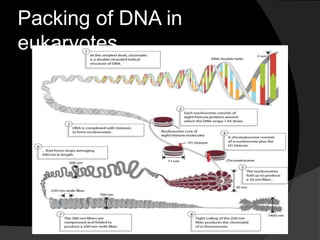
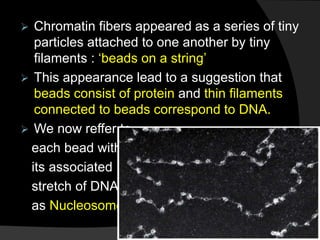
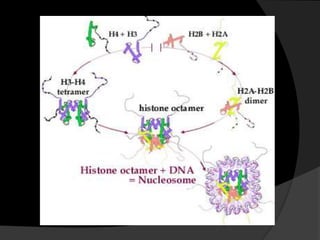
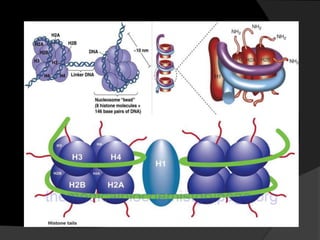
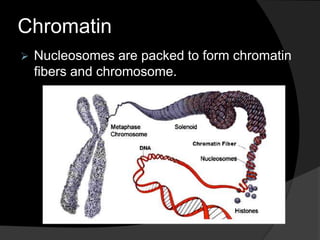
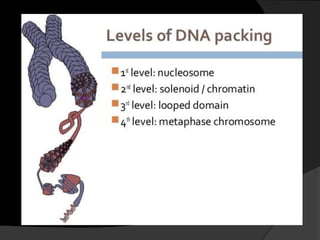
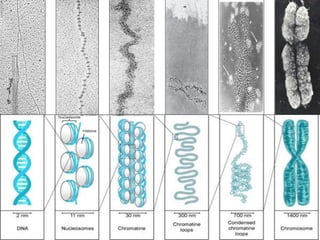
This document discusses how DNA is packaged in eukaryotic cells through the formation of nucleosomes and chromatin. It explains that DNA must be highly condensed to fit inside the nucleus. This is achieved through the wrapping of DNA around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which are further compacted into chromatin fibers and then chromosomes. Key points covered include the composition and structure of nucleosomes, the types and organization of histone proteins, and how successive levels of DNA compaction allow for enormous lengths of DNA to be compactly stored within the cell.