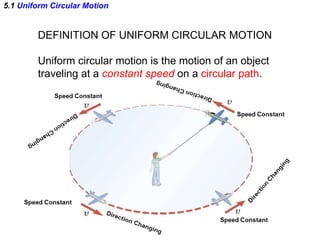
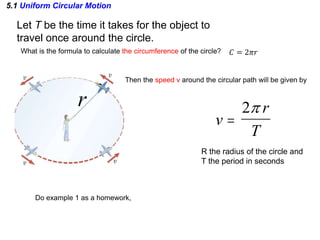
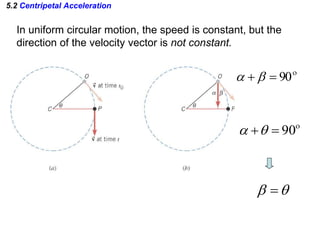
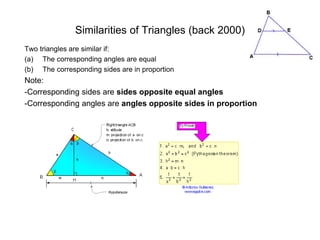
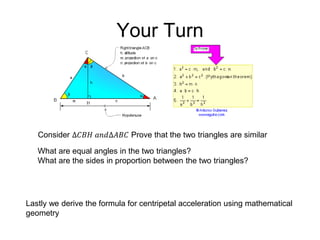
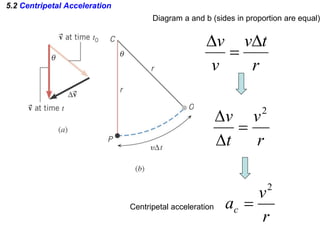
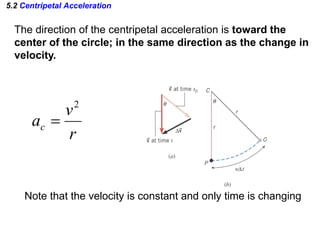
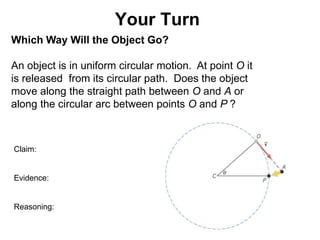
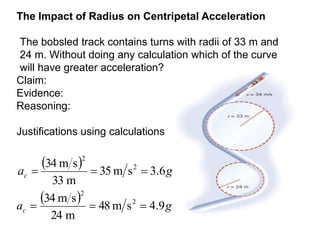
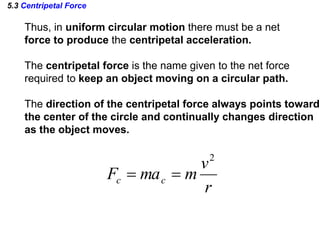
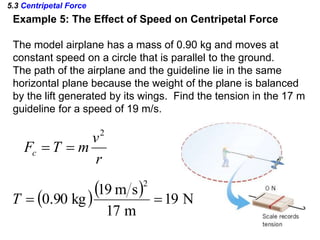
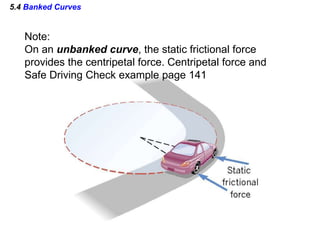
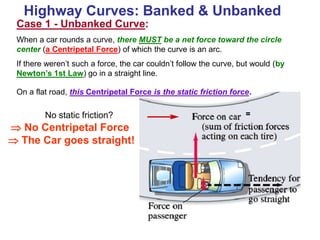
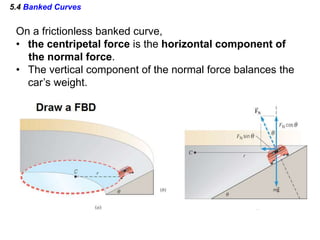
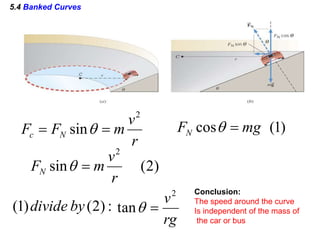
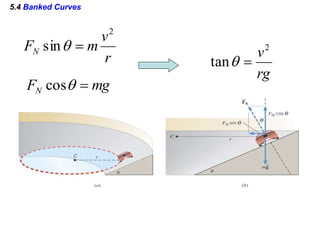
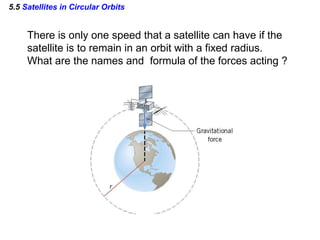
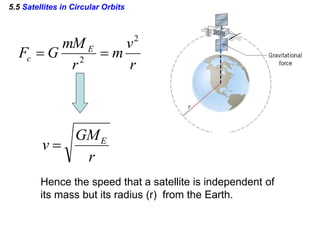
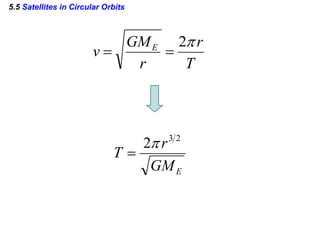
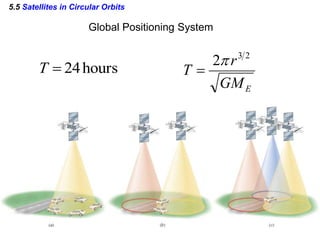
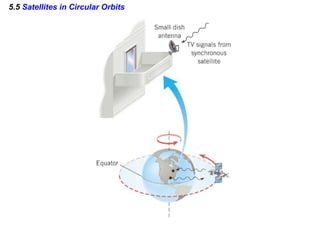
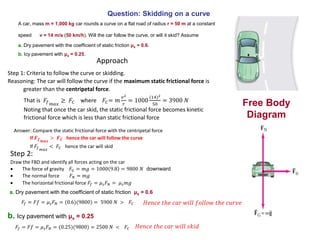
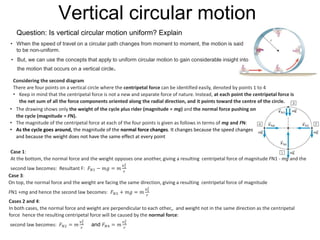
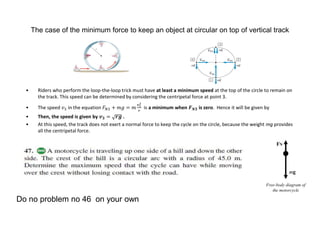
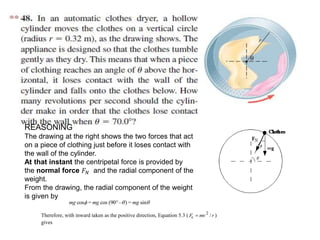
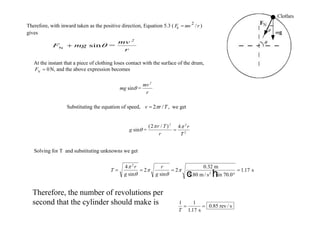
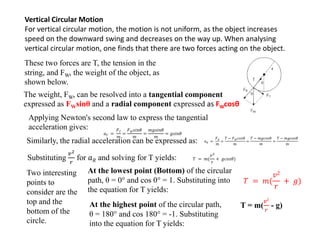
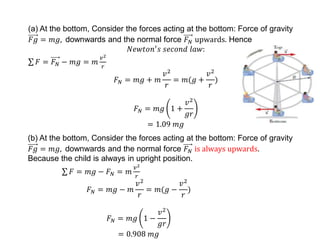
This document discusses uniform circular motion and related concepts. It begins by defining uniform circular motion as motion at constant speed in a circular path. It then derives the formula for centripetal acceleration and explains that a centripetal force is needed to provide the acceleration toward the center required for circular motion. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating centripetal force for different objects in circular motion, including effects of speed and radius. The document also discusses banked curves and satellites in circular orbits, providing the relevant equations and example calculations.