1. The document discusses gravitational fields and the simple pendulum experiment. It describes how the period of a pendulum is affected by the mass of the bob and the length of the string. The experiment can be used to calculate the acceleration due to gravity.
2. Gravitational potential energy is introduced. Lifting an object increases its gravitational potential energy, which is defined to be zero at an infinite distance. Calculations of gravitational potential energy are shown for objects near and far from Earth.
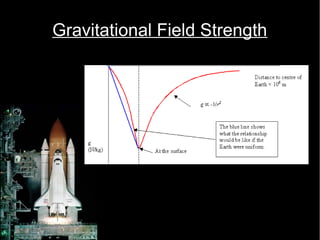
3. The formula for gravitational field strength is derived, showing that it decreases with the square of the distance from the object's center. Values of g are calculated for the major planets based on their masses and radii.