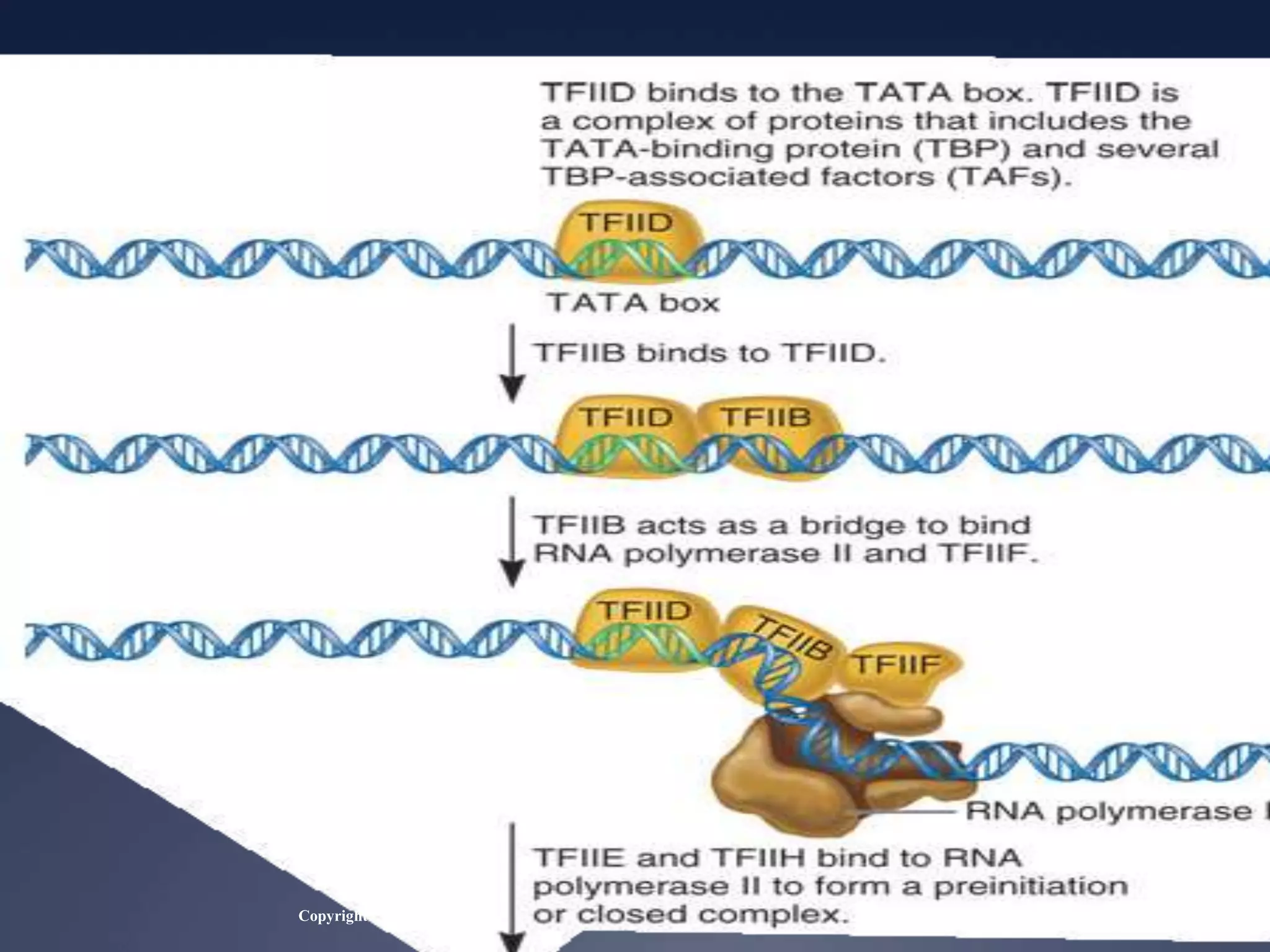
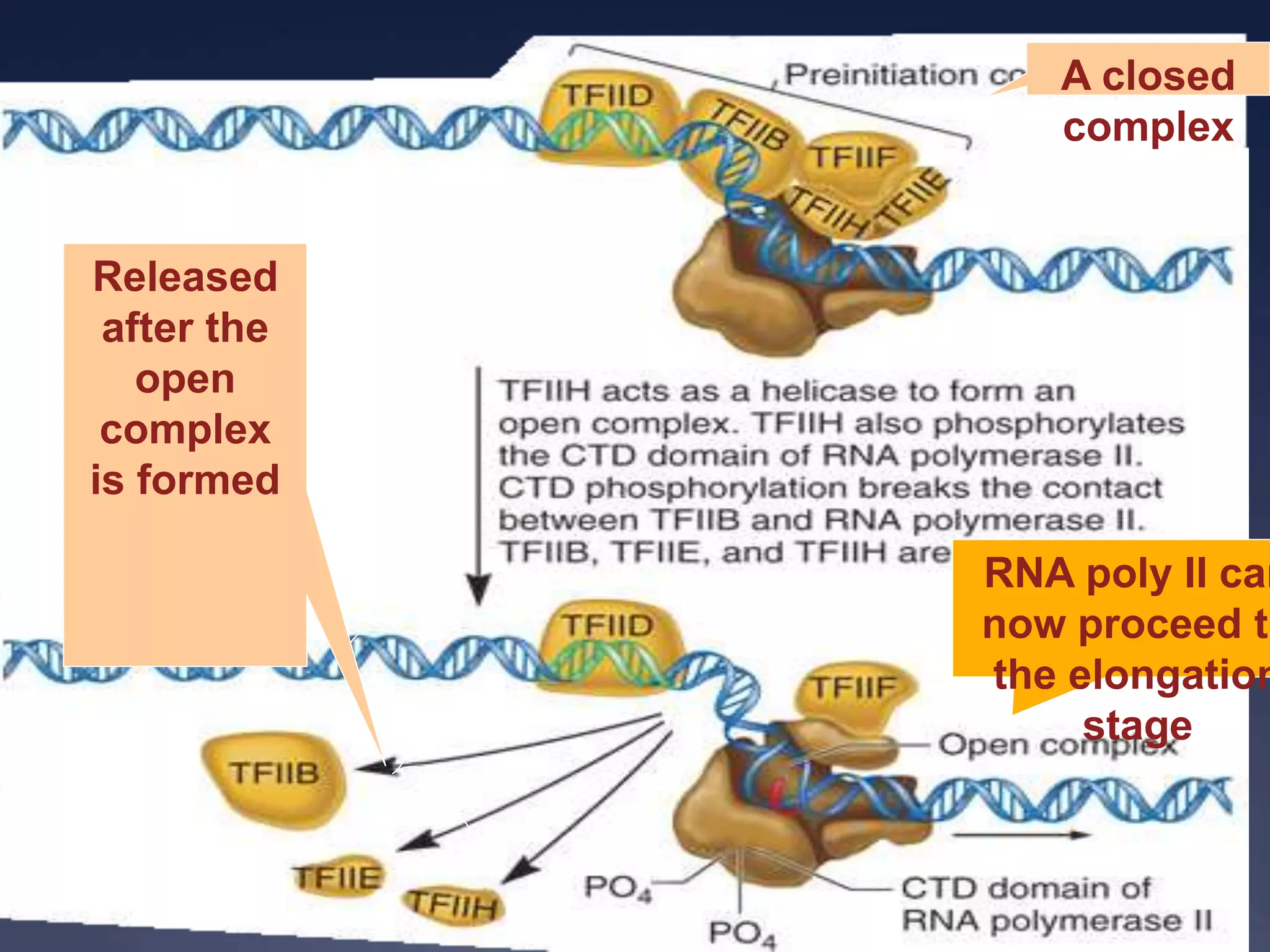
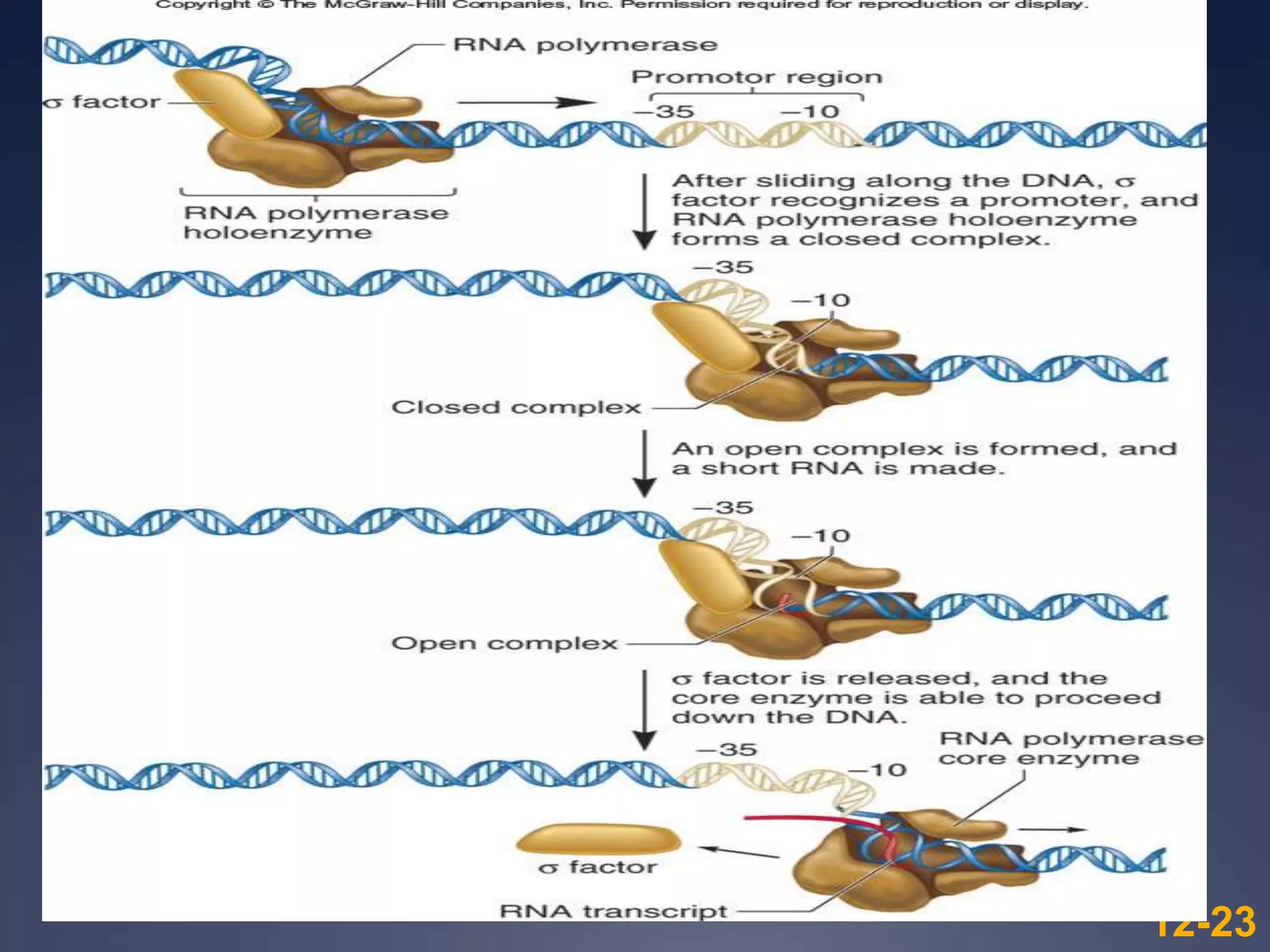
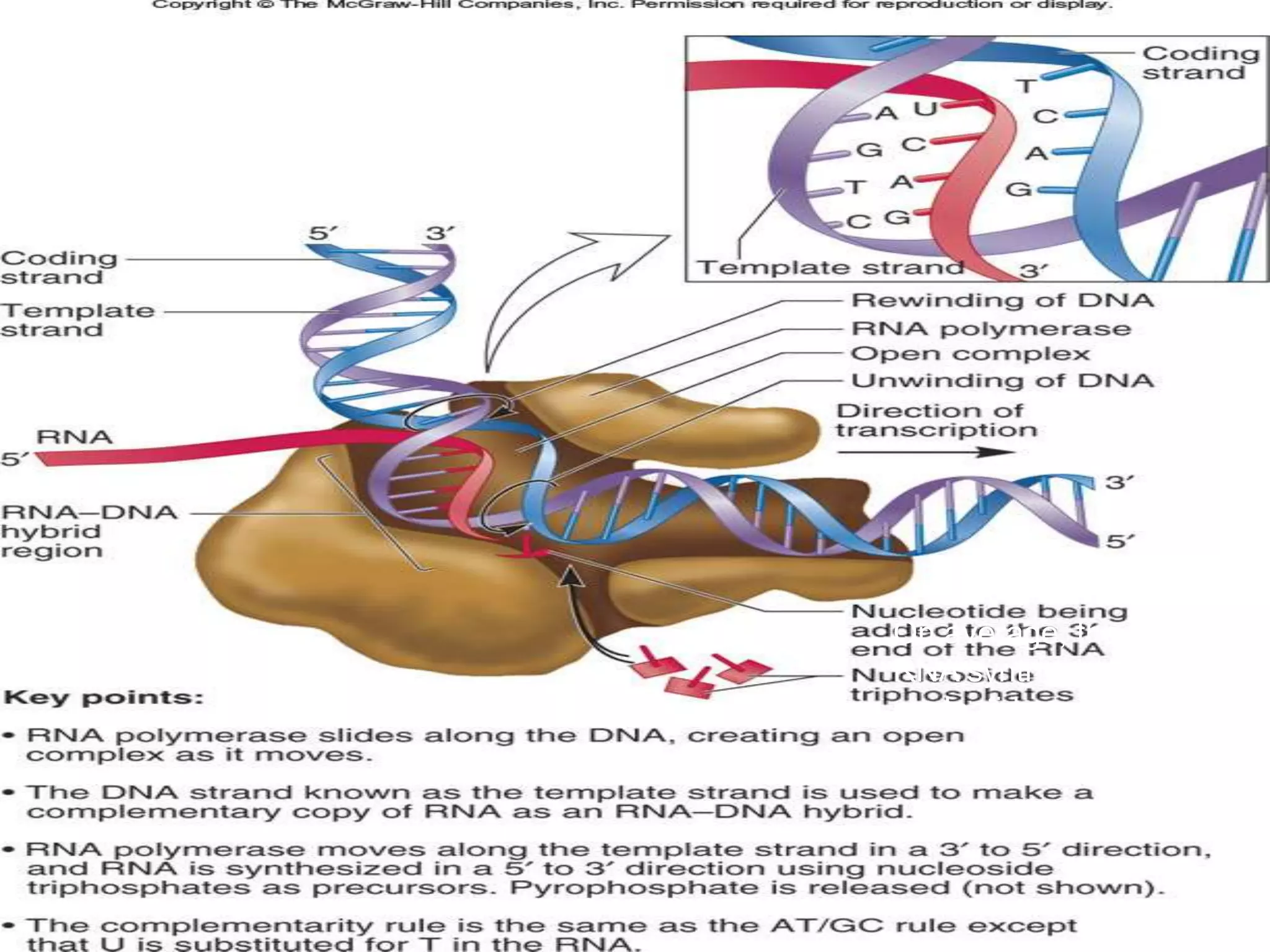
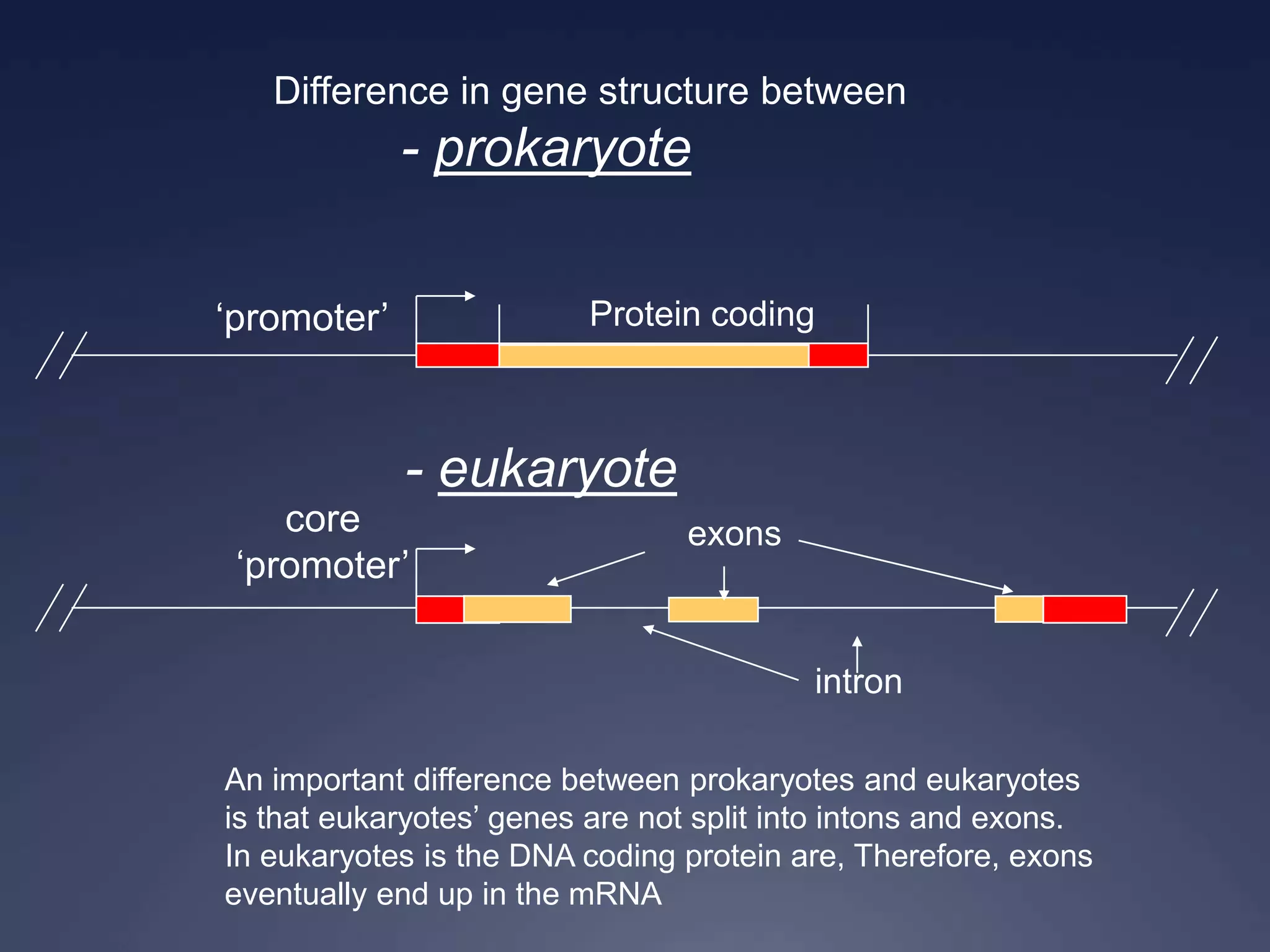
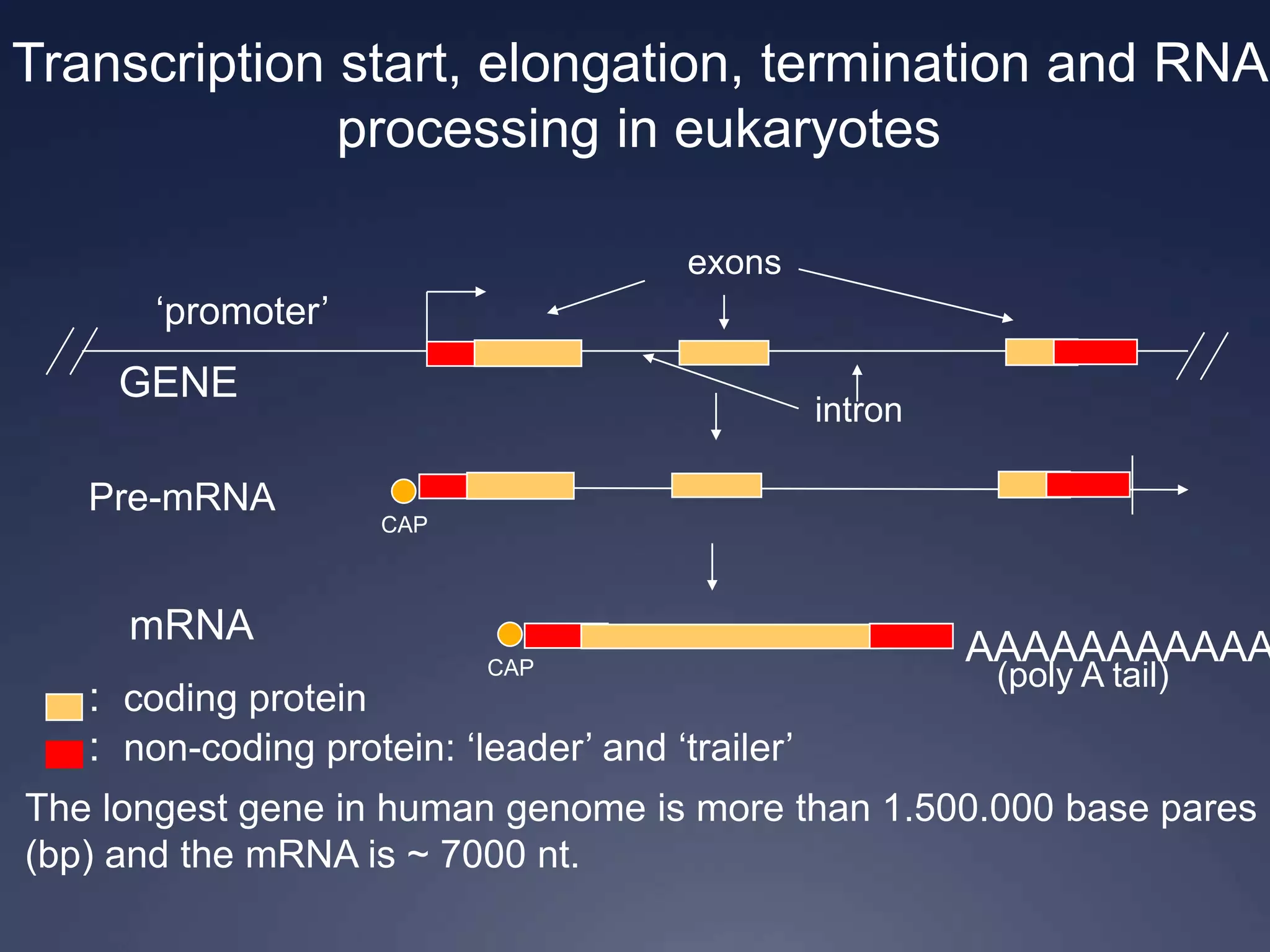
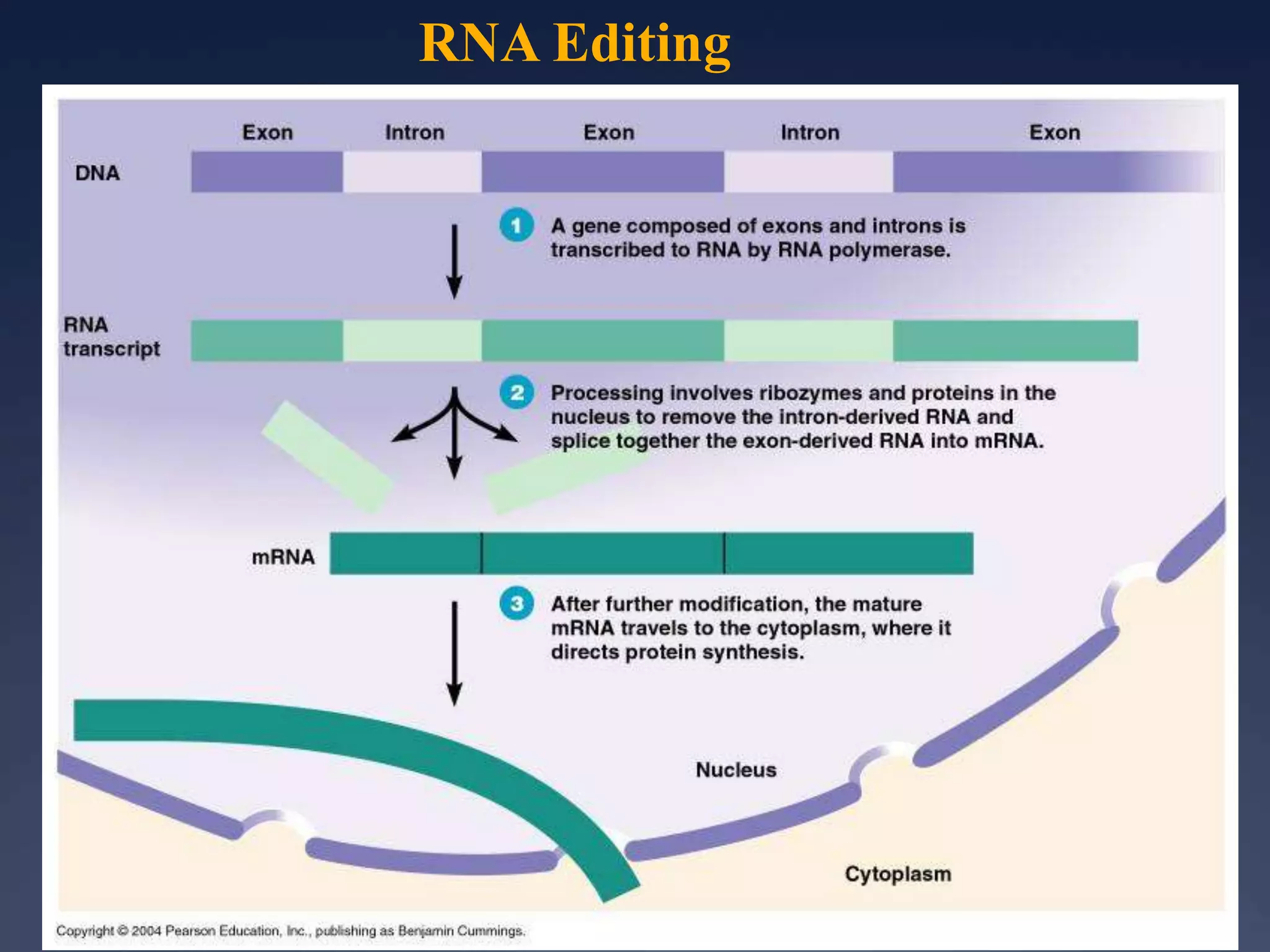
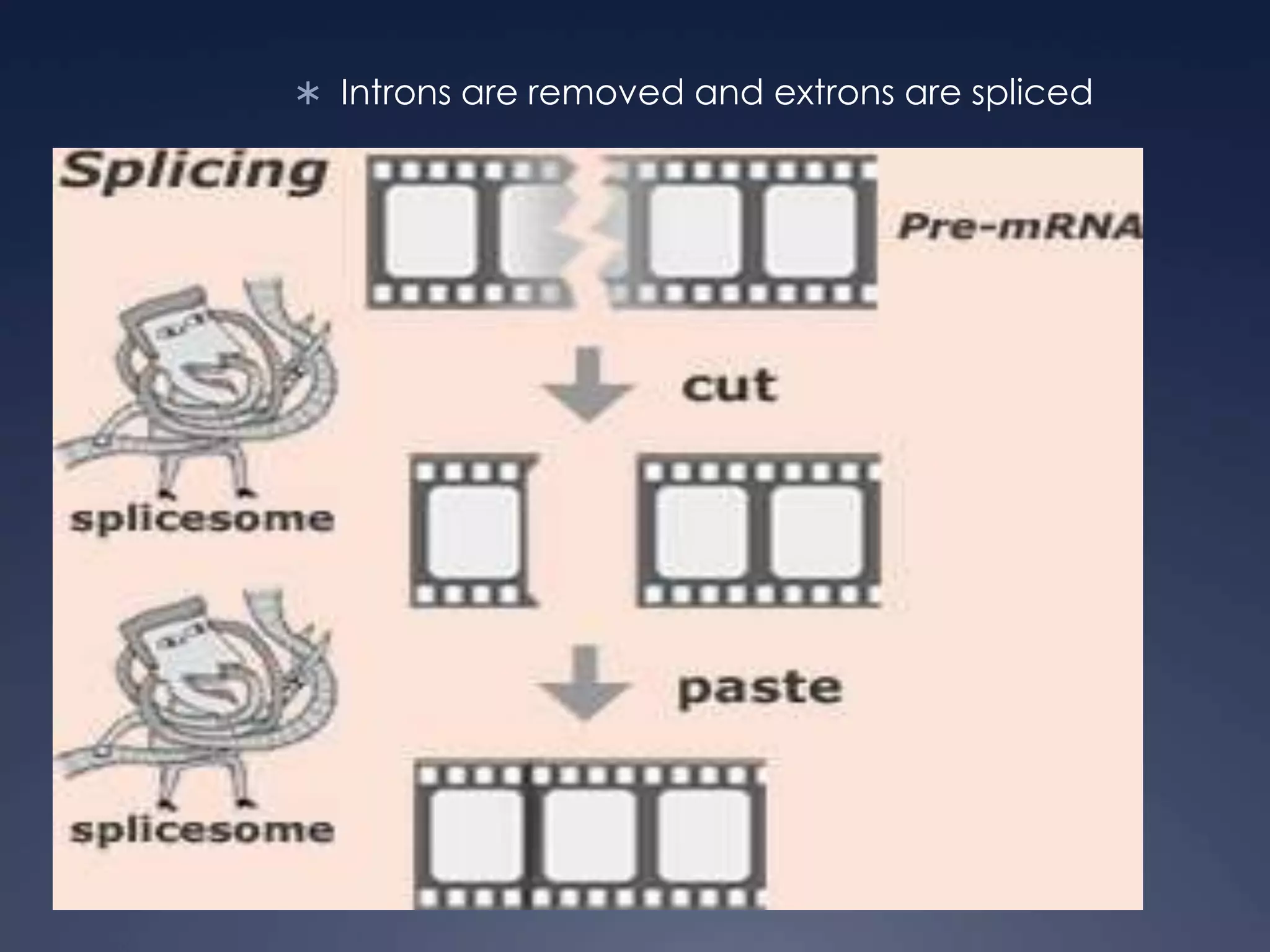
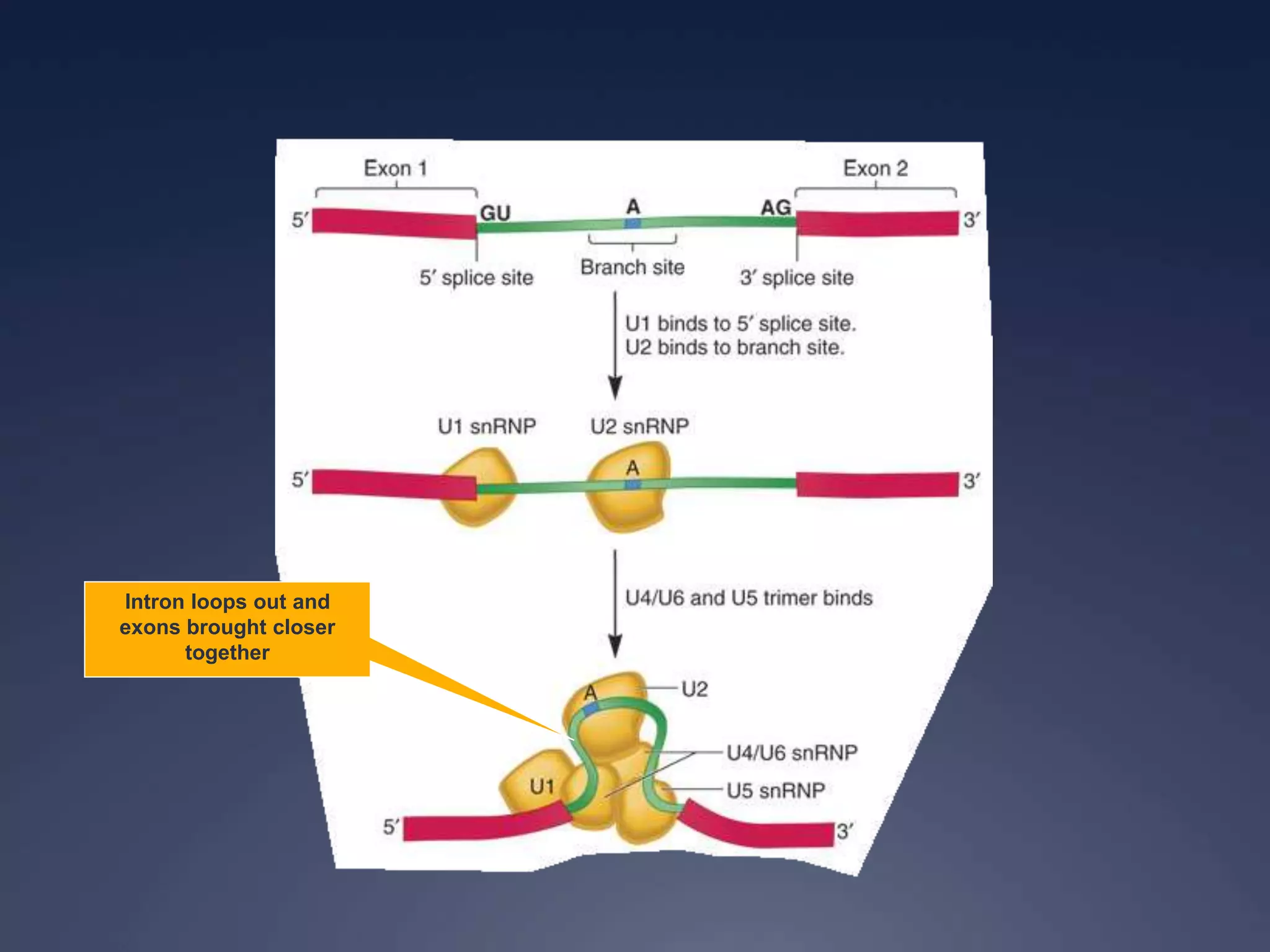
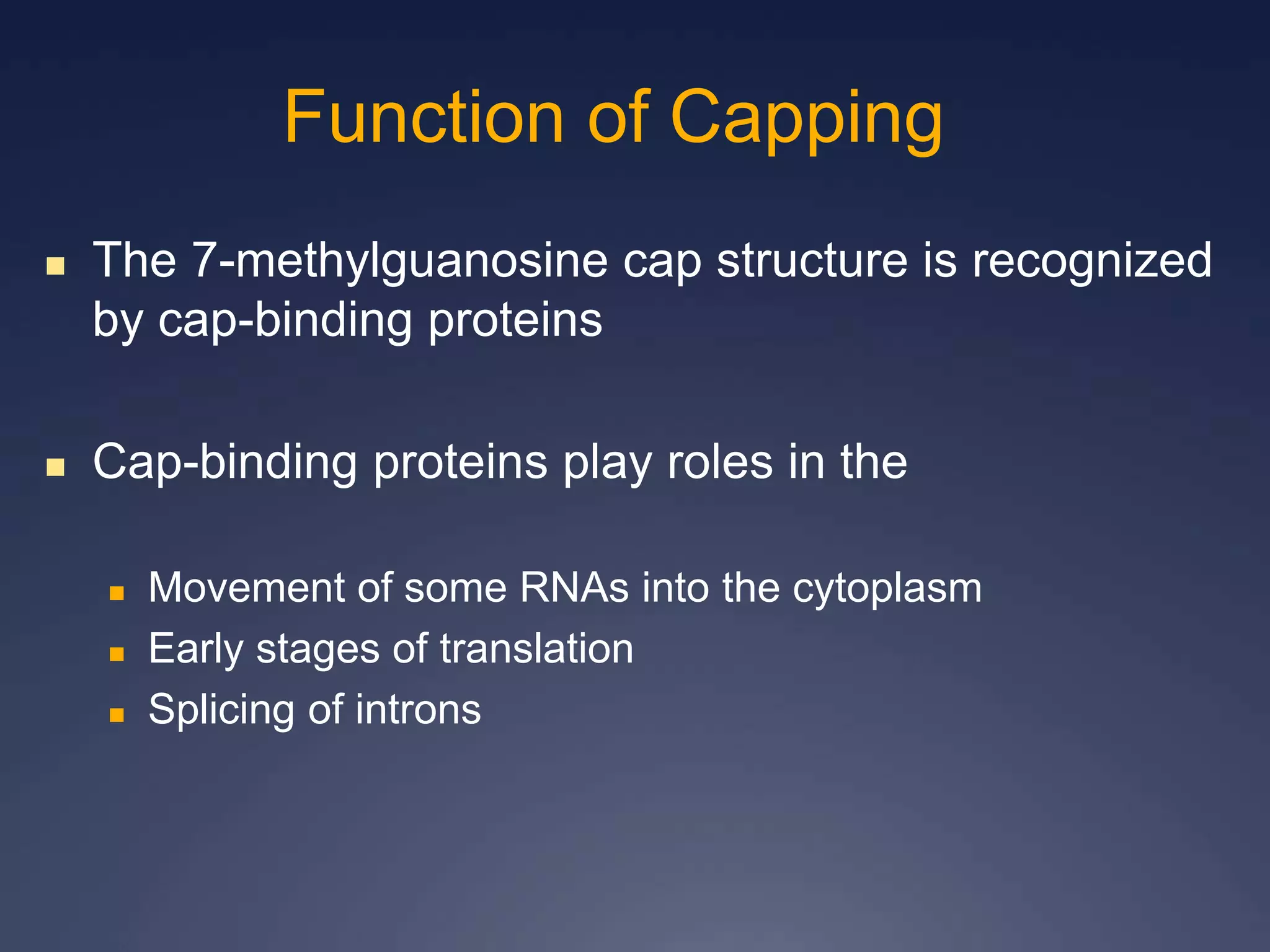
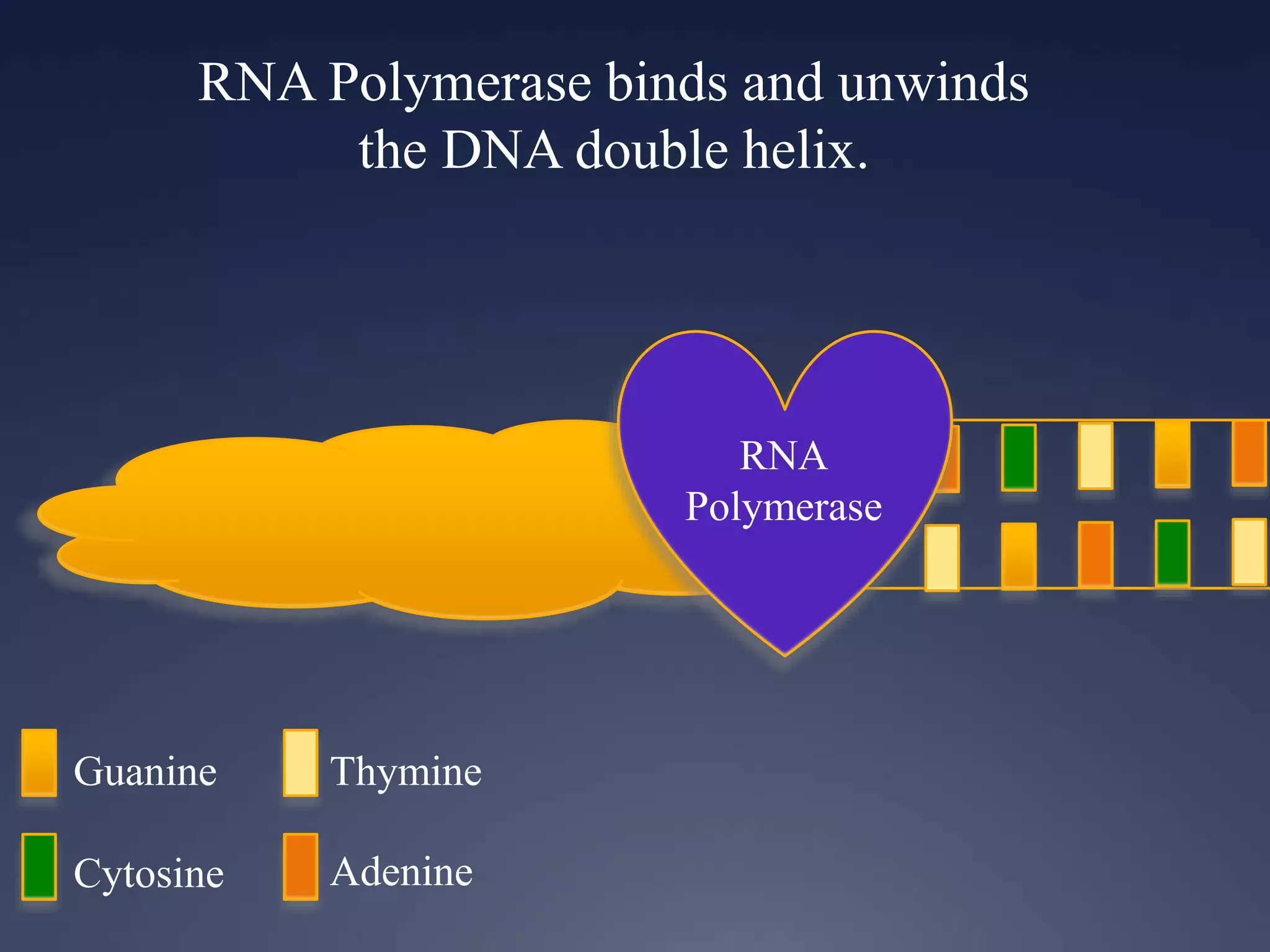
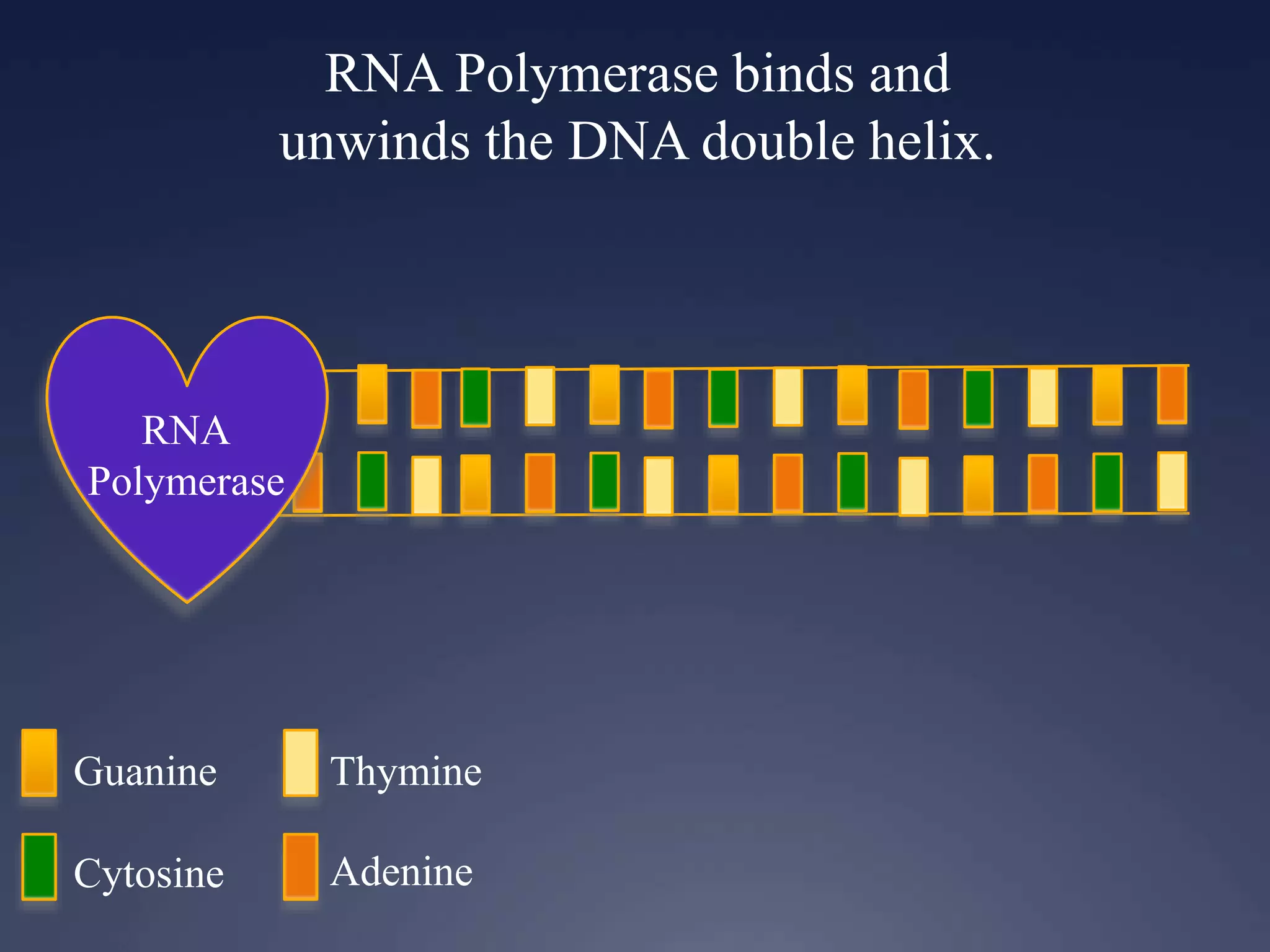
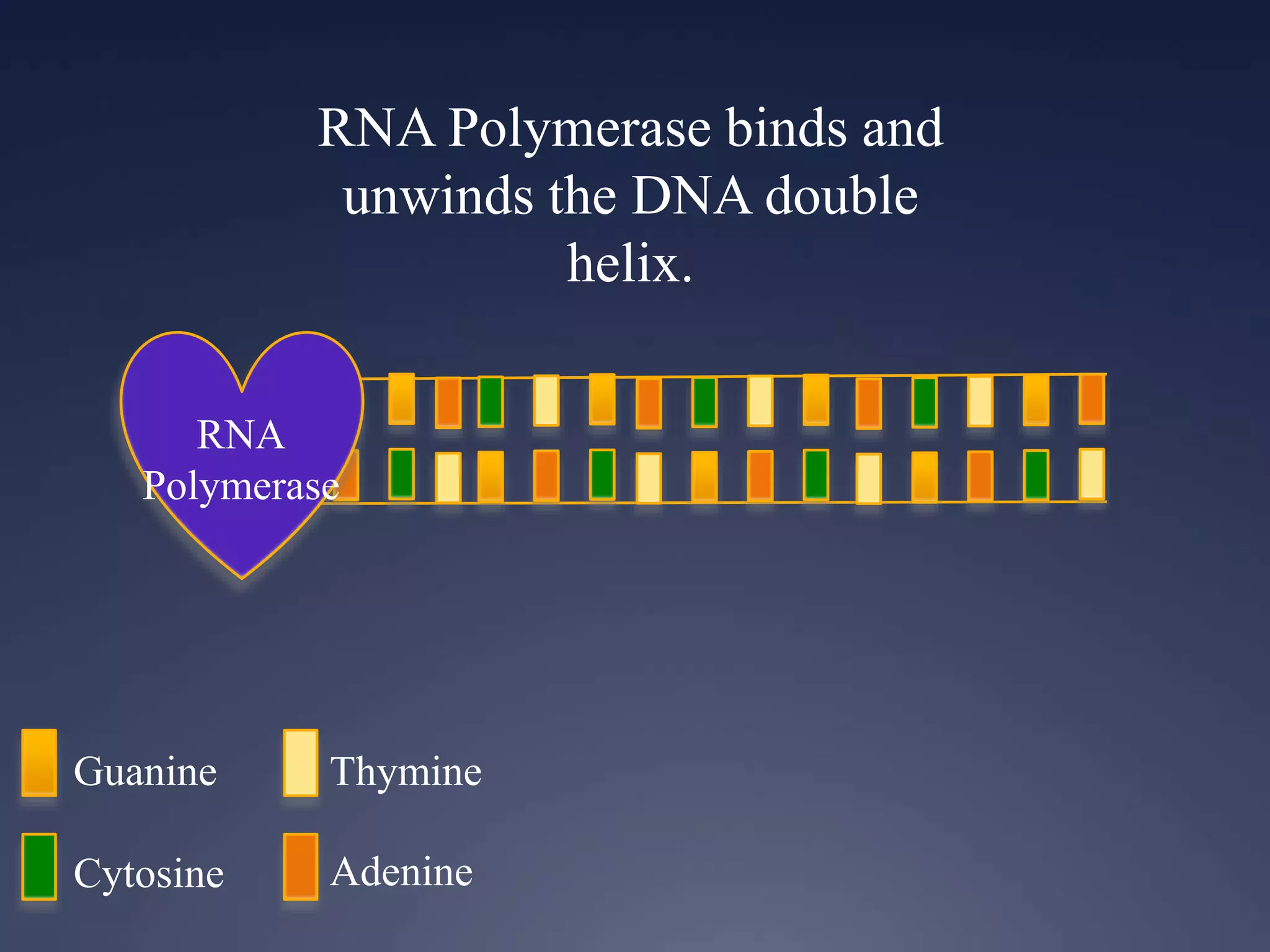
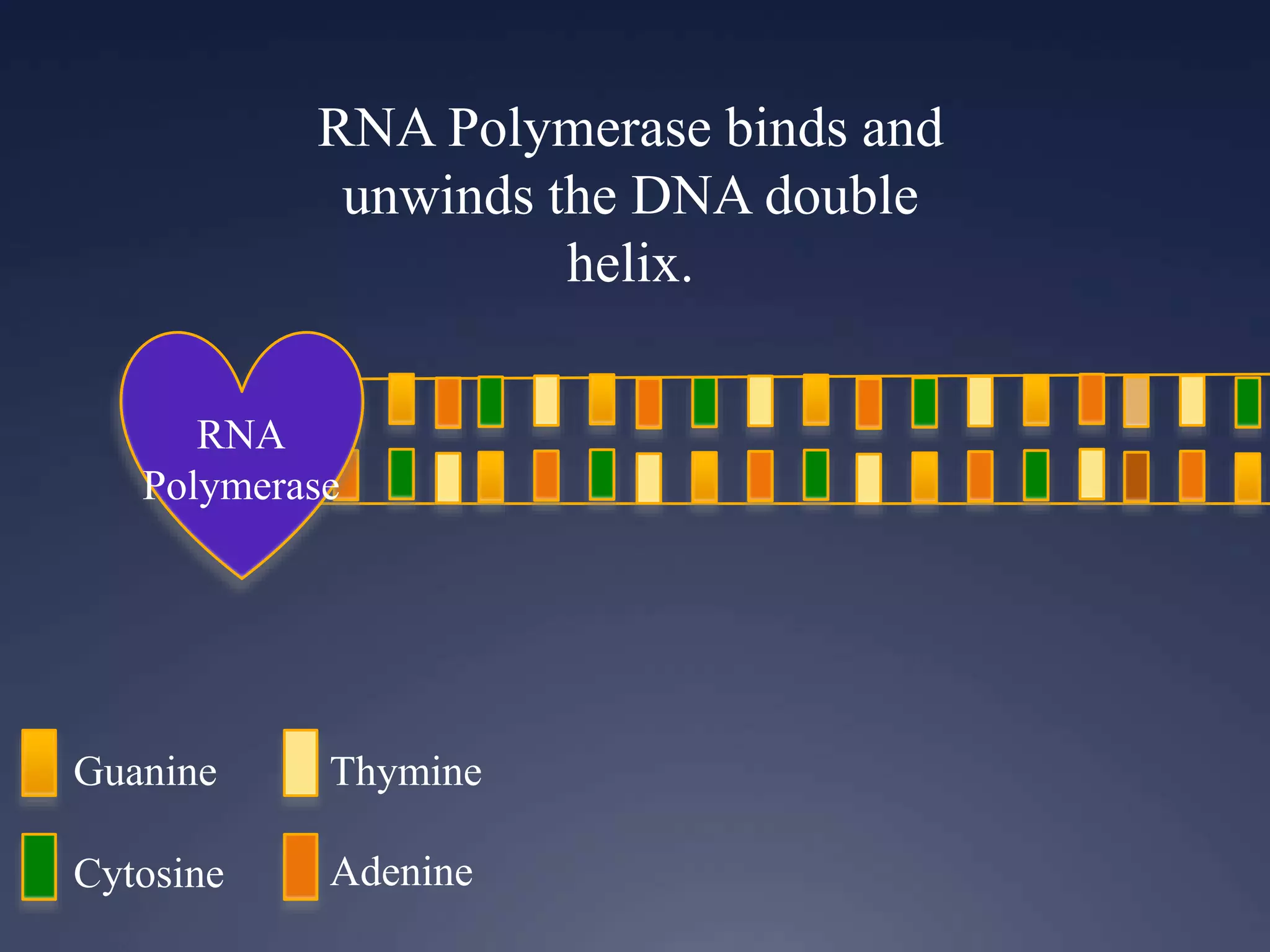
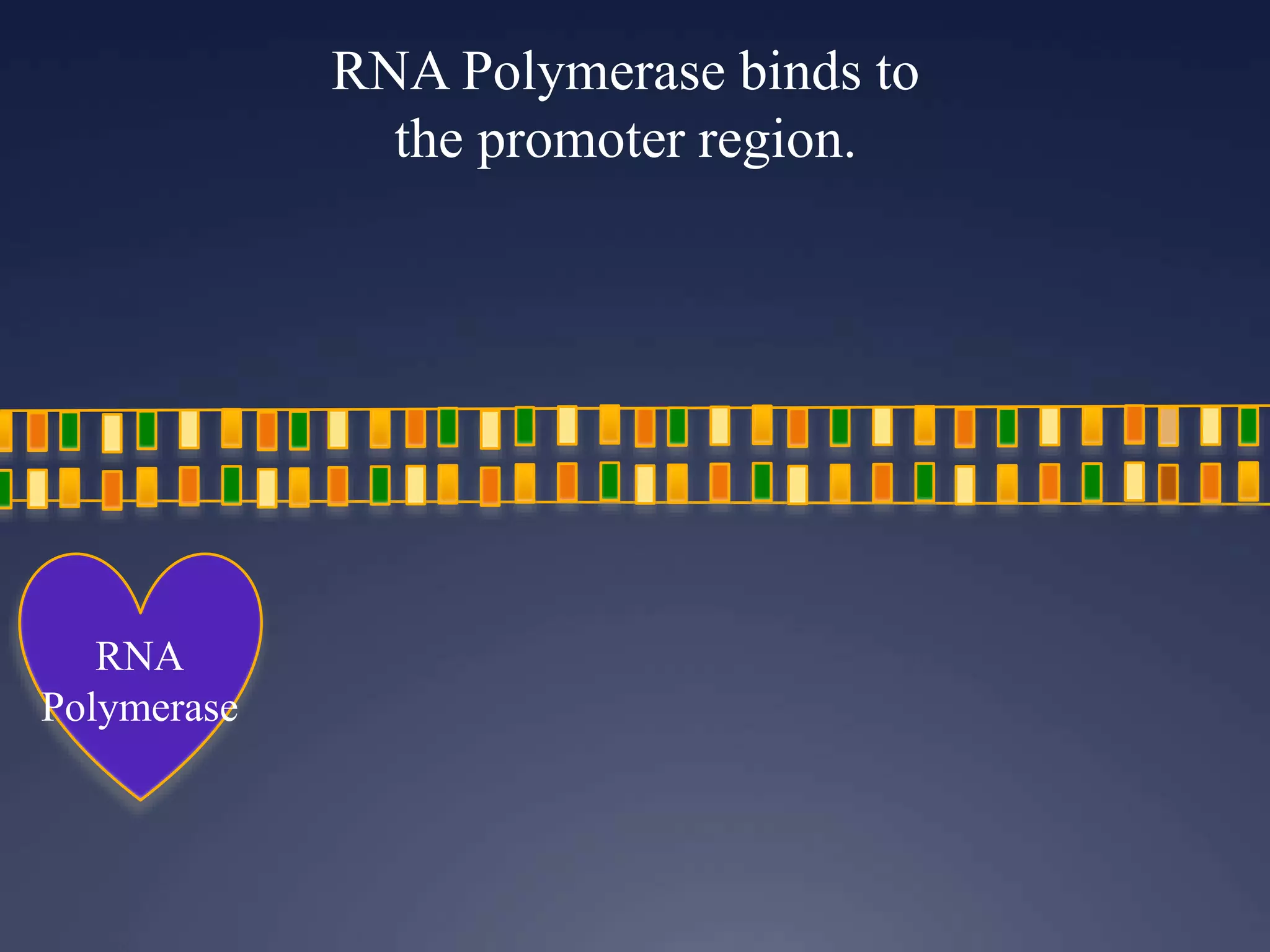
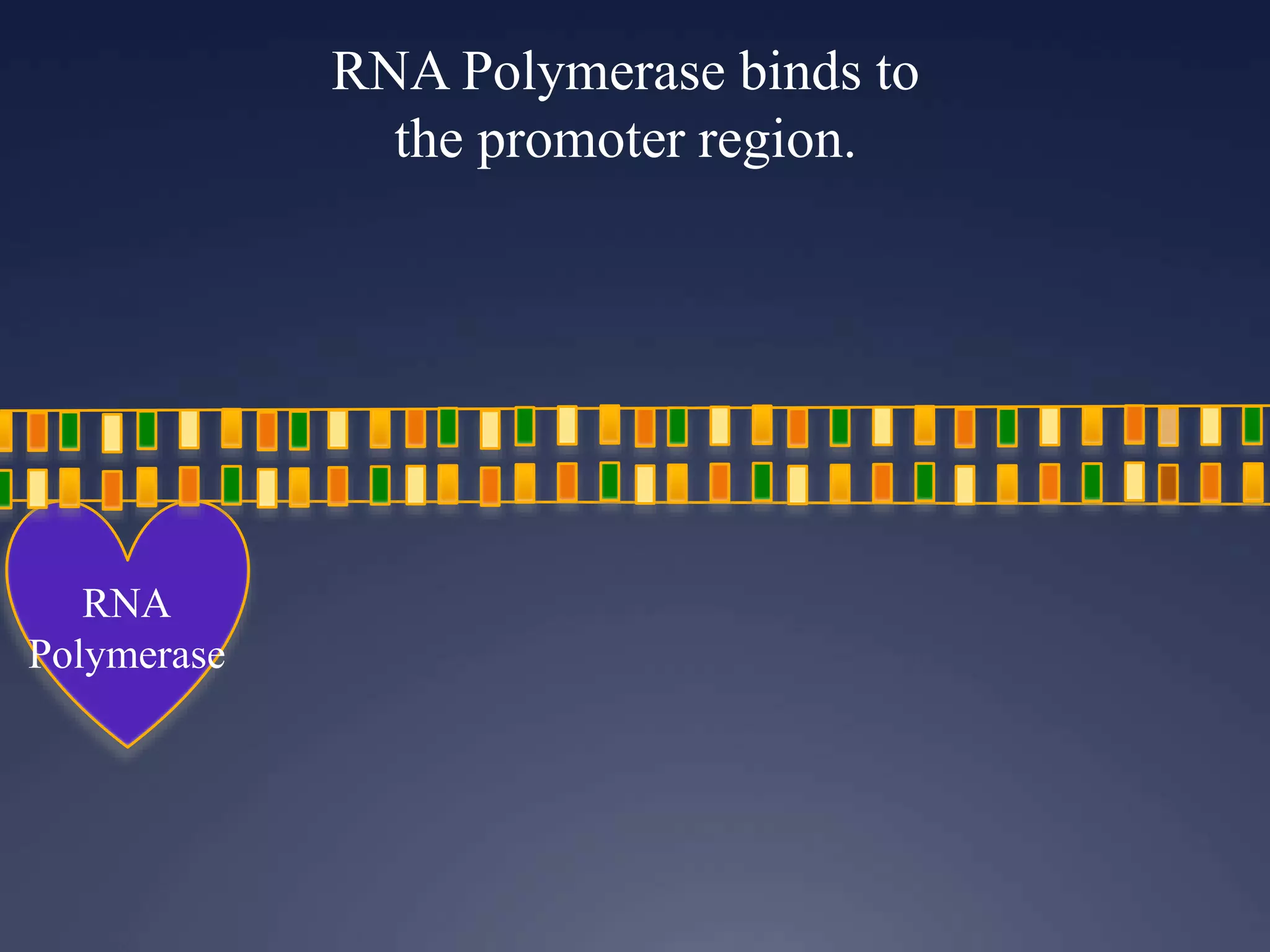
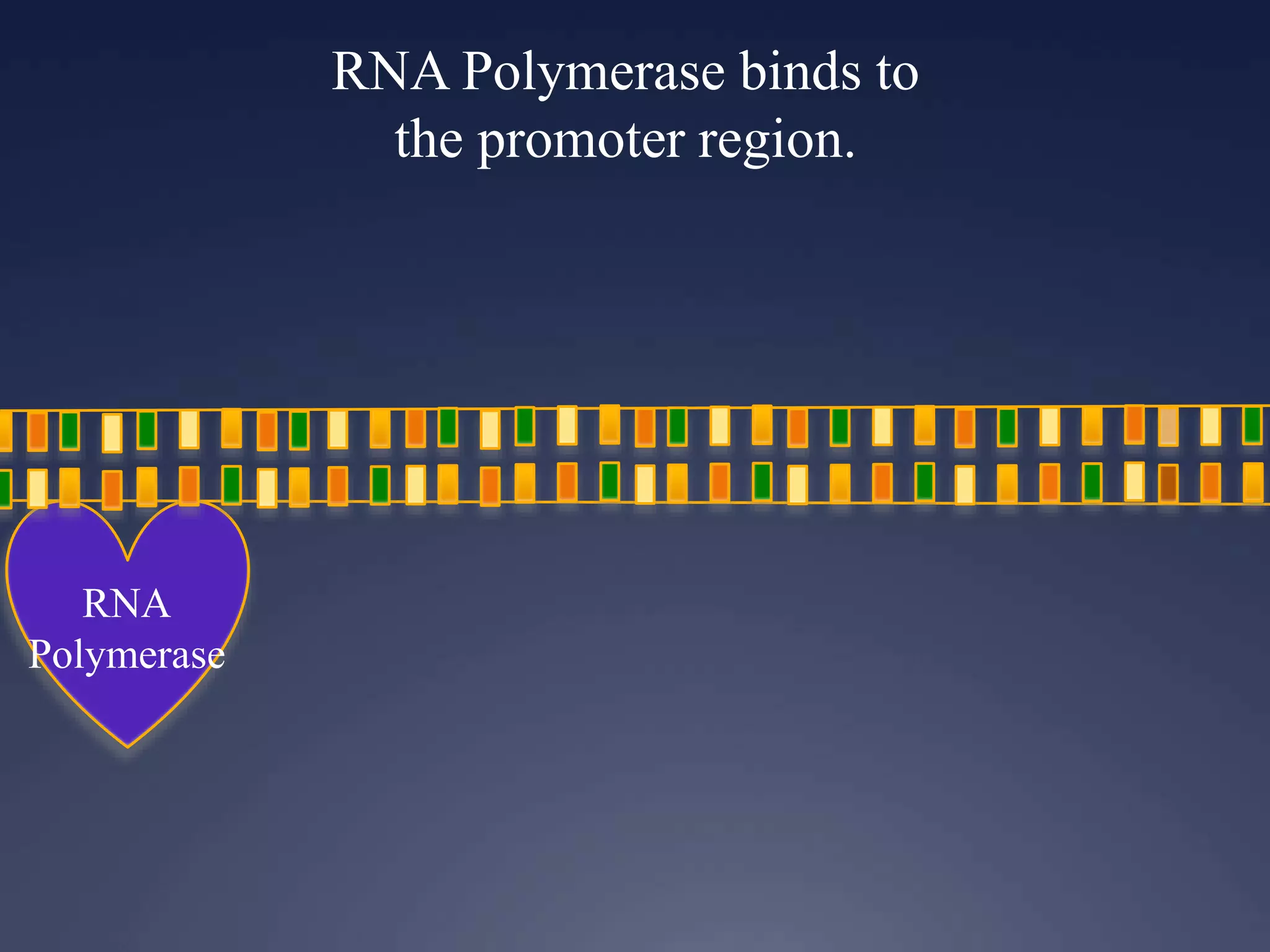
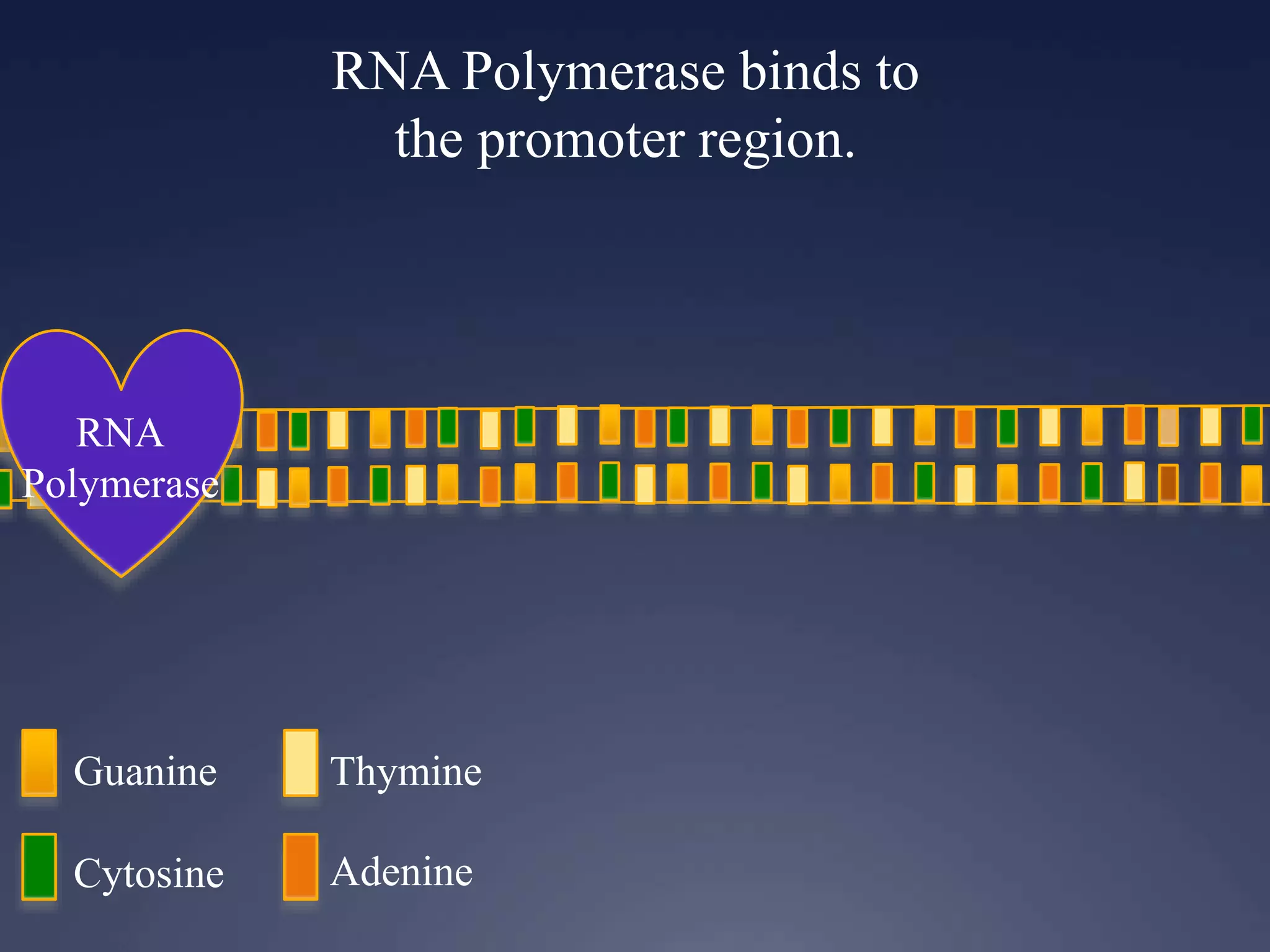
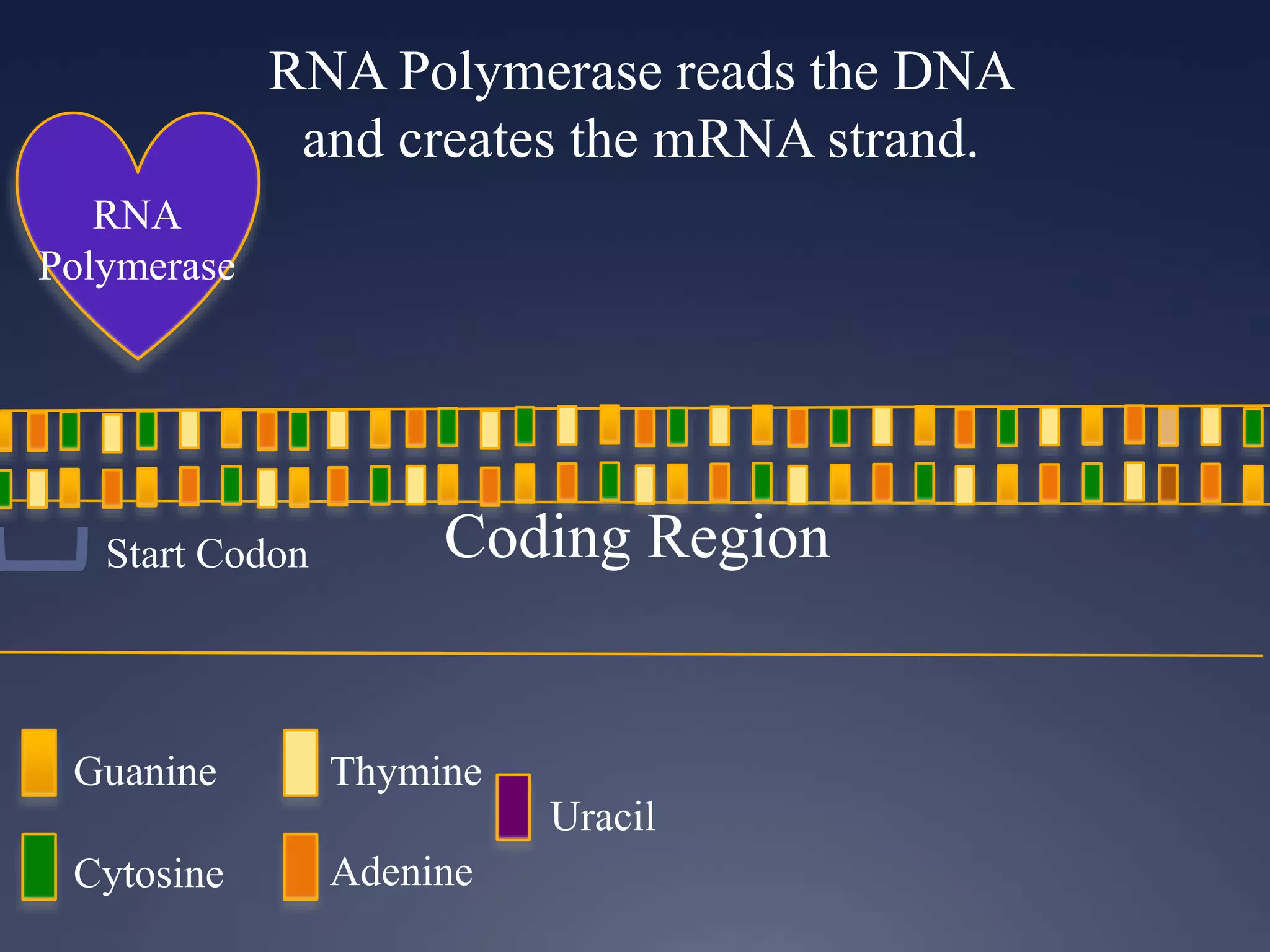
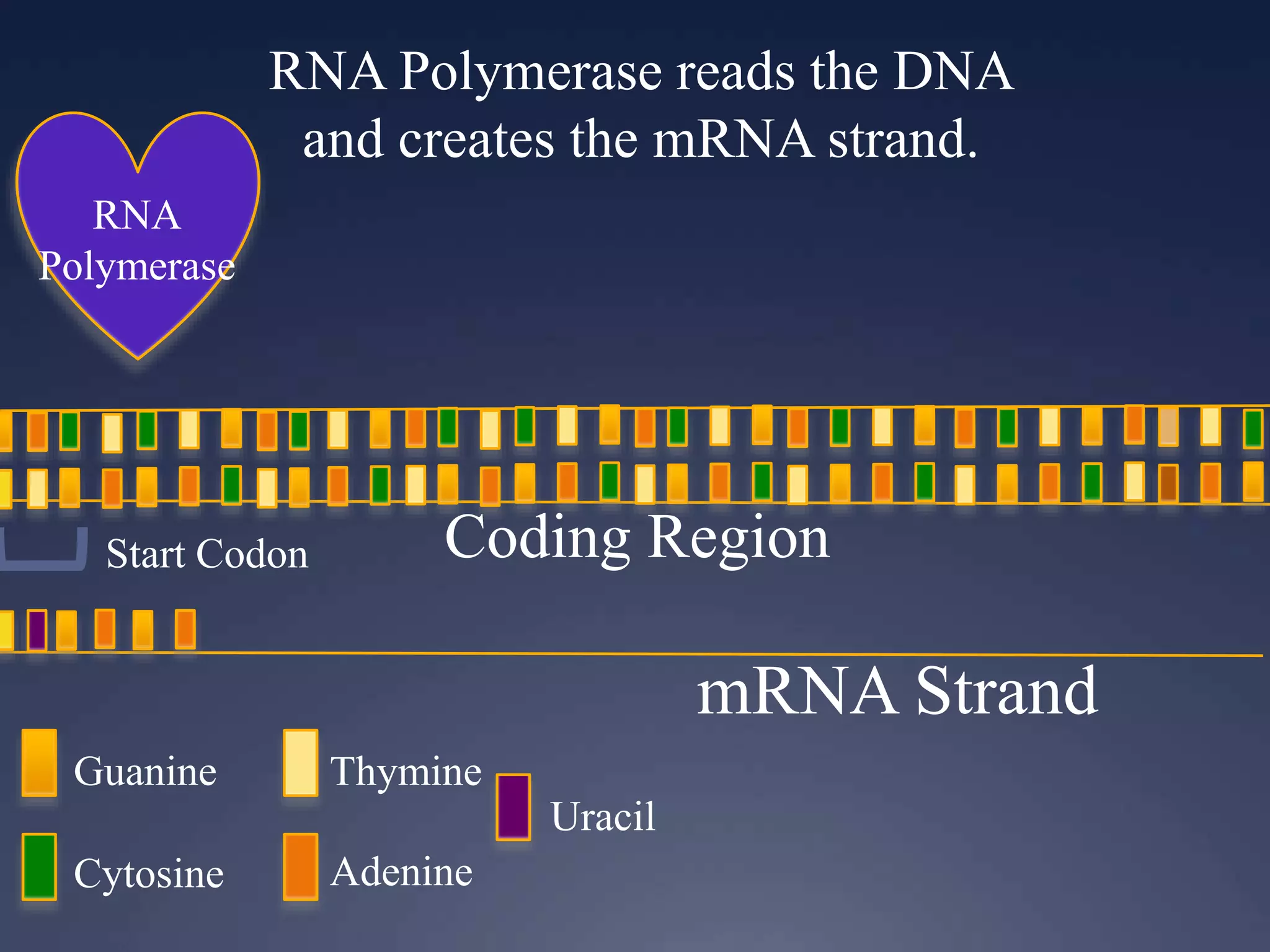
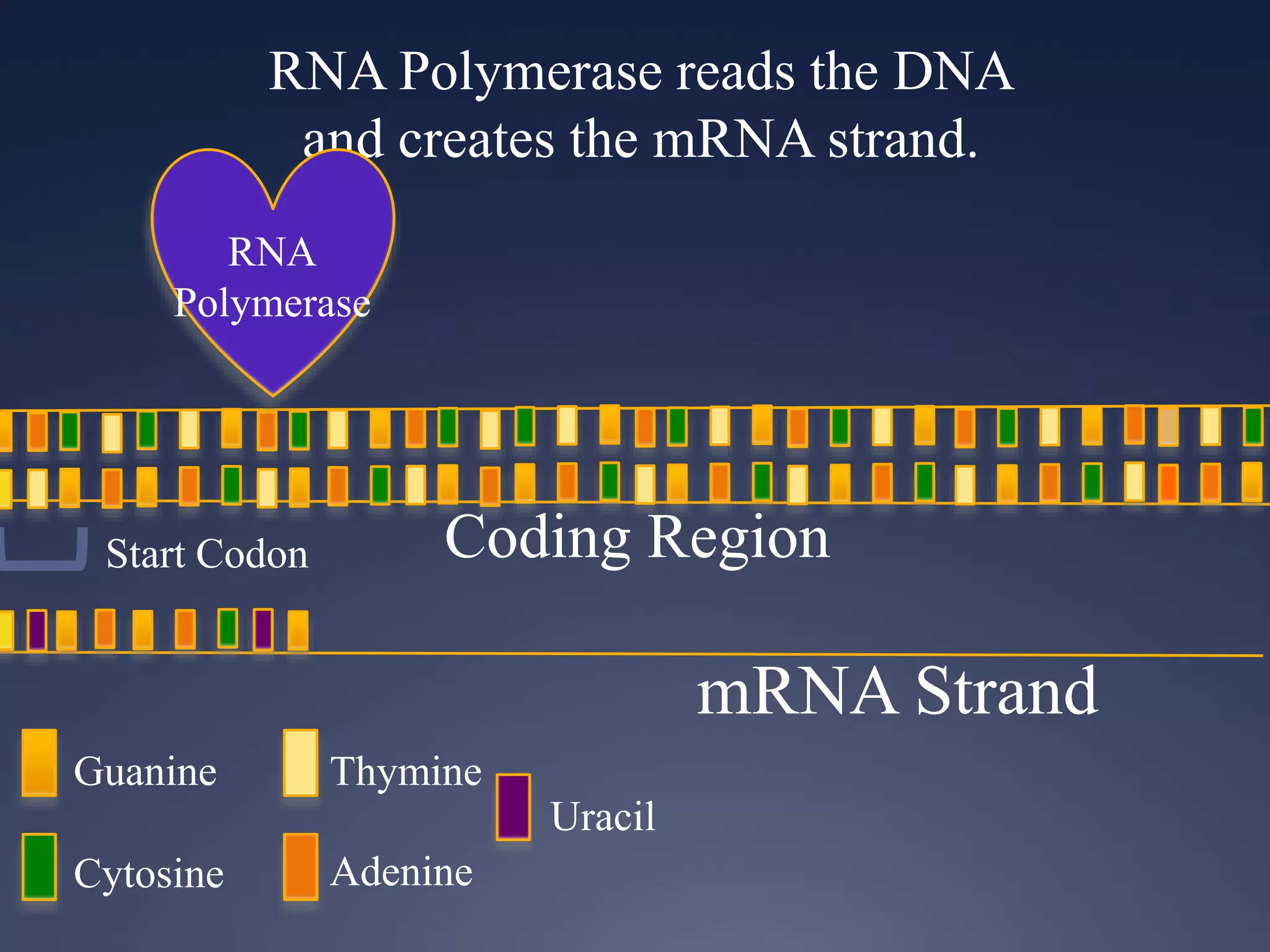
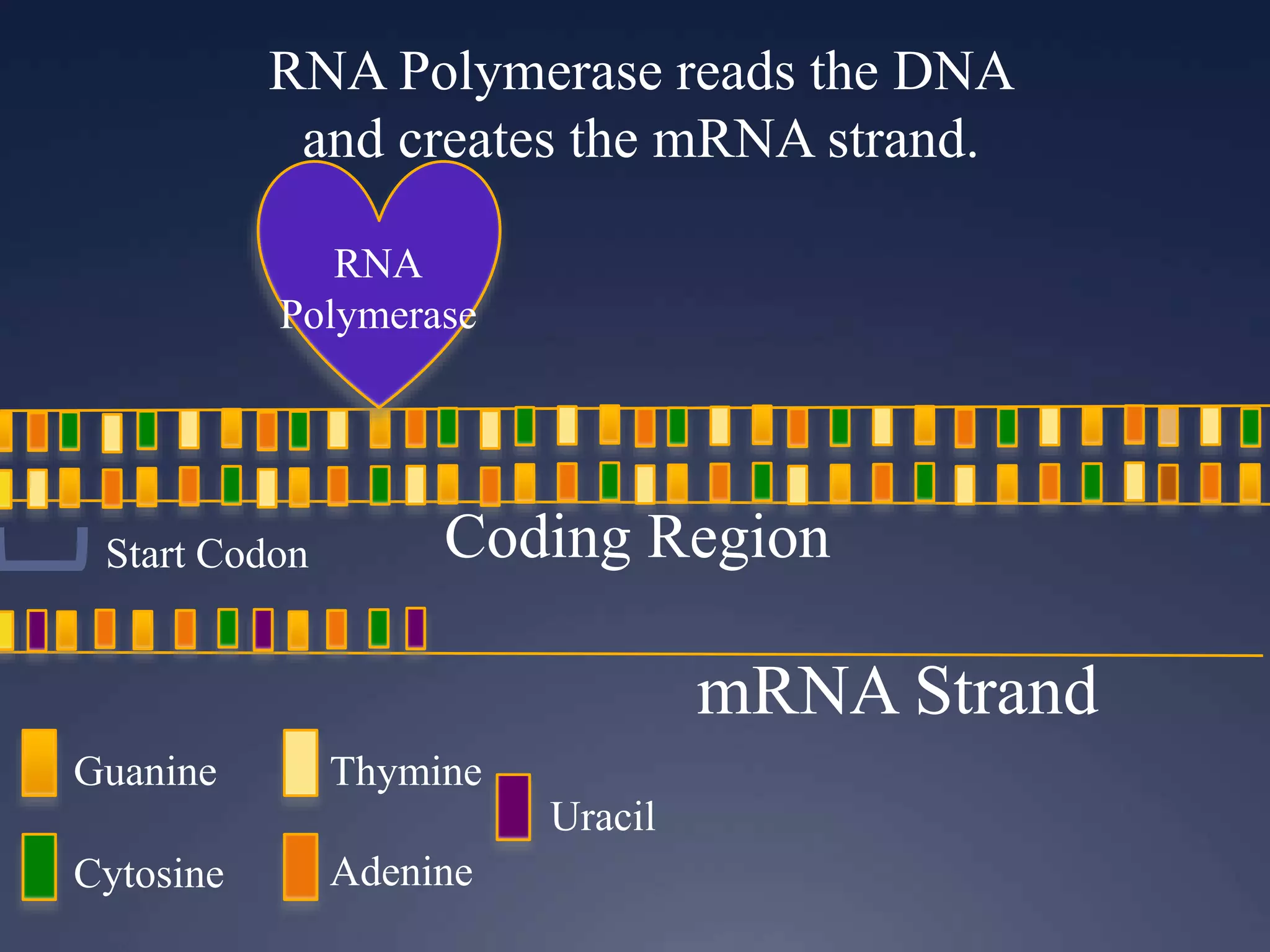
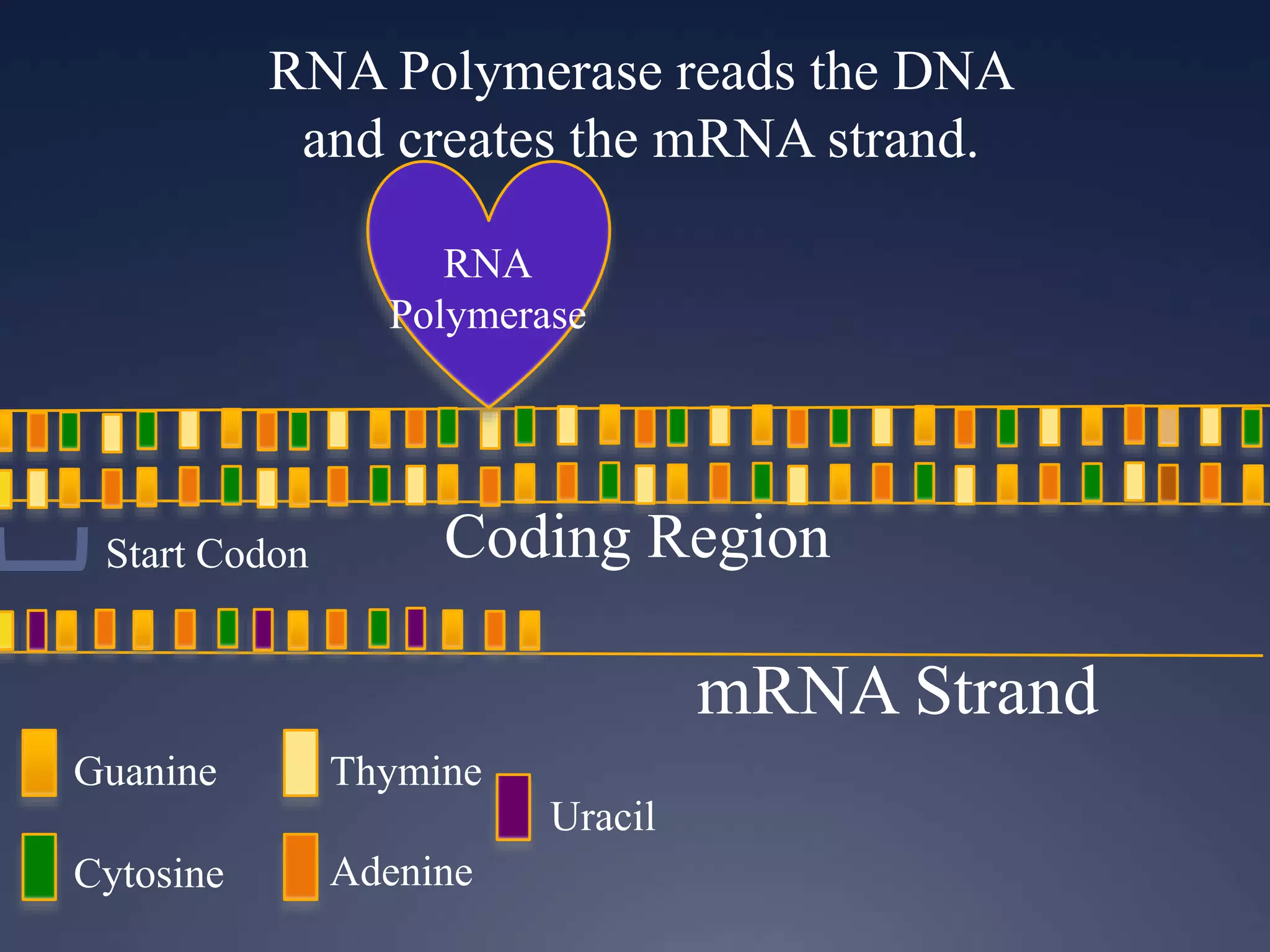
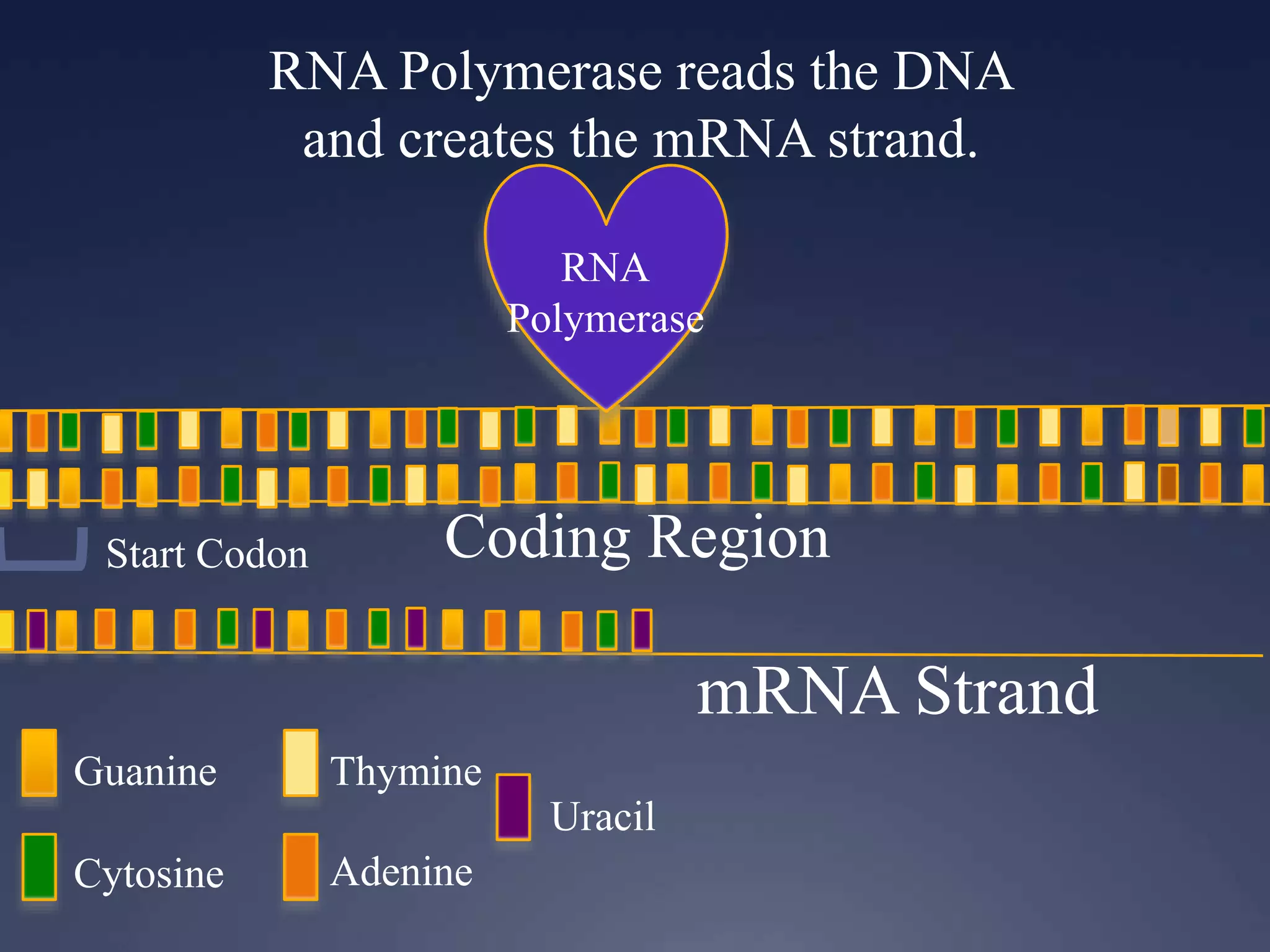
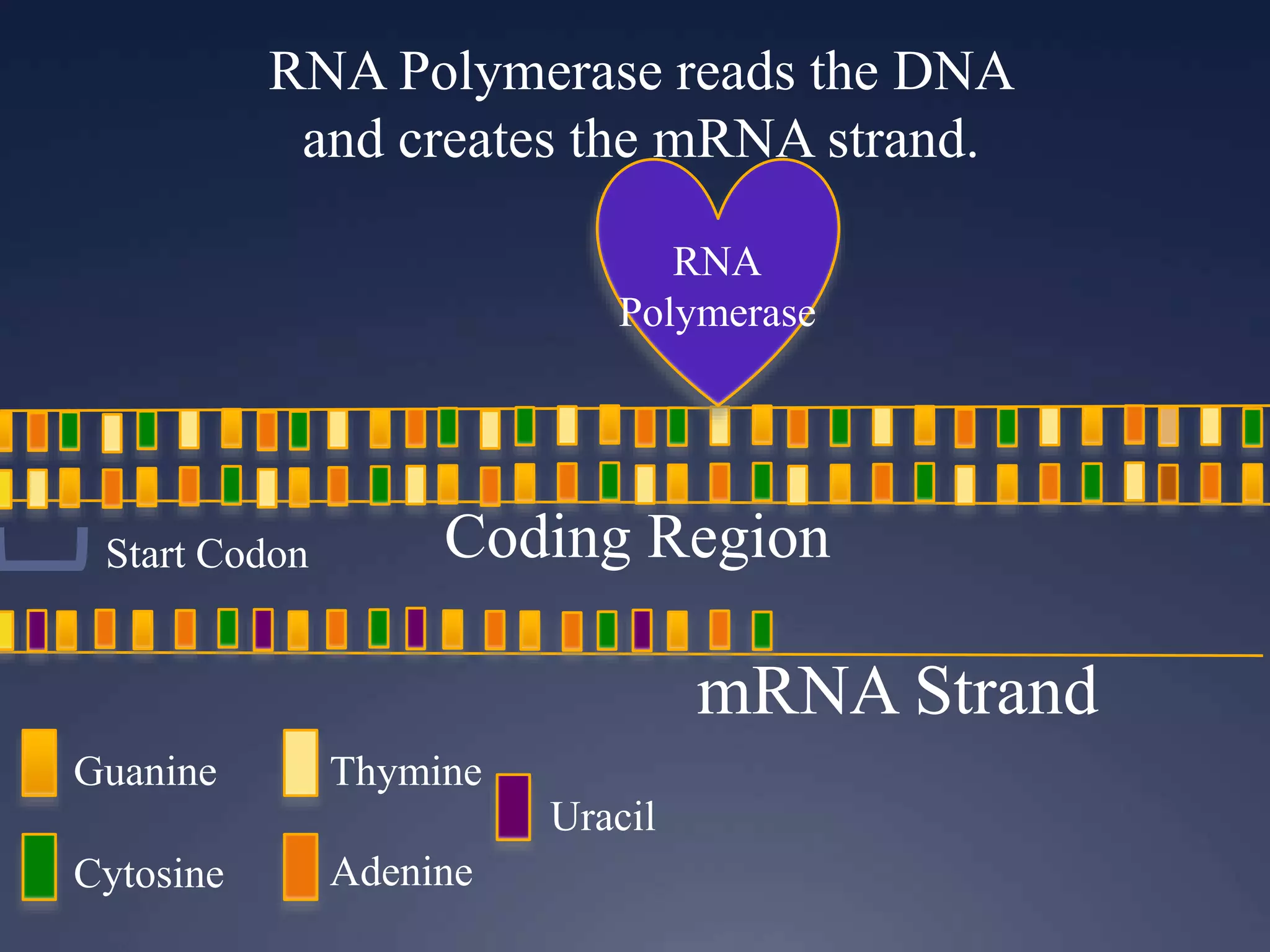
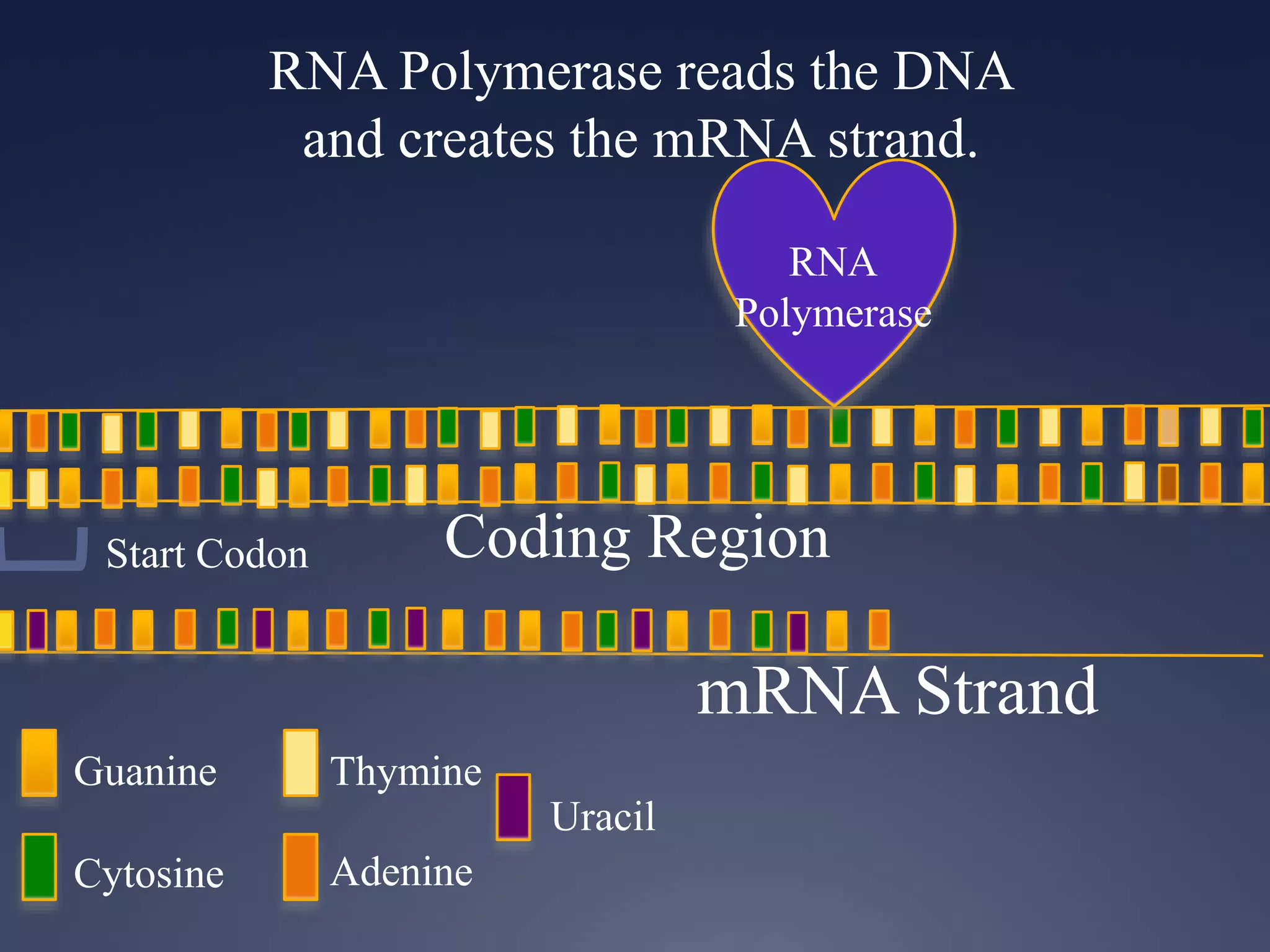
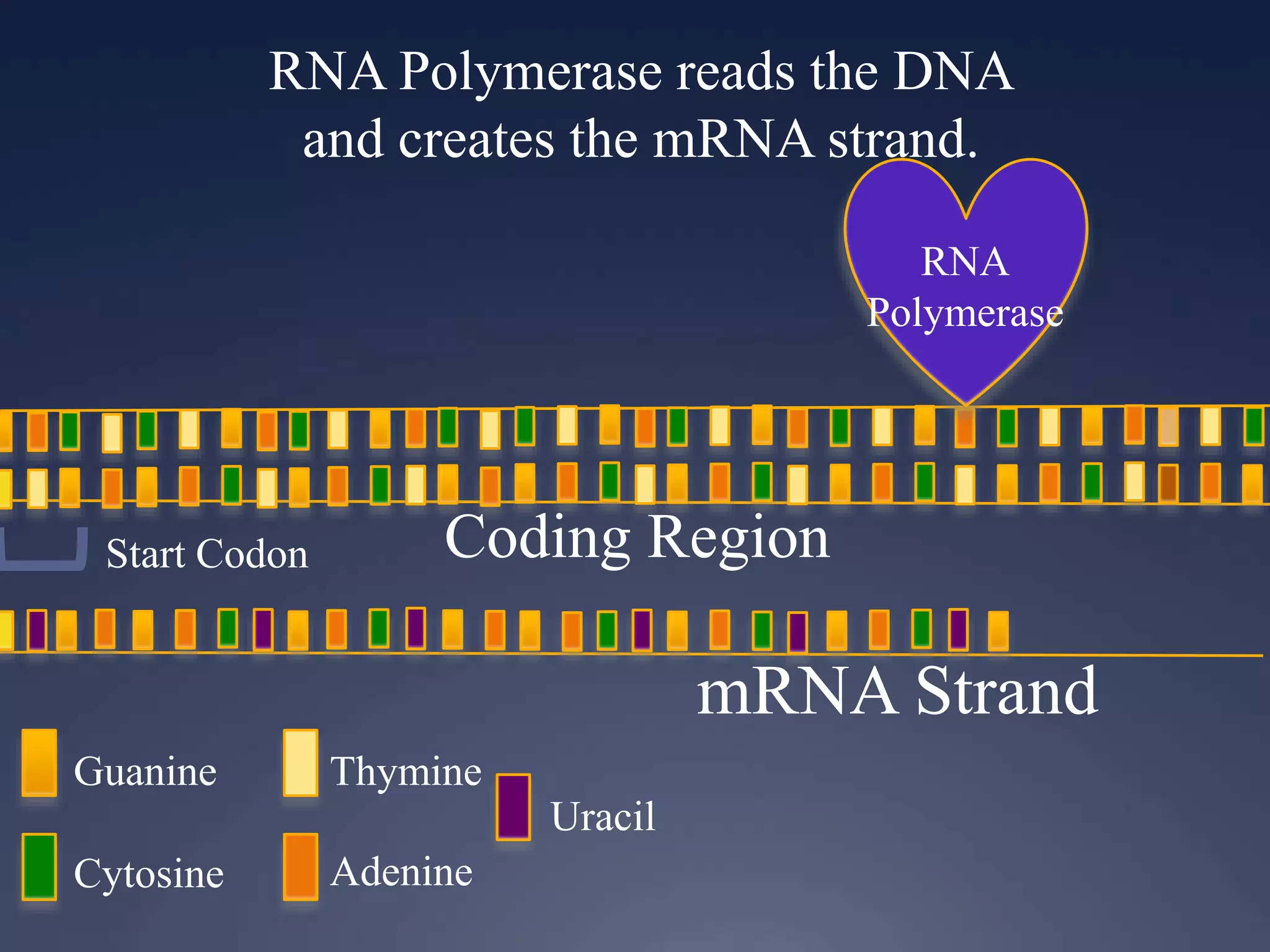
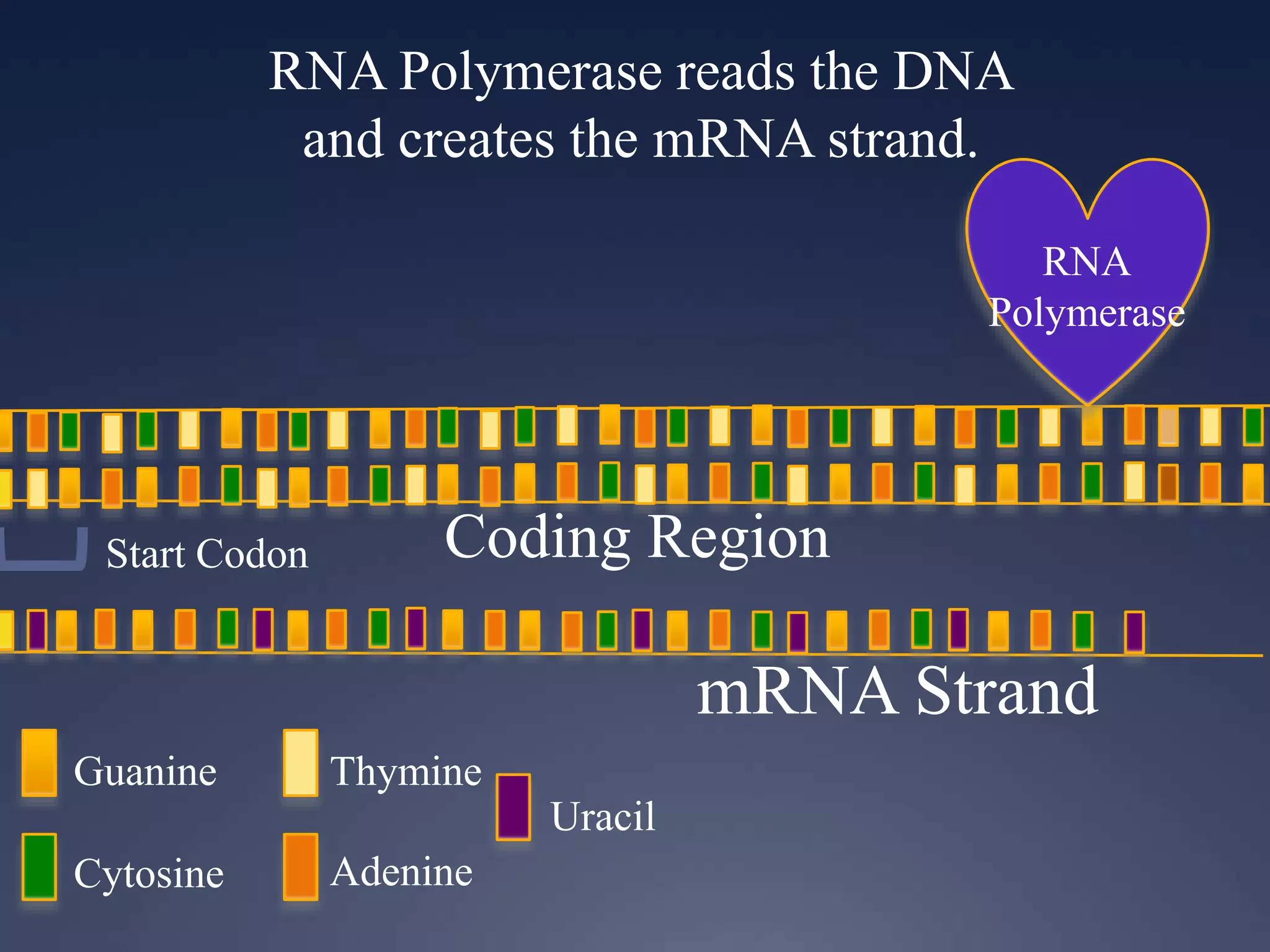
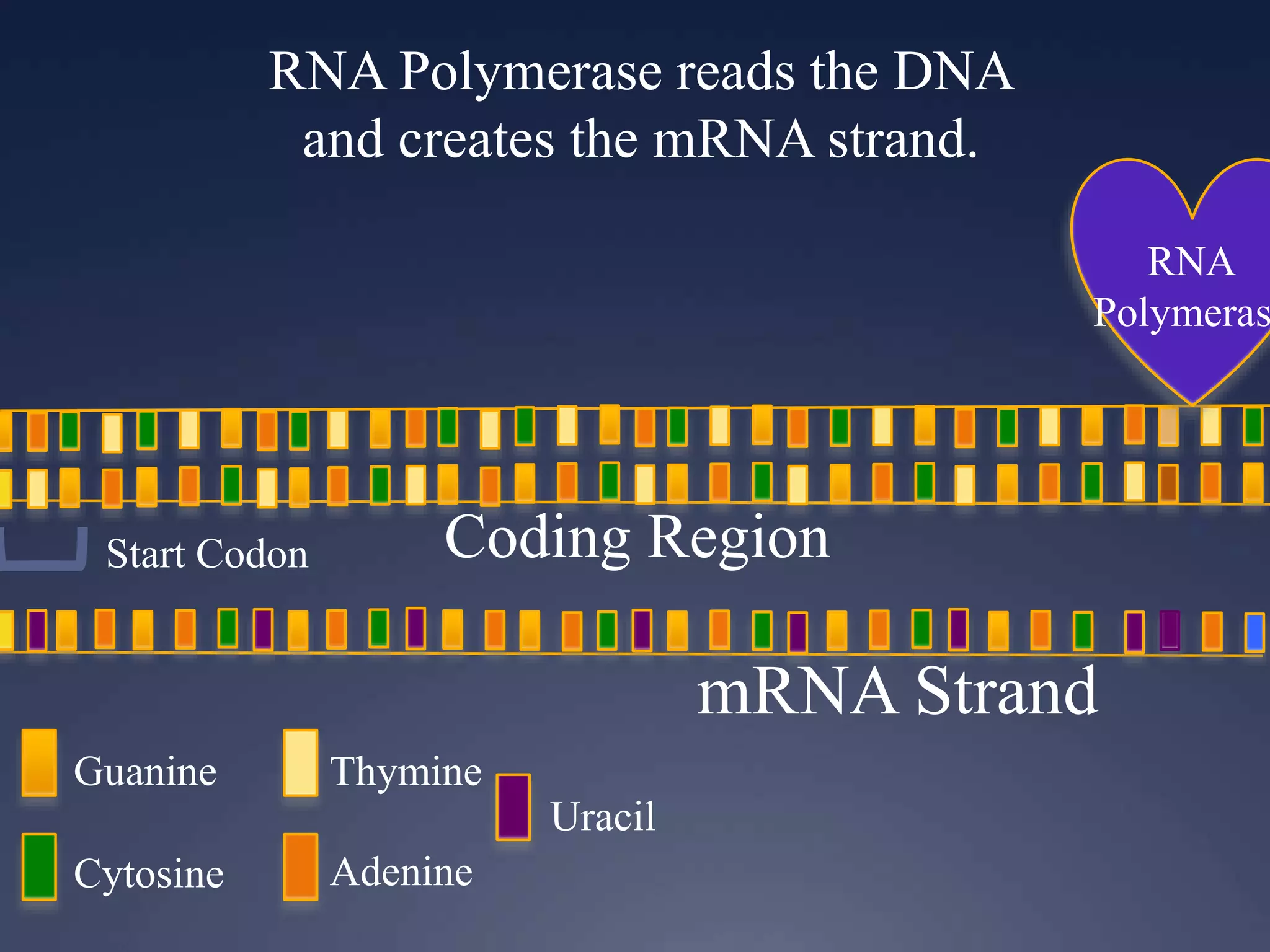
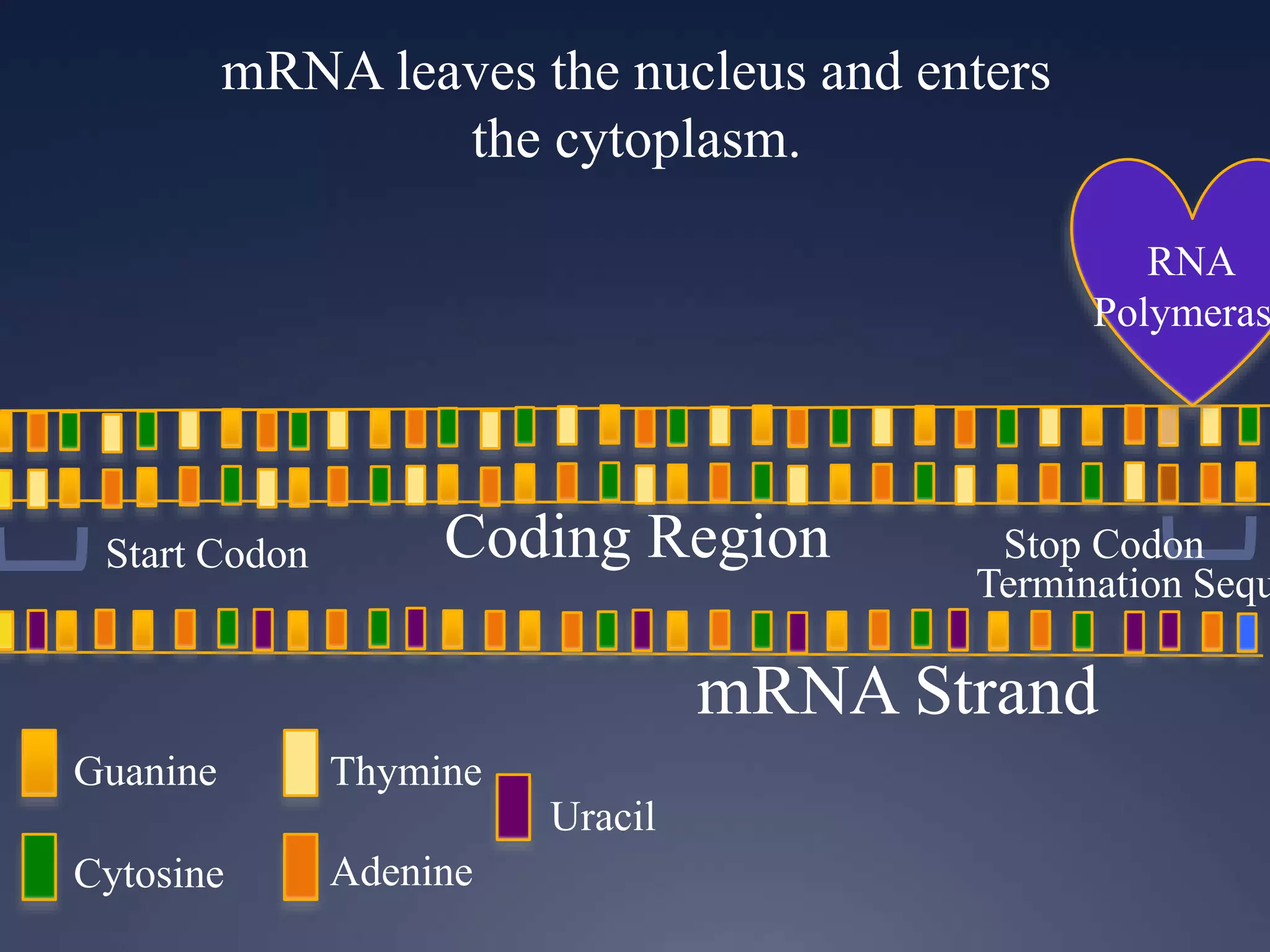
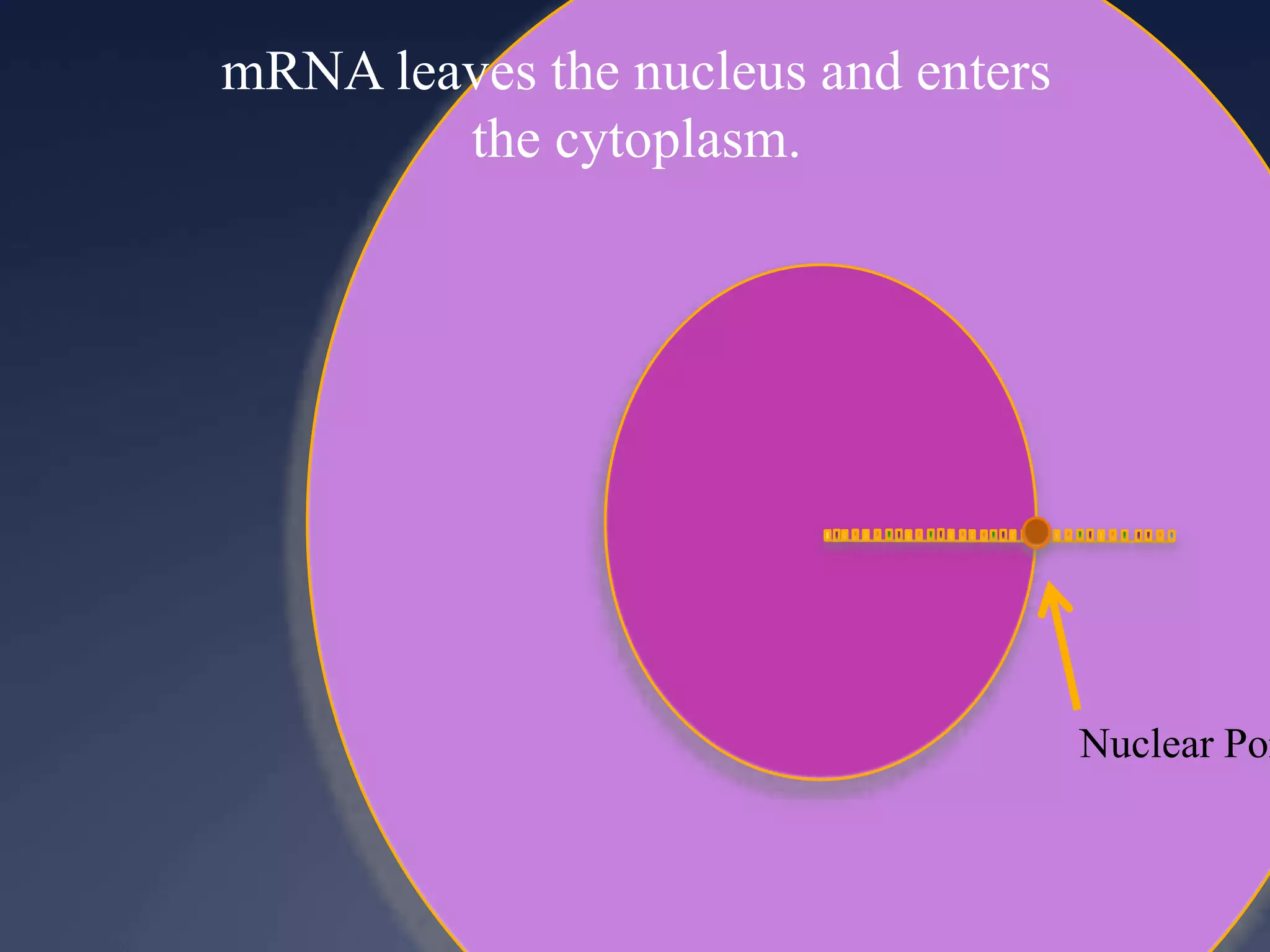
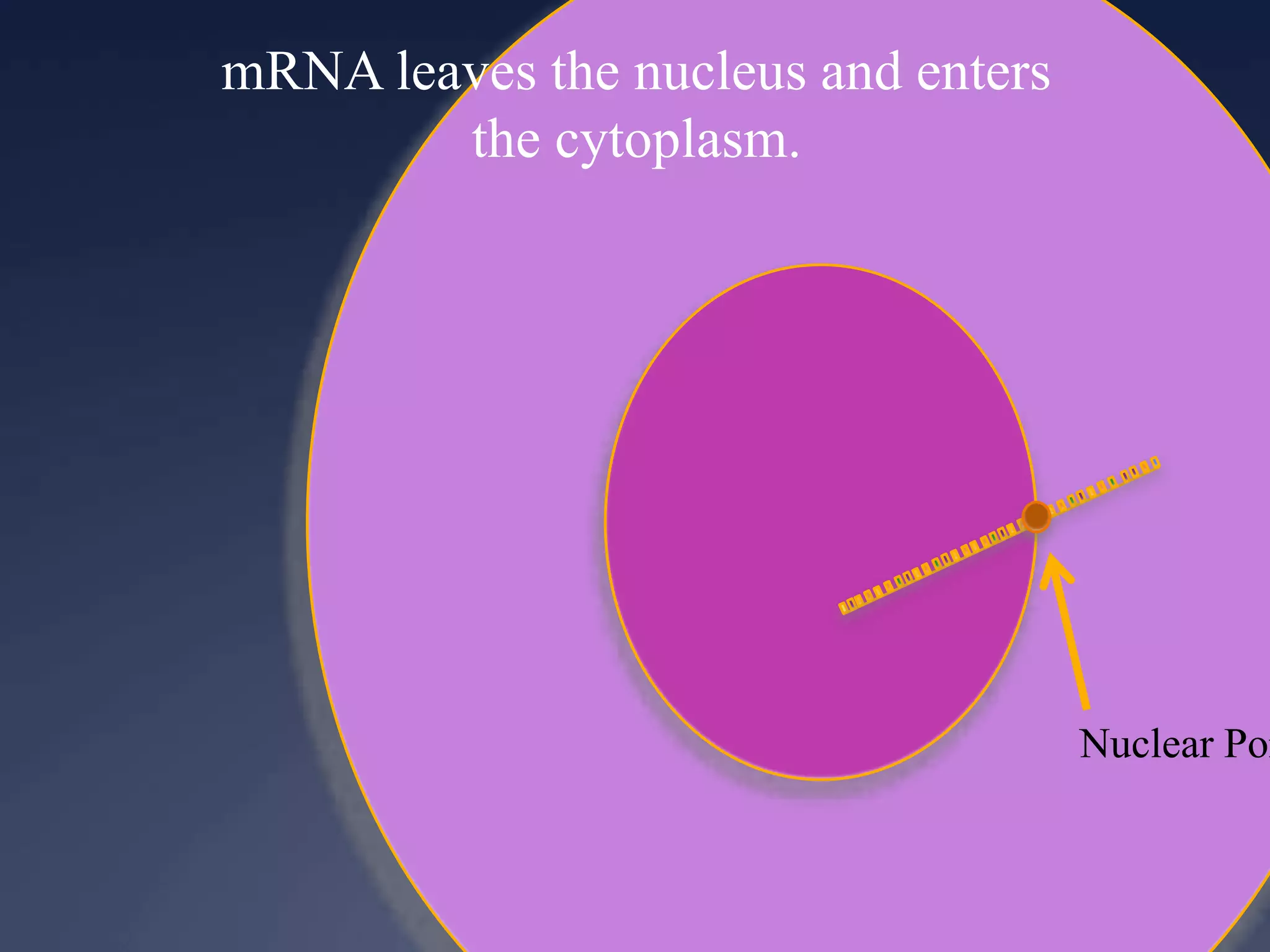
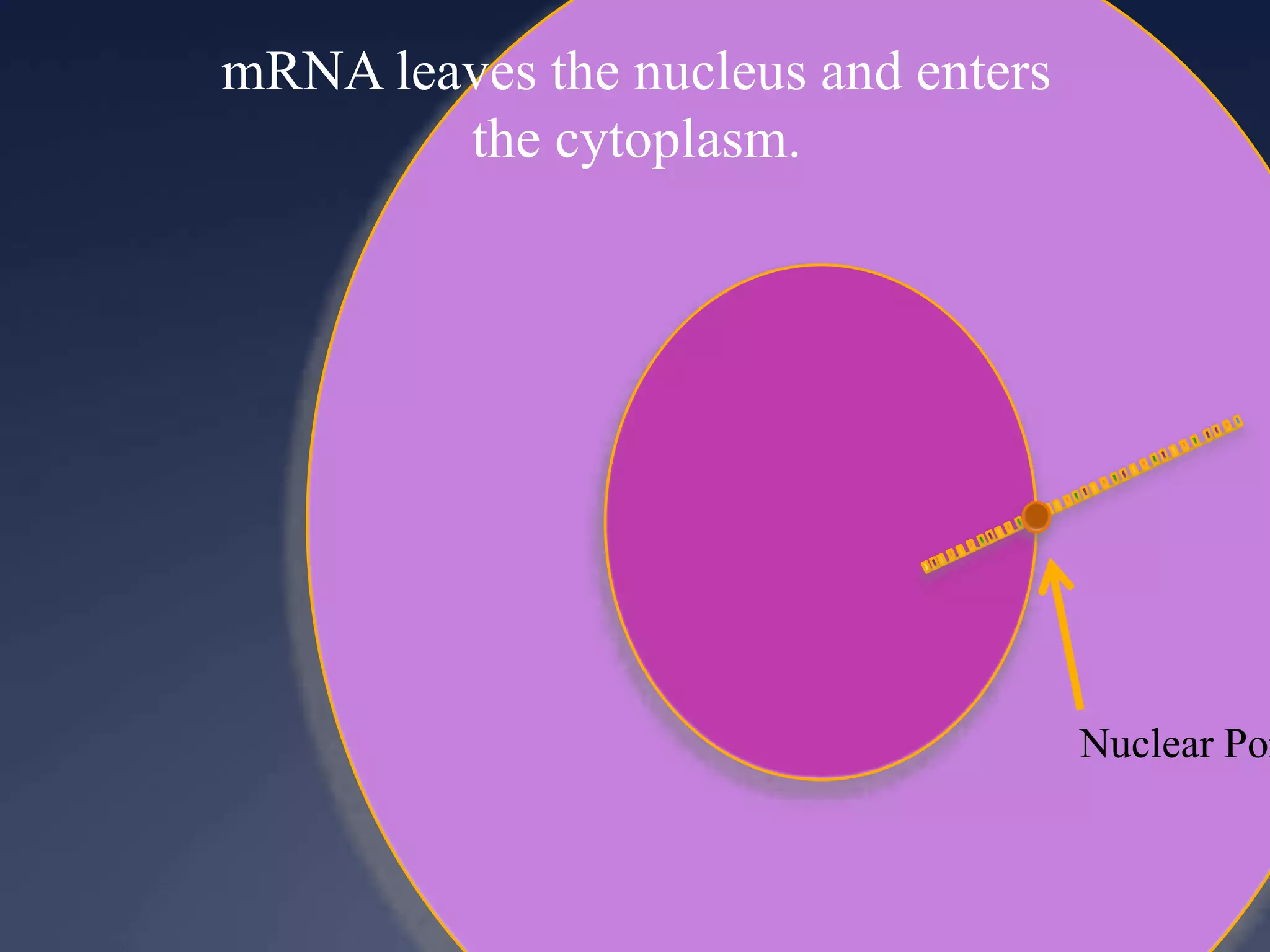
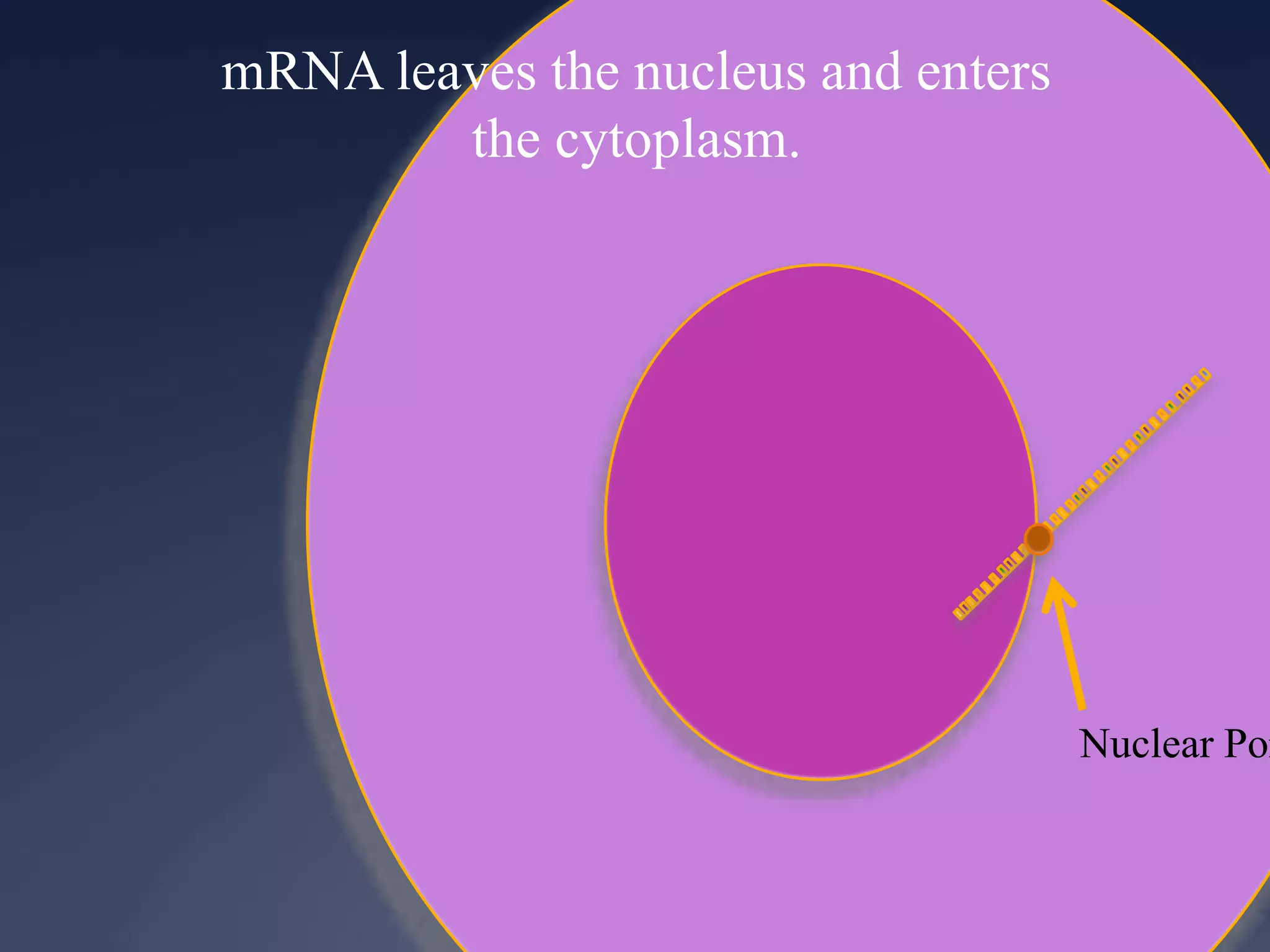
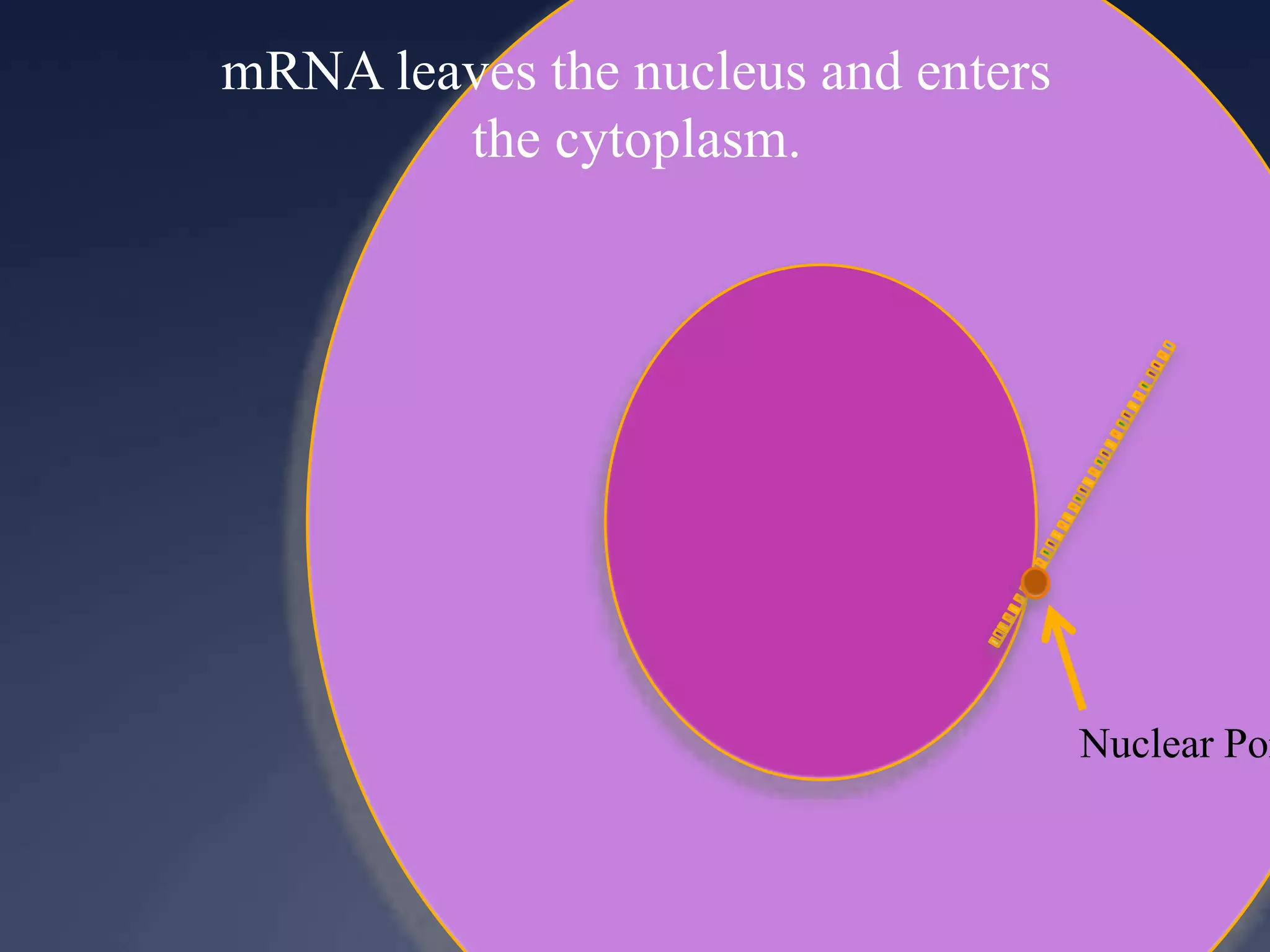
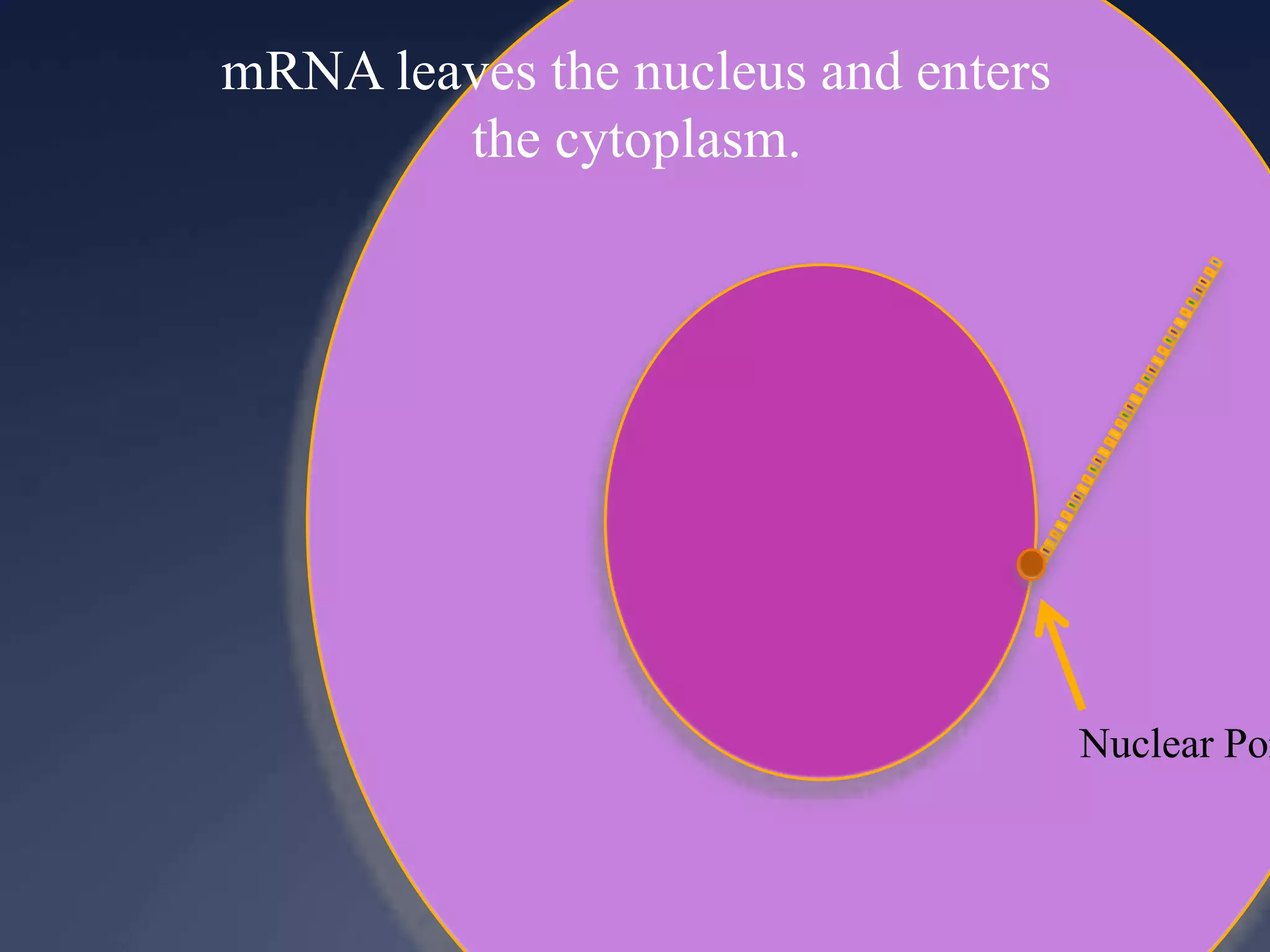
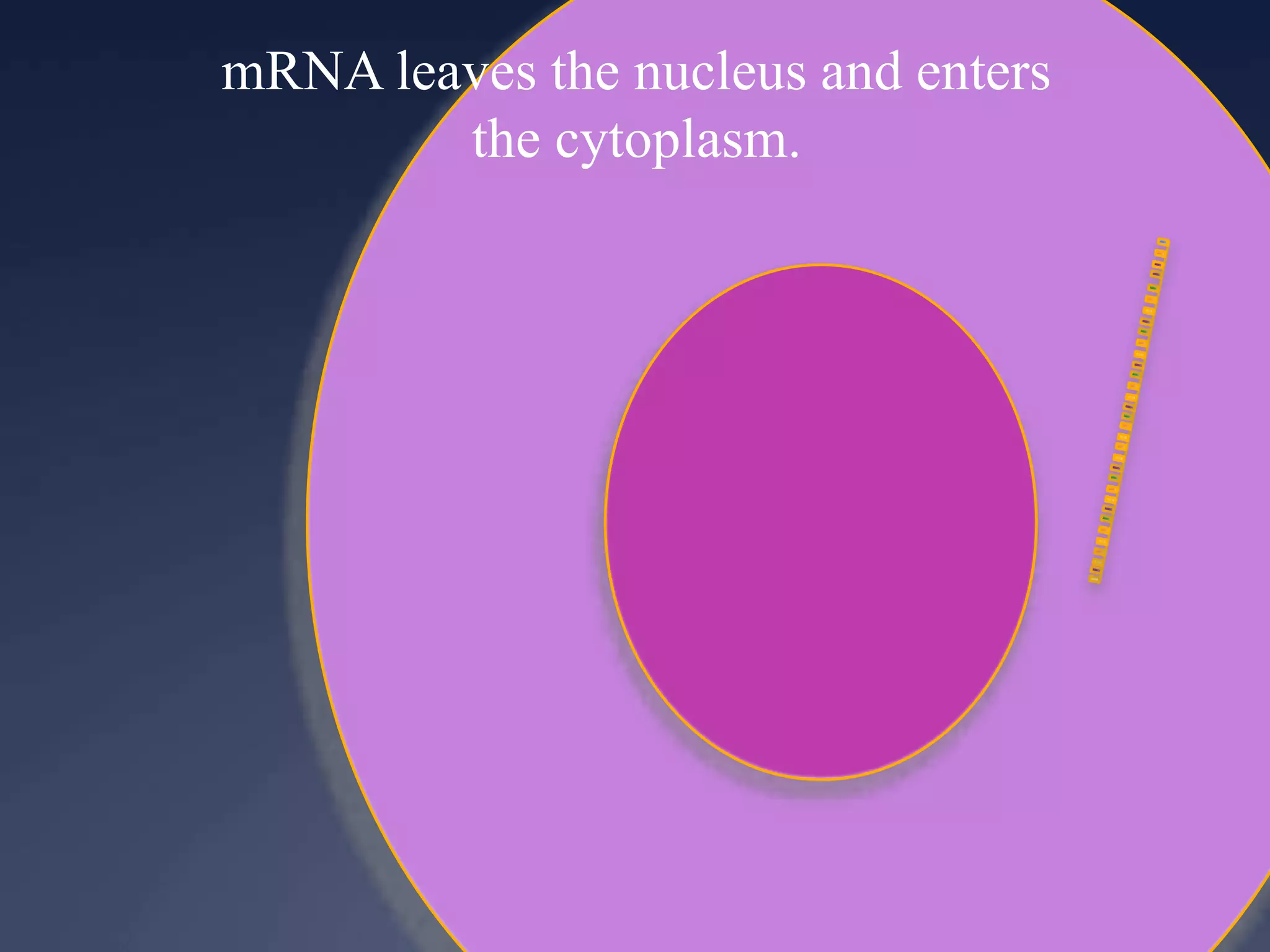
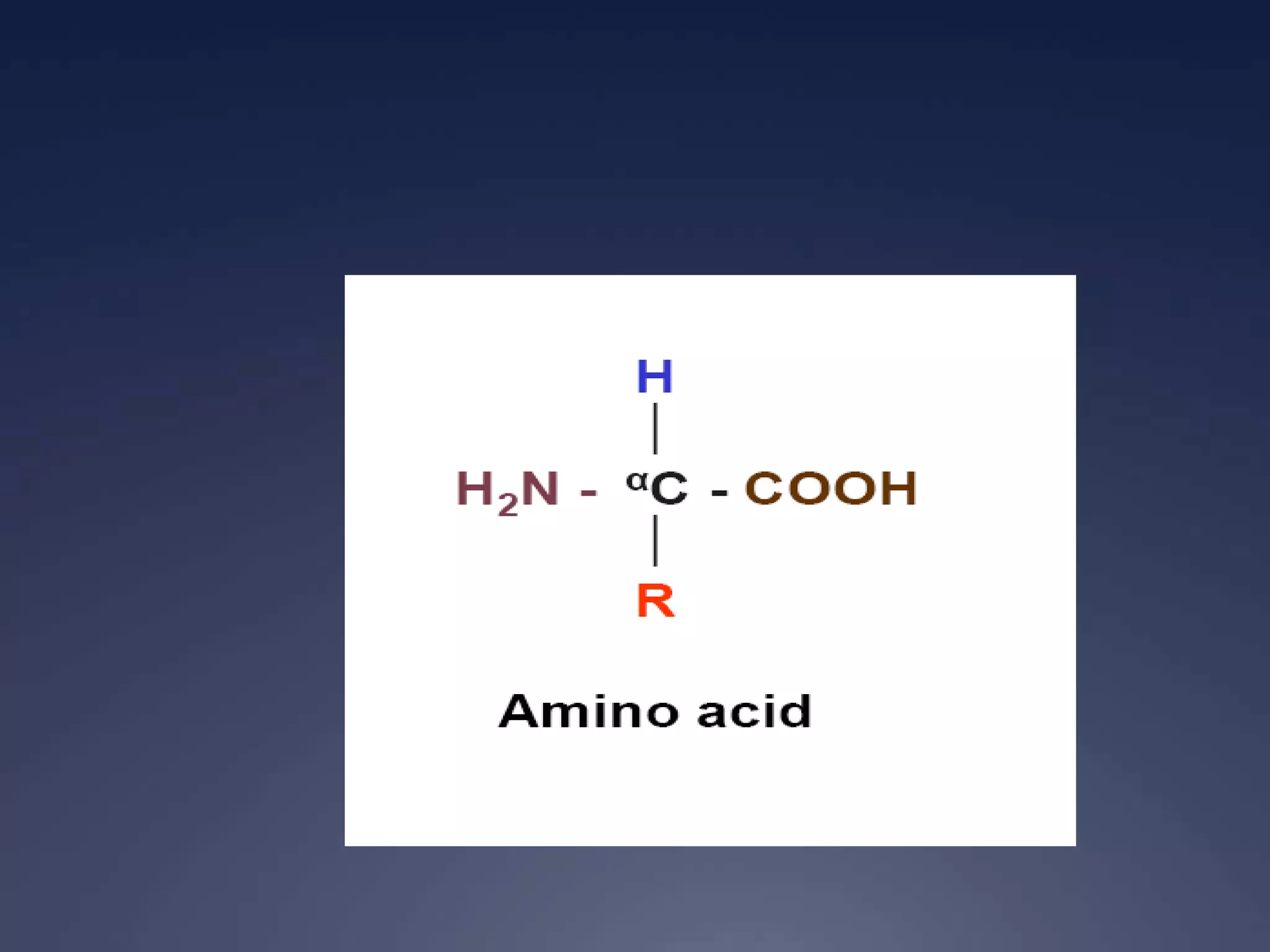
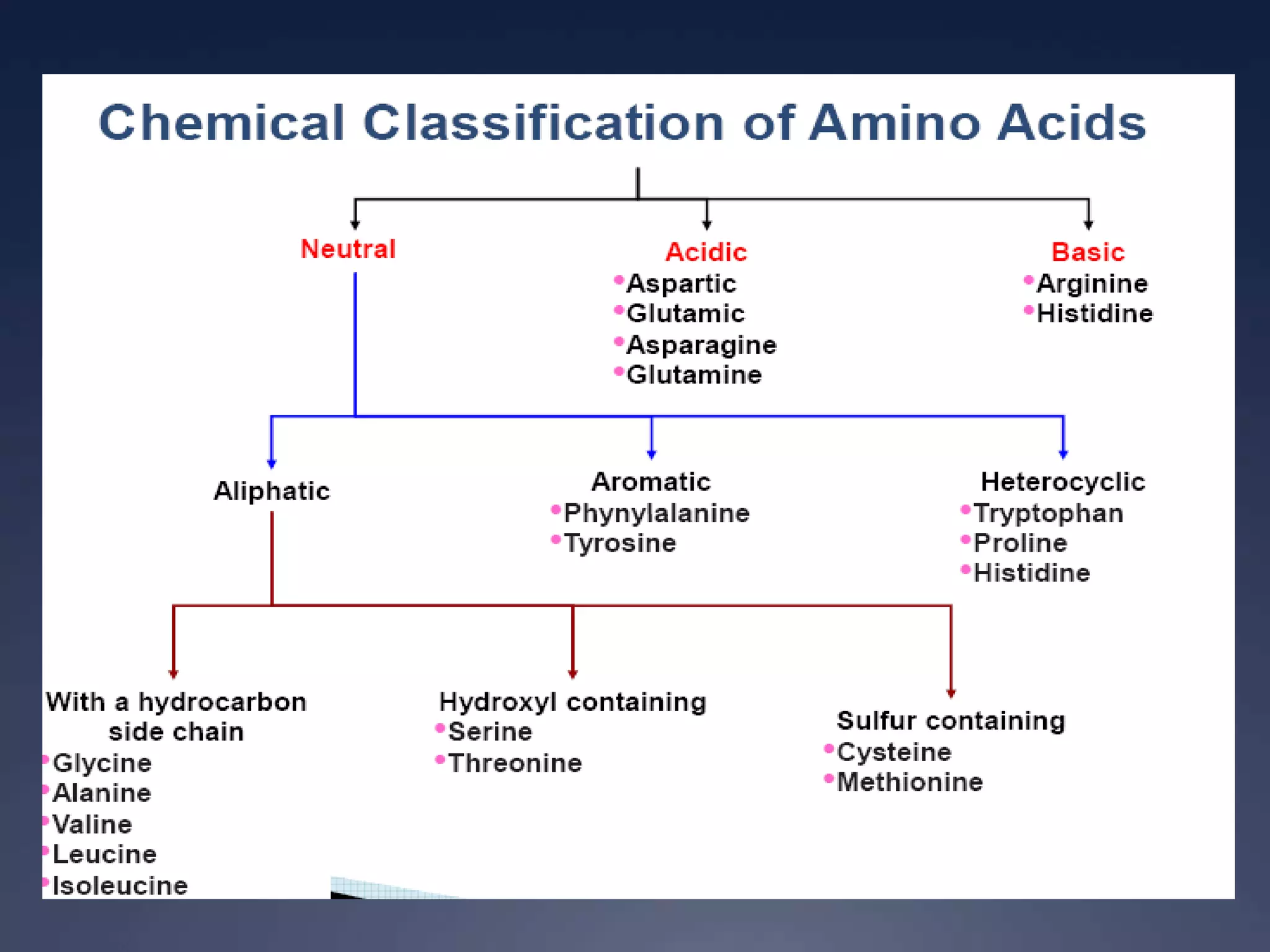
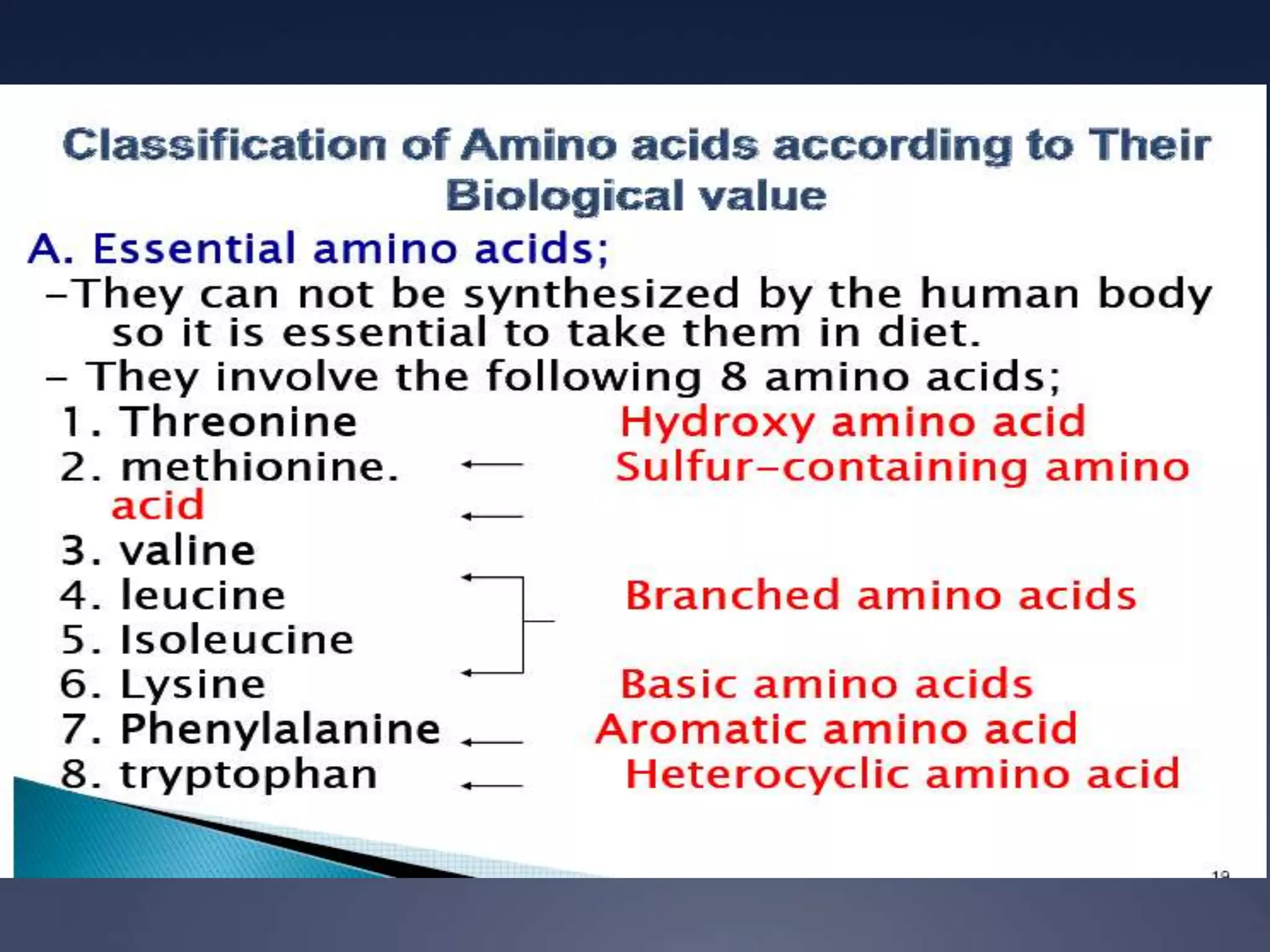
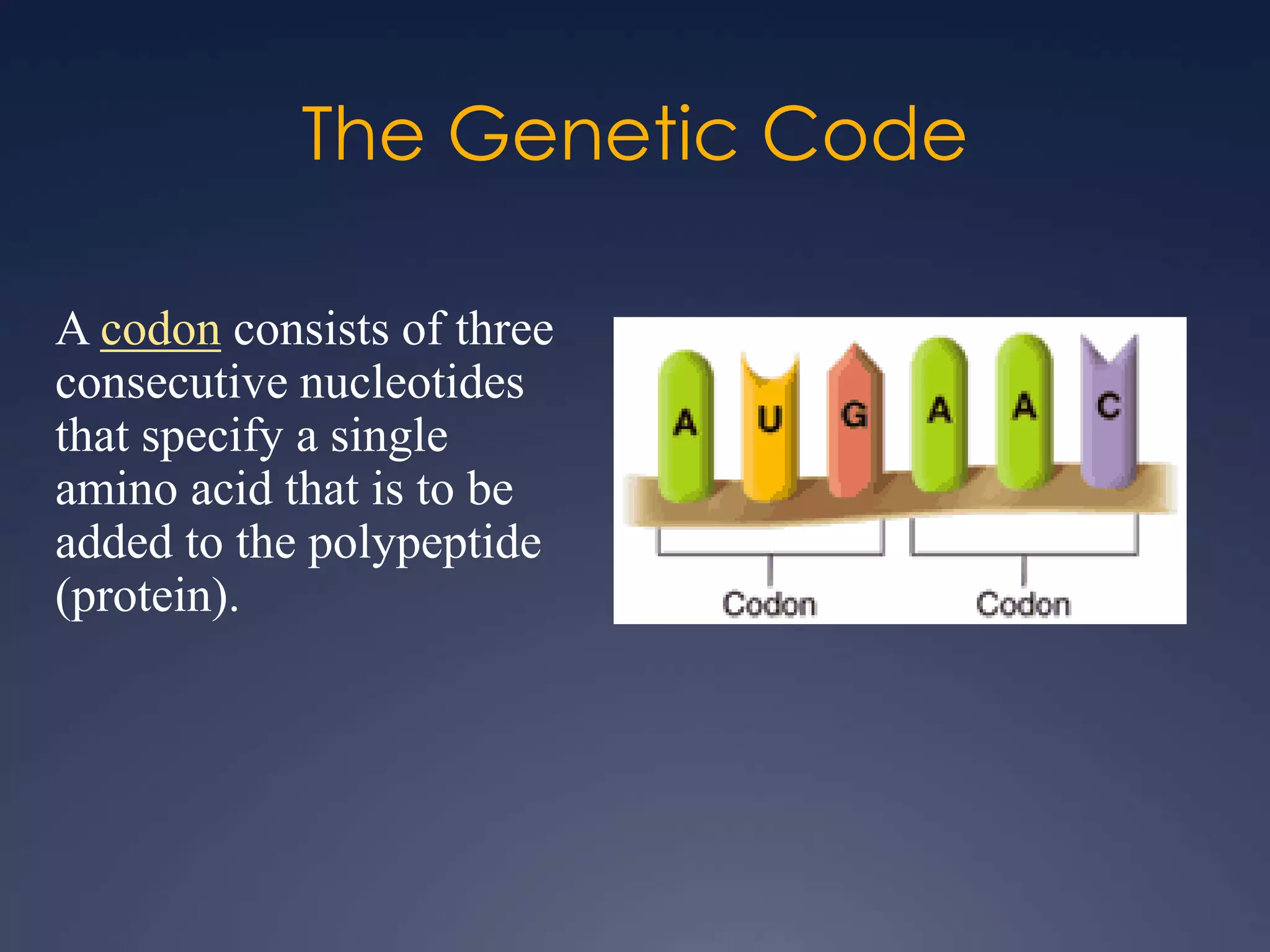
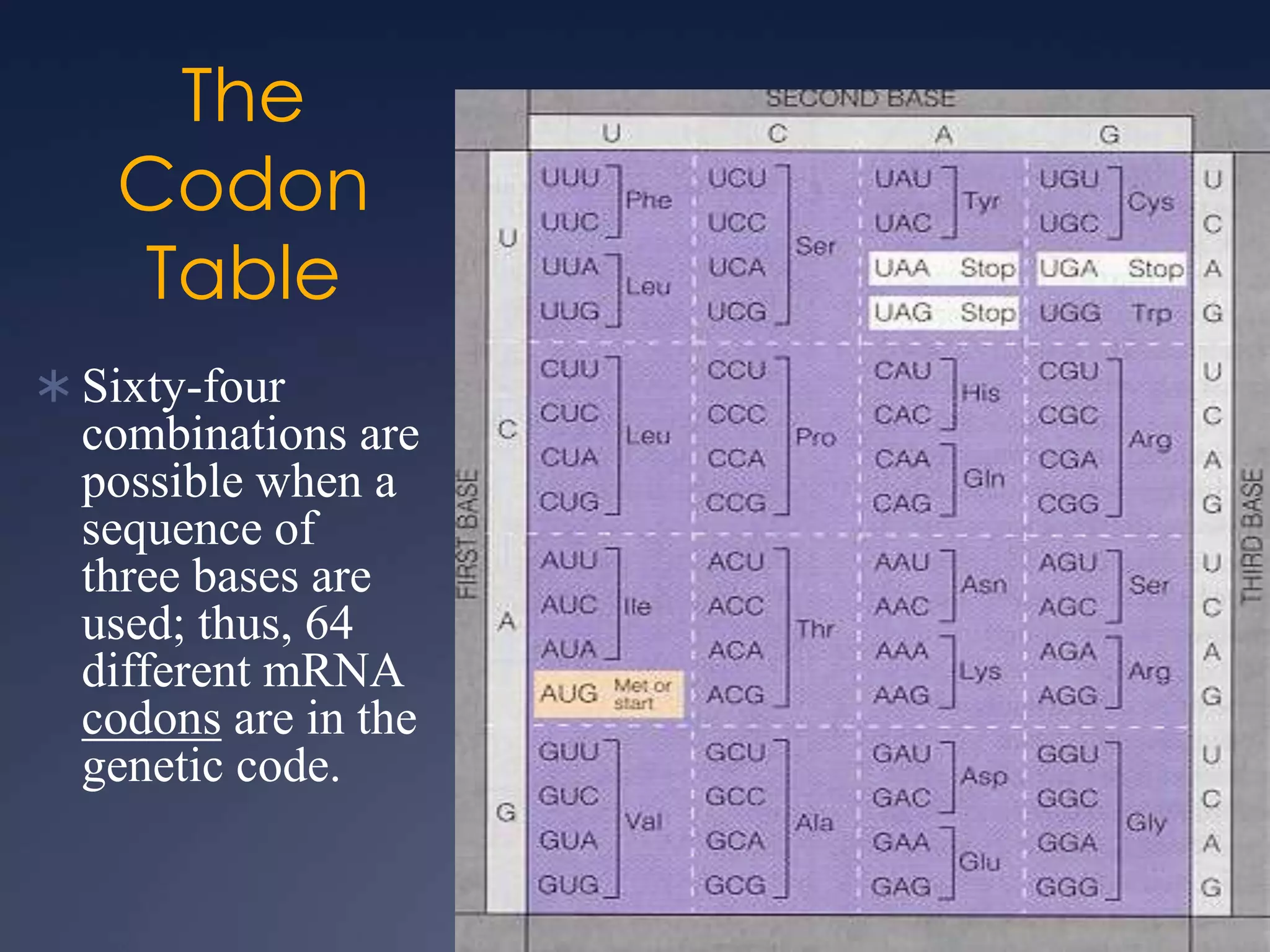
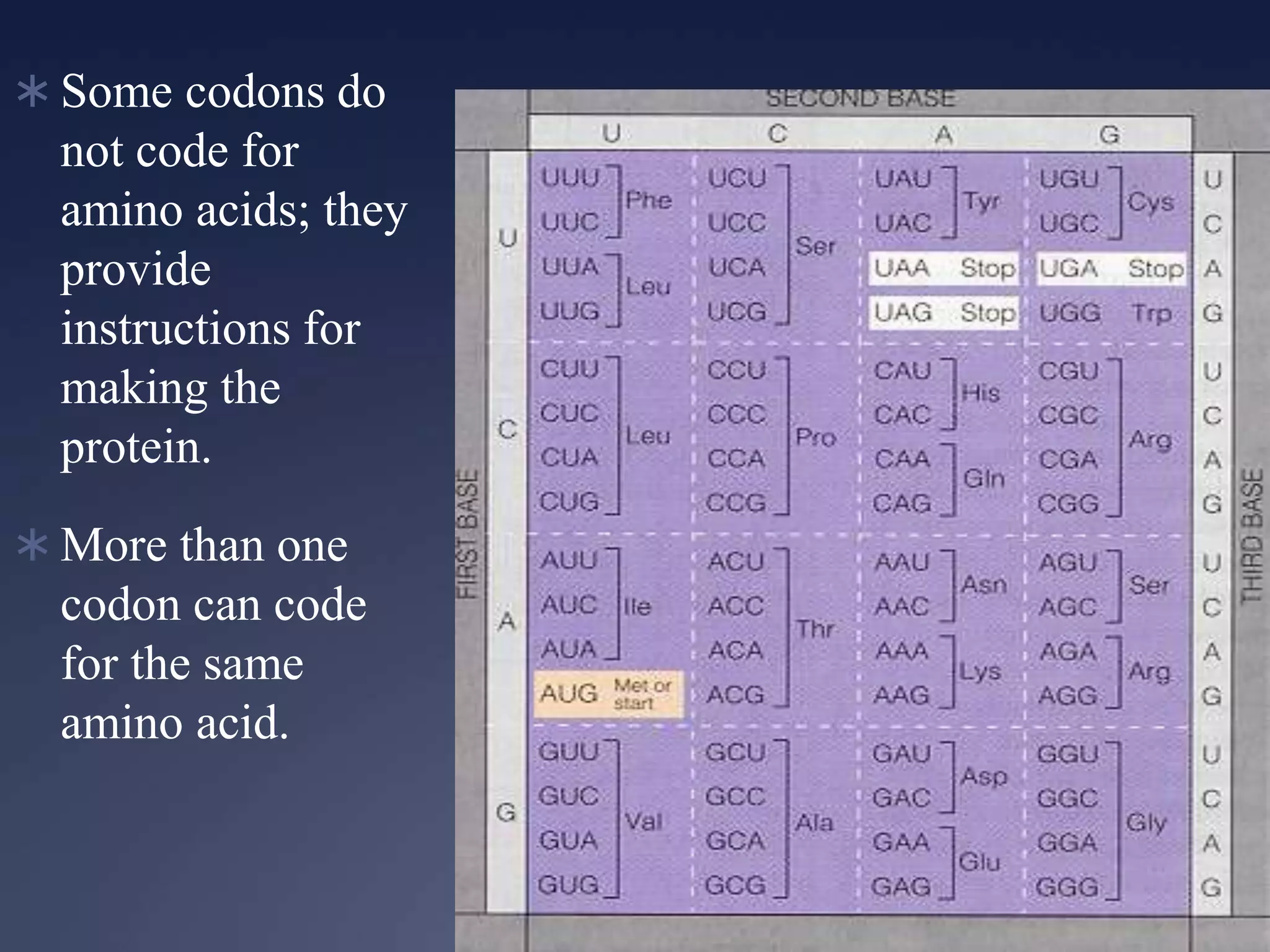
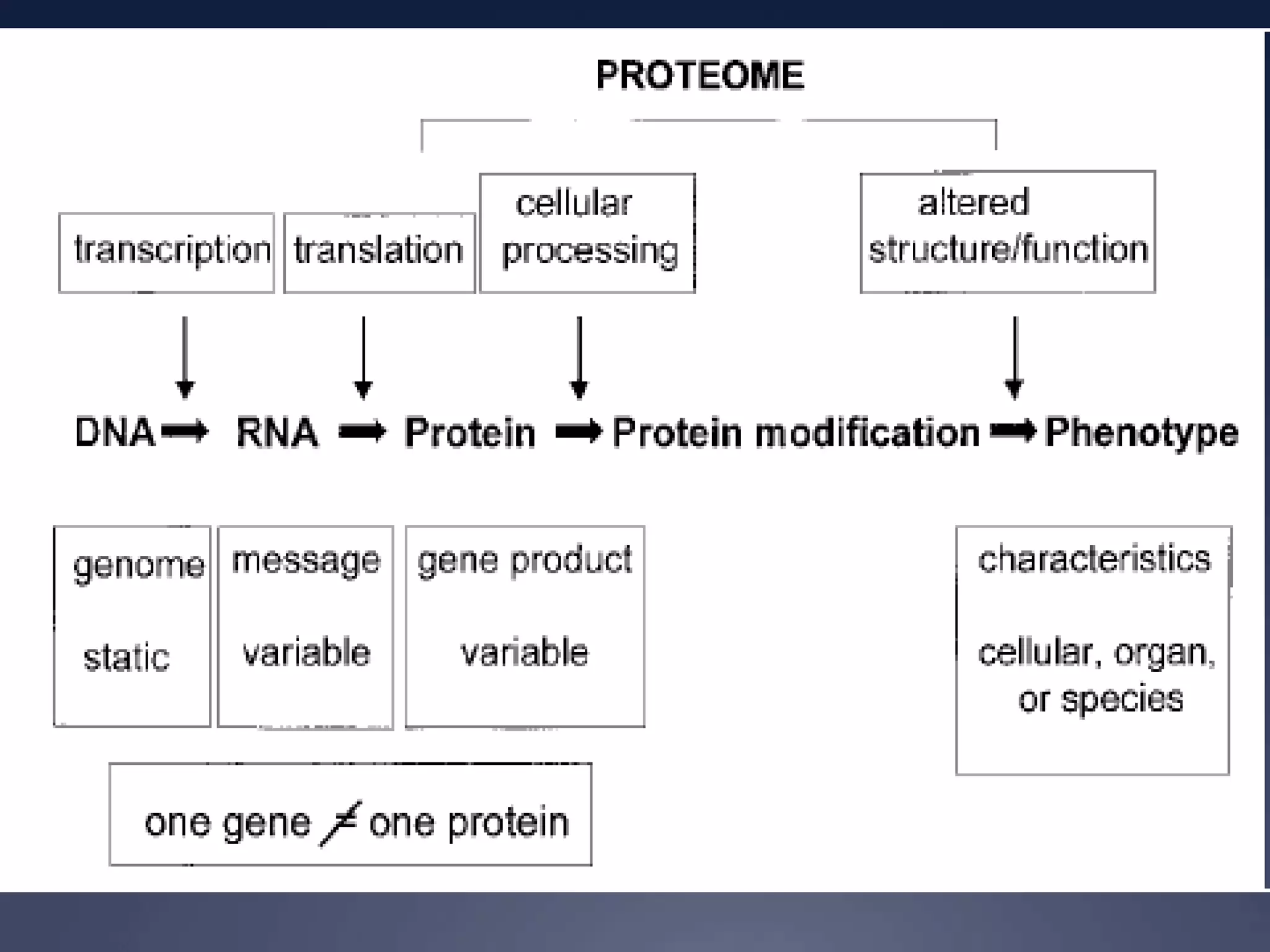
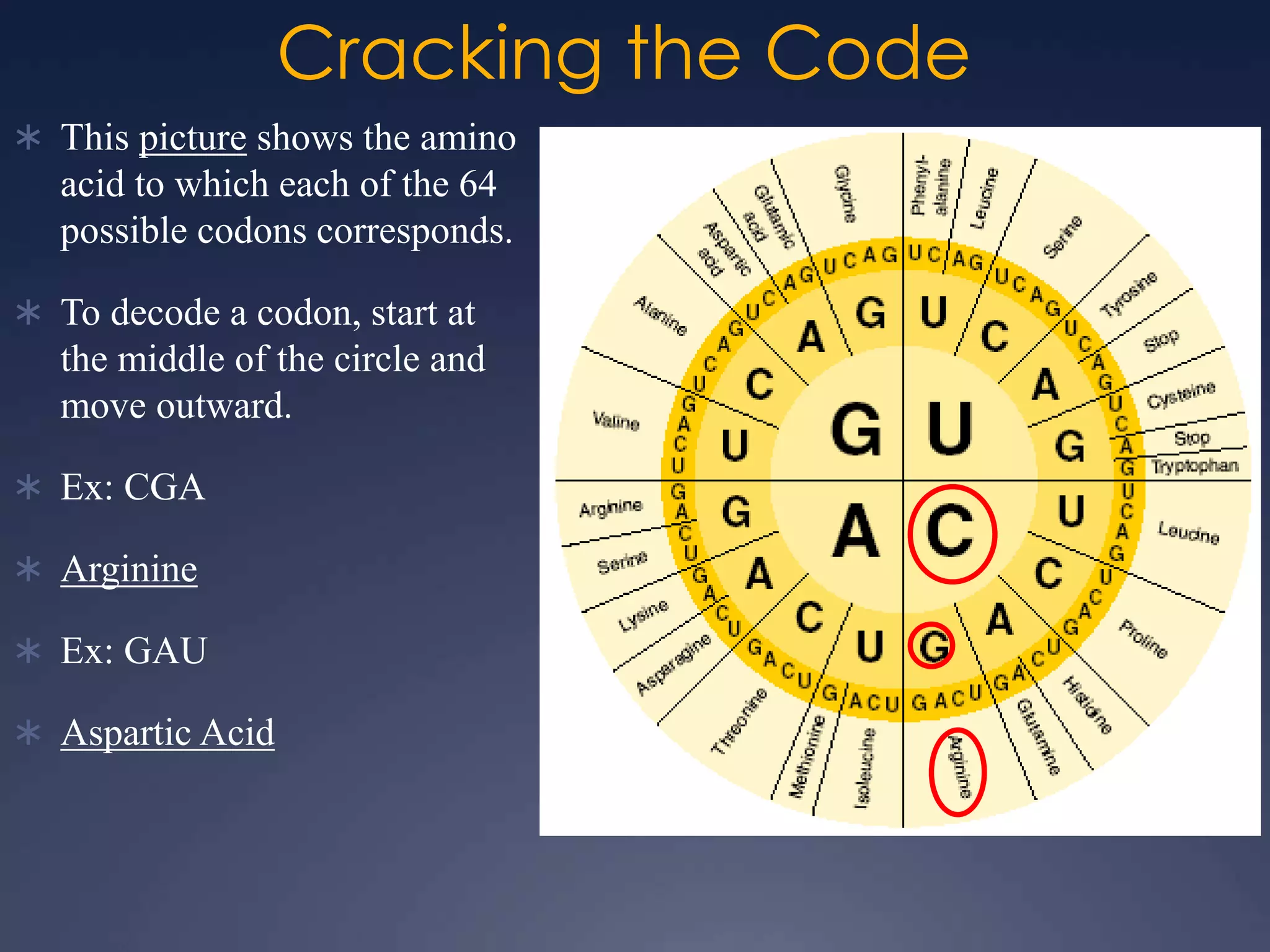
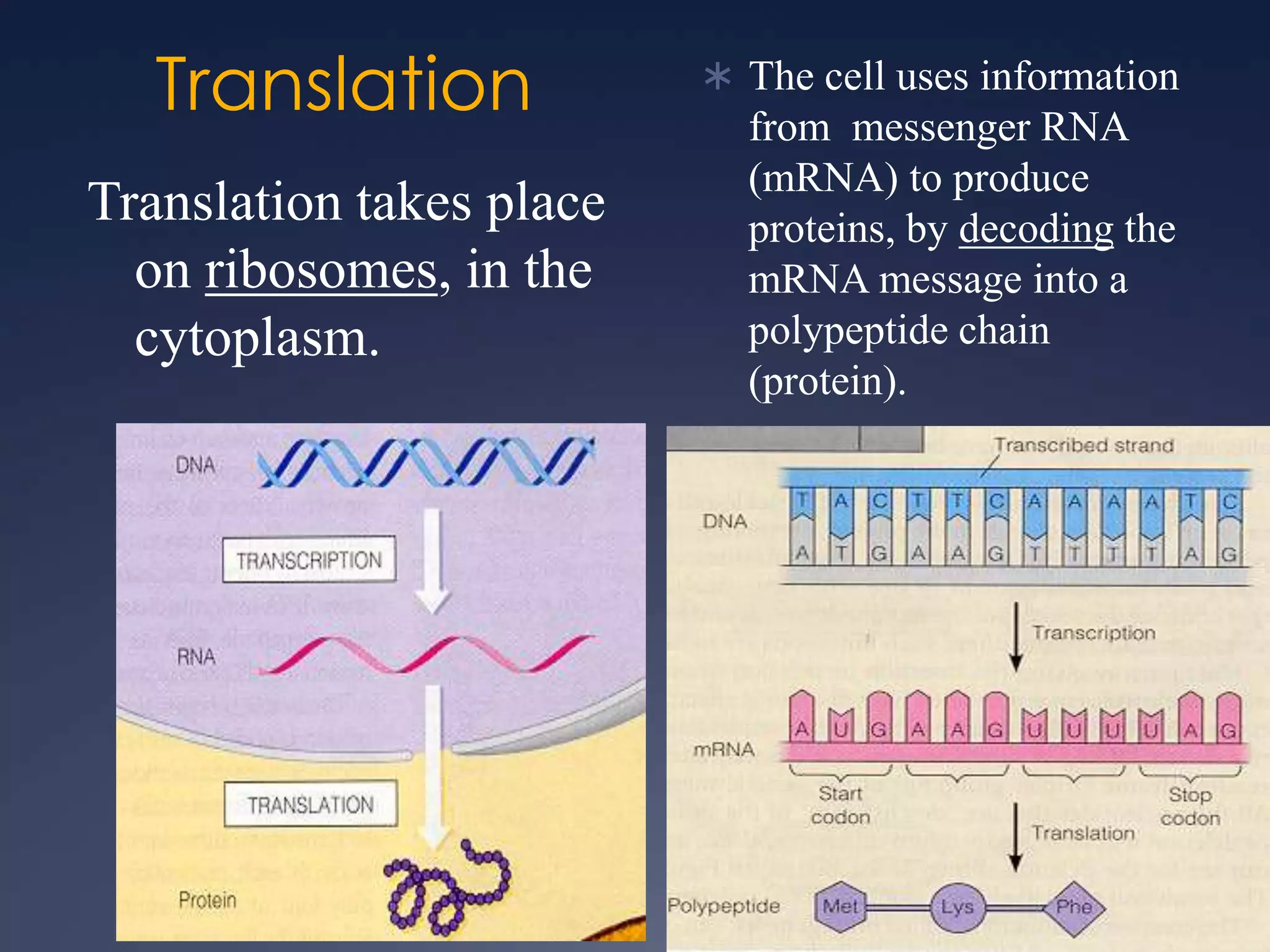
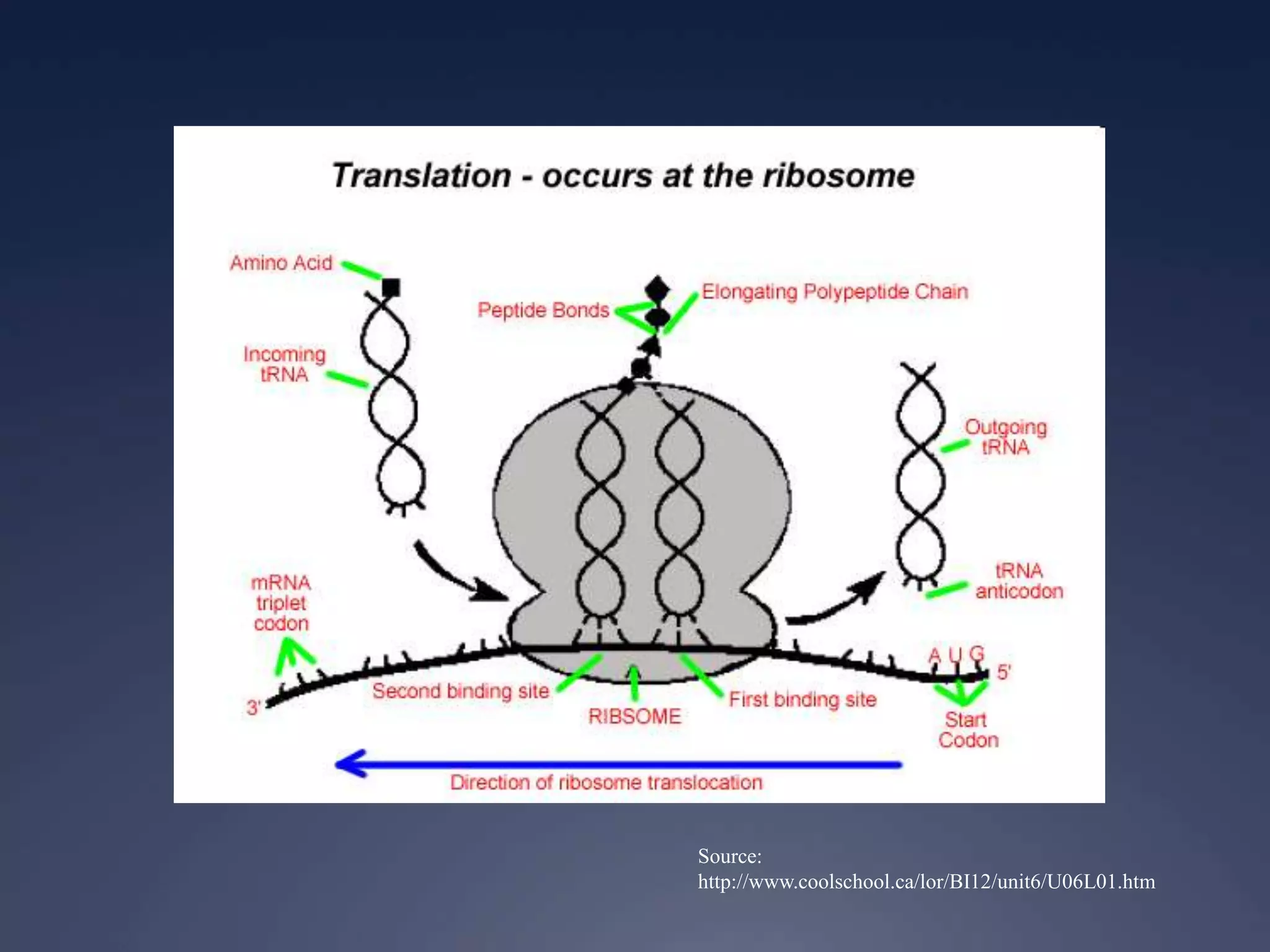
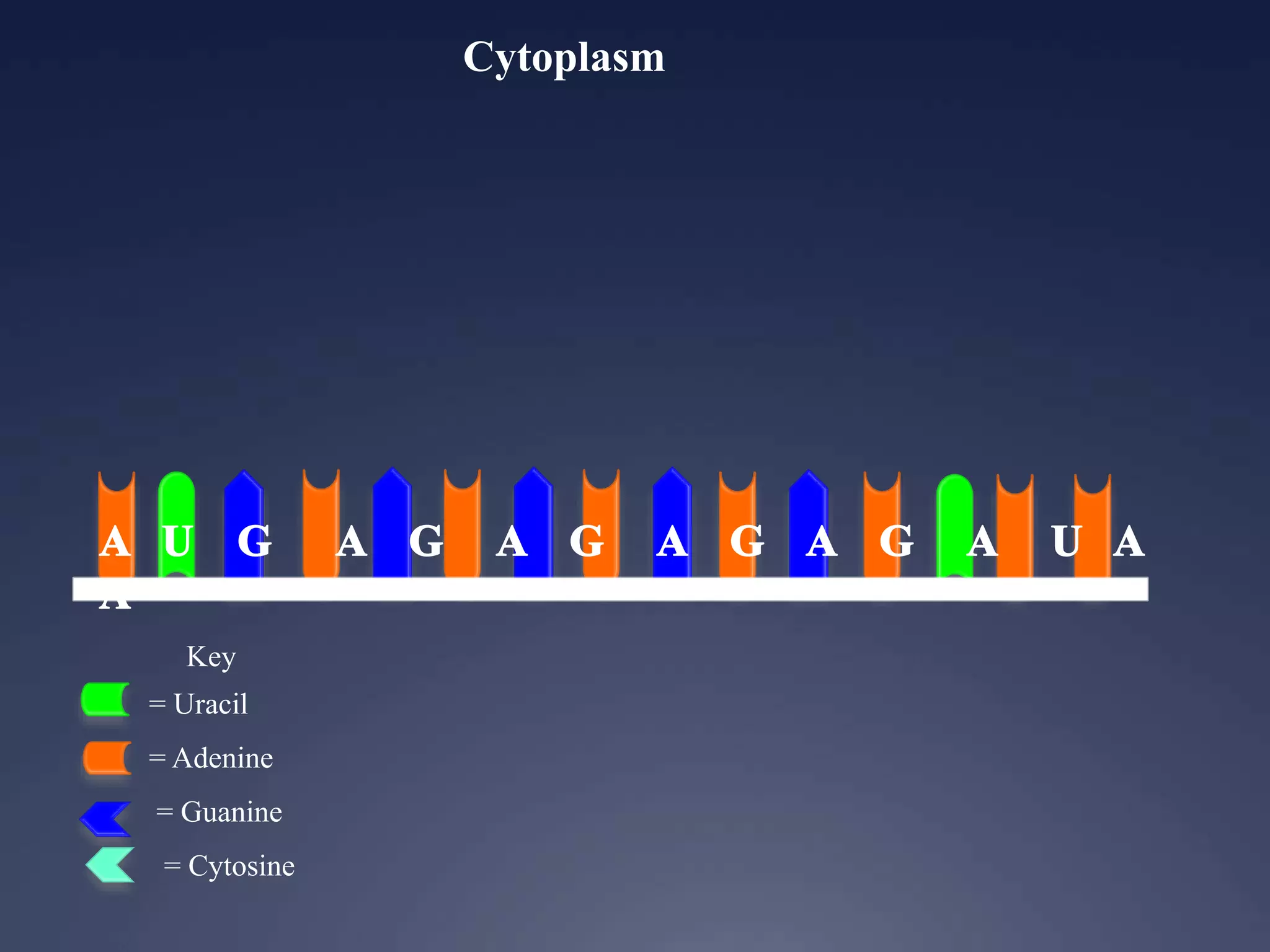
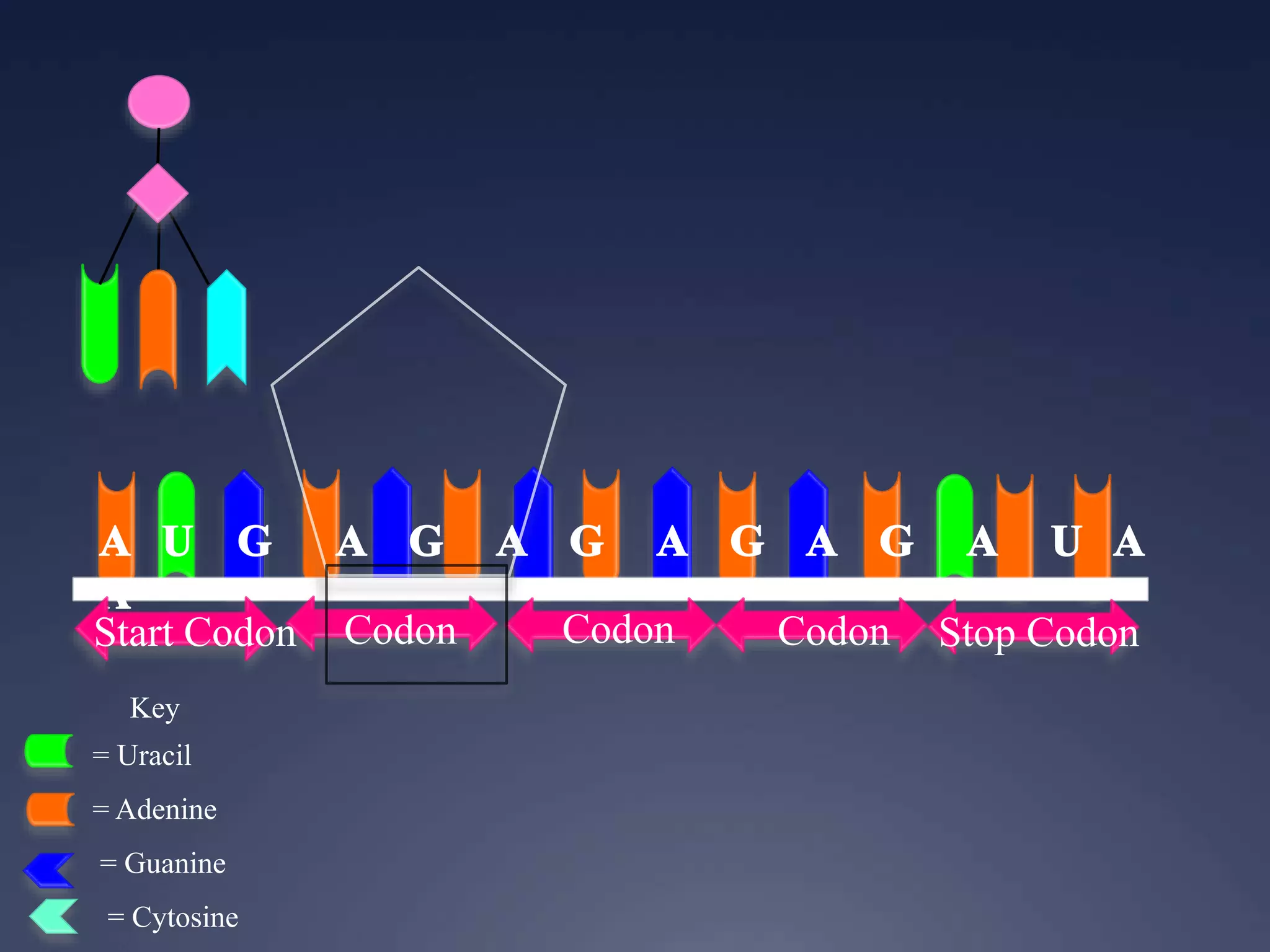
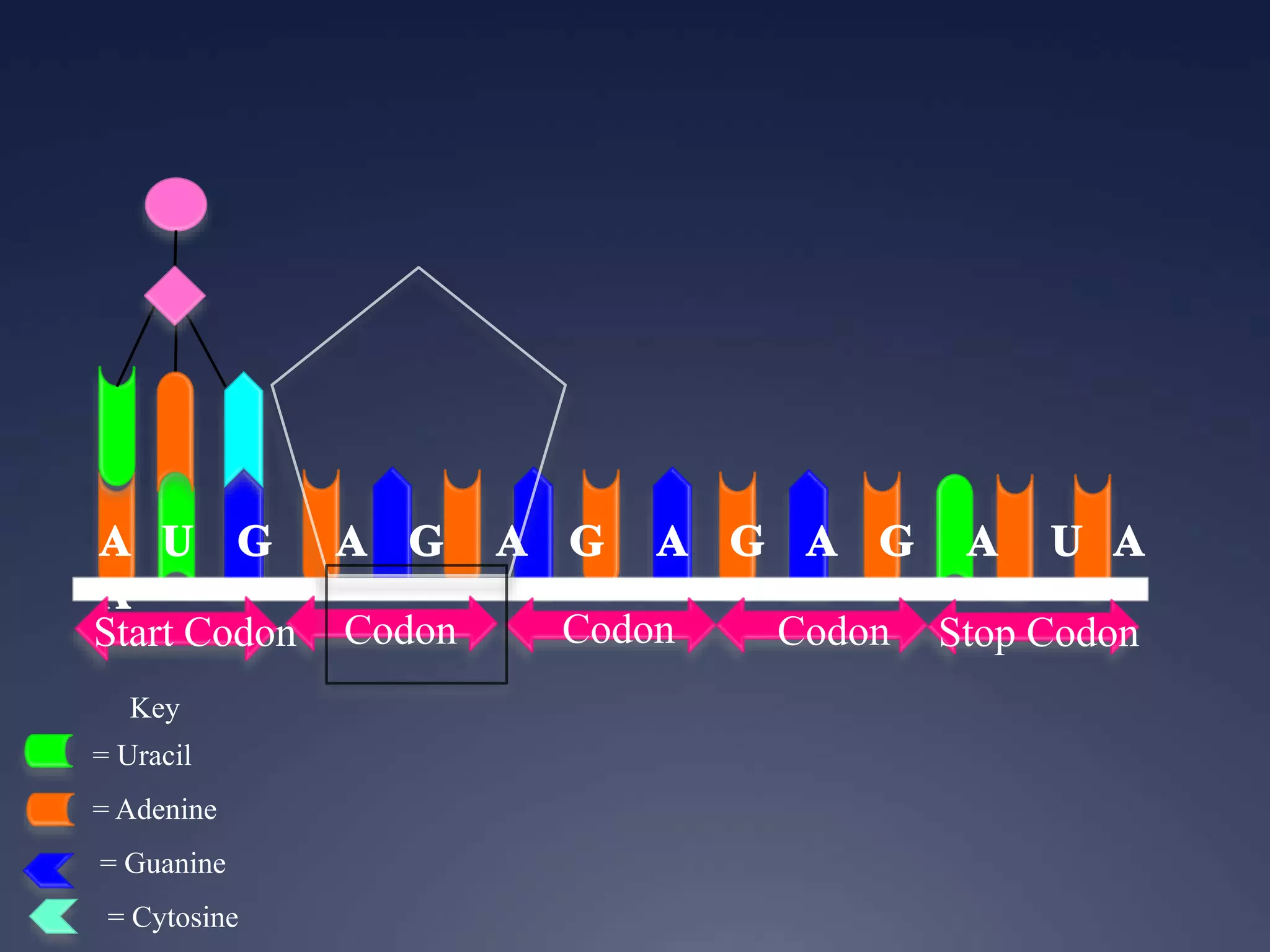
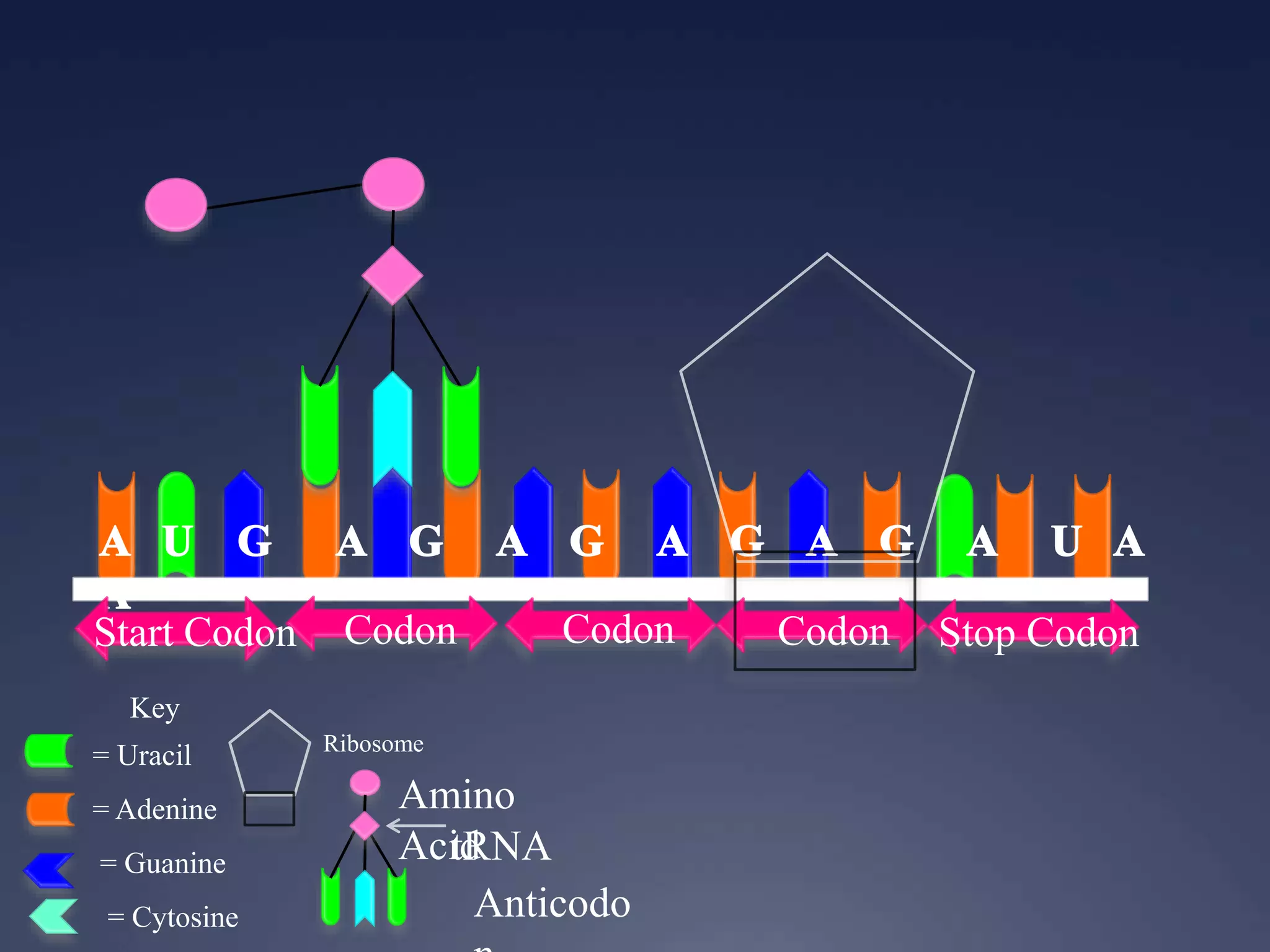
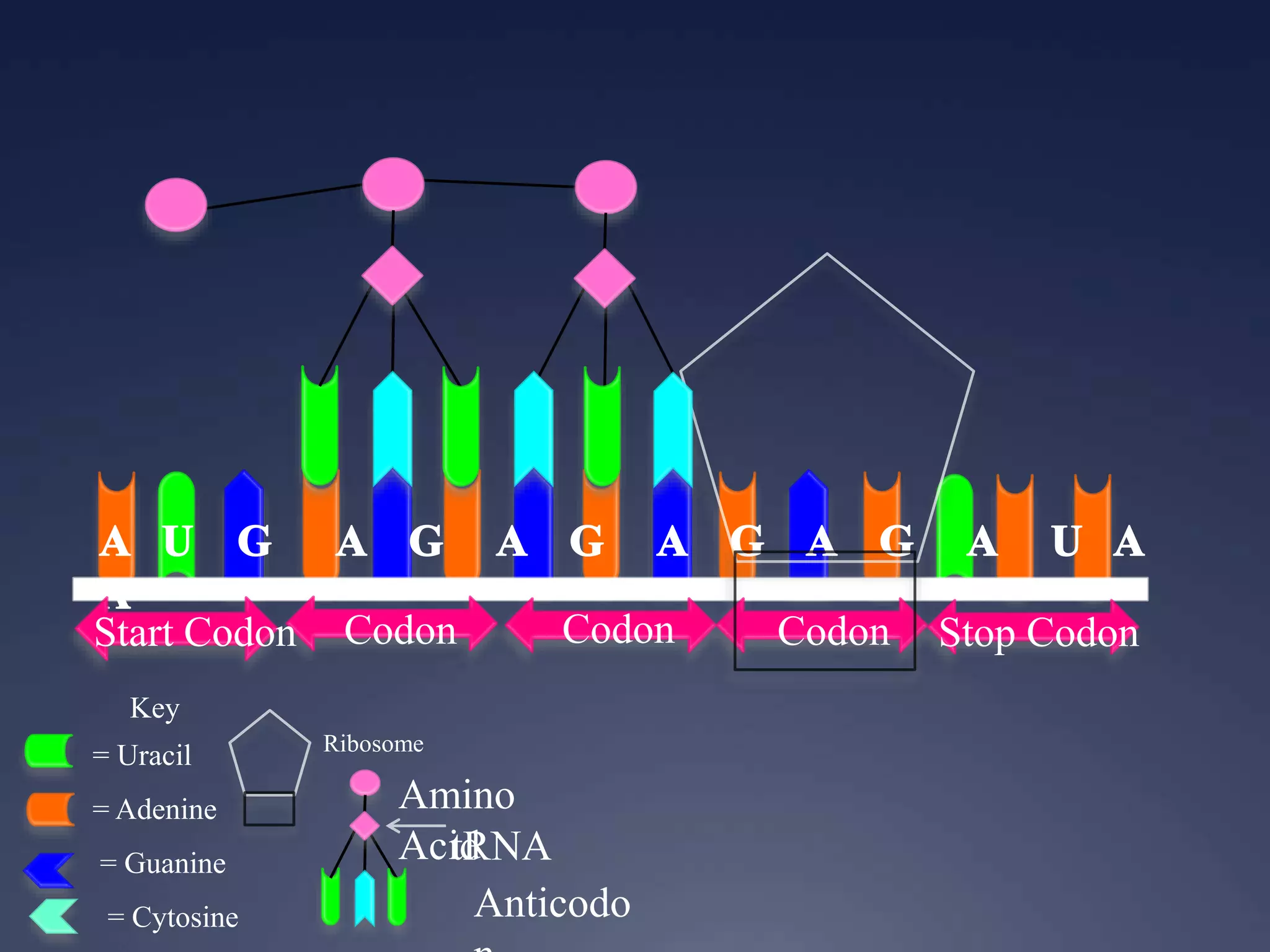
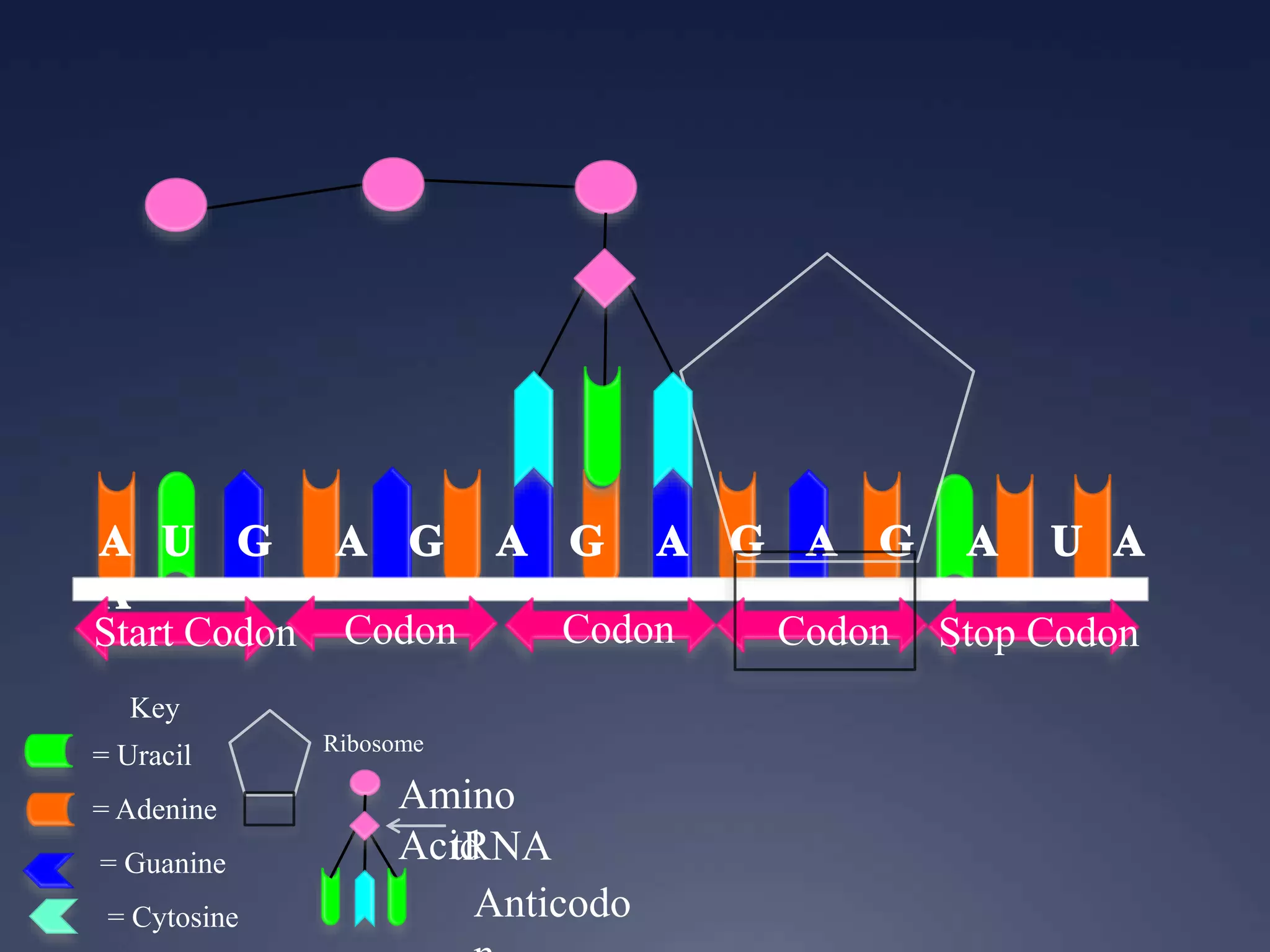
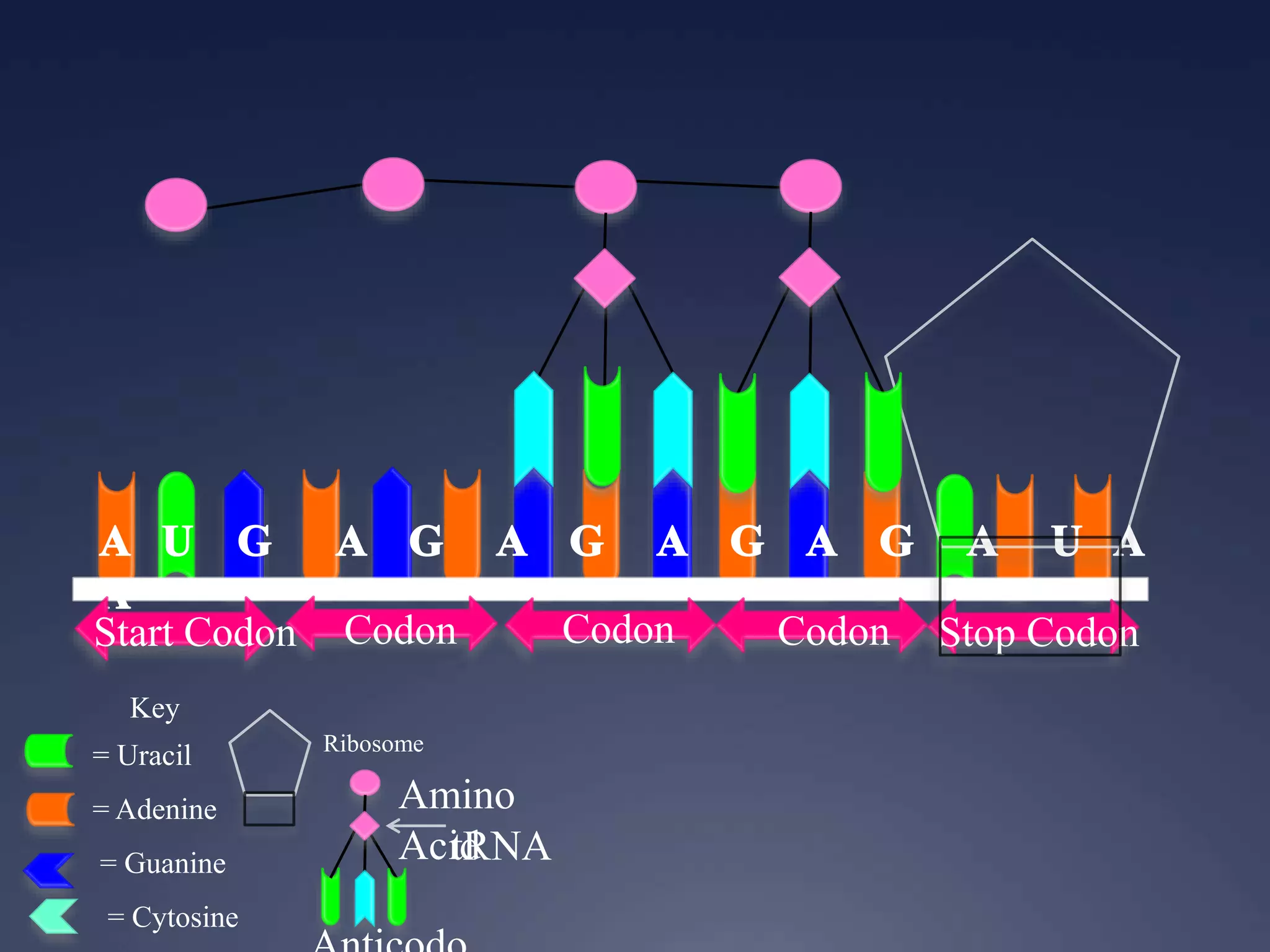
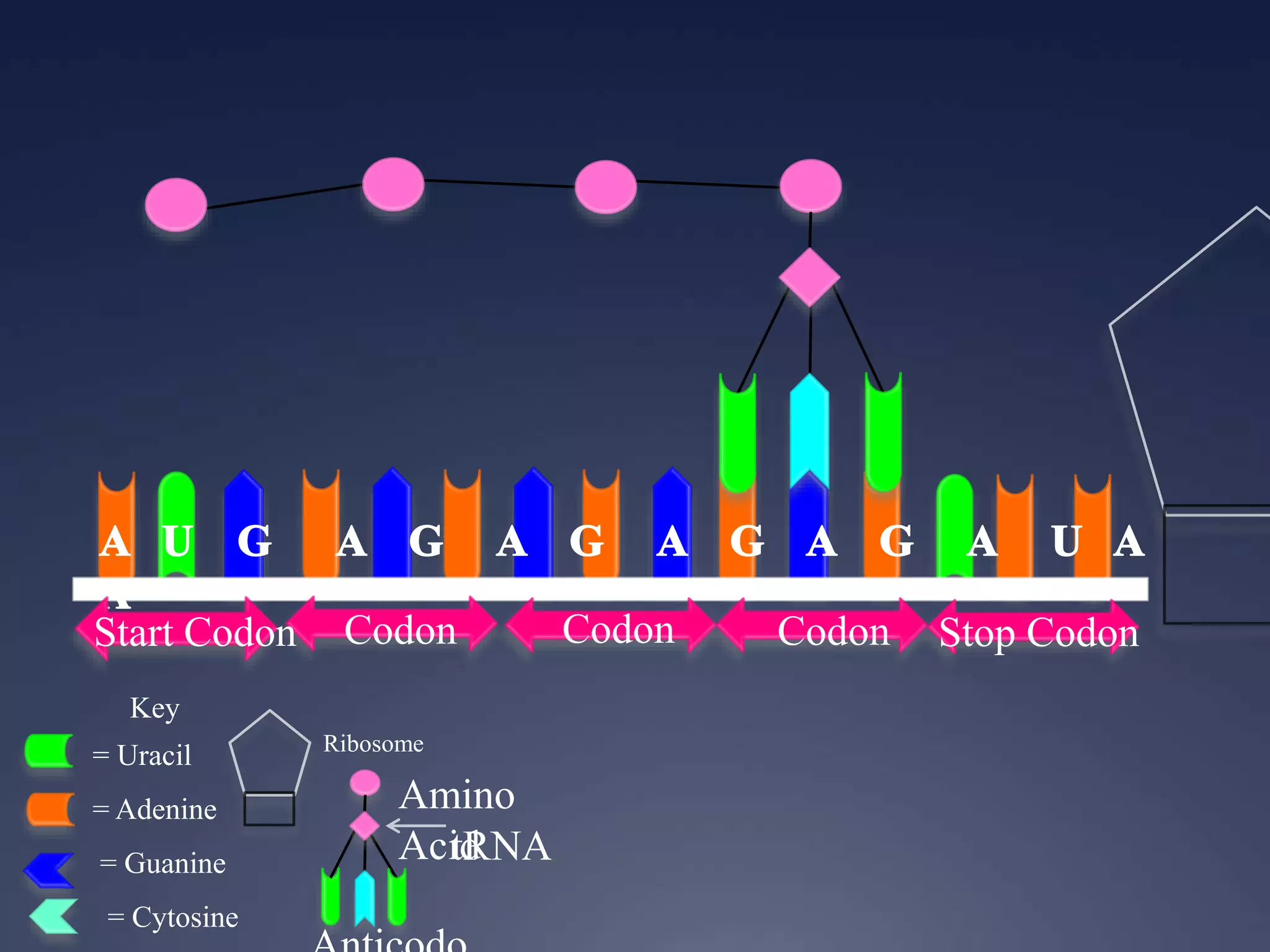
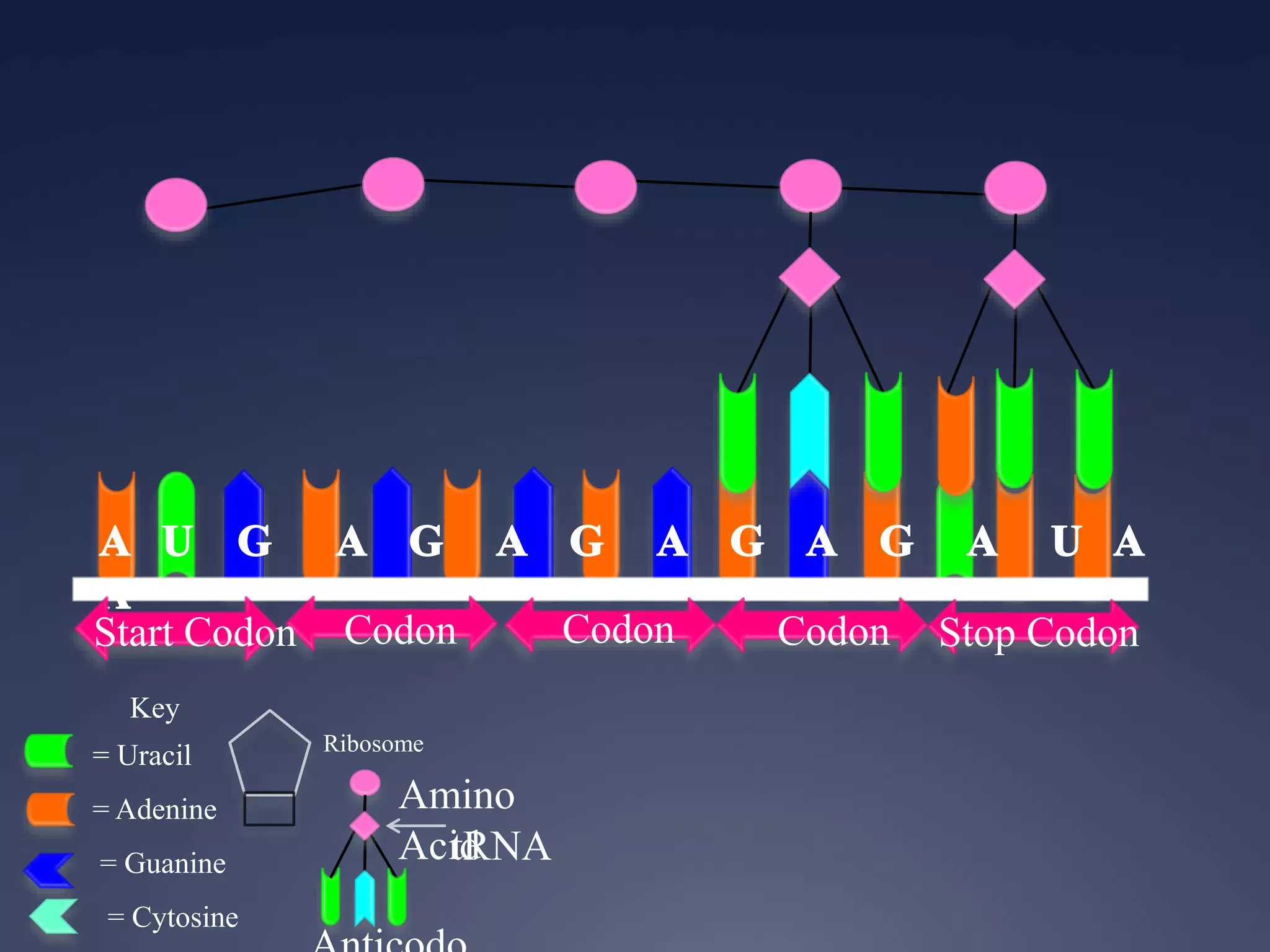
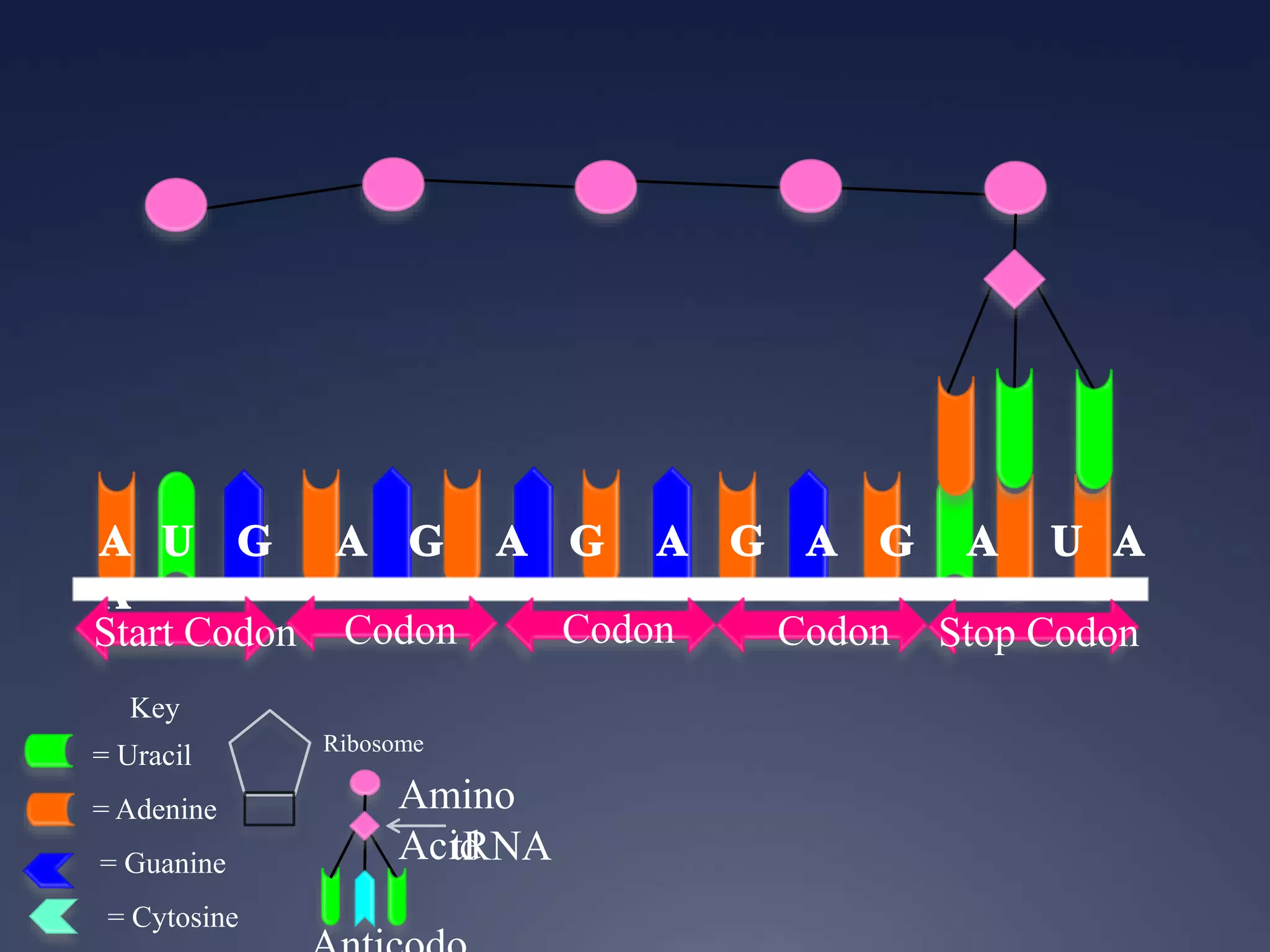
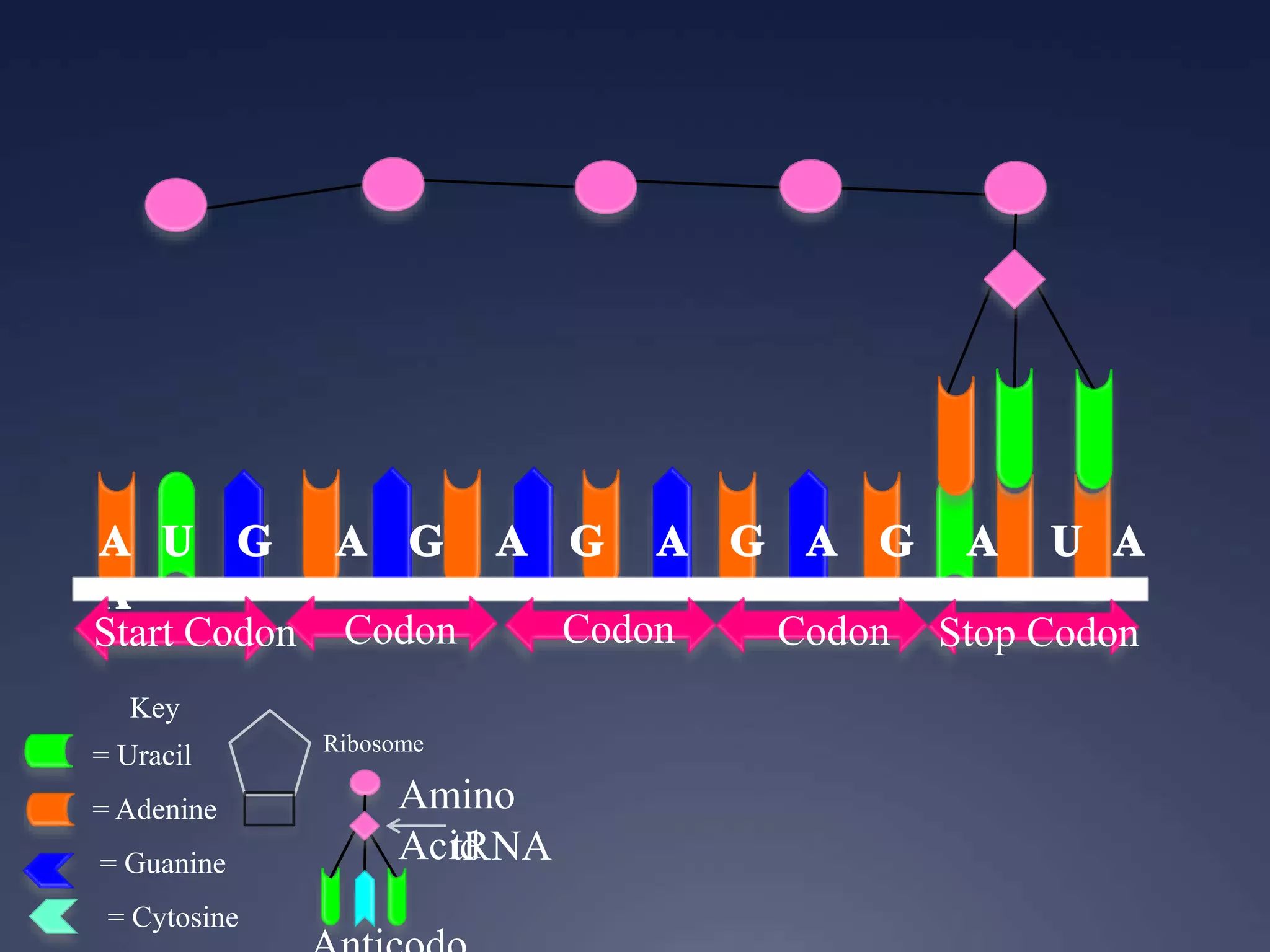
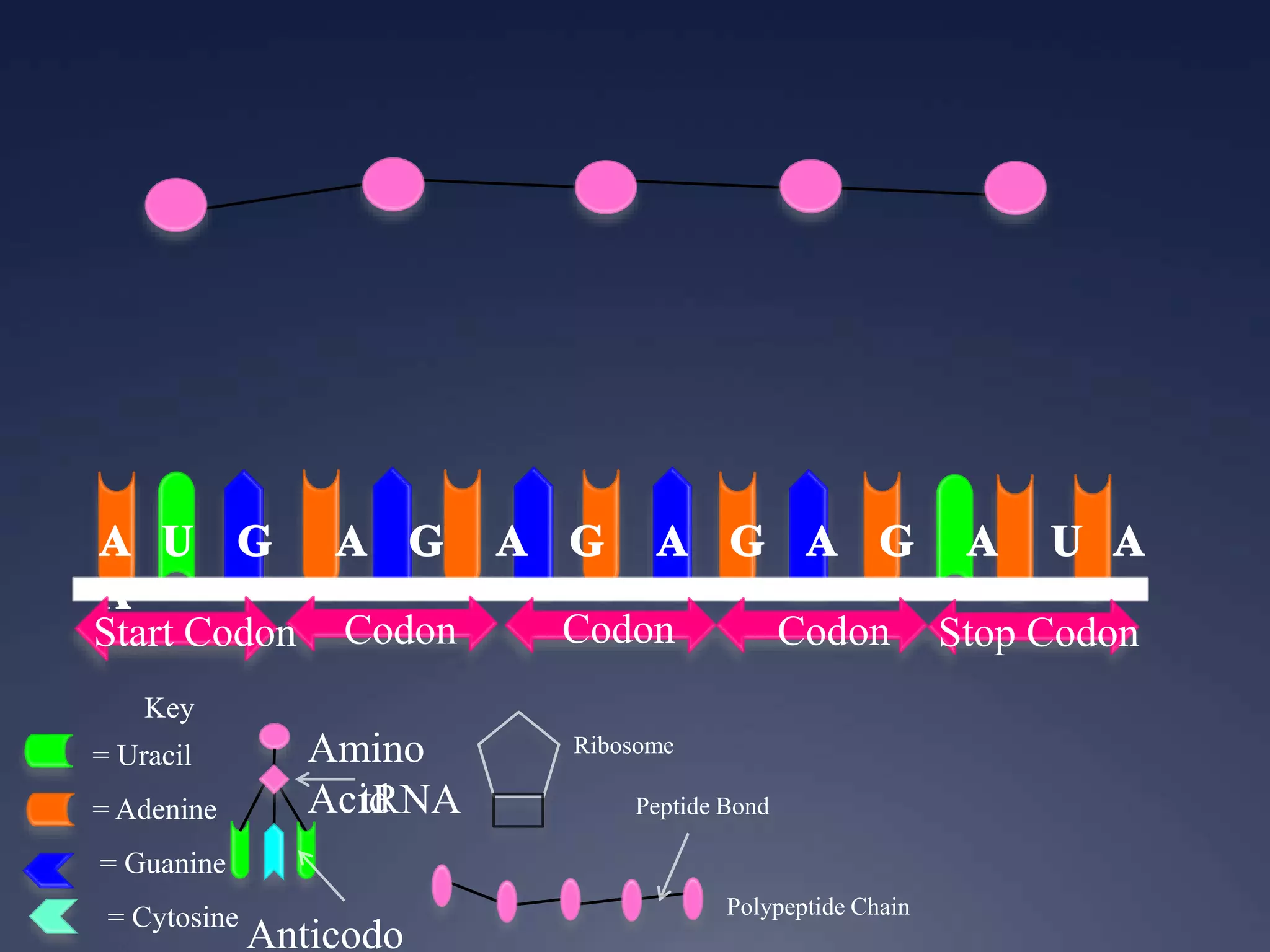
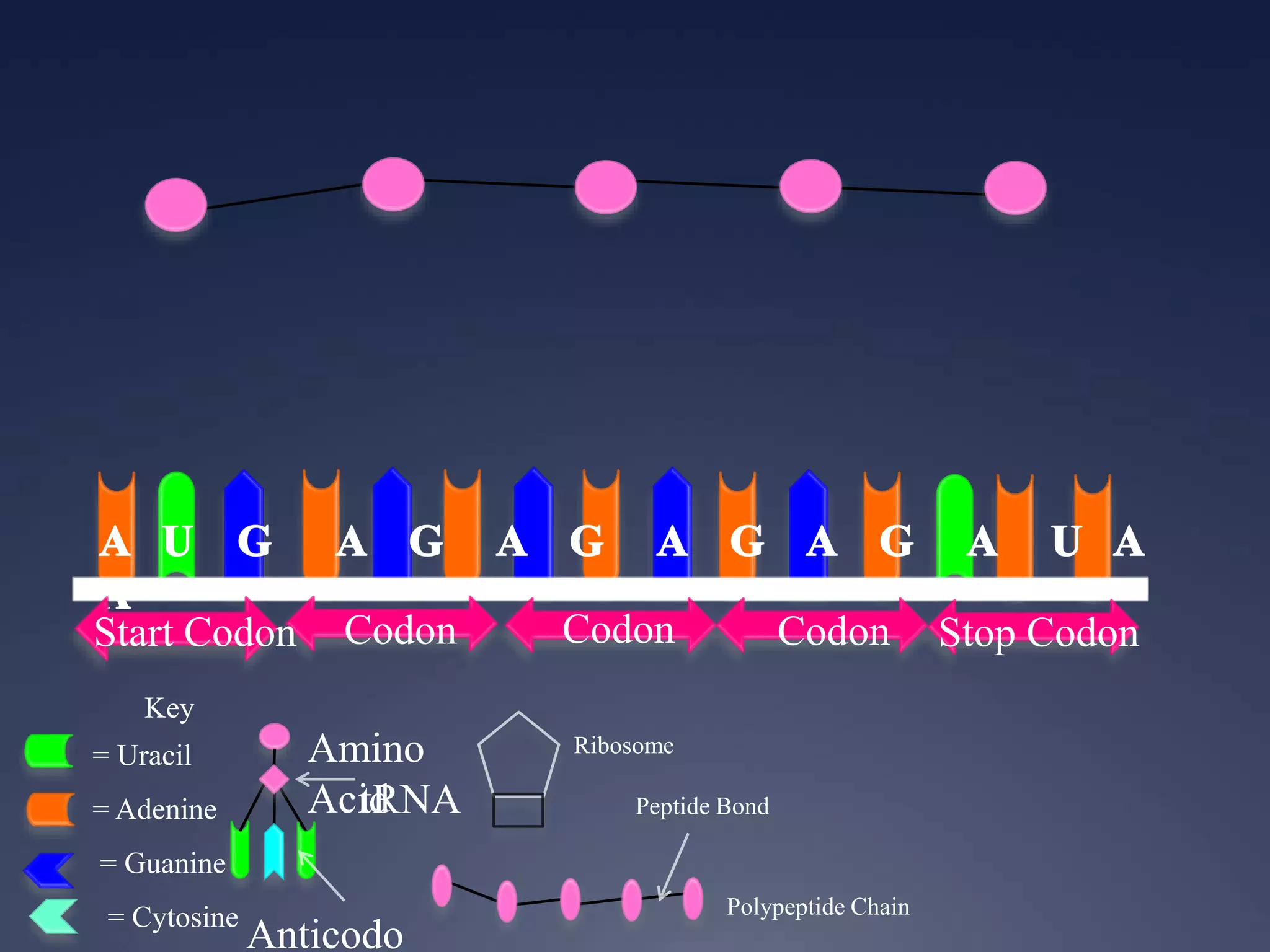
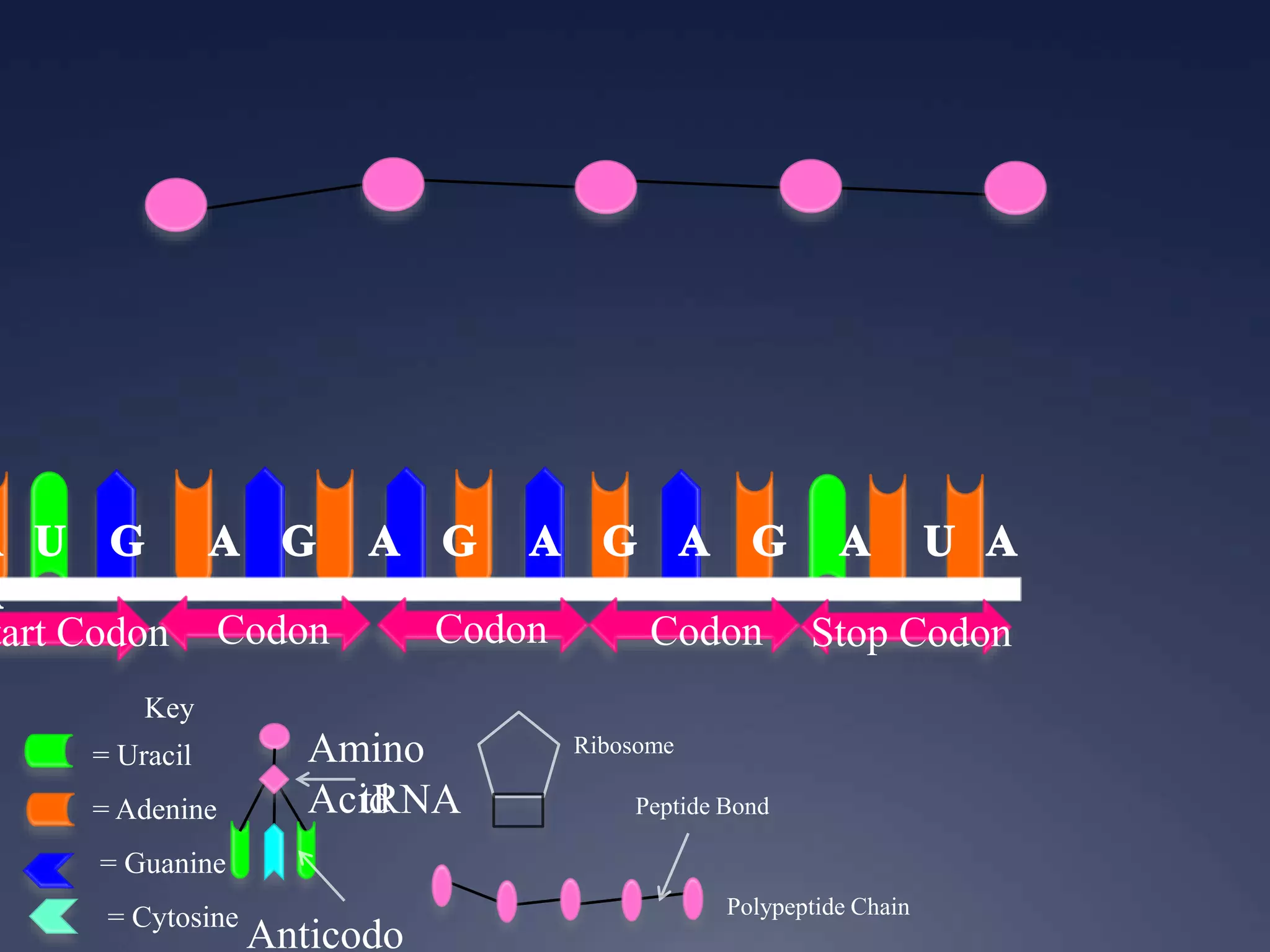
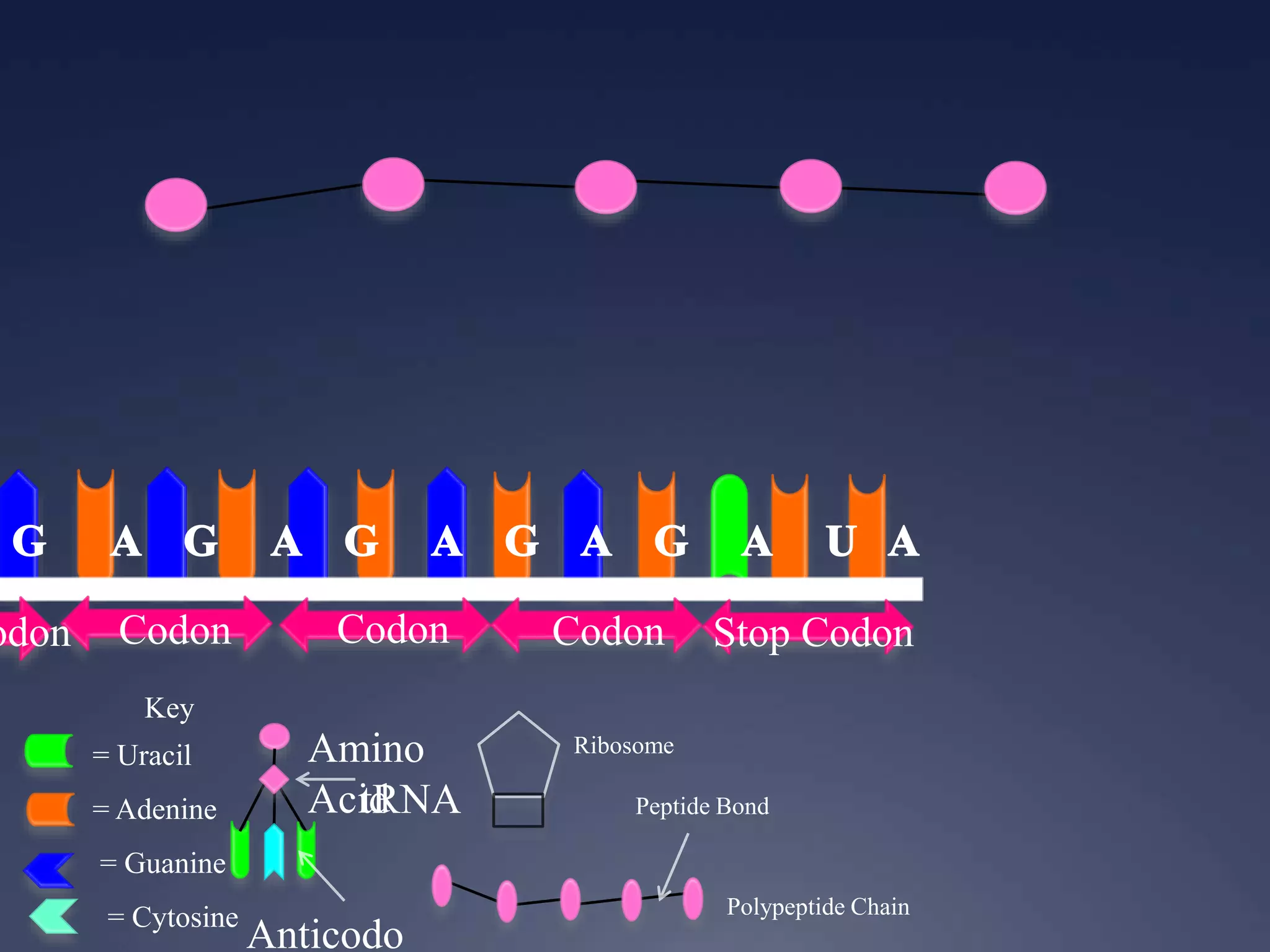
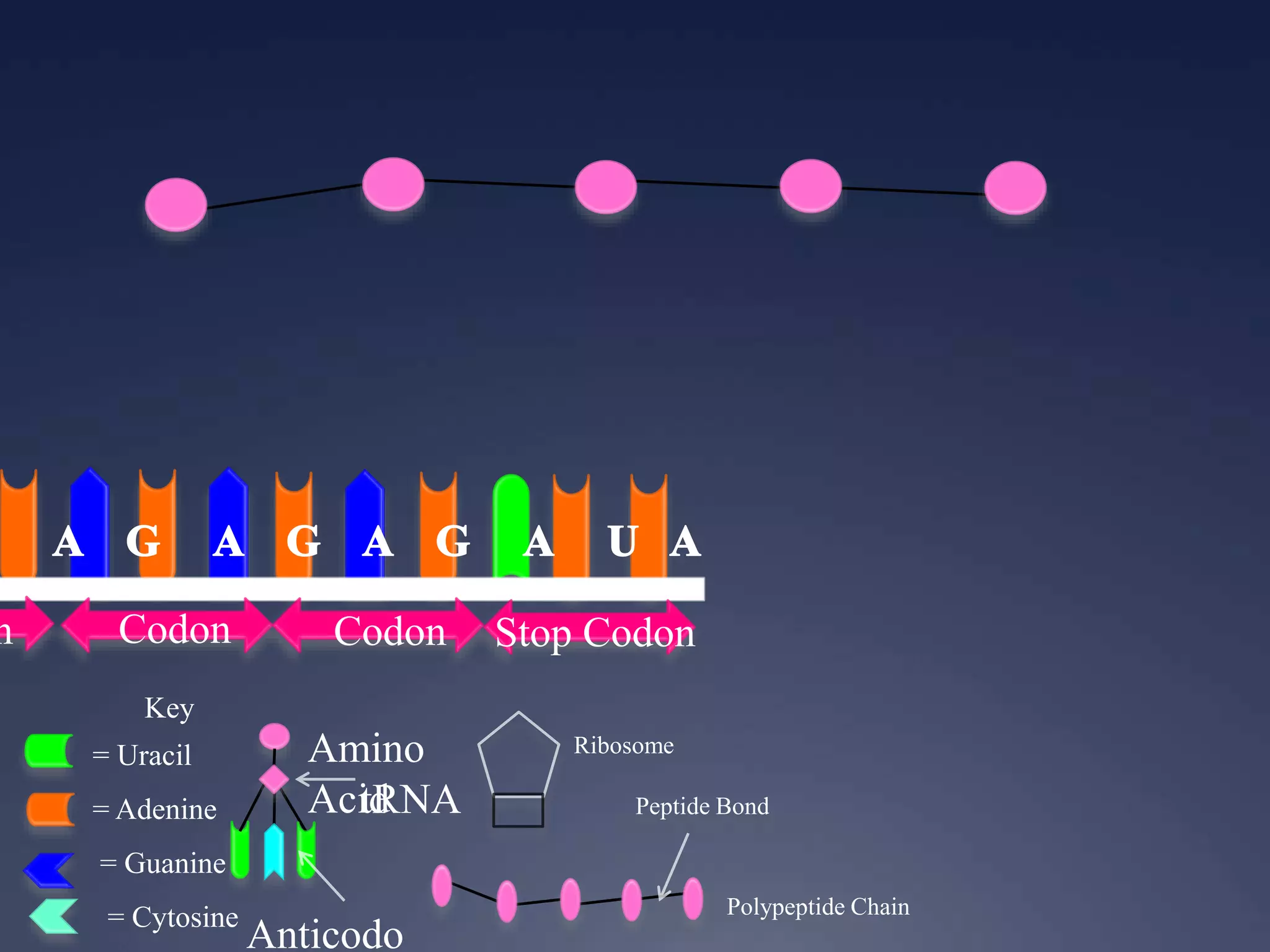
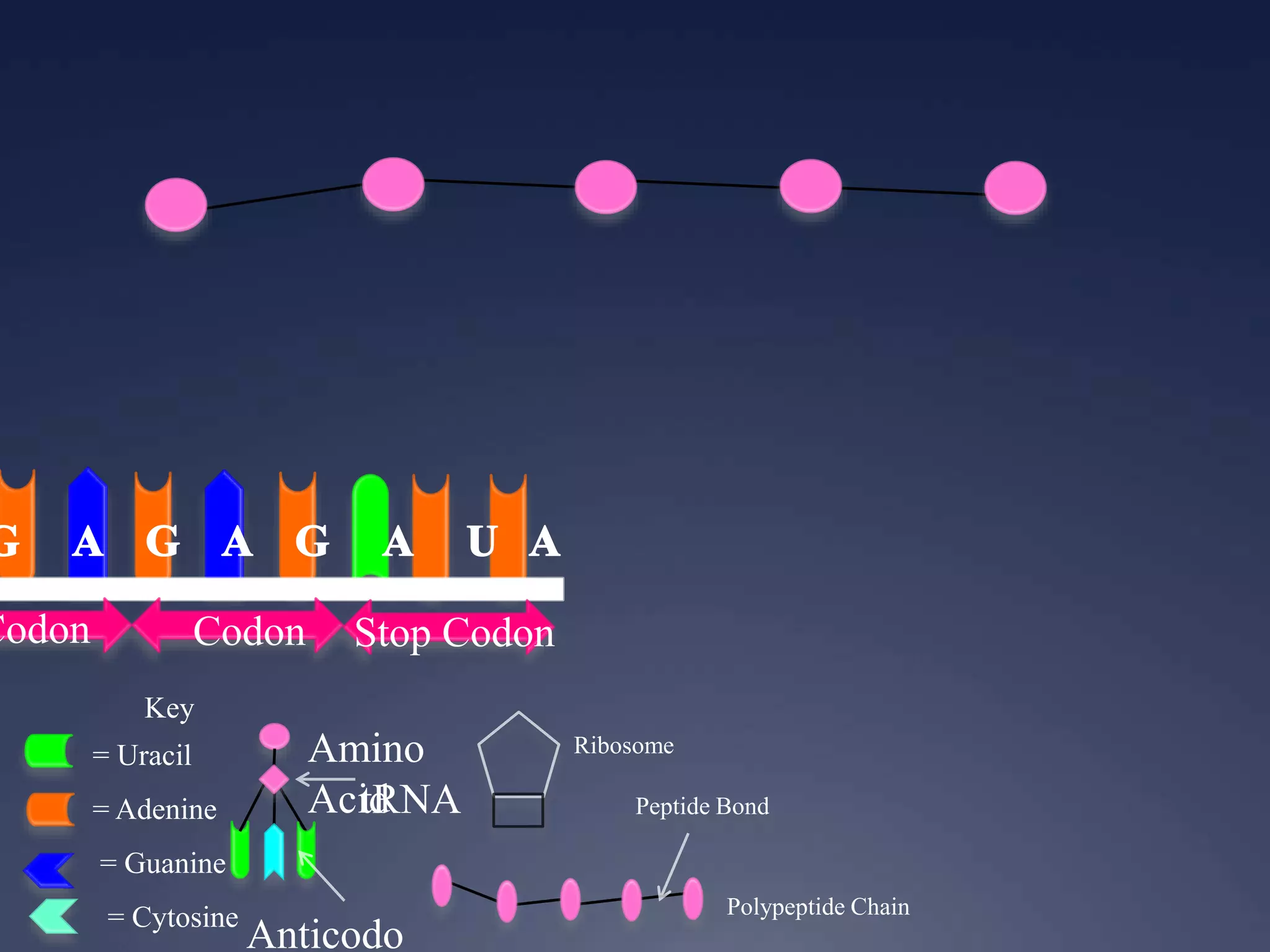
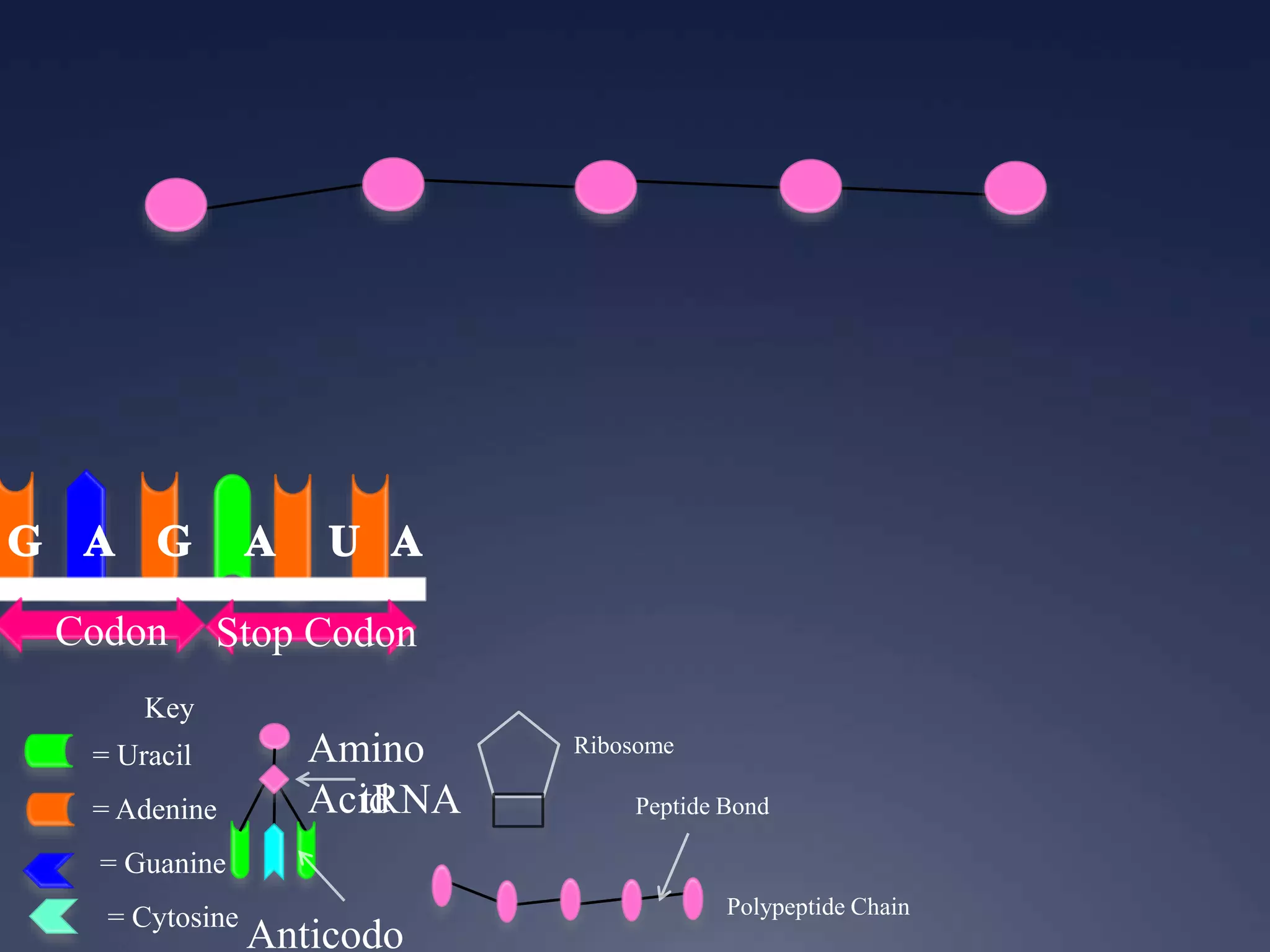
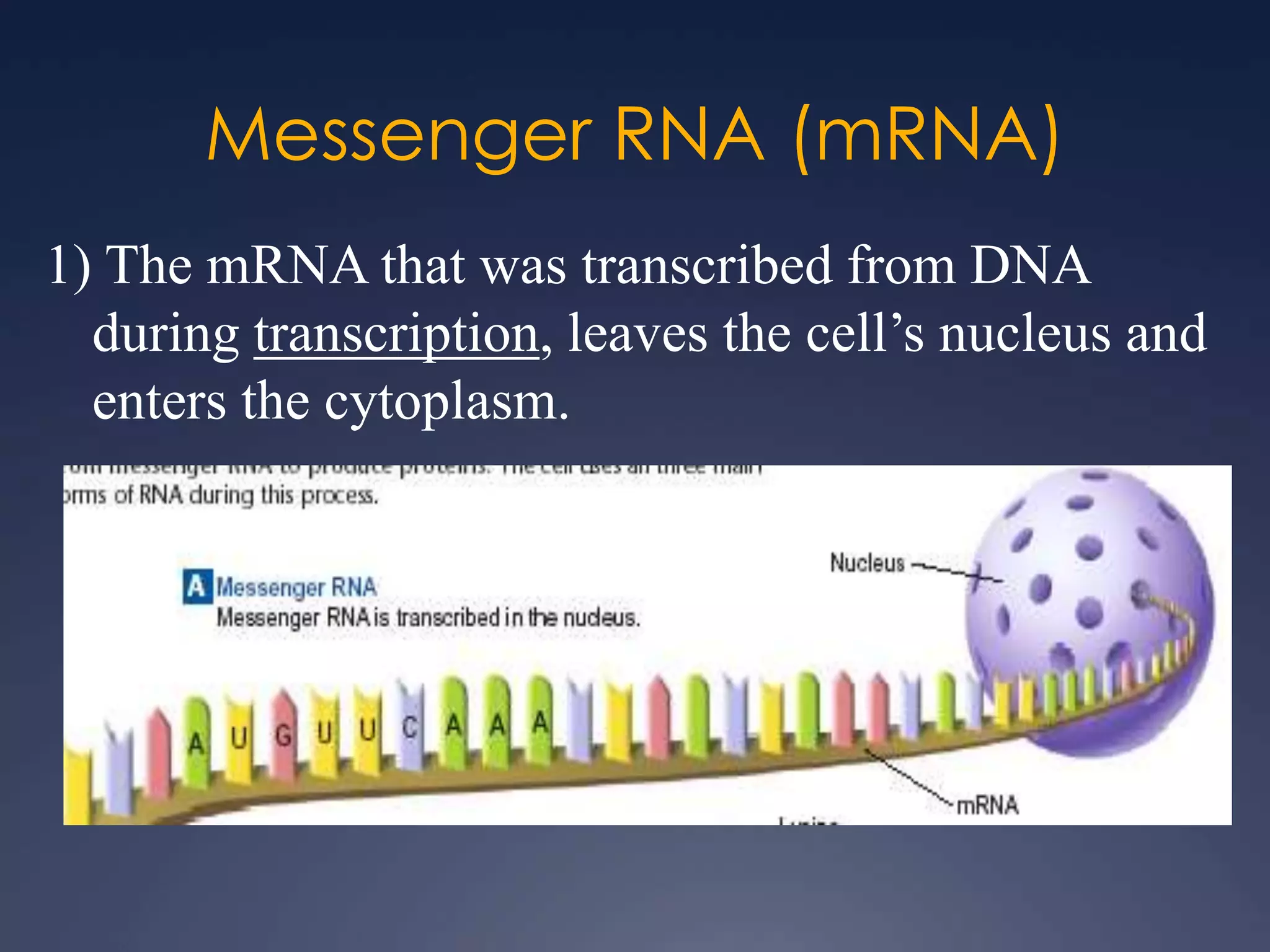
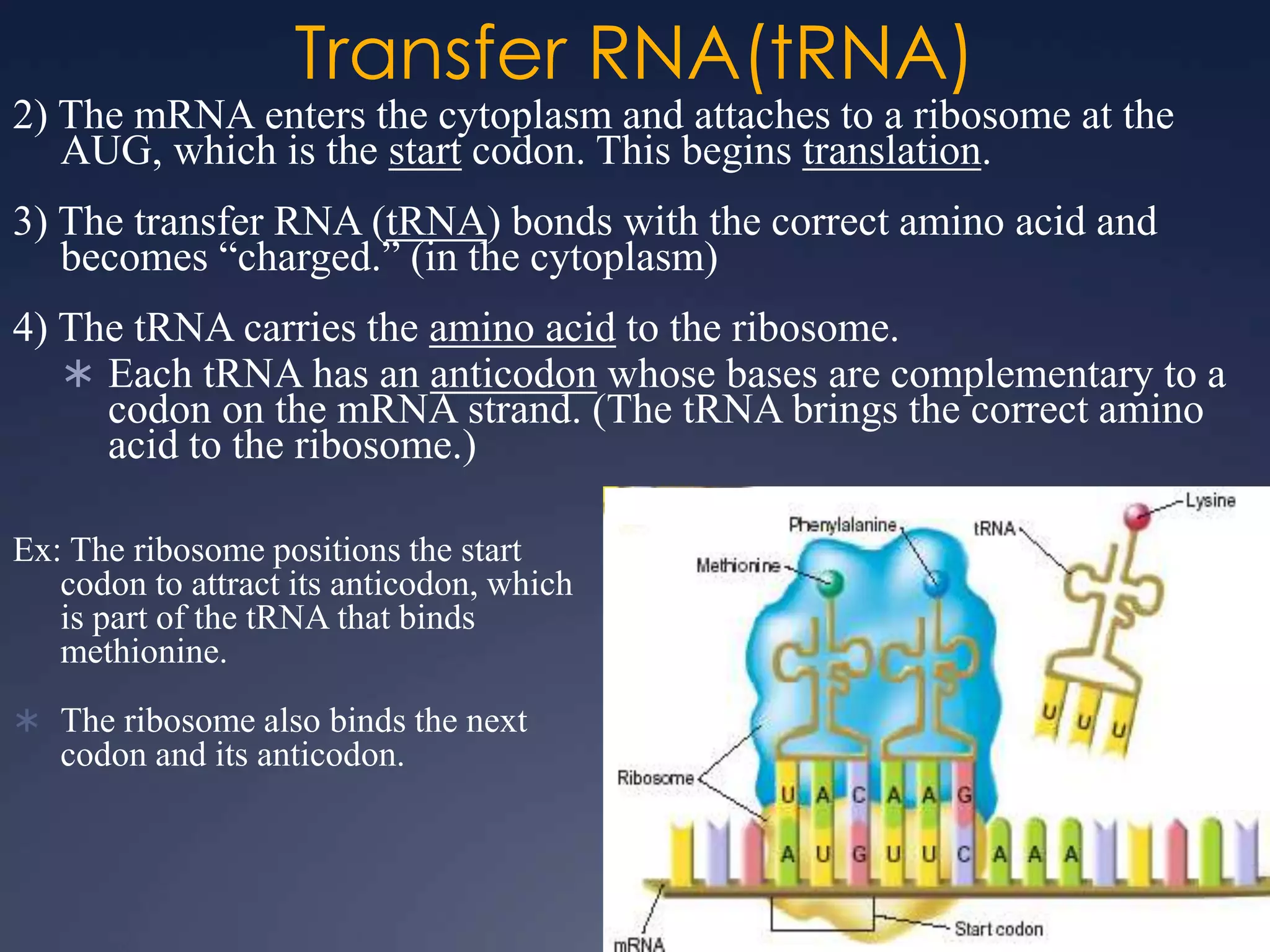
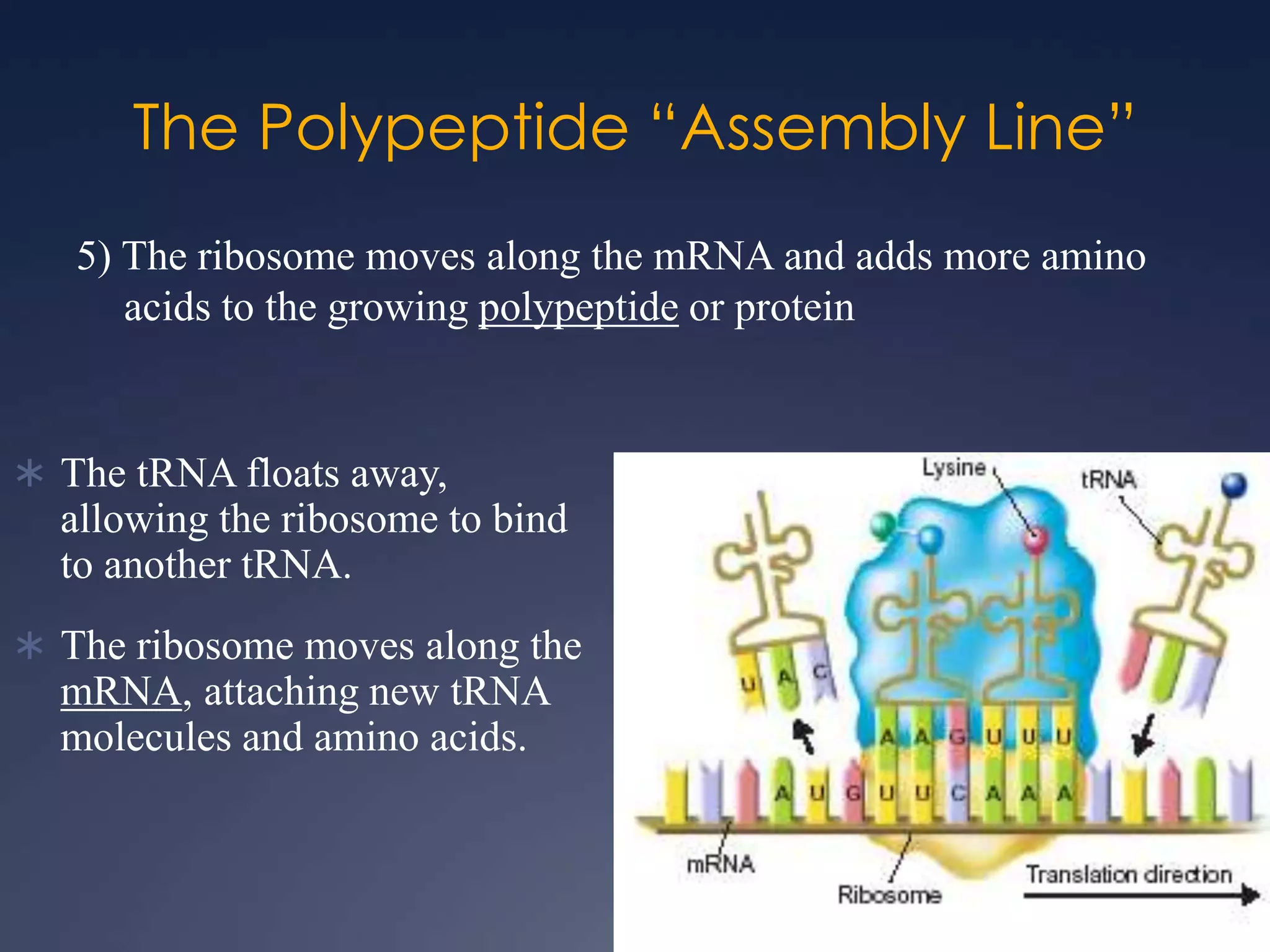
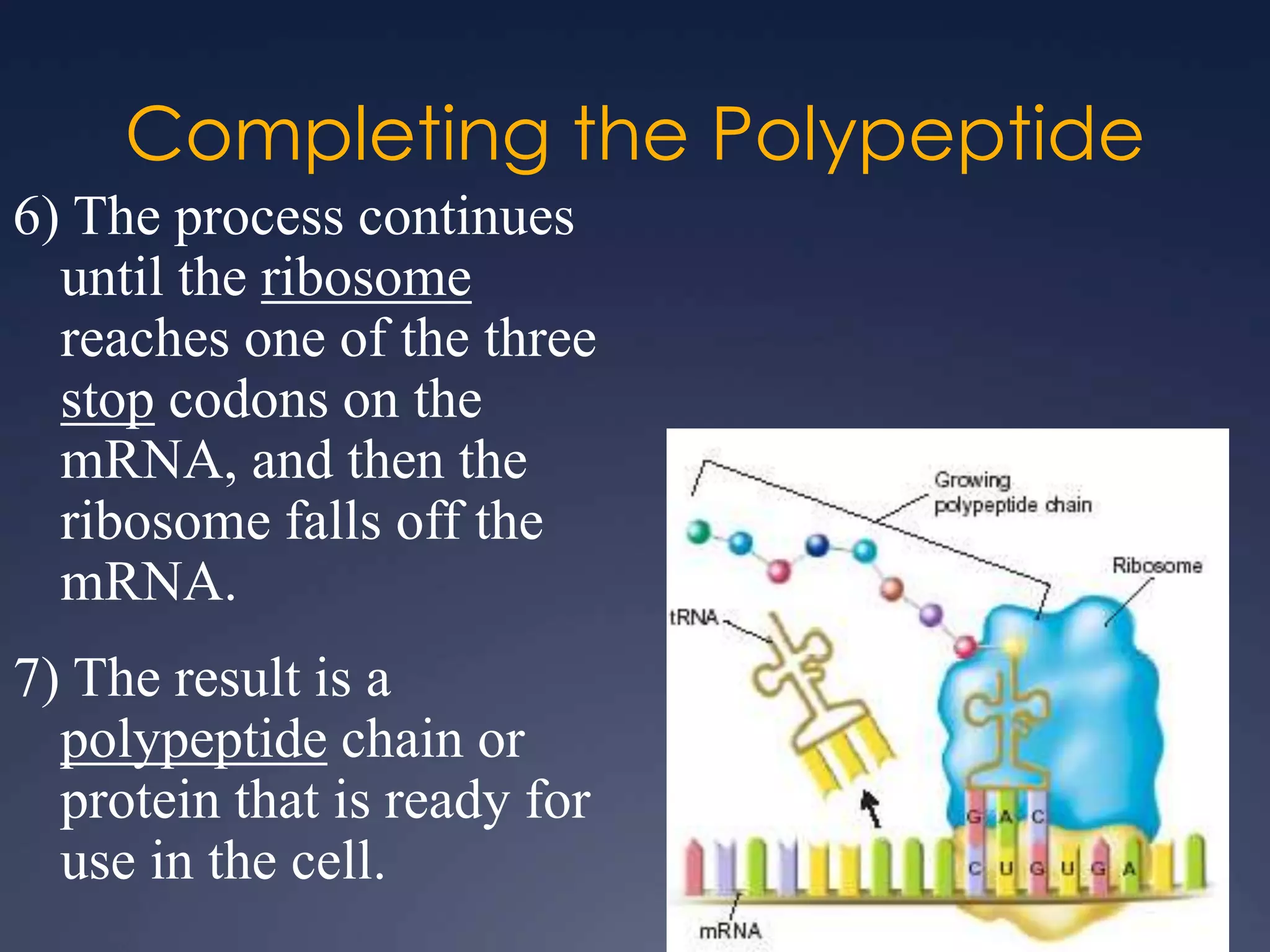
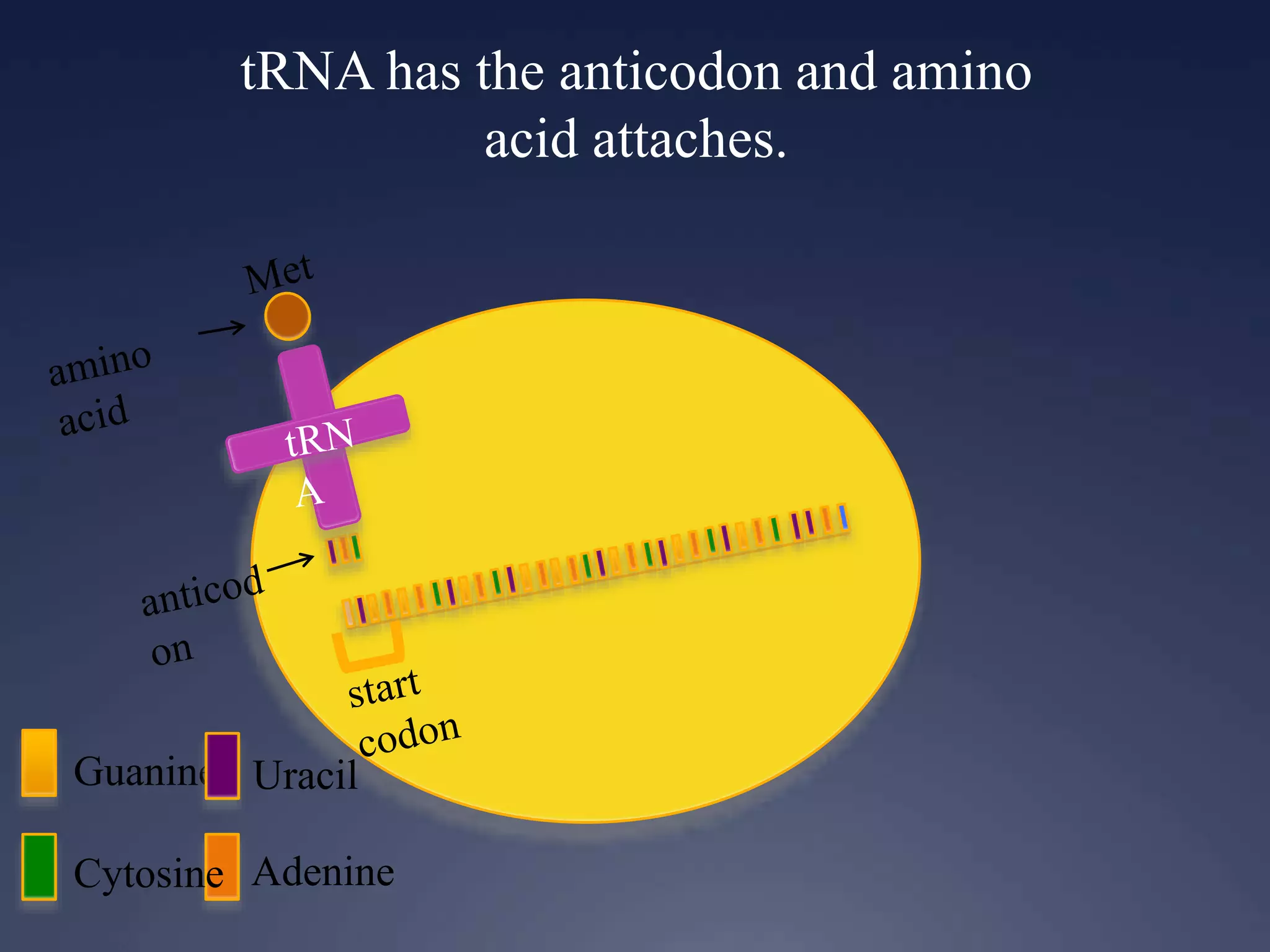
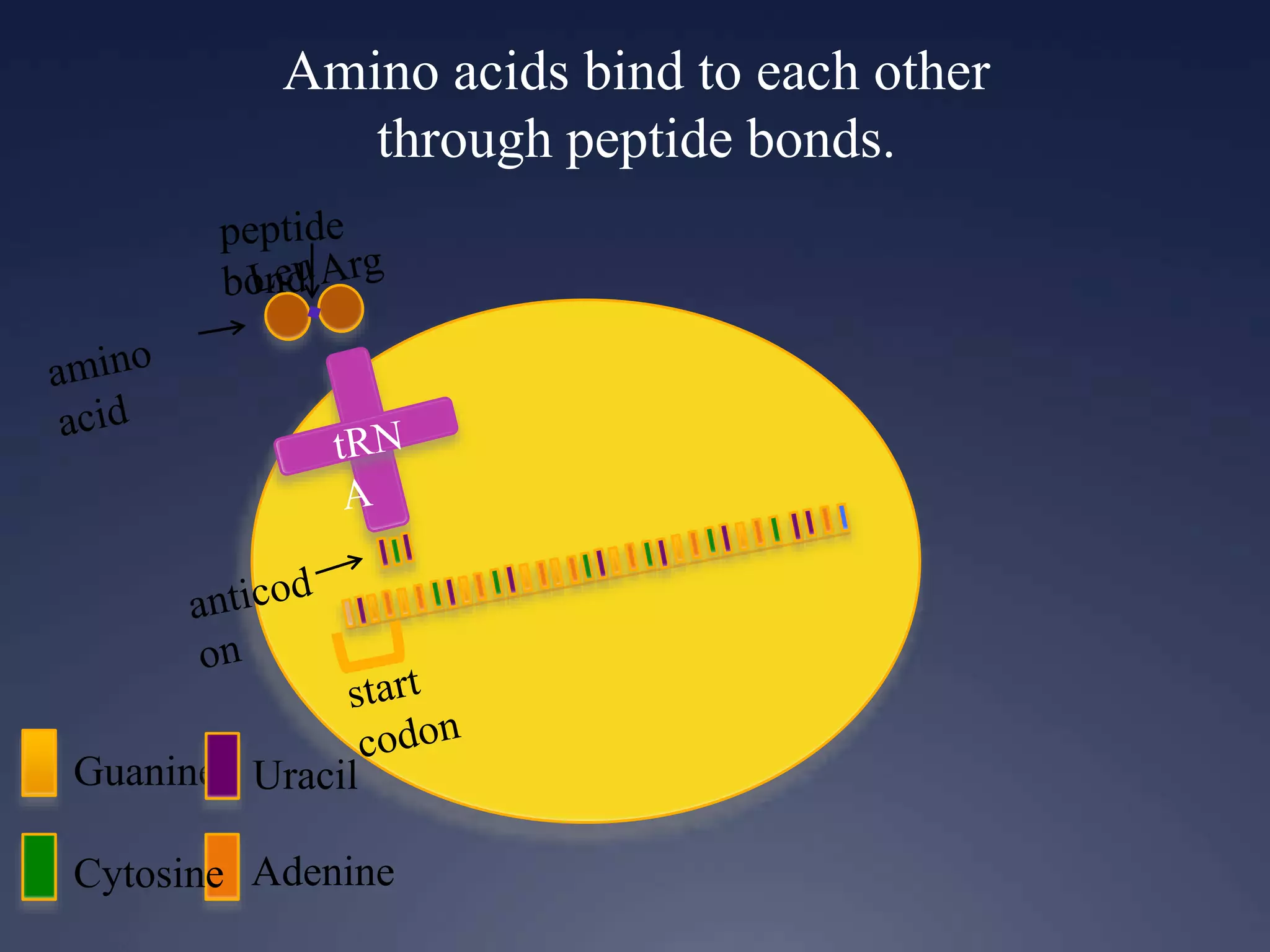
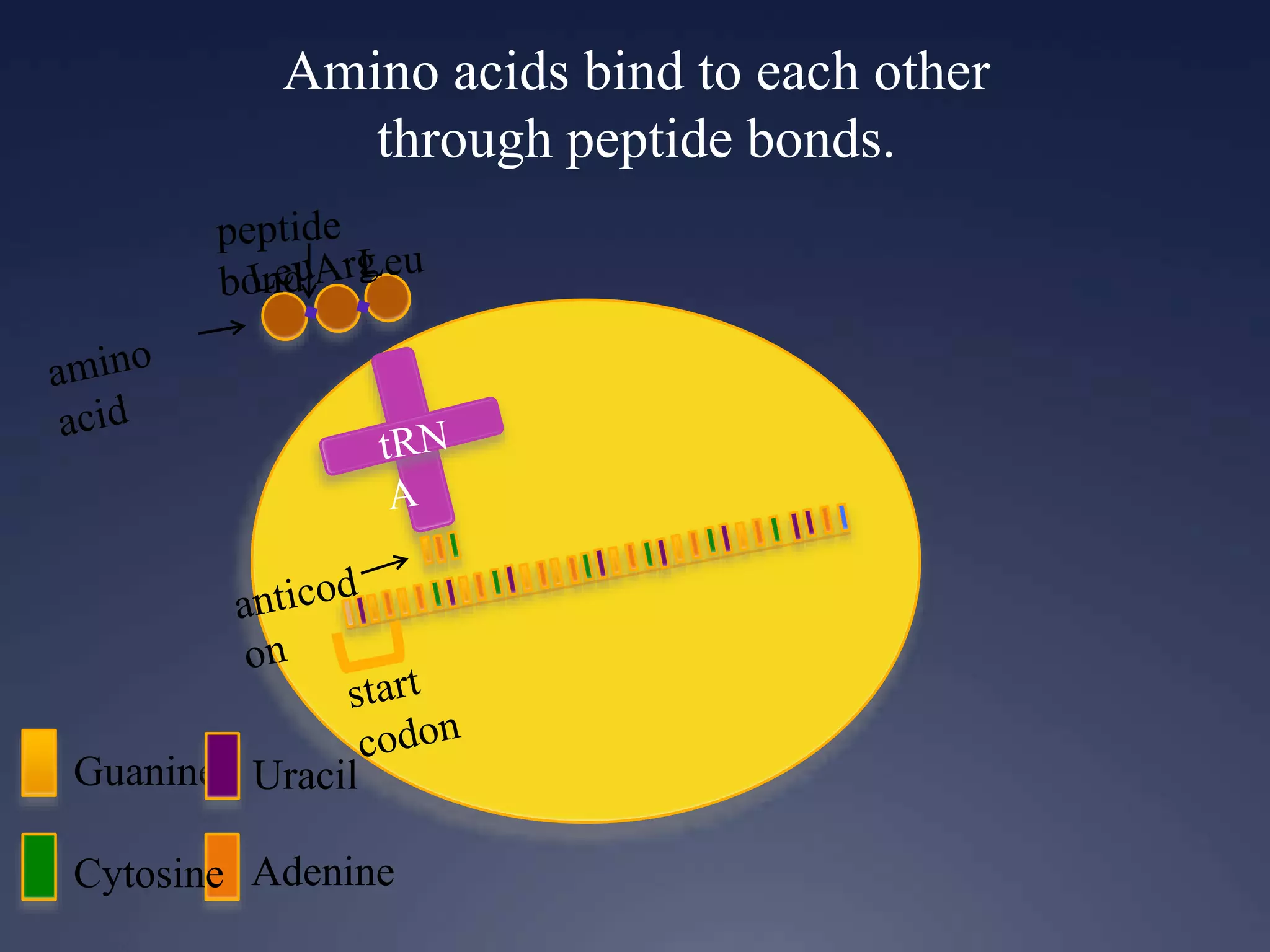
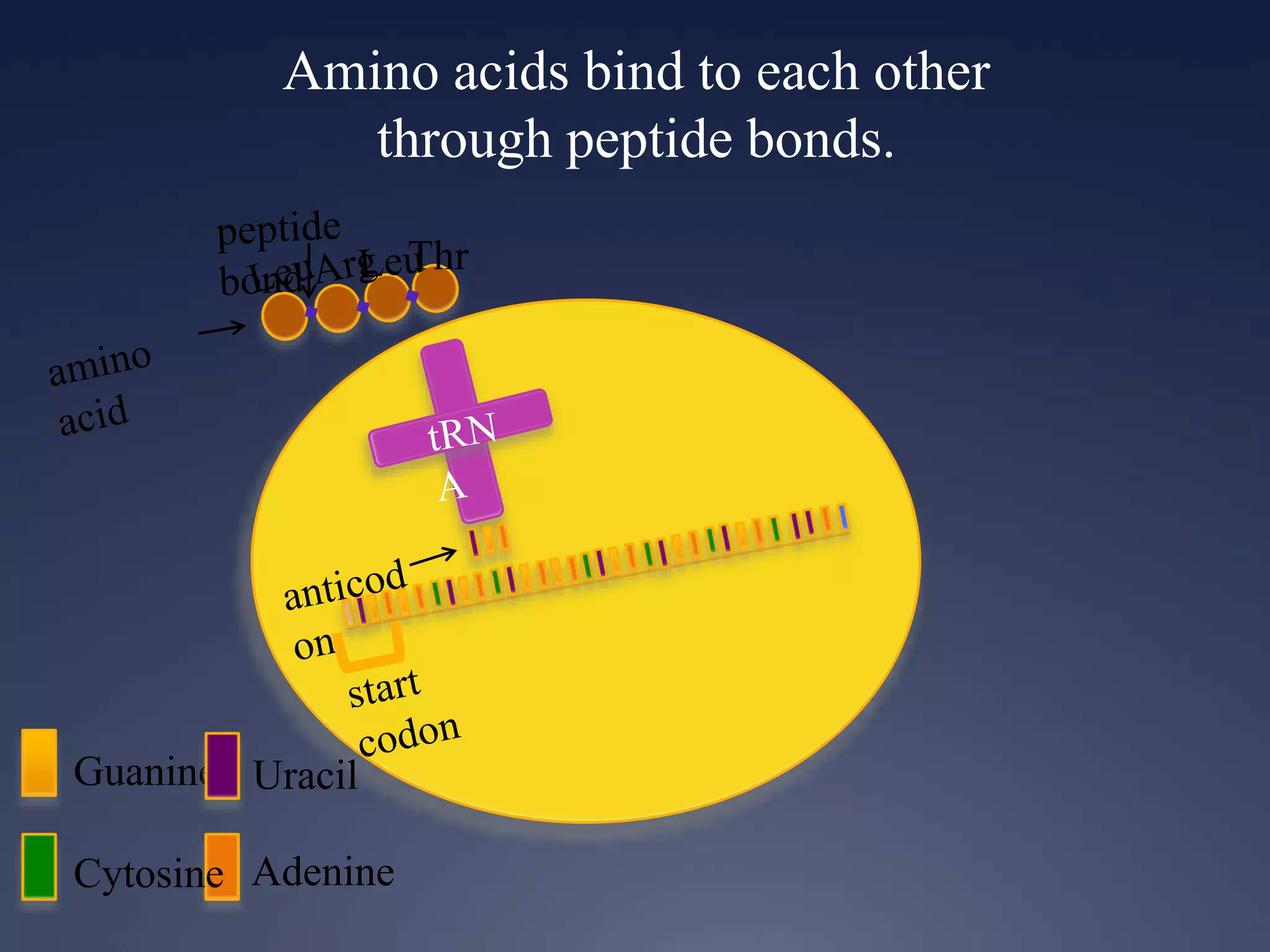
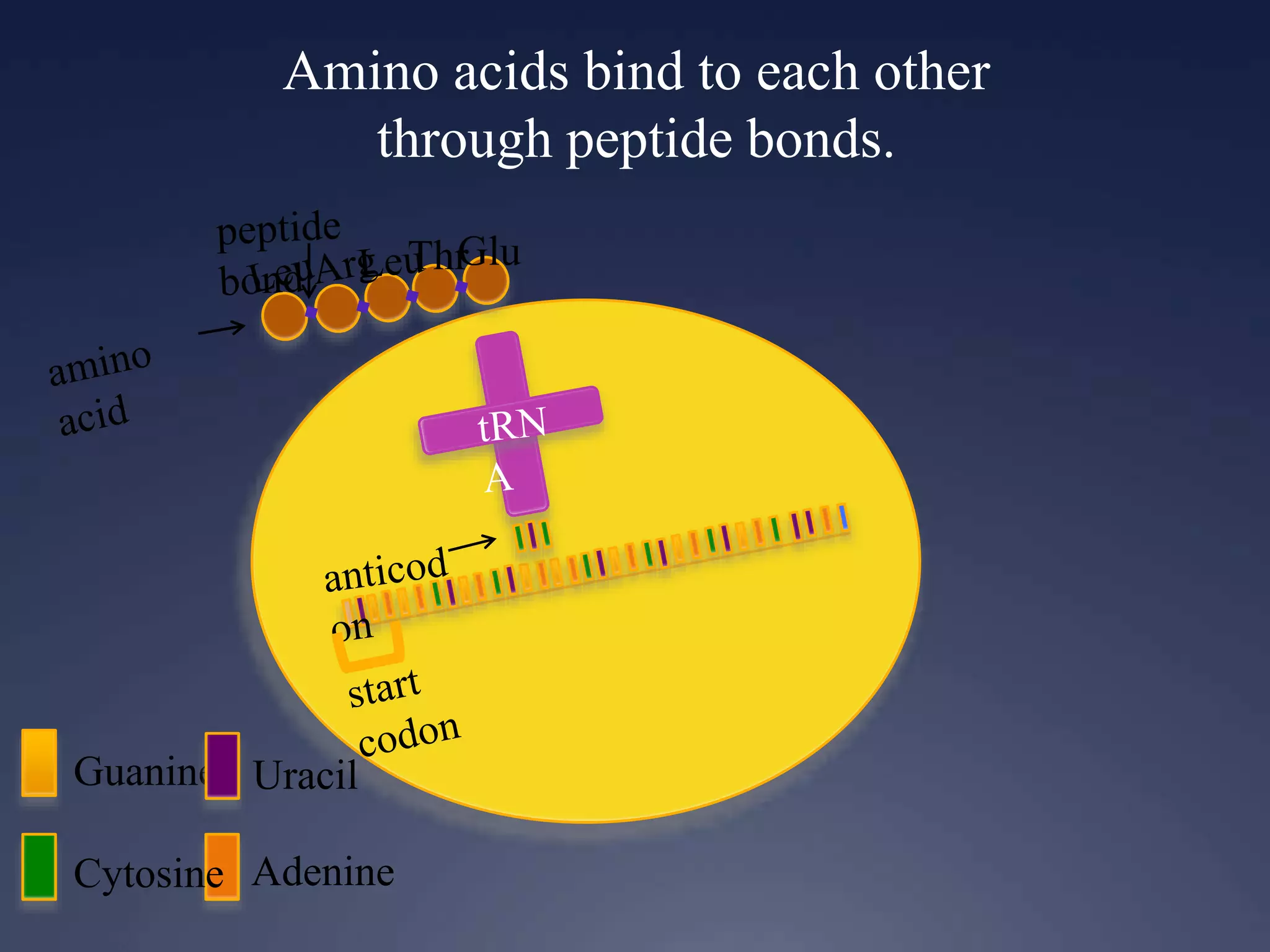
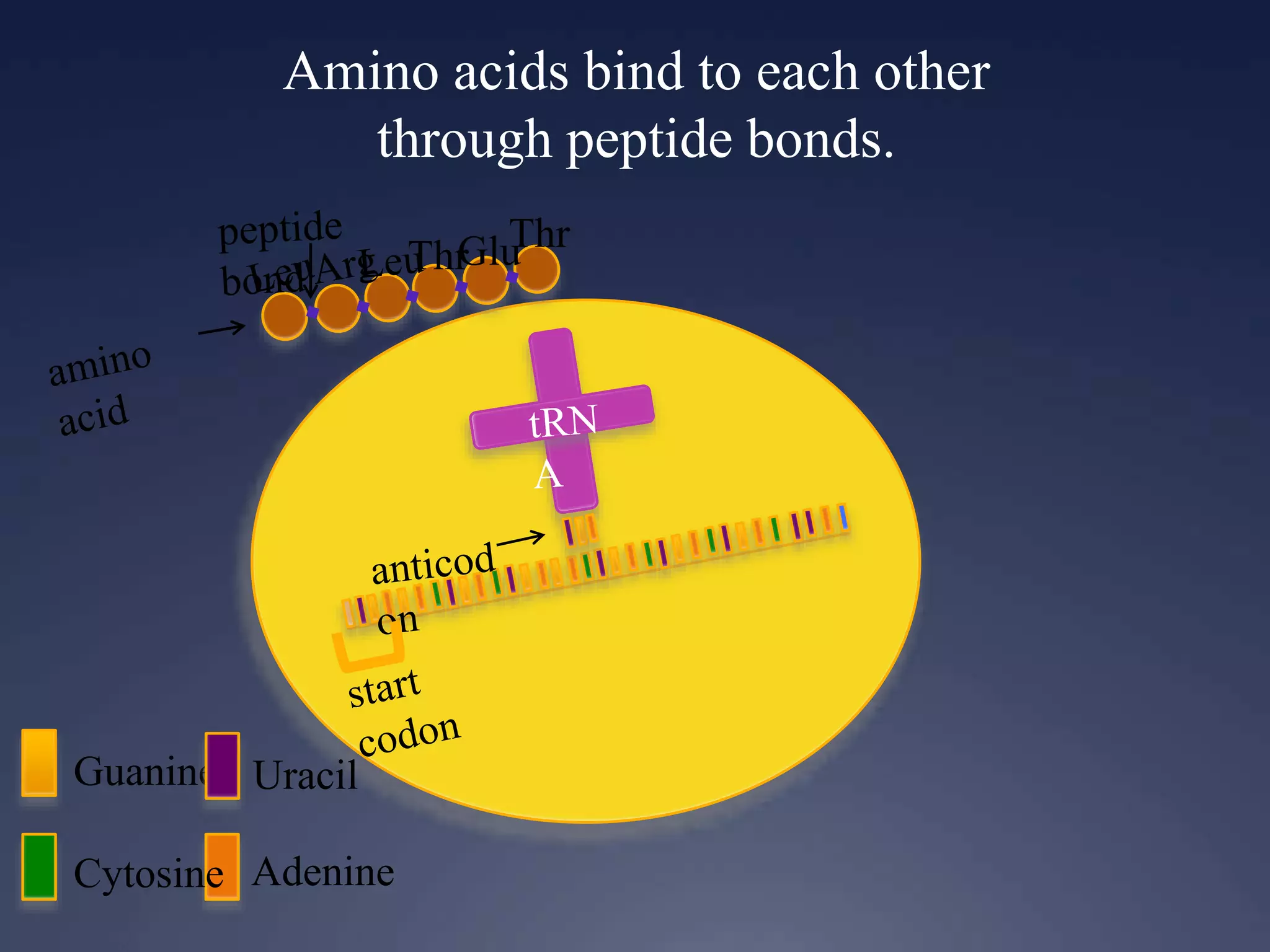
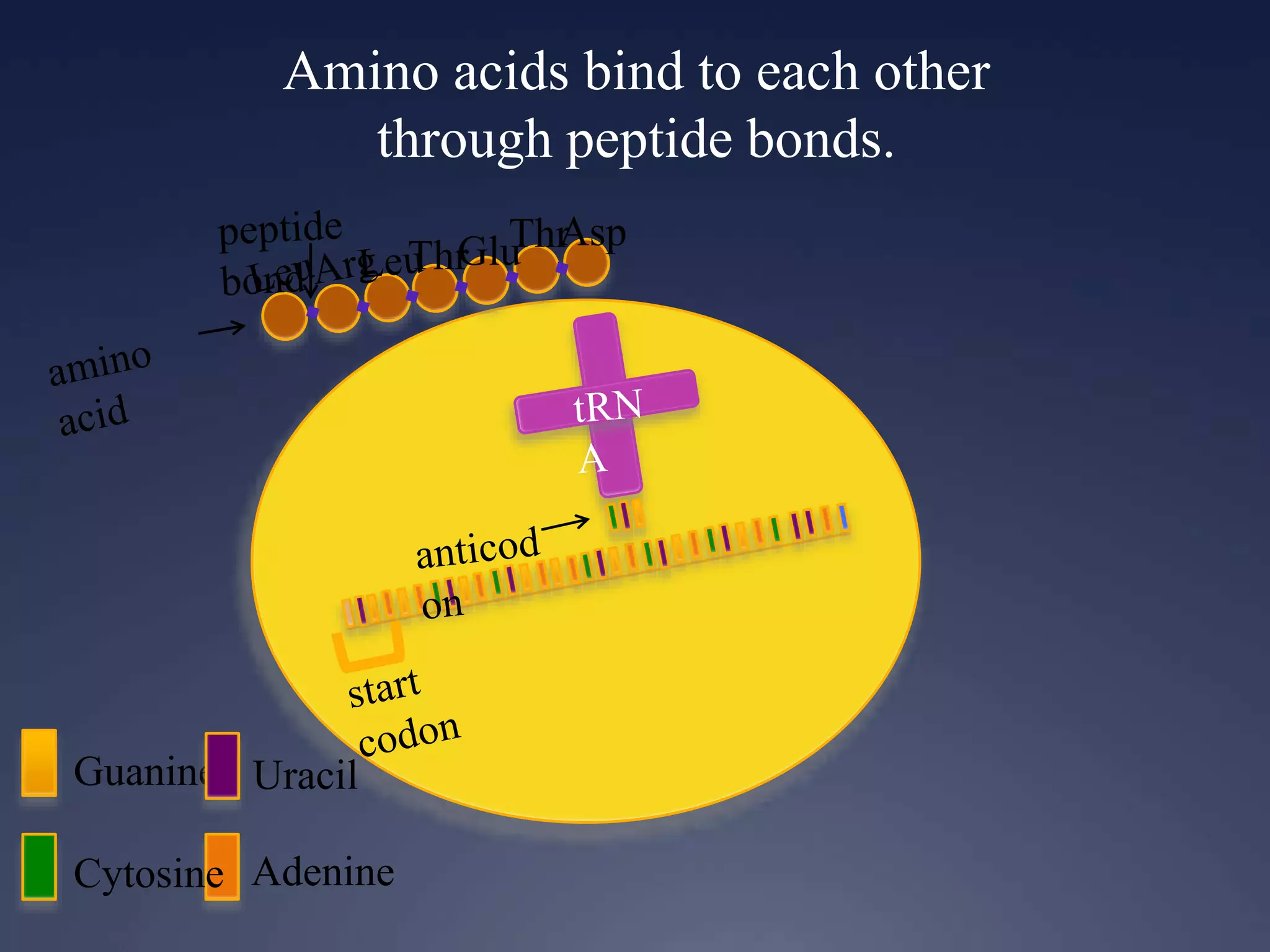
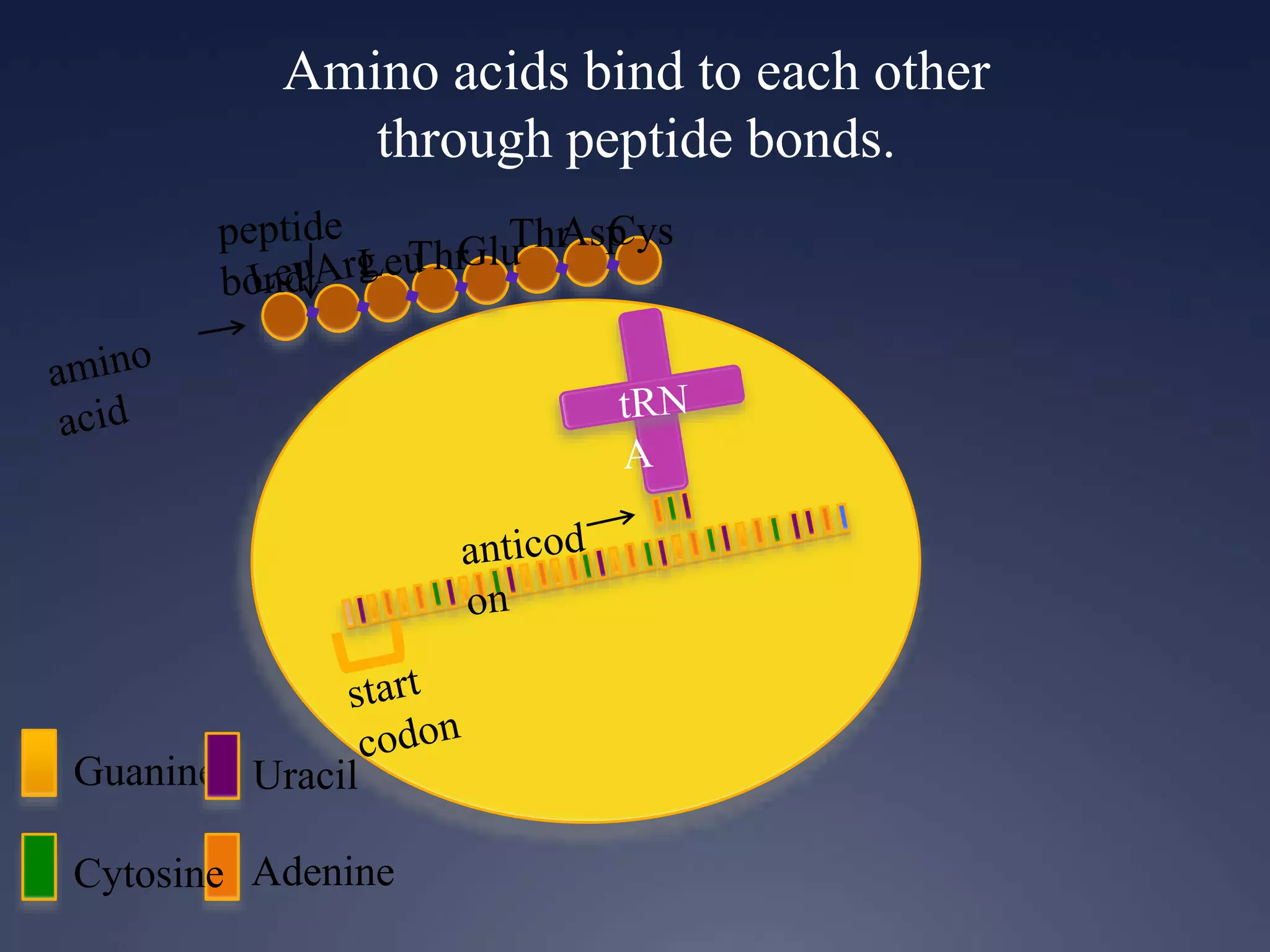
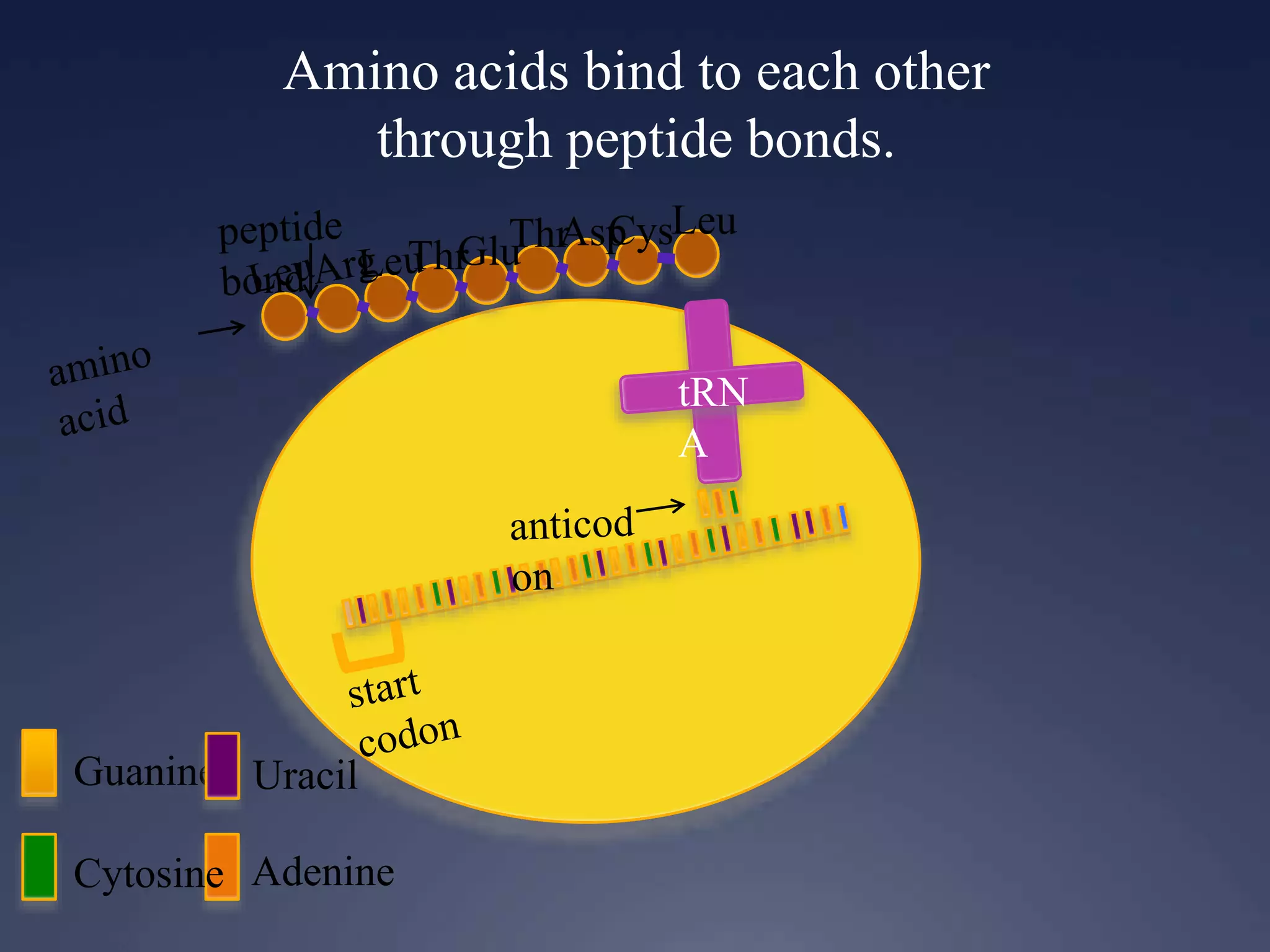
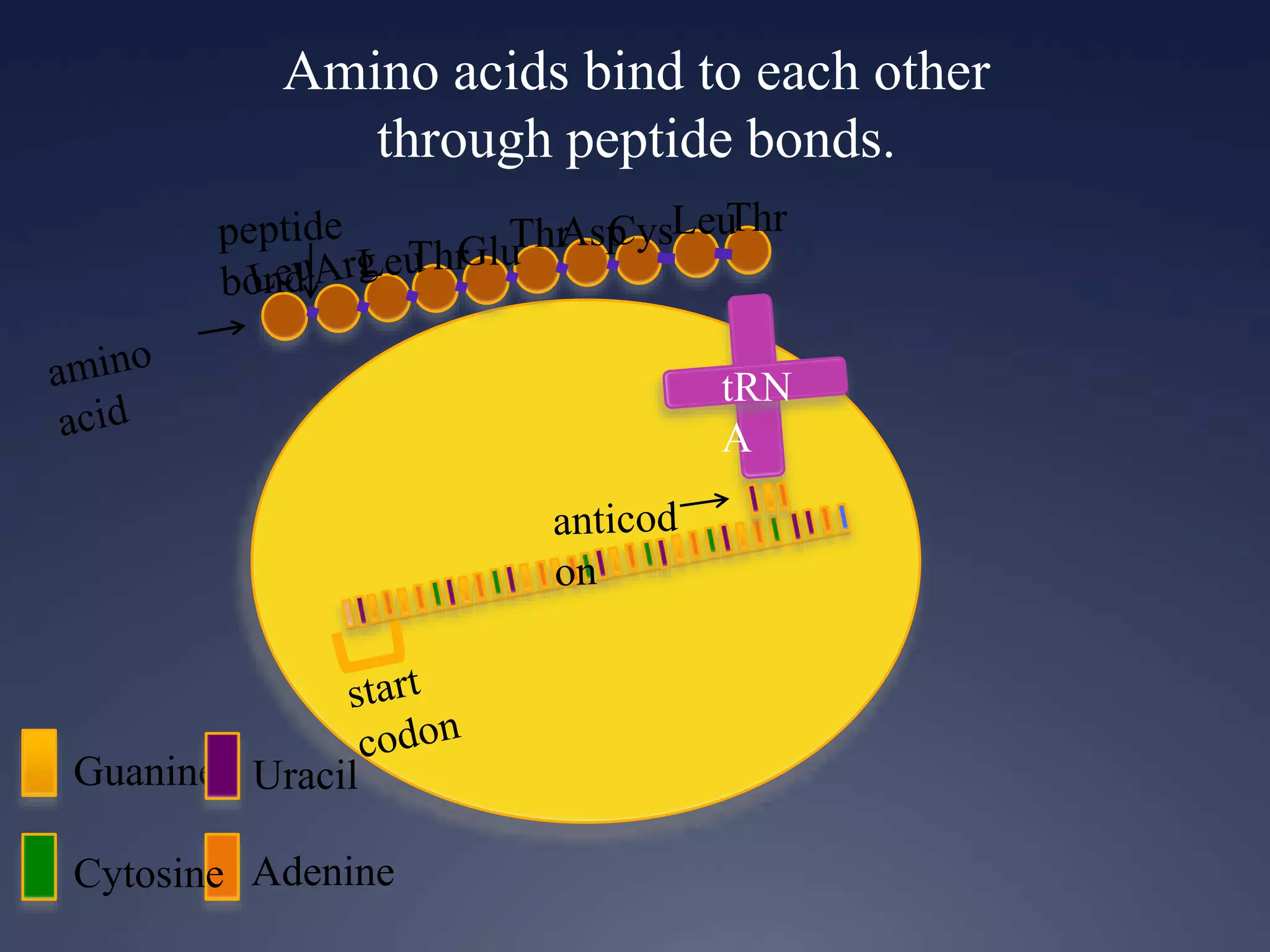
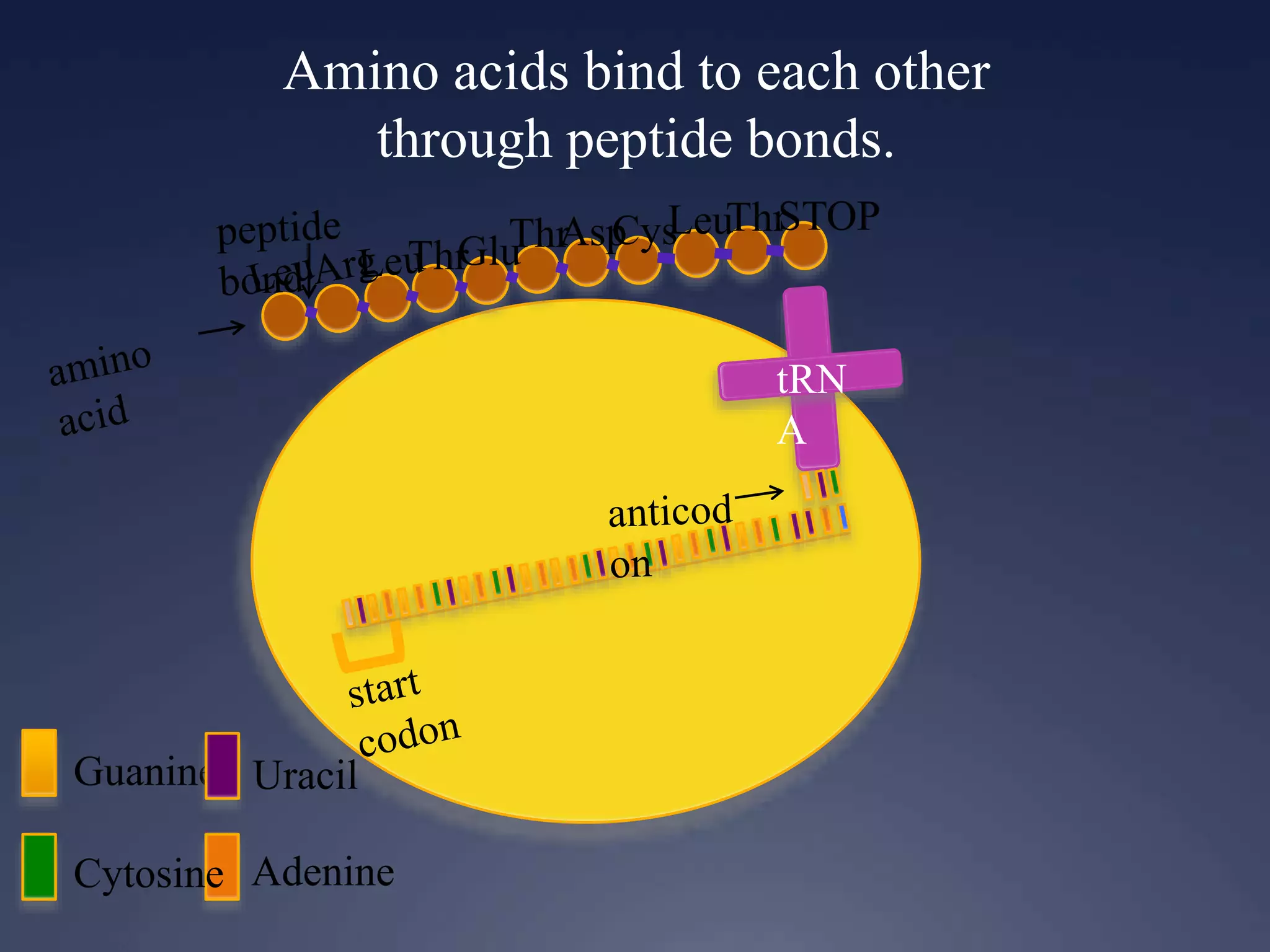
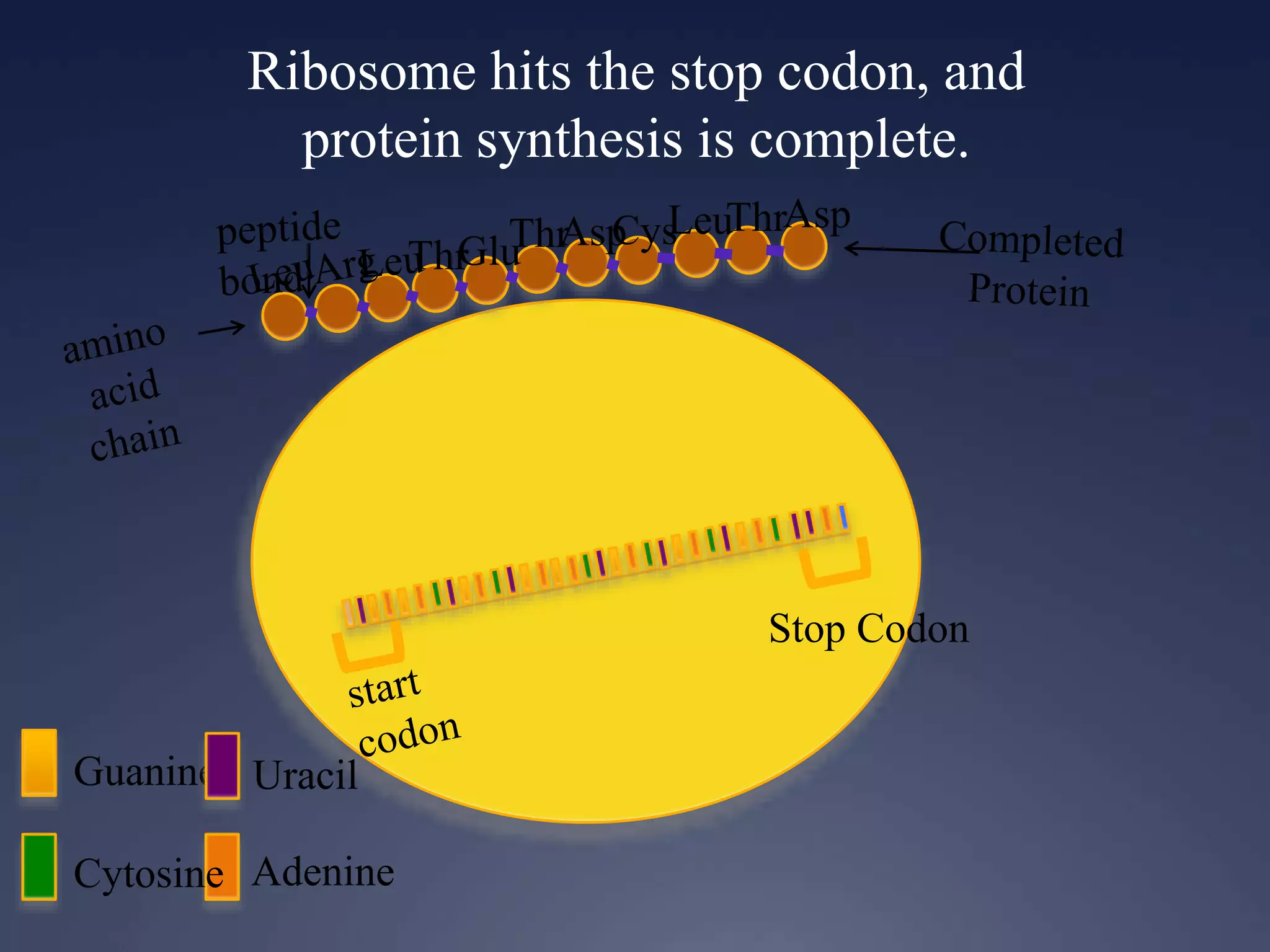
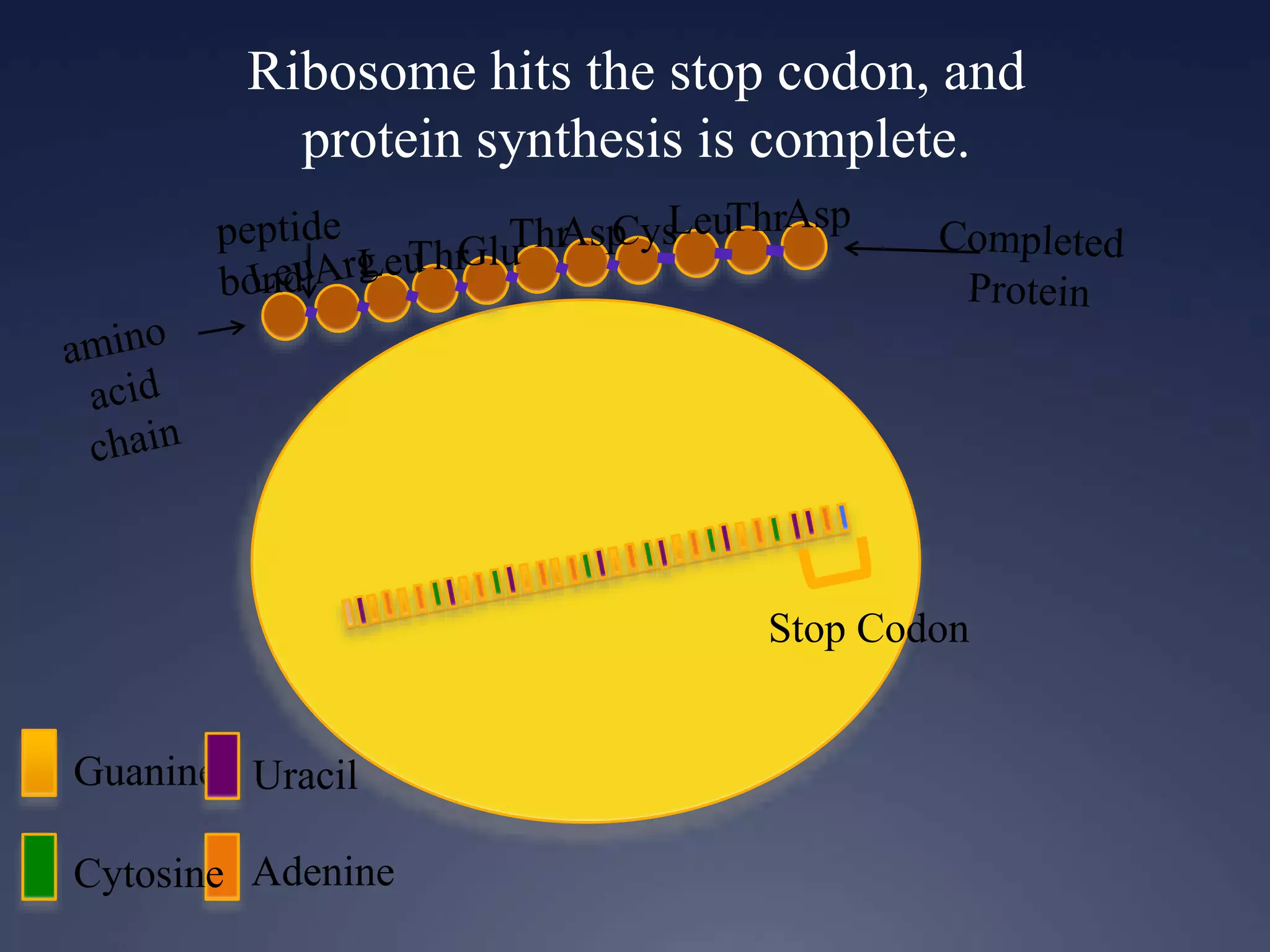
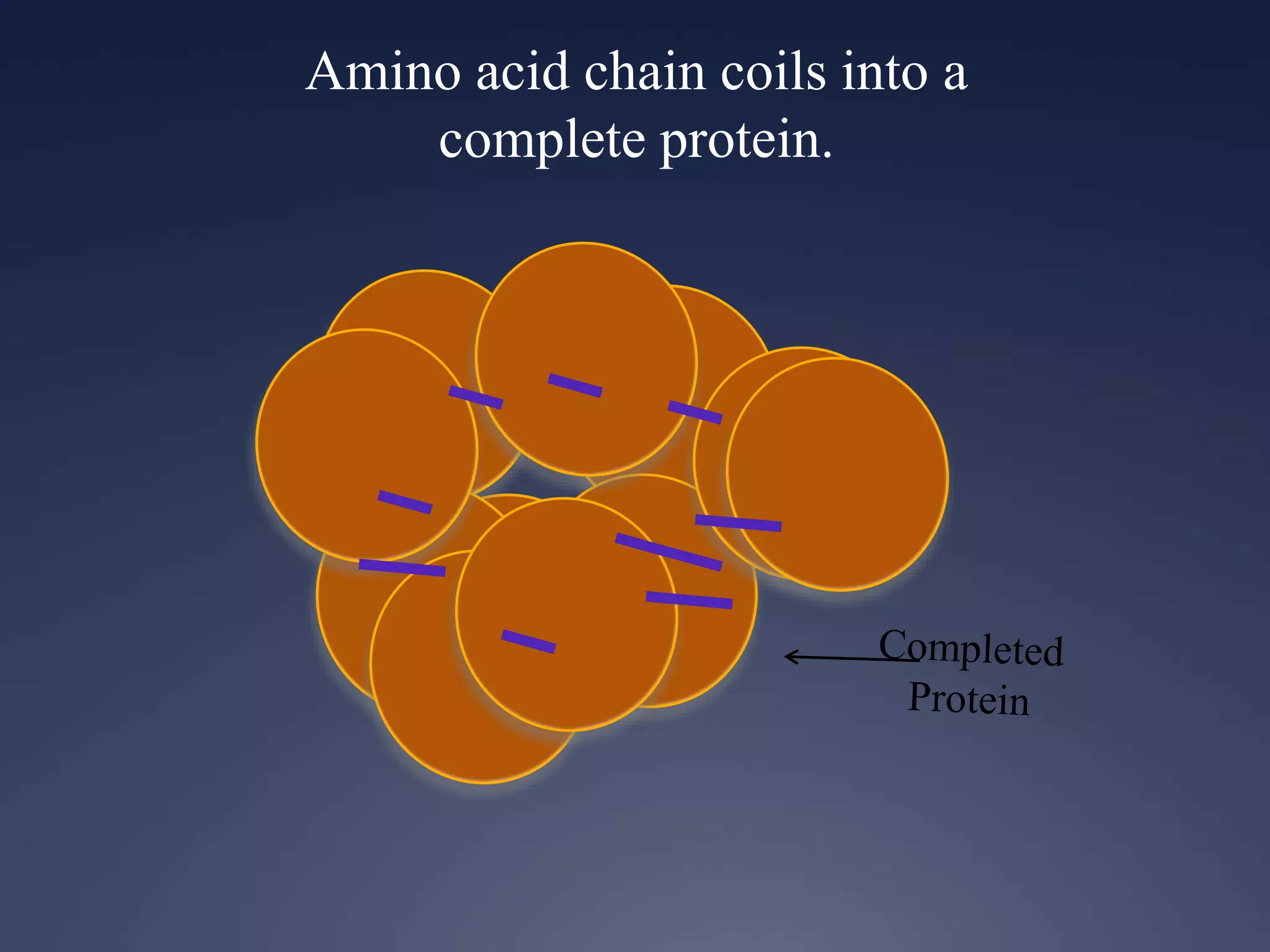
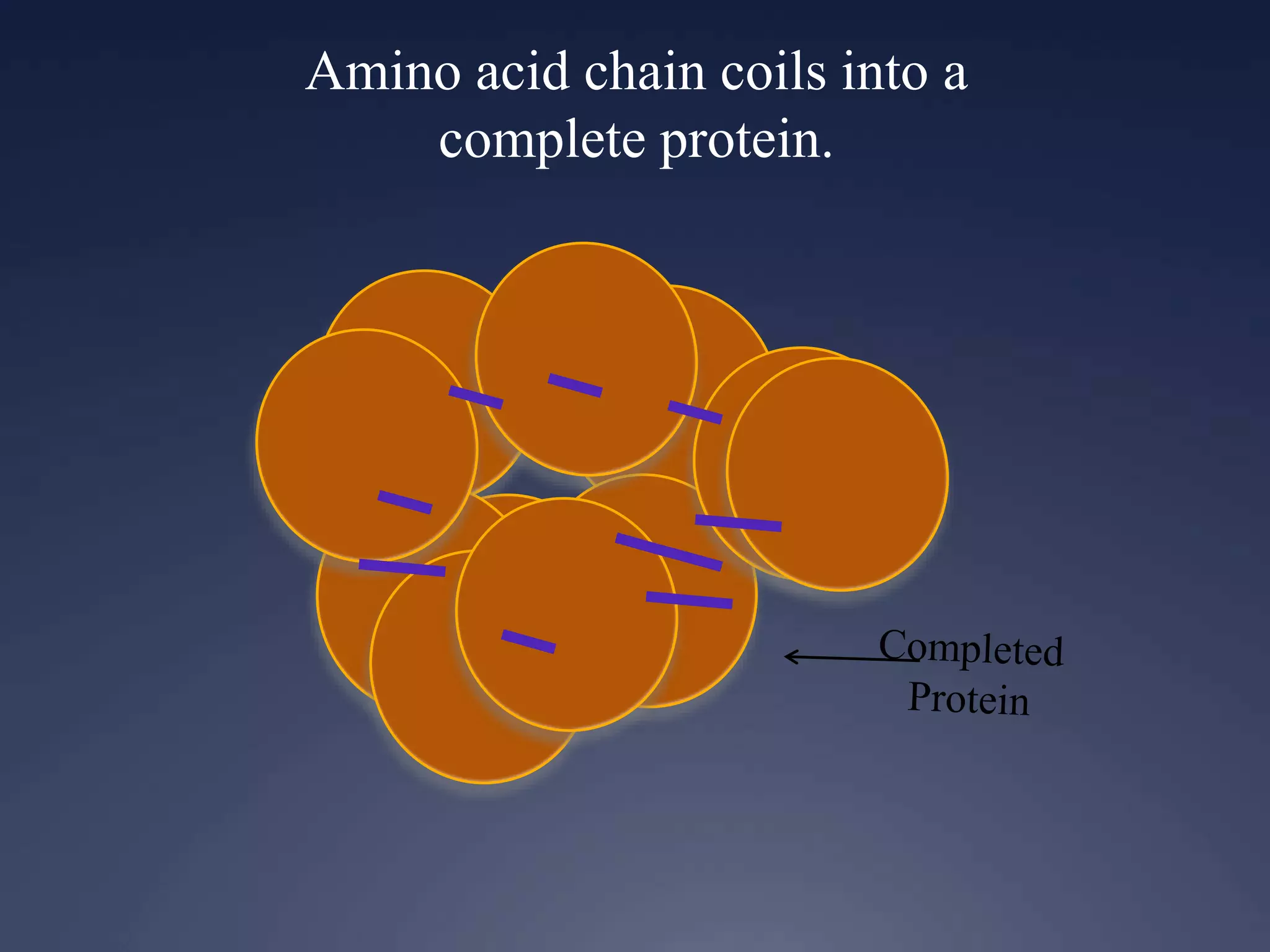
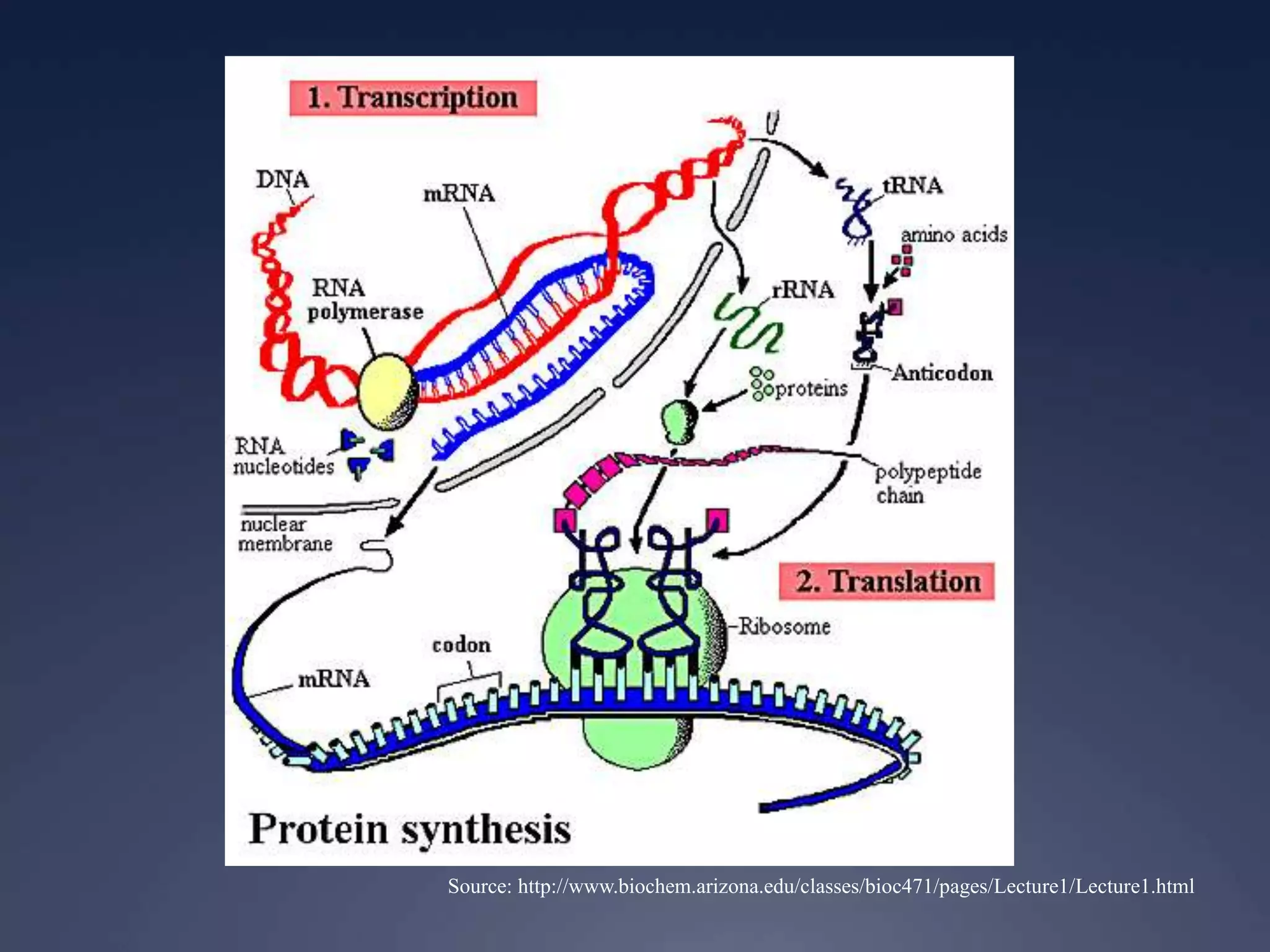
RNA is synthesized from DNA in a process called transcription. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA and separates the strands. In elongation, RNA nucleotides bind to the template DNA strand to form mRNA. In termination, hairpin loops form in the newly synthesized RNA causing transcription to stop. The primary mRNA transcript then undergoes processing where introns are removed and exons are spliced together to form the final mRNA.