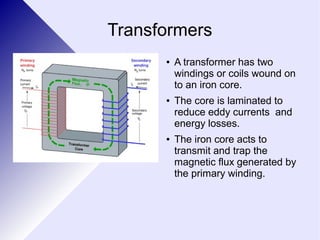
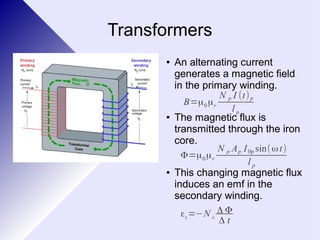
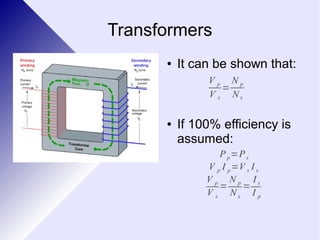
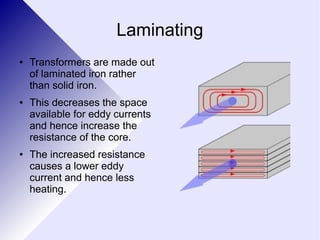
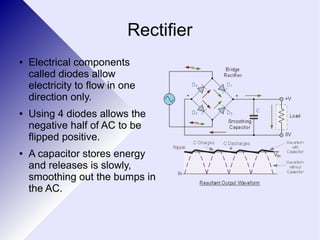
Transformers are electrical devices that convert alternating current from one voltage to another by using two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core. Transformers that step up voltage increase it, while transformers that step down voltage decrease it. They work by generating a changing magnetic field in the primary coil using AC power, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of turns between the two coils determines the ratio of voltages out and in. While efficient, transformers have some energy losses through eddy currents in the core and resistance in the windings. They are widely used to adjust voltages for transmission on power grids and in devices.