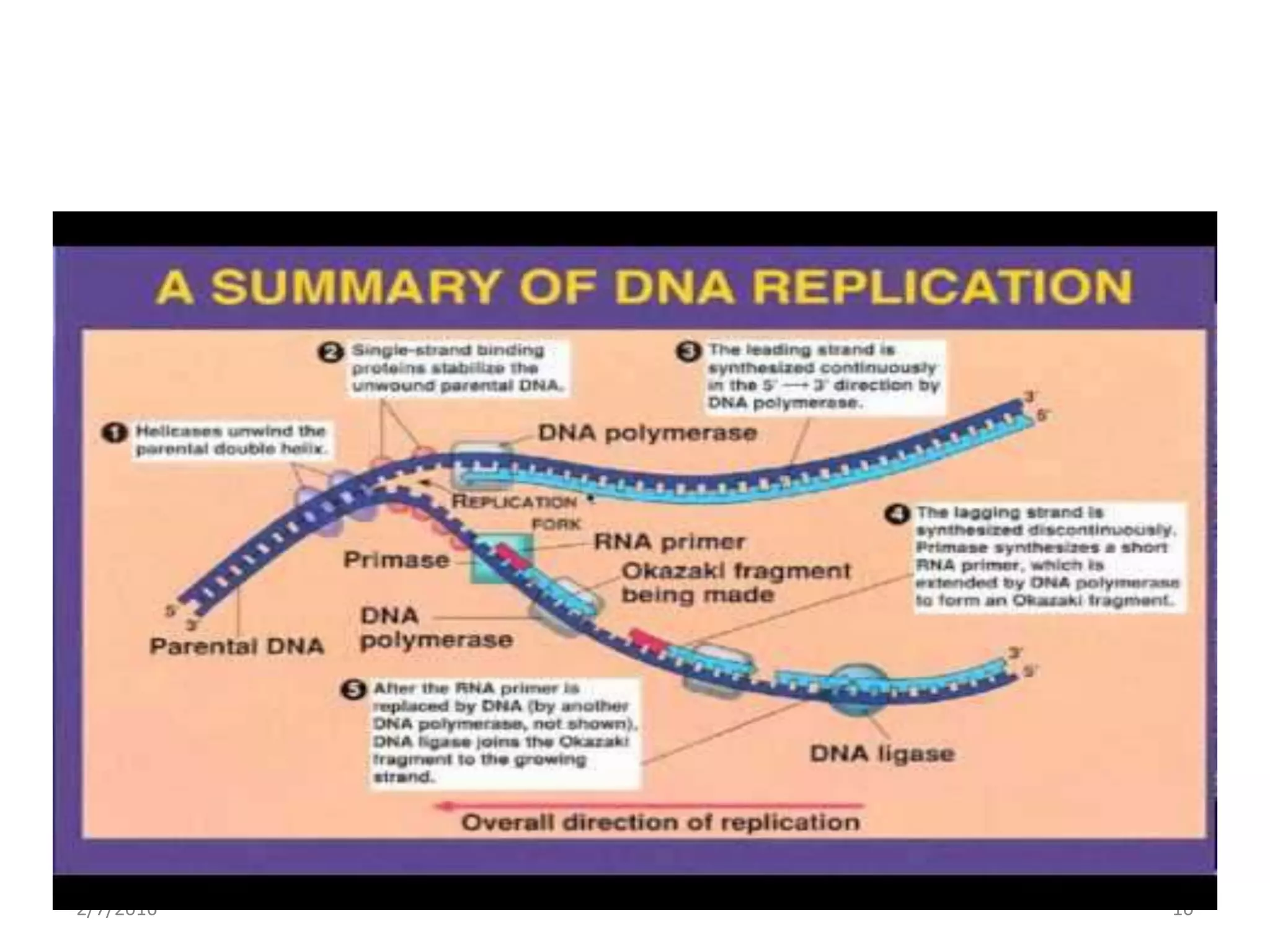
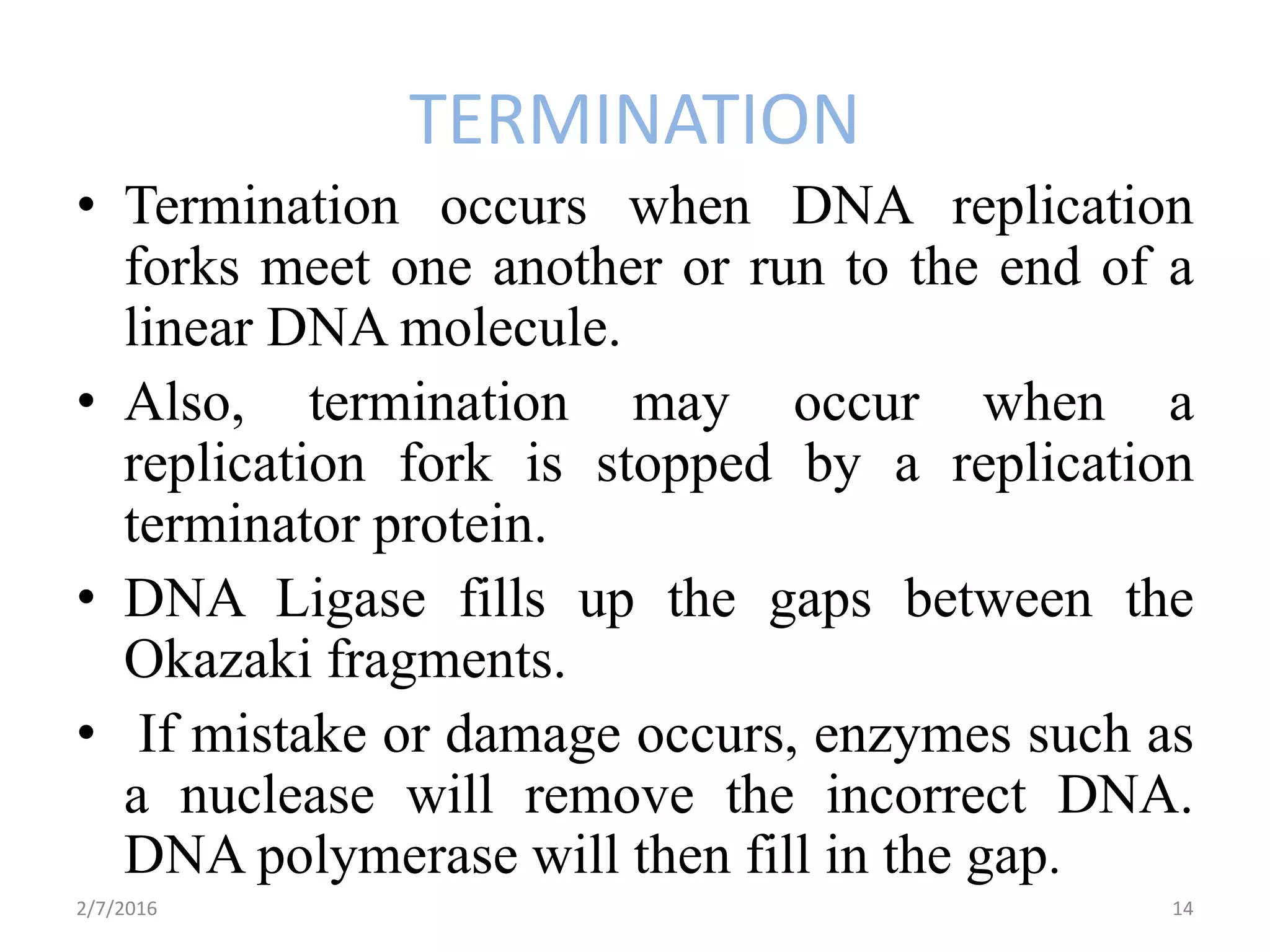
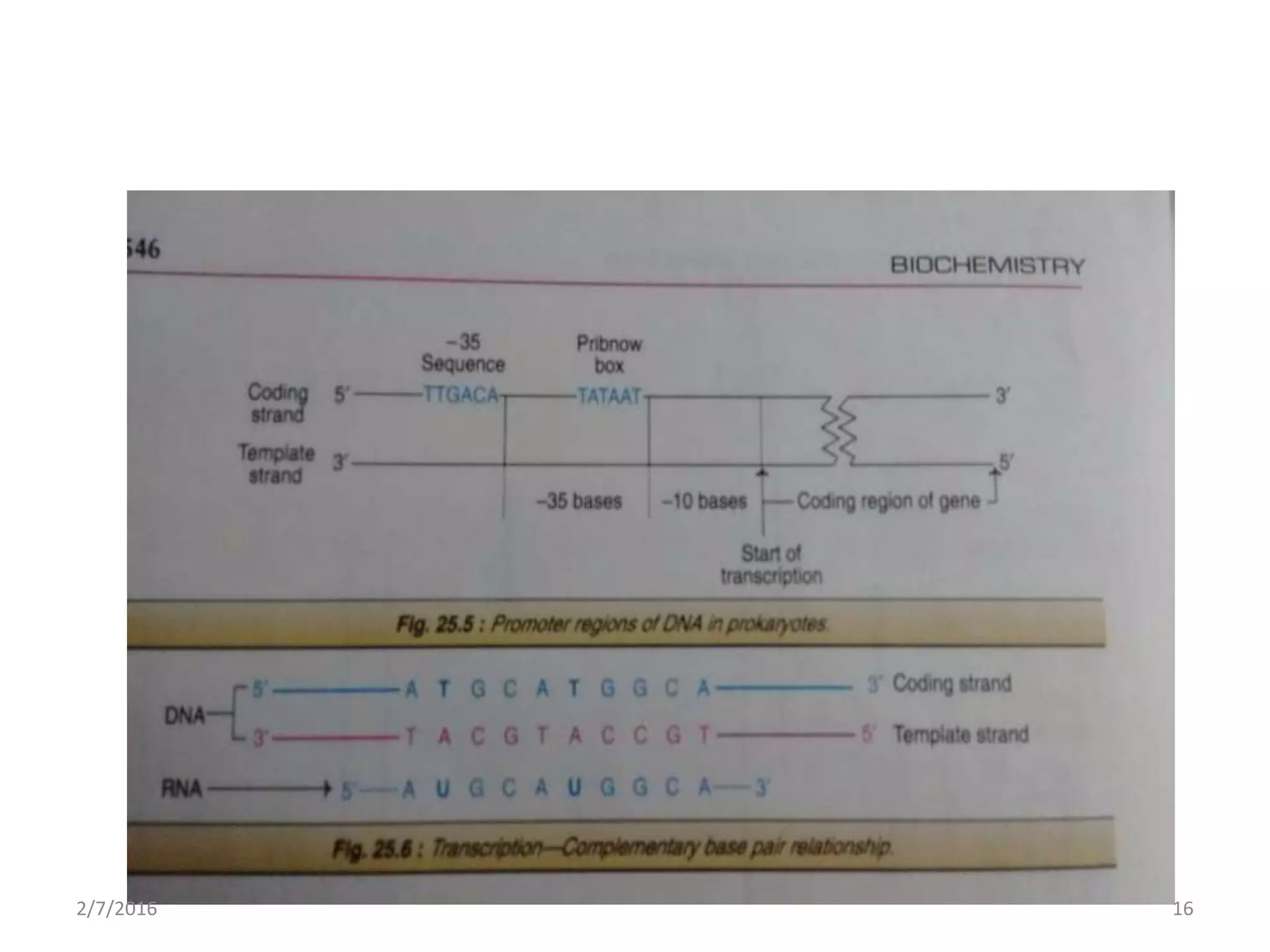
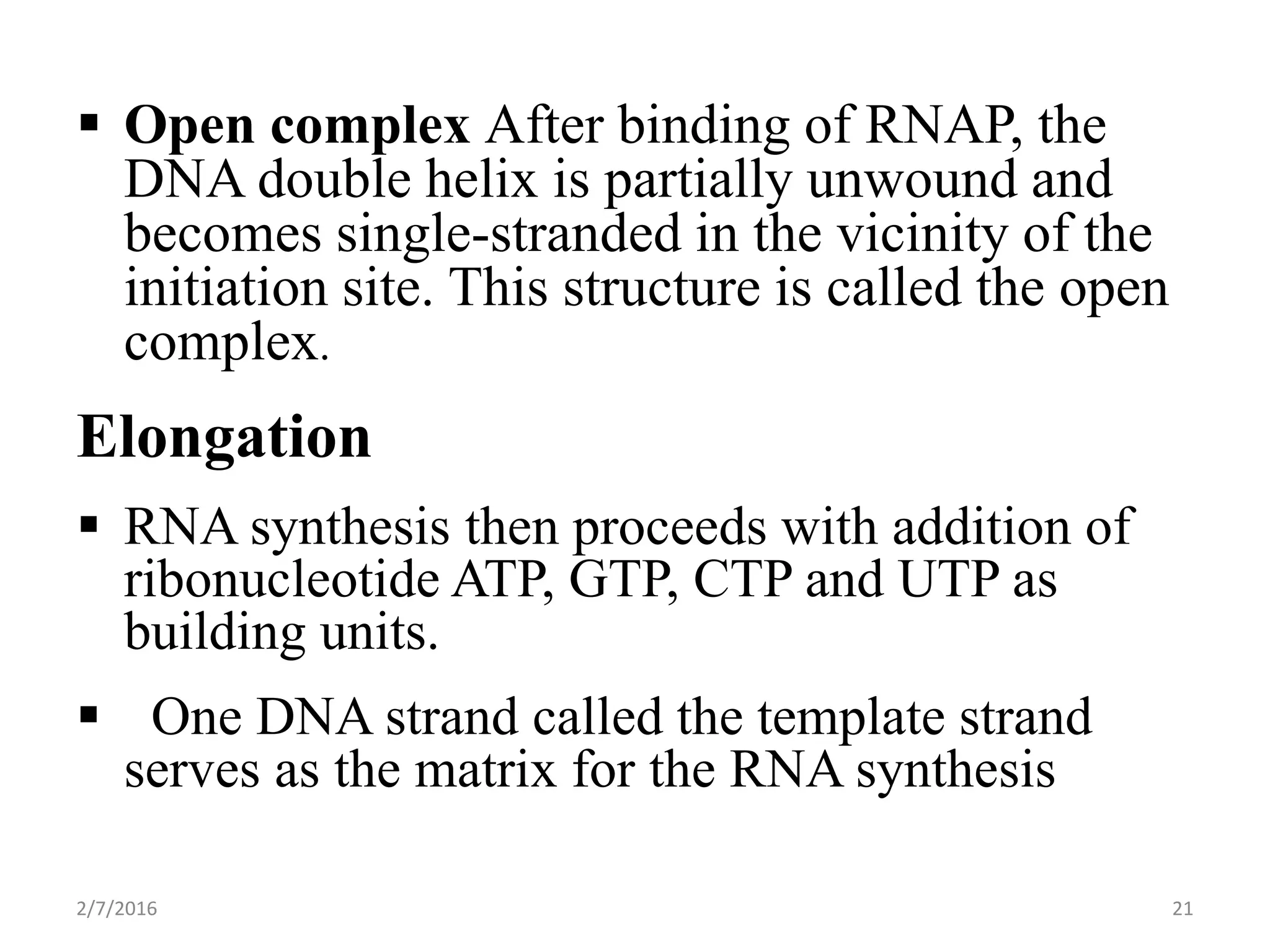
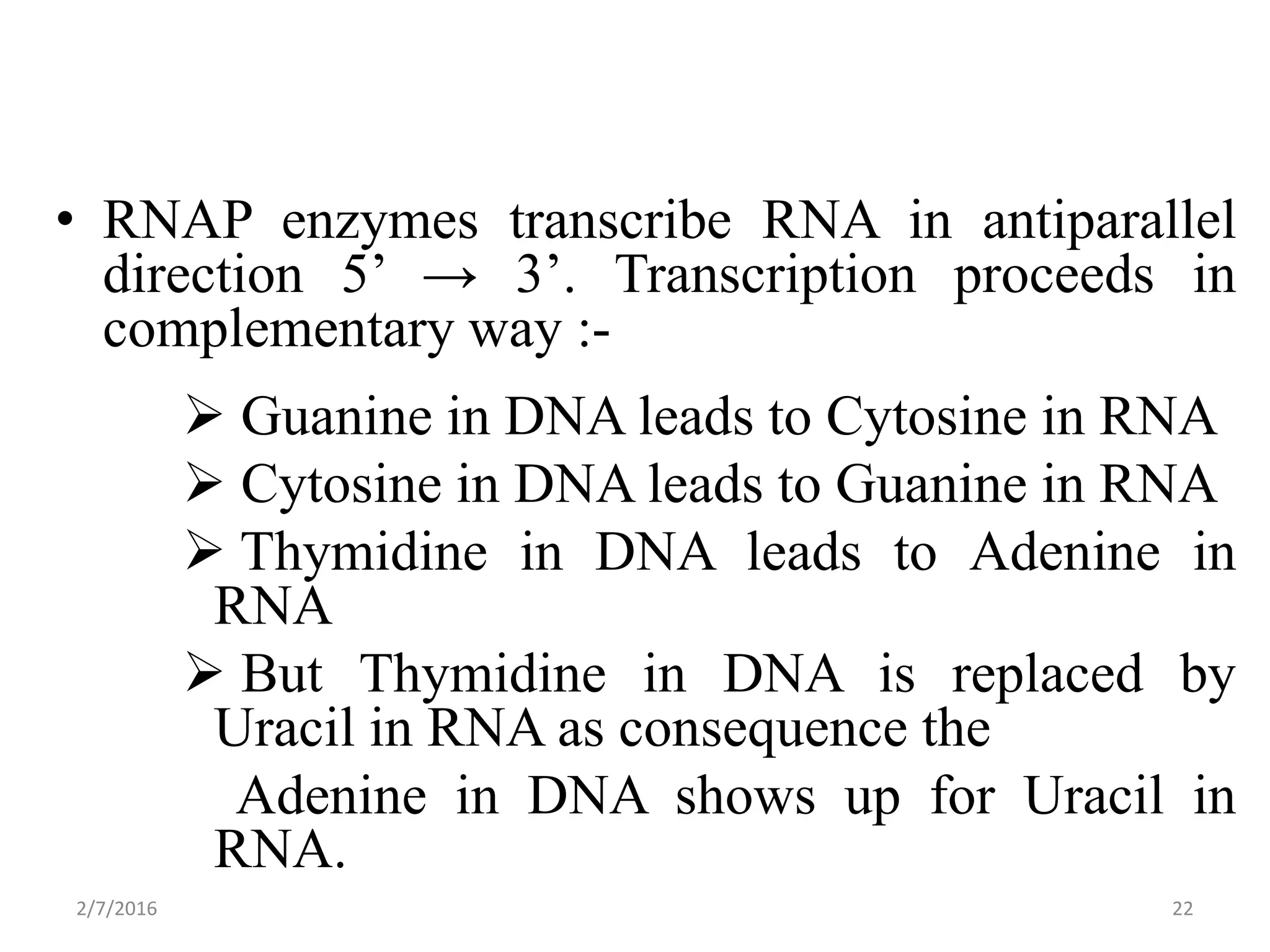
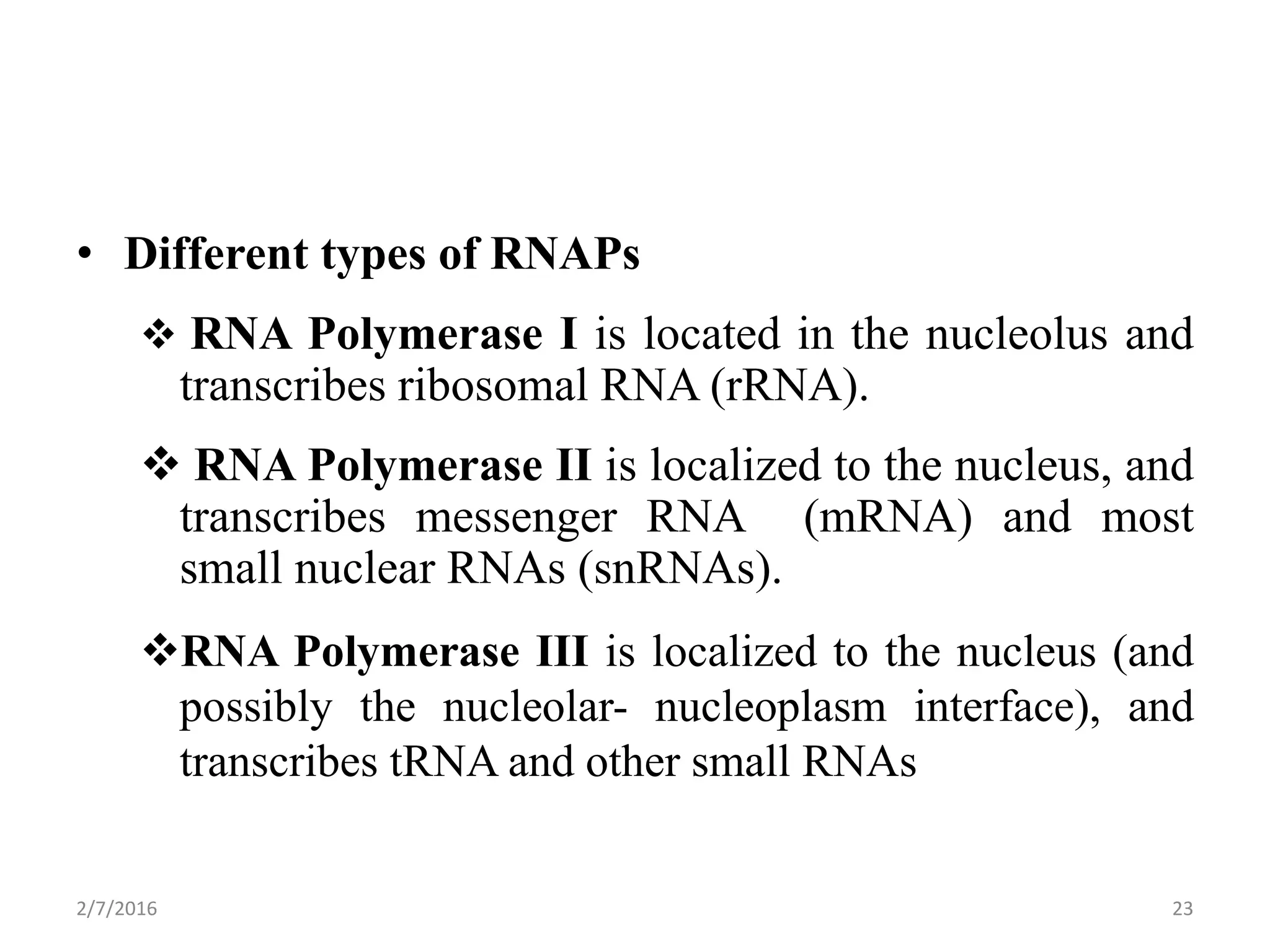
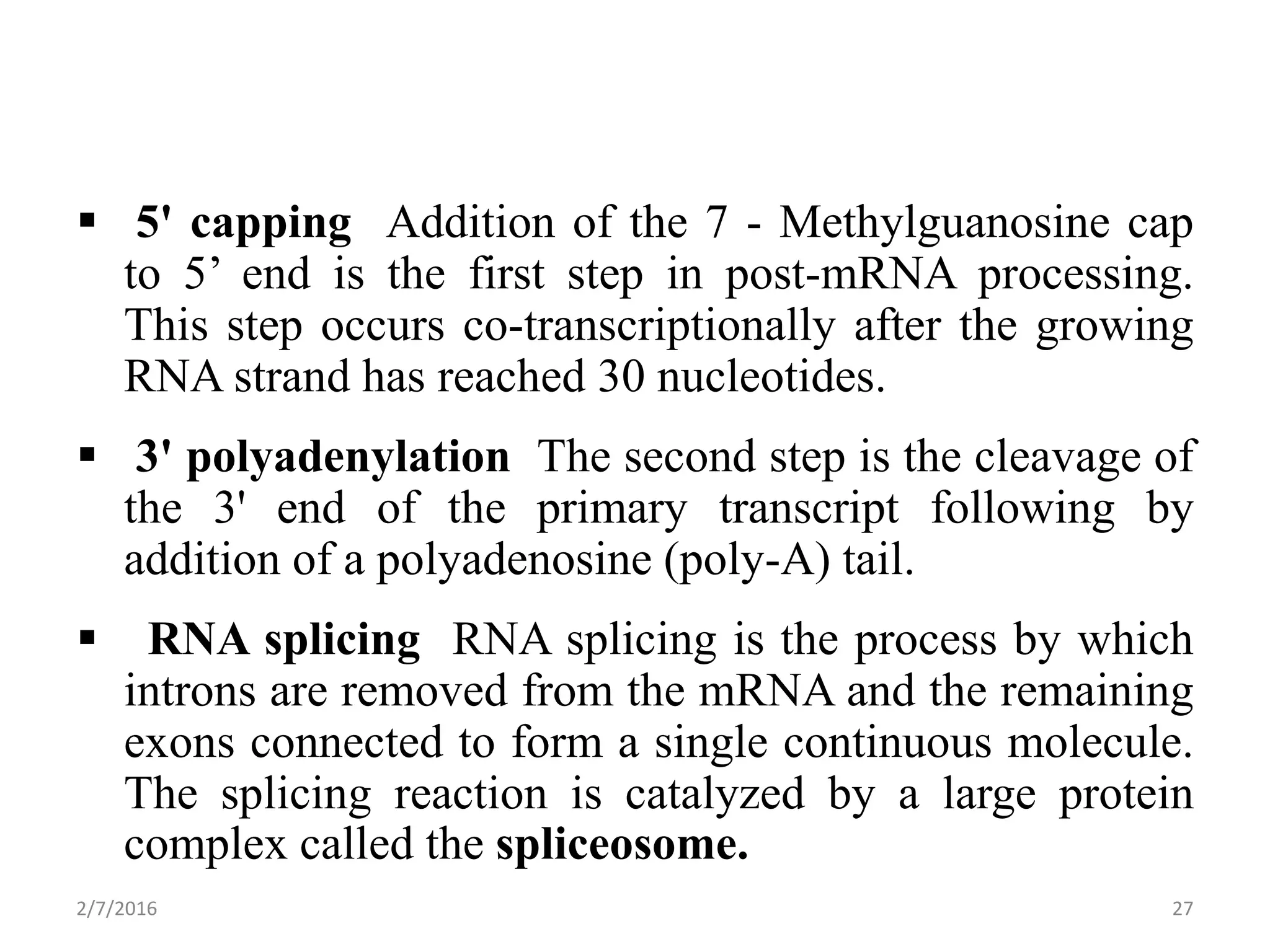
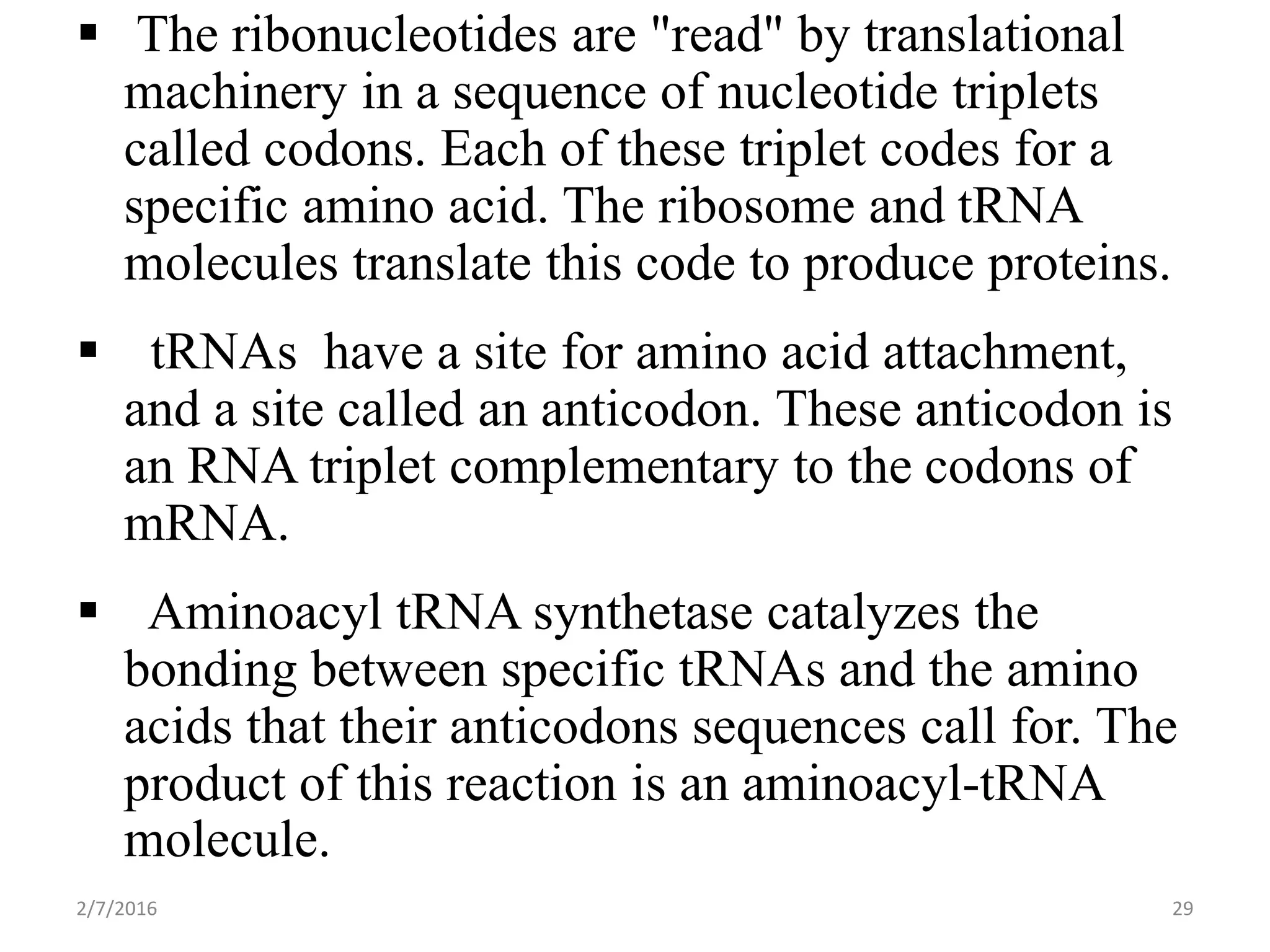
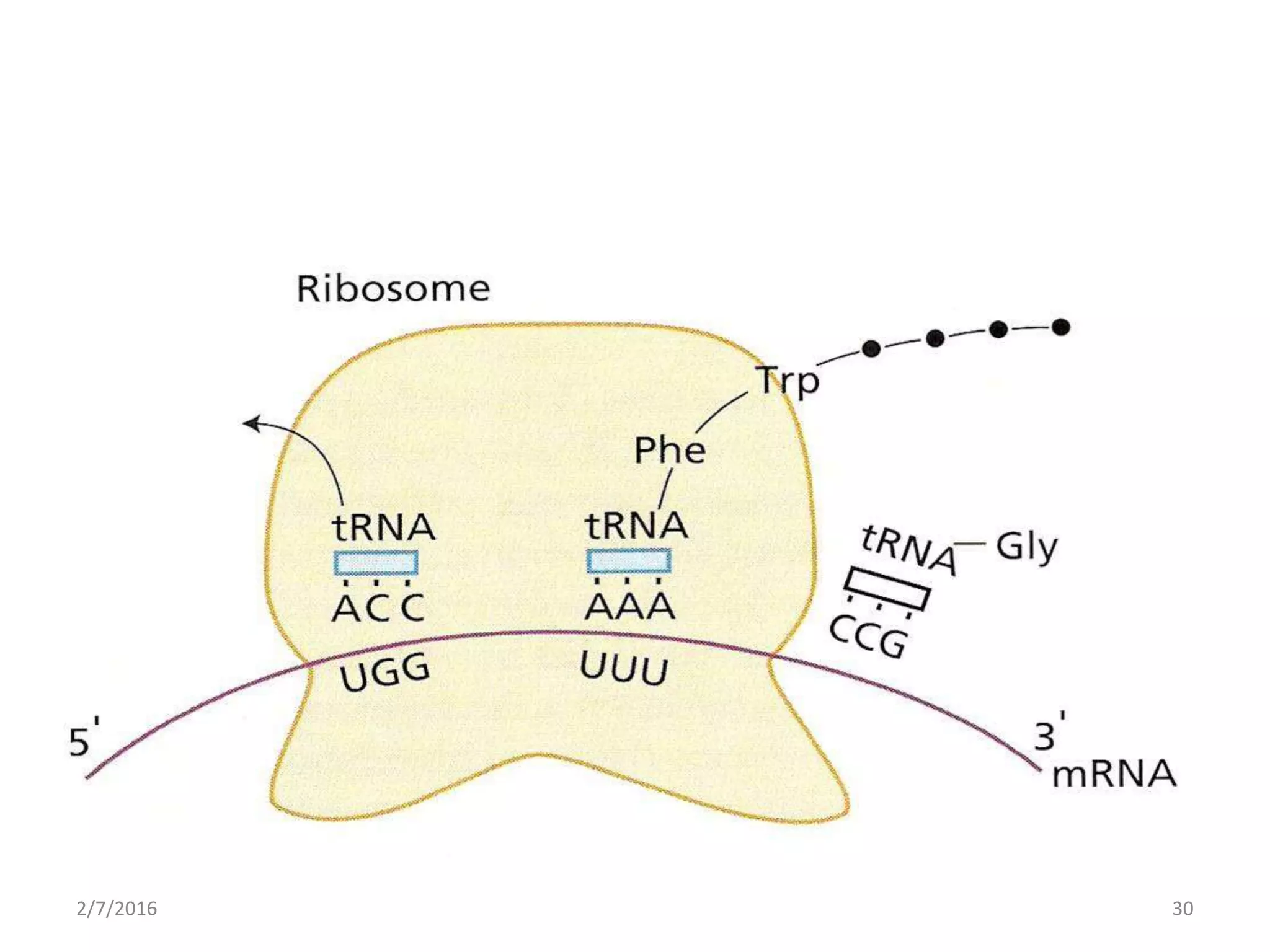
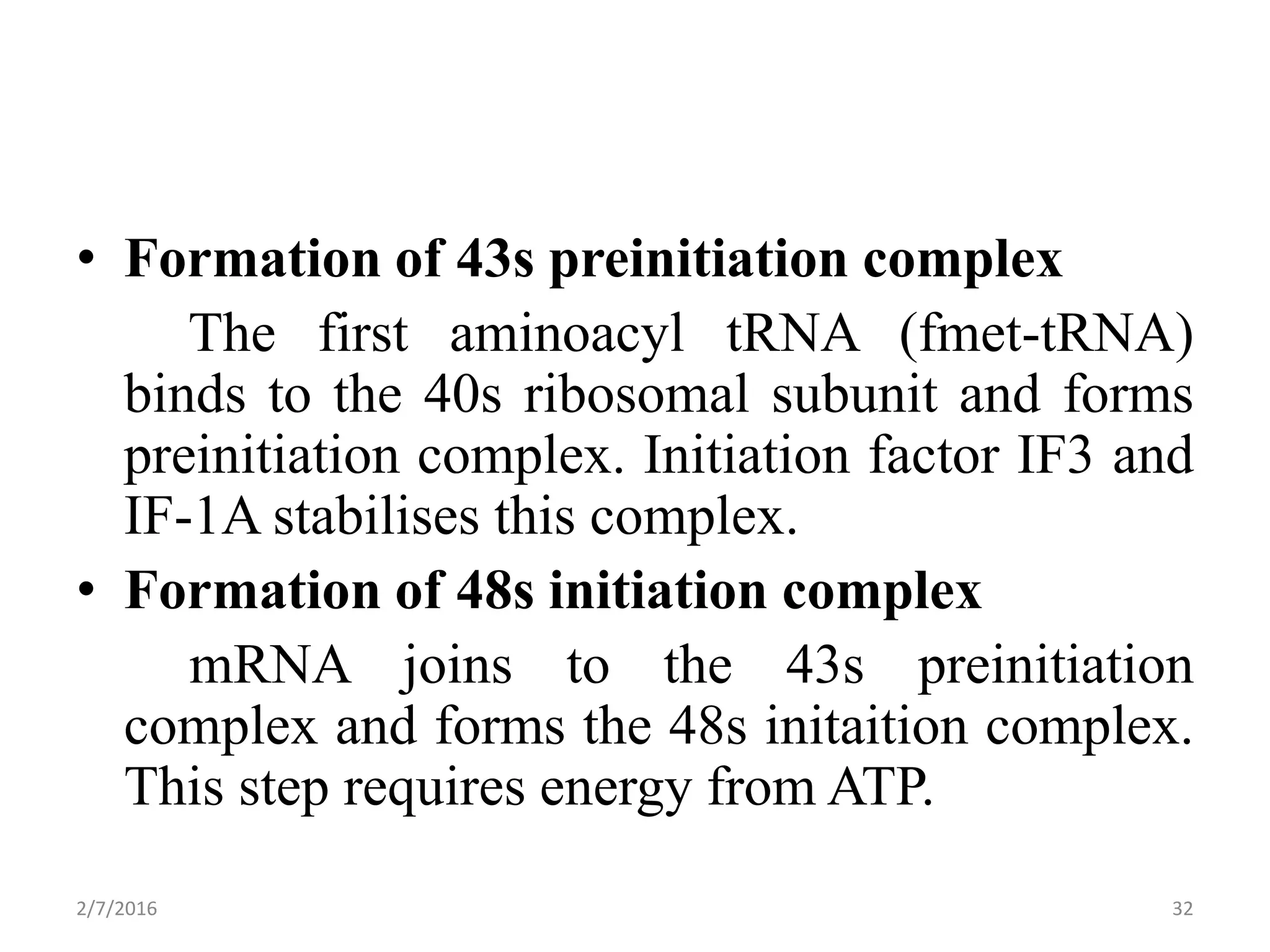
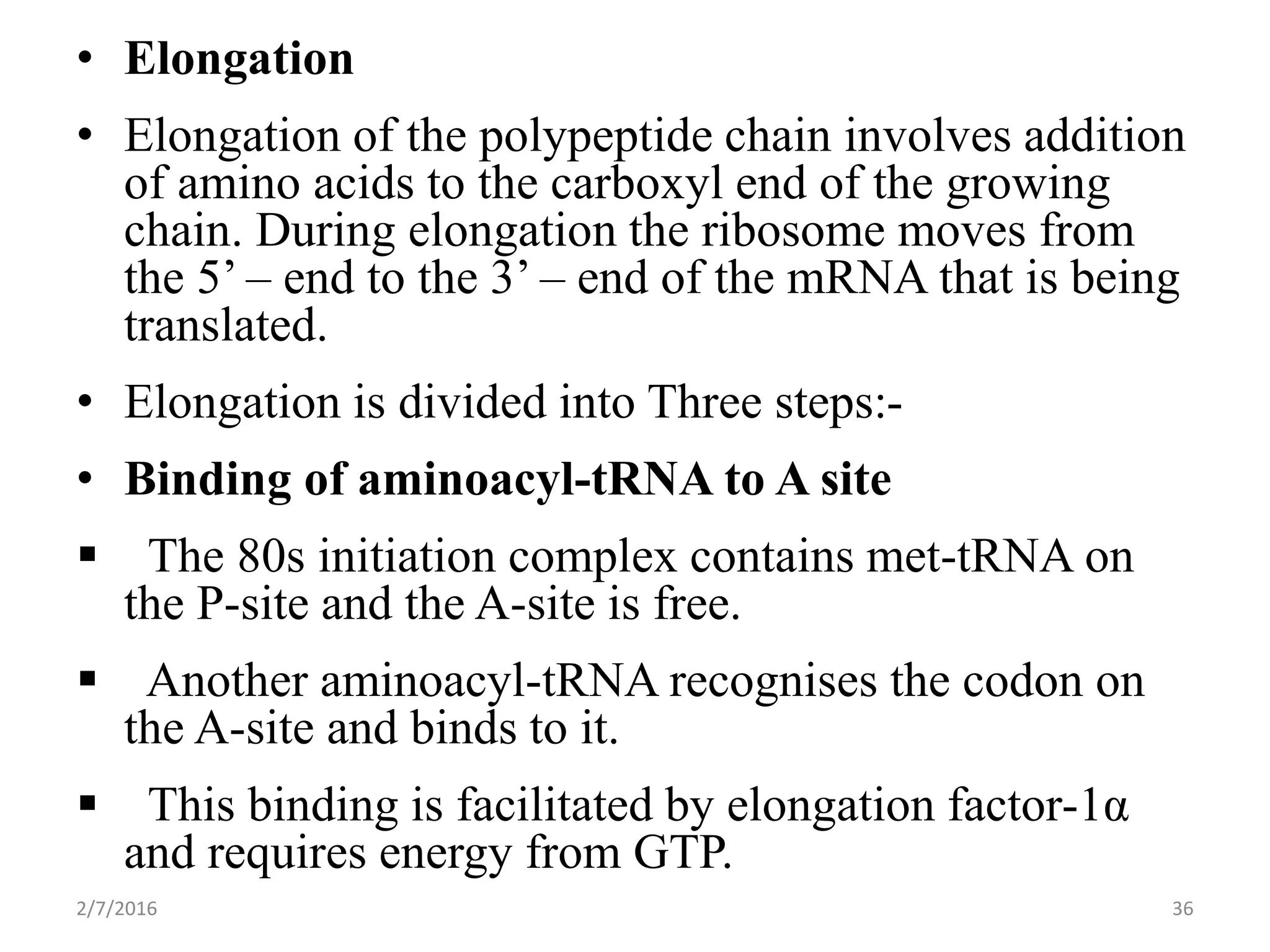
Gene expression is the process by which genetic information encoded in DNA is converted into structures and functions within cells. It involves three main steps: replication, transcription, and translation. Replication copies DNA to produce identical daughter molecules. Transcription converts the DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA). Translation then uses the mRNA to produce proteins through the joining of amino acids specified by the mRNA's codon sequence. These three steps together allow genetic information to direct the production of the RNA and protein molecules that drive cellular functions and inheritance of traits.