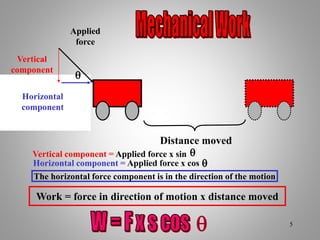
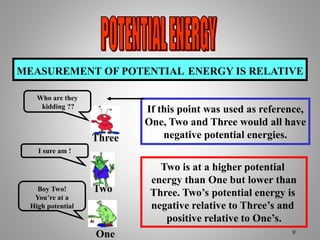
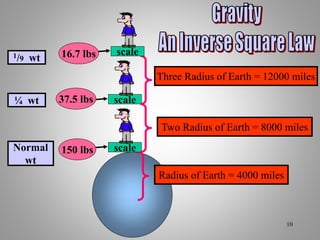
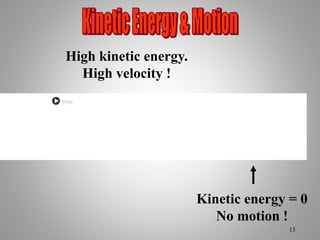
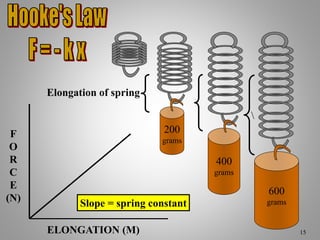
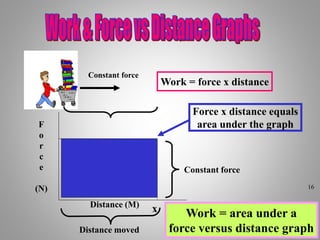
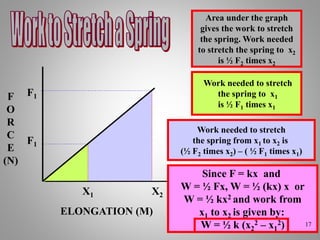
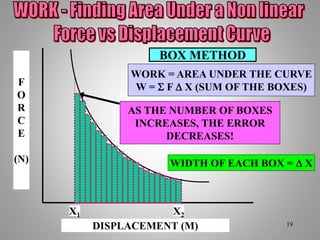
The document provides an overview of work and energy in physics, defining work as the product of force and distance moved in the direction of the applied force. It explains different types of mechanical energy, including gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, and elastic potential energy, along with their formulas. Additionally, it covers the concept of measuring energy relative to gravitational fields and different conditions affecting the work done.