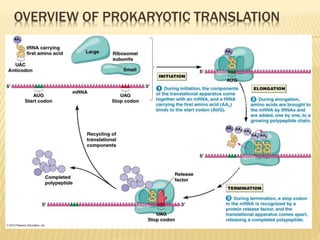
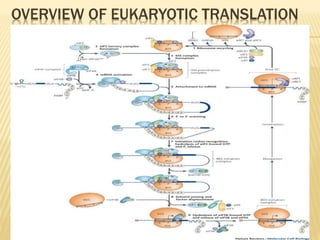
1. Translation is the process of converting the genetic code in mRNA into a protein by reading the mRNA codons in groups of three and adding the appropriate amino acids specified by tRNA.
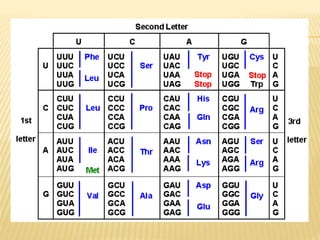
2. There are 64 possible codons made up of combinations of the 4 bases in mRNA, with 3 codons serving as stop signals. tRNA contains anticodons that pair with mRNA codons and carry the corresponding amino acid.
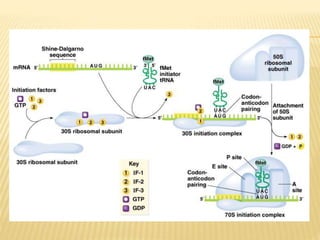
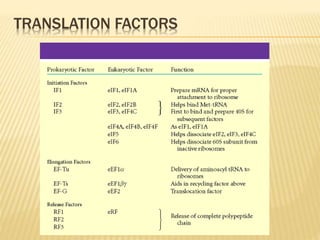
3. The basic steps of translation include initiation of protein synthesis at the start codon, elongation through sequential addition of amino acids specified by mRNA codons, and termination when a stop codon is reached.