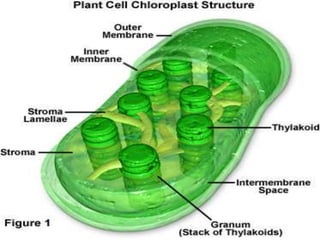
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is circular, double-stranded DNA found in chloroplasts. cpDNA ranges in size from 120-2000kb depending on the species. It contains genes that encode components of the chloroplast protein synthesis machinery like rRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal proteins. It also contains genes for photosynthesis proteins. While cpDNA was originally derived from cyanobacteria, chloroplasts have become dependent on the plant cell nucleus for many genes as cpDNA has lost much of its original genetic information over evolutionary time. Comparisons of cpDNA sequences between species has provided insights into chloroplast and plant evolutionary relationships.