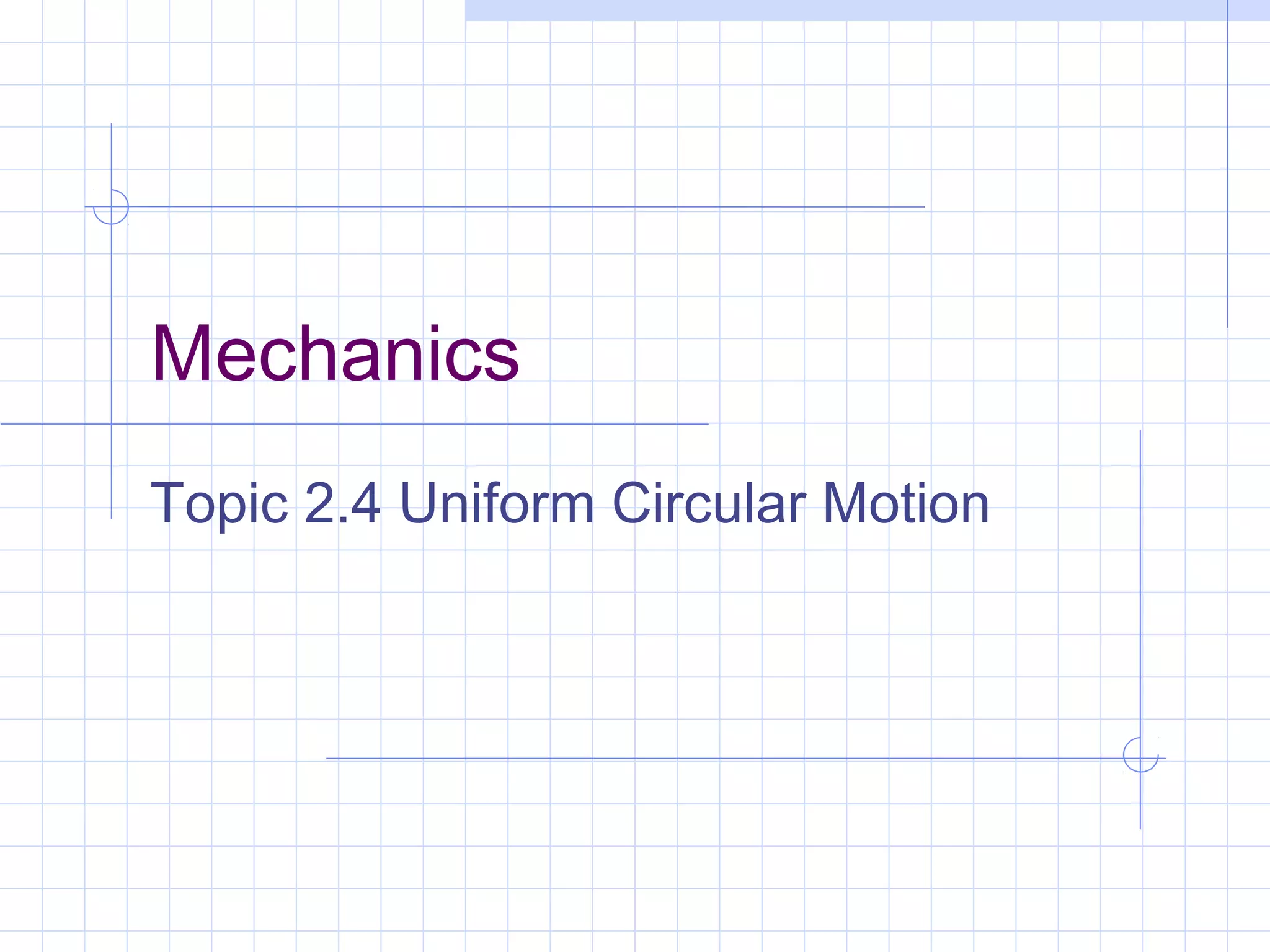
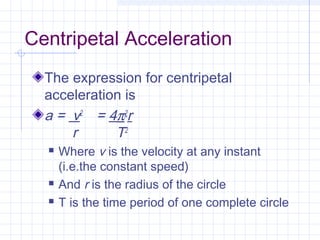
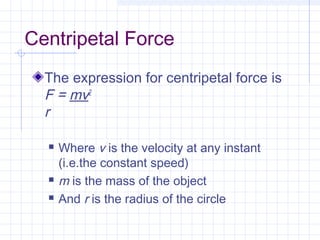
Uniform circular motion requires an acceleration directed towards the center of the circle due to the changing direction of velocity as an object moves at a constant speed in a circle. This centripetal acceleration can be calculated using the object's velocity and the radius of the circle. A centripetal force is also required to provide the necessary centripetal acceleration, and this force can be calculated using the object's mass, velocity, and the radius. Examples of centripetal force include gravity on the moon, friction on car tires, and tension in a swung rope.