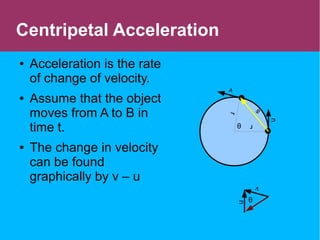
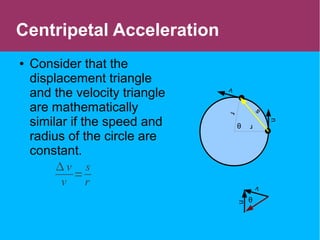
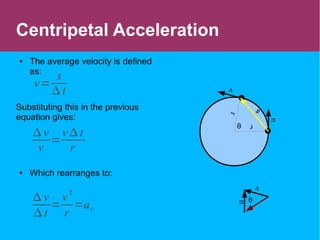
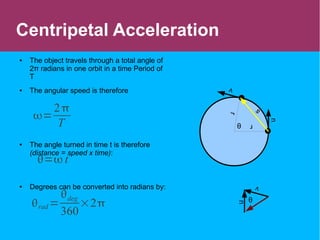
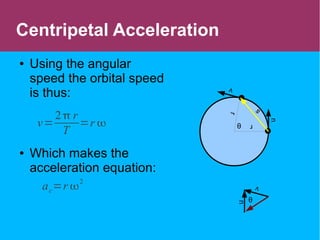
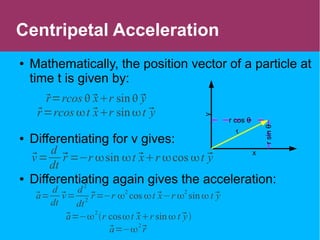
This document discusses circular motion and centripetal acceleration. It defines centripetal acceleration as the acceleration an object experiences when moving in a circular path, which causes a change in the direction of motion towards the center of the circle. The document provides equations for centripetal acceleration, relating it to the object's velocity, radius of the circular path, and angular speed. Examples are given of forces that provide centripetal acceleration, such as gravity keeping the moon in orbit or friction keeping cars from slipping outward while turning.