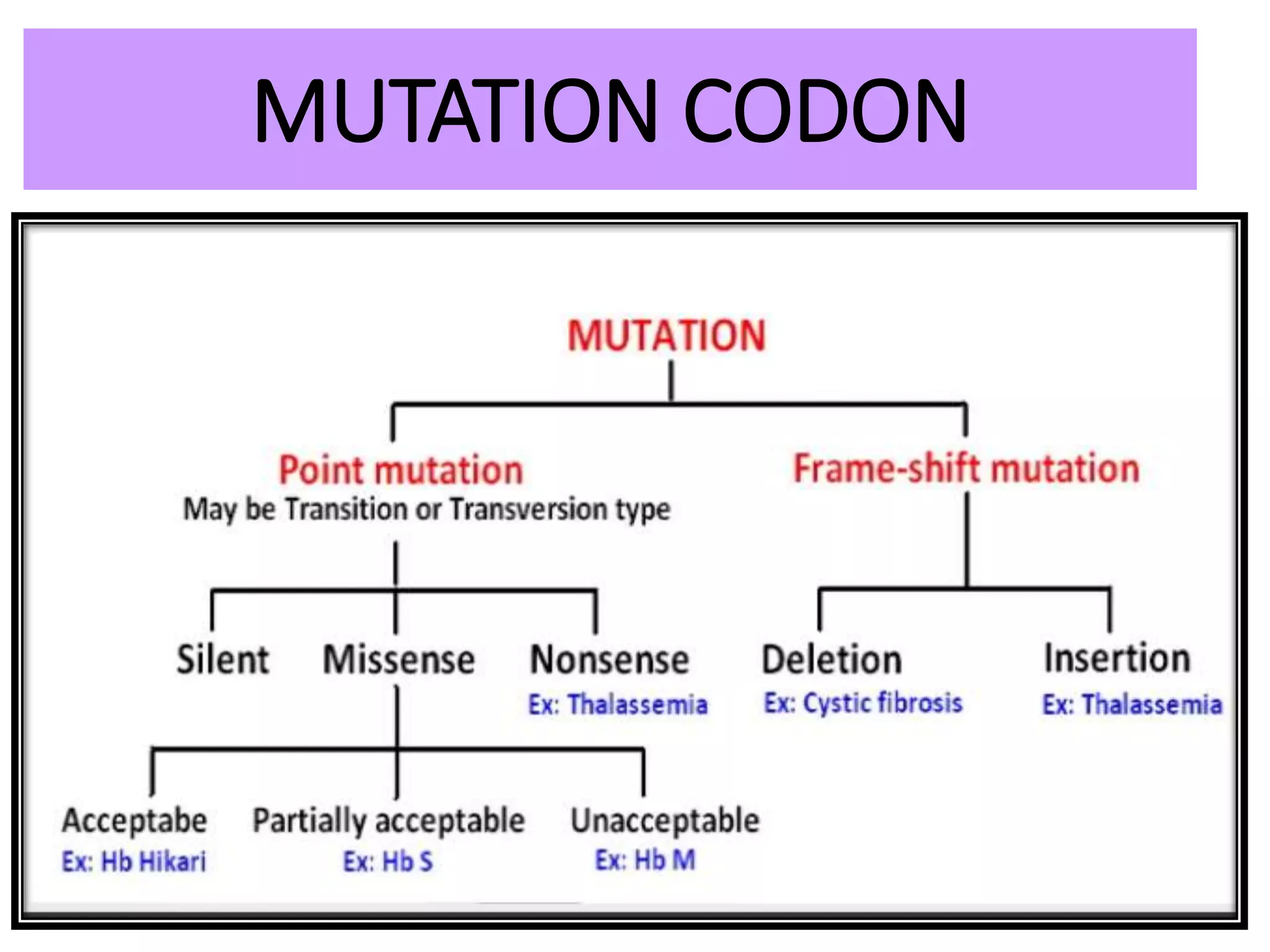
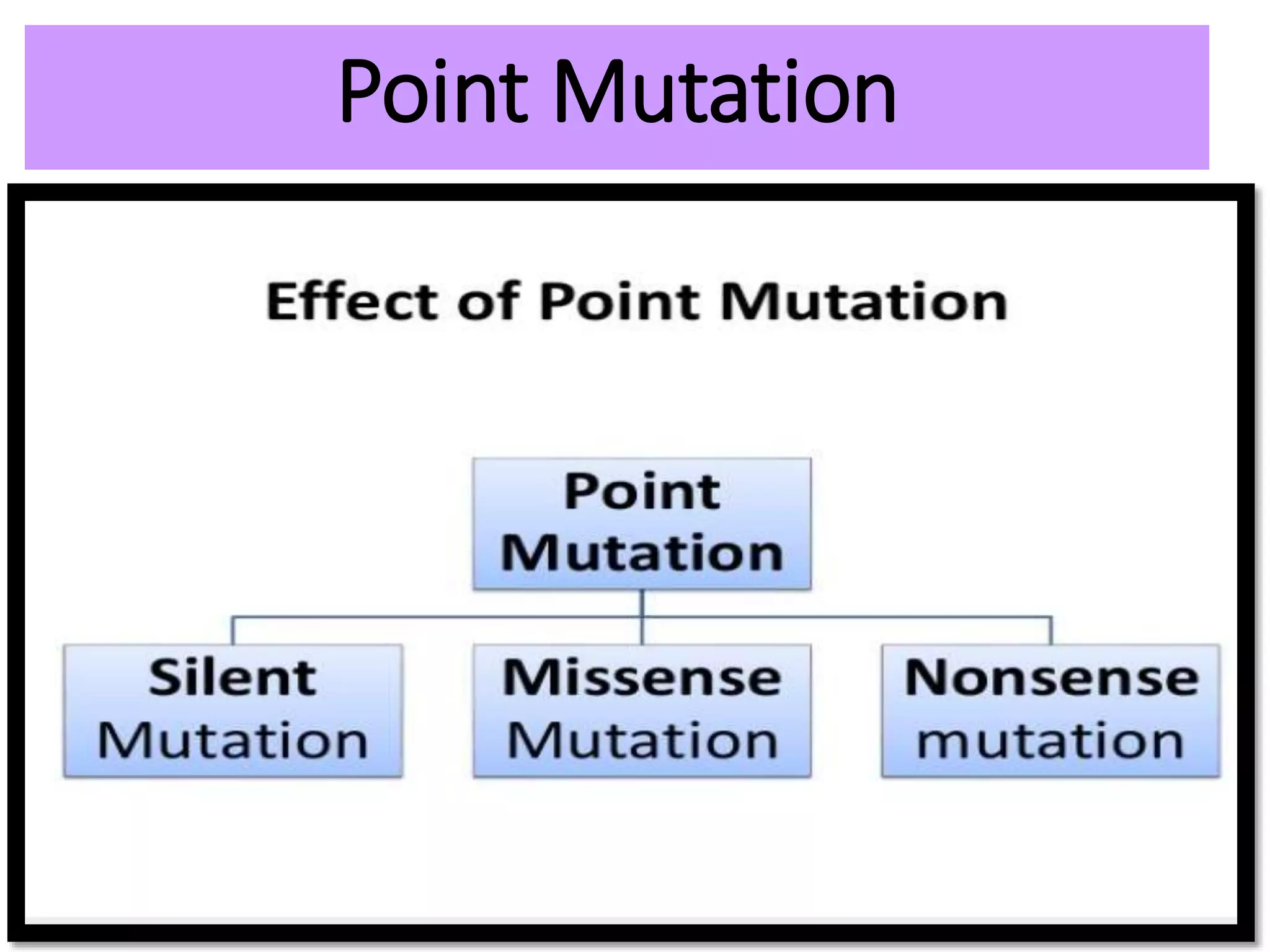
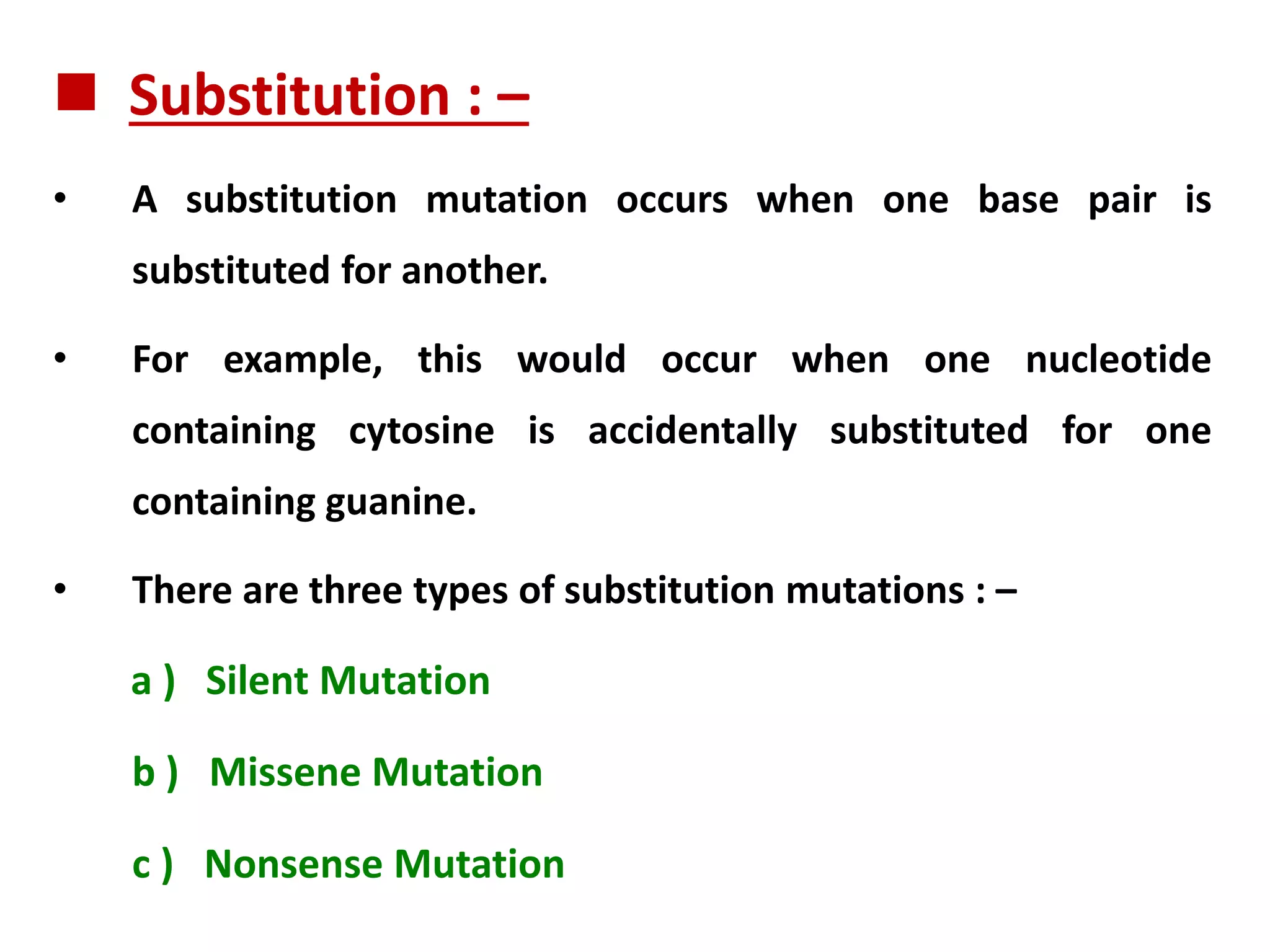
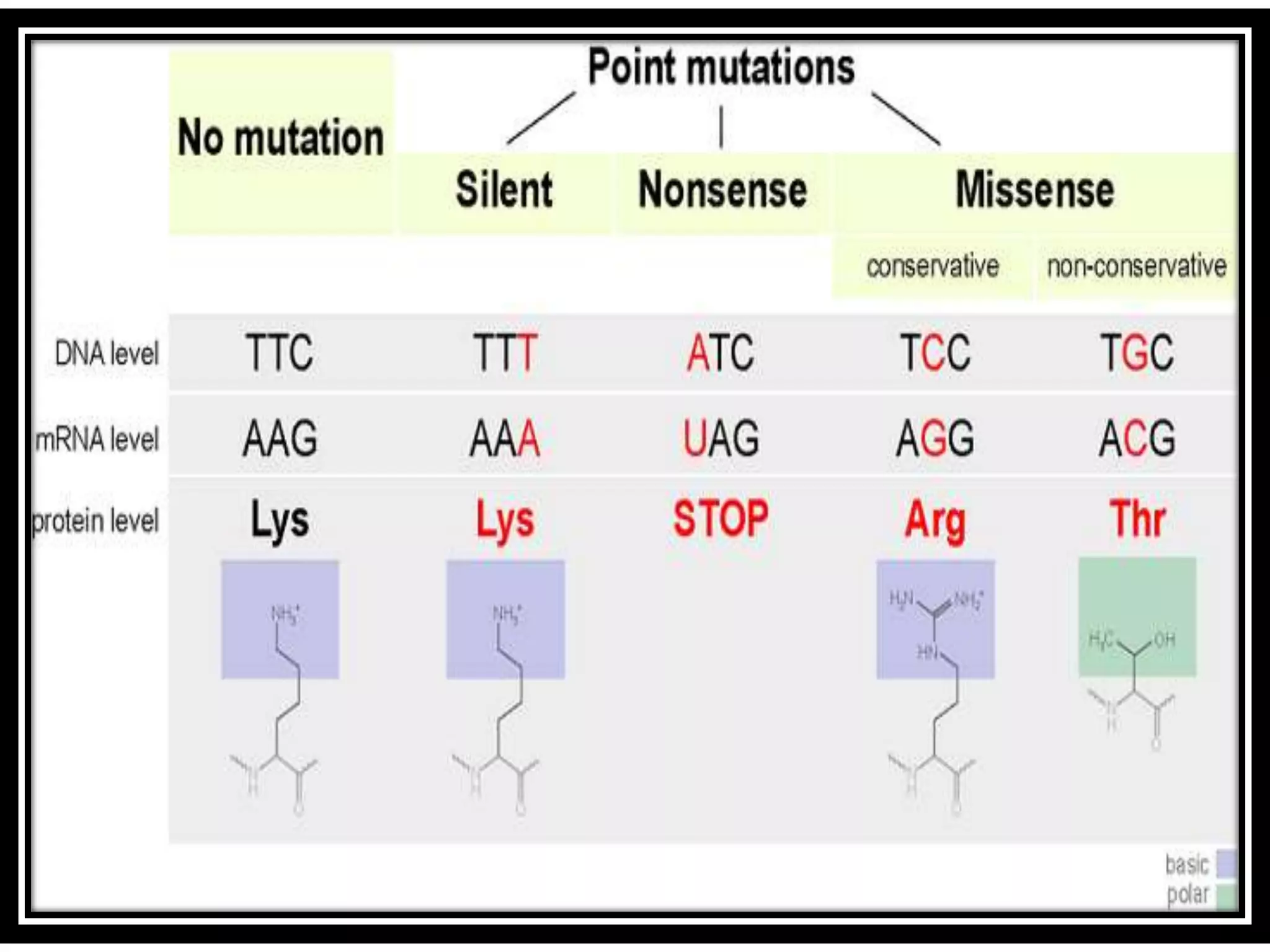
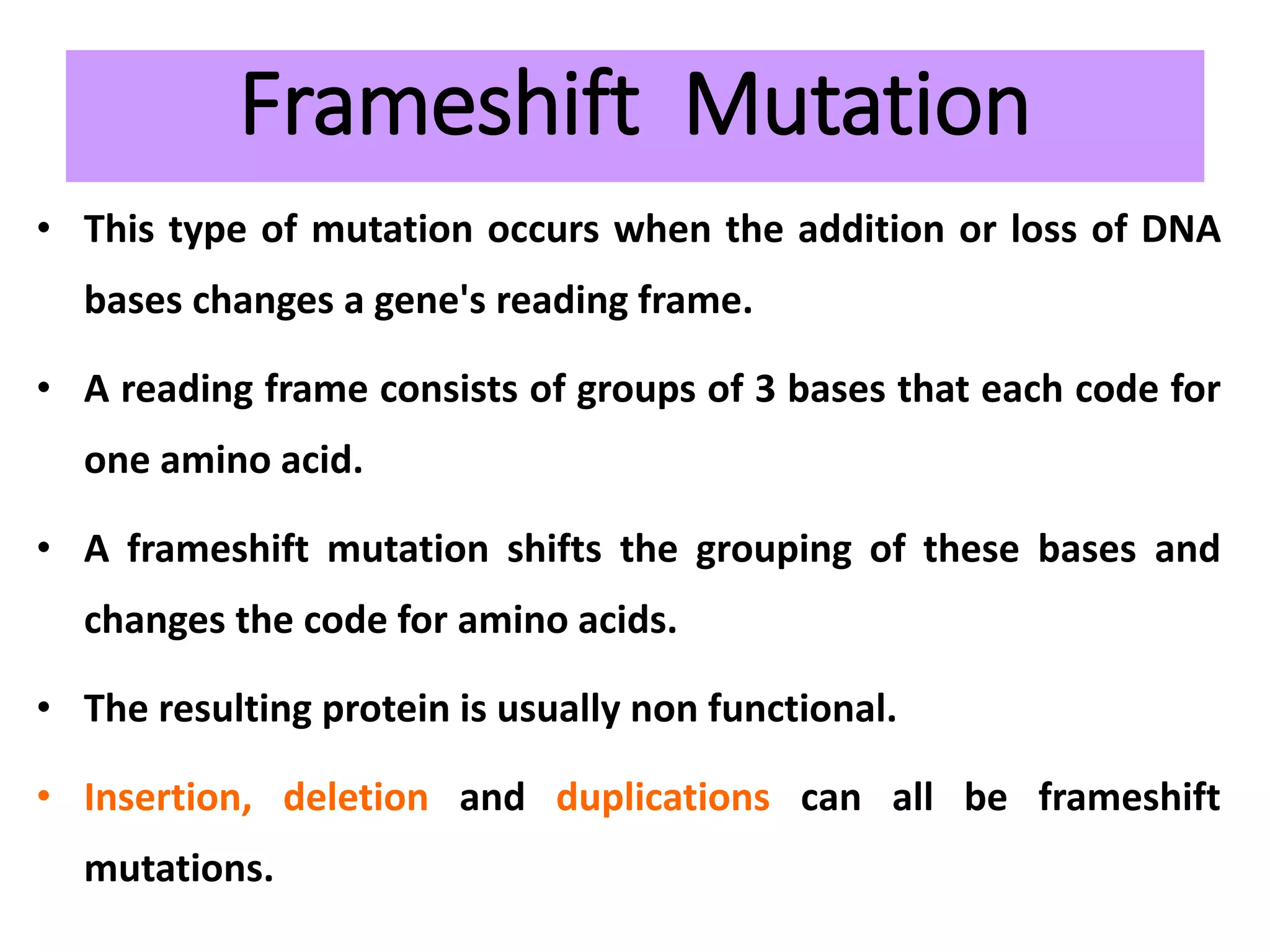
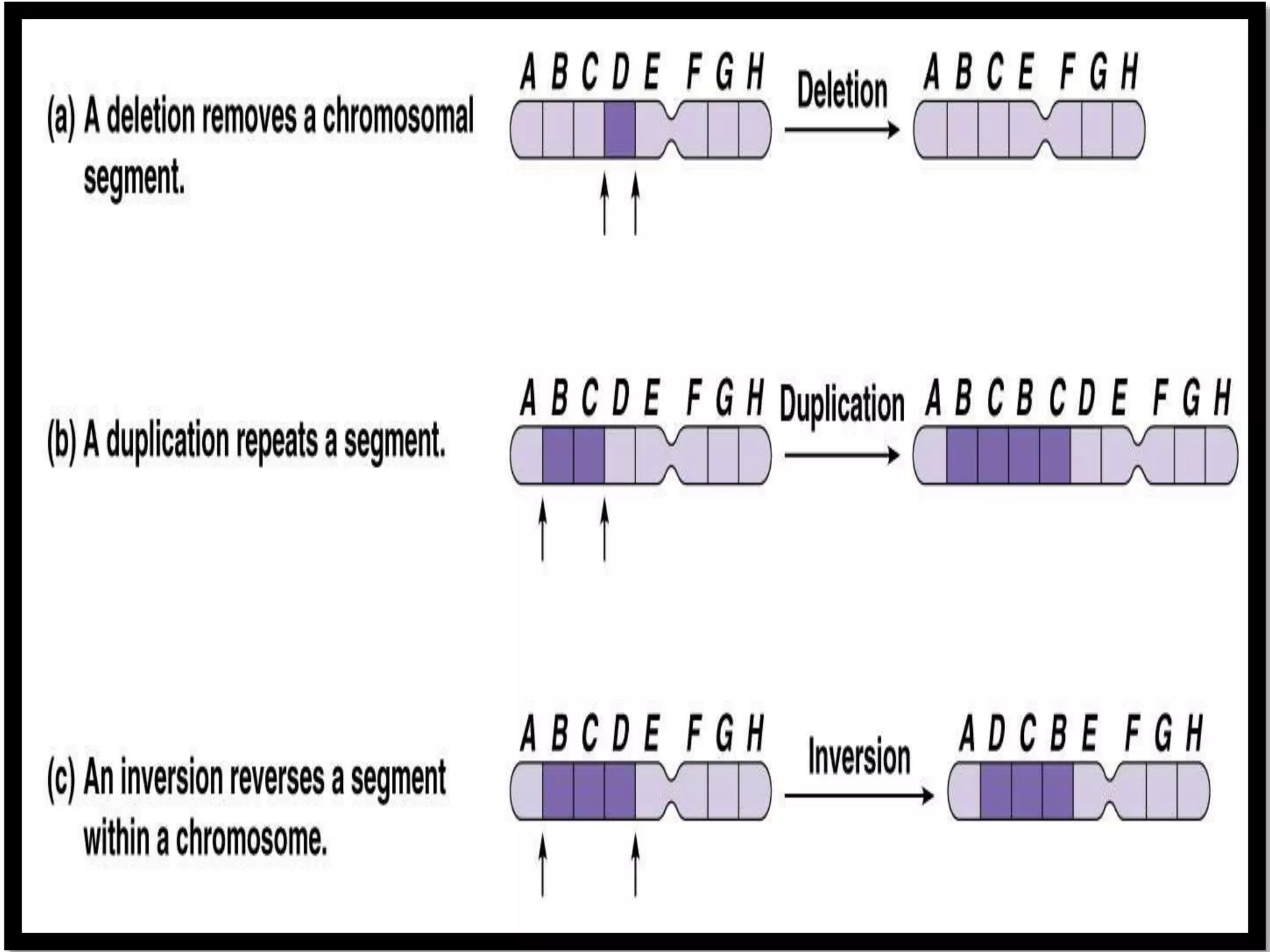
This document discusses initiation codons, termination codons, mutation codons, and the genetic code. It begins by explaining that initiation codons (usually AUG) code for methionine and signal the start of protein translation. Termination codons (UAG, UAA, UGA) do not code for amino acids and cause the release of the polypeptide chain. Point mutations include substitutions, insertions, deletions, and frameshifts that can alter the amino acid sequence. The genetic code is the set of rules by which nucleic acid sequences are translated into proteins.




![TERMINATION CODONS
• There are 3 stop codons in the genetic code – UAG, UAA, and UGA.
• These codons are also known as nonsense codons or termination
codons as they do not code for an amino acid.
• The three stop codons have been named as amber [ UAG ] , opal or
umber [ UGA ] and ochre [ UAA].
• Amber or UAG was discovered by Charles Steinberg and Richard
Epstein and they named it amber after the German meaning of the
last name of their friend Harris Bernstein.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/initiationandterminationcodonsmutationandgeneticcode-181113063456/75/Initiation-and-termination-codons-mutation-and-genetic-code-8-2048.jpg)