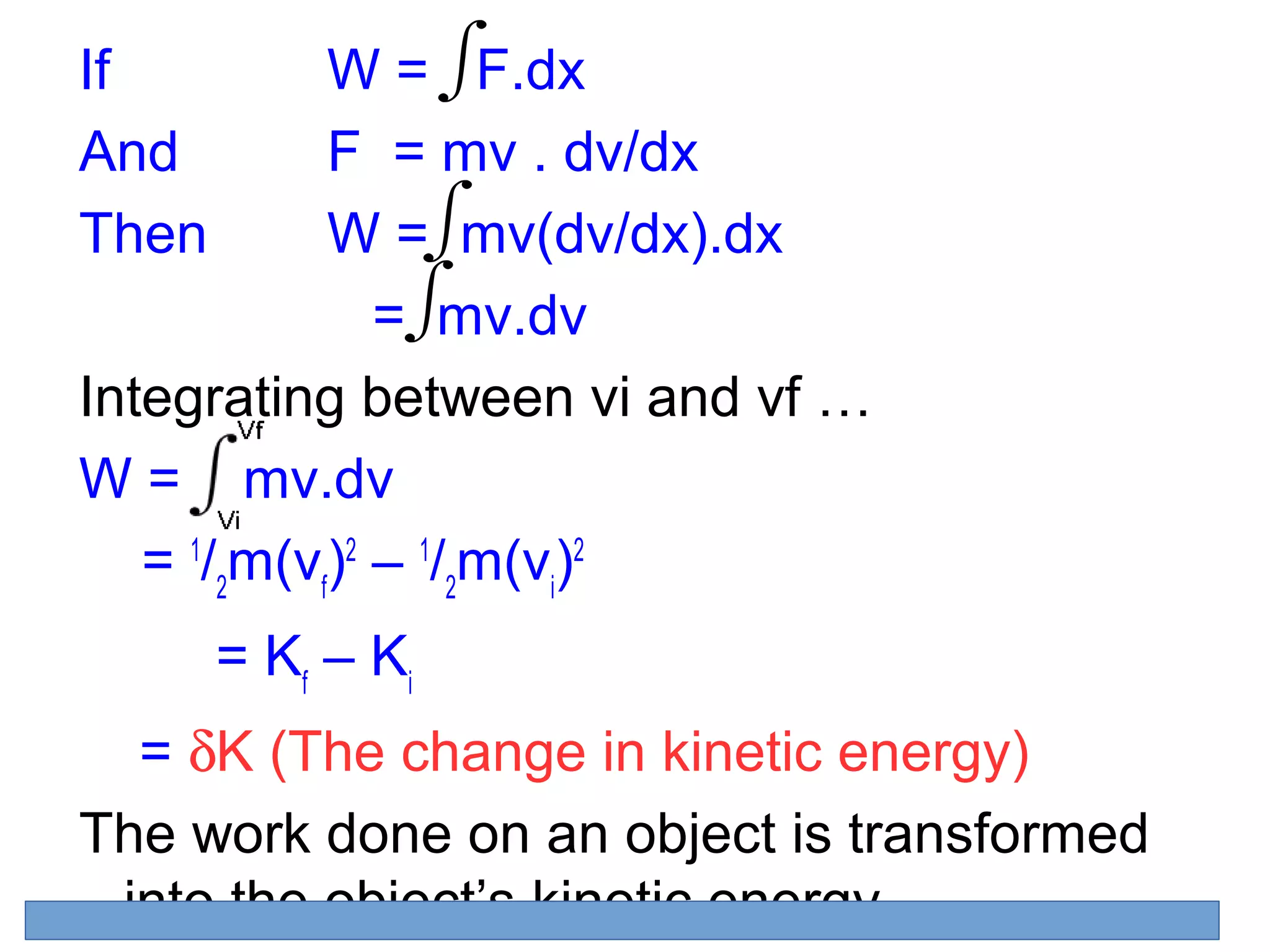
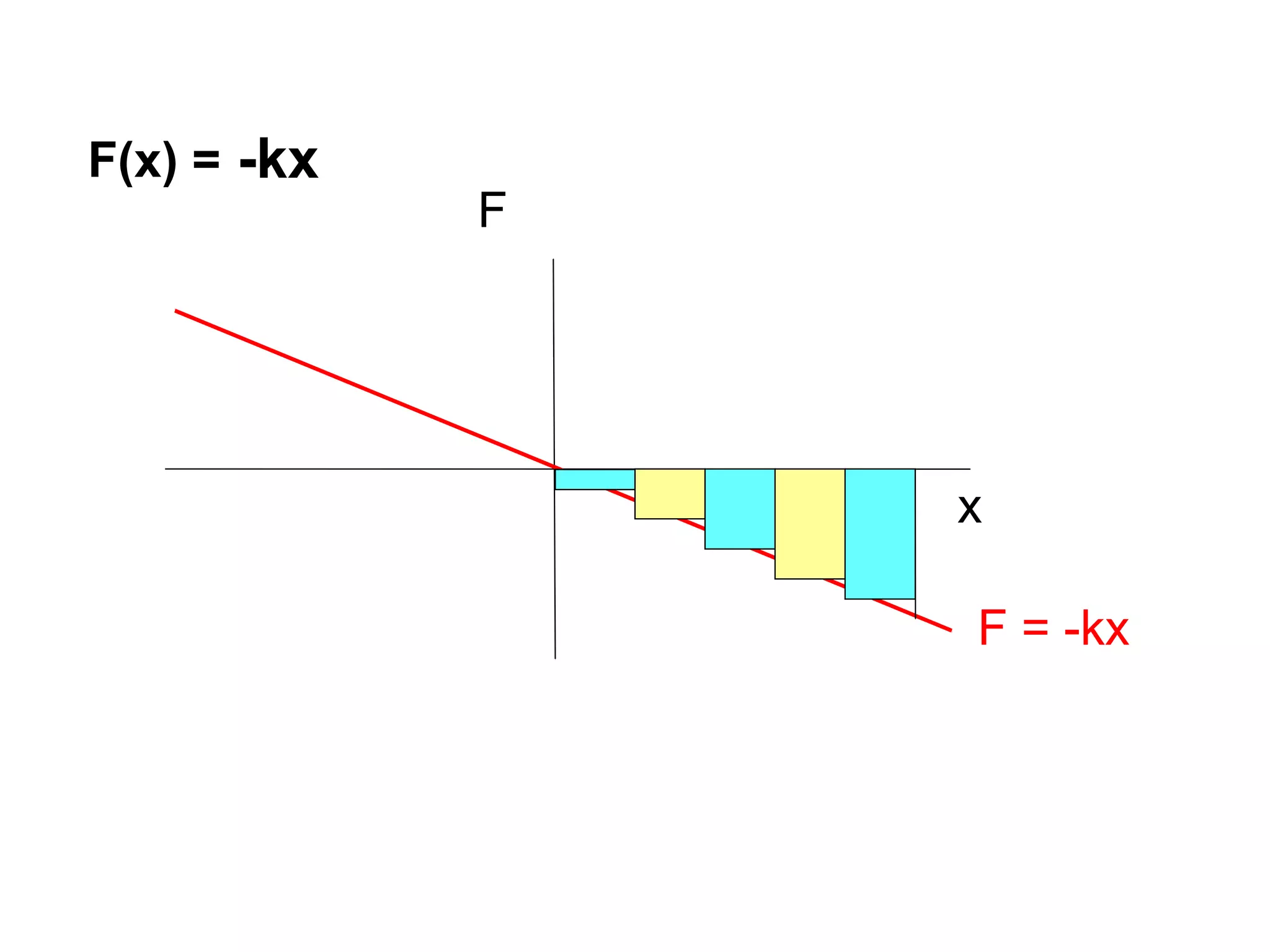
Work is defined as the force applied over a distance. Only forces parallel to the direction of motion do work. Work can be calculated for constant and variable forces. The work-energy theorem states that work done on an object changes its kinetic energy. Power is the rate at which work is done and is calculated as work divided by time. Instantaneous power uses calculus to calculate the power at an instant in time as the rate of change of work with respect to time.






















![Solution
Work Done by spring
Work Done by spring
= F(x).dx
= -kx.dx
= -1
/2
kx2
= -2.5 [0.22
– 0.12
]
= -2.5 [0.04 – 0.01]
= -0.075 J](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aworkenergyandpower-170330045200/75/A-work-energy-and-power-23-2048.jpg)