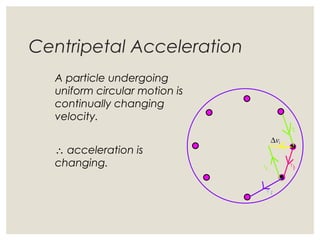
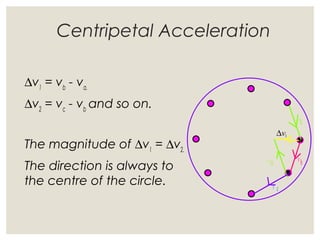
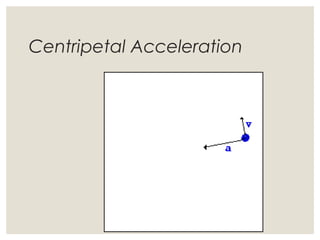
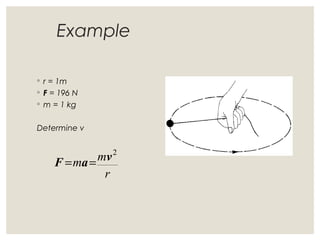
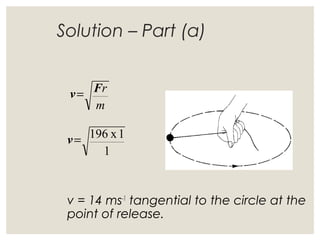
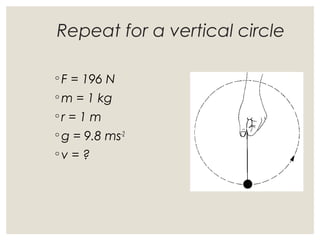
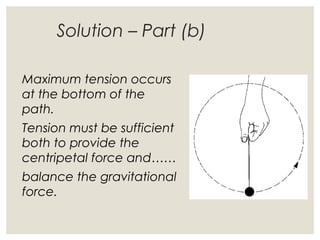
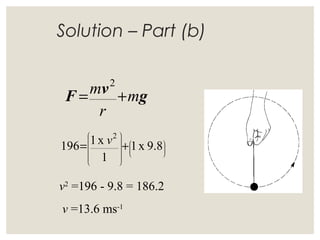
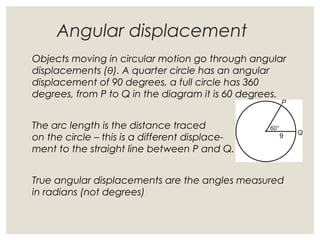
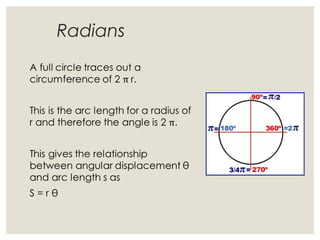
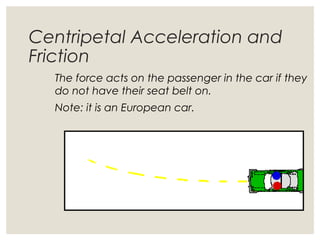
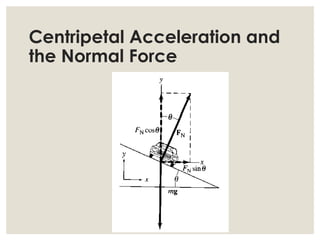
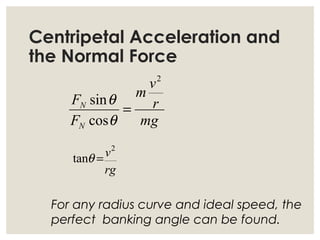
1. Circular motion involves an object moving in a circular path at a constant speed. While the speed is constant, the velocity is always changing since it is changing direction.
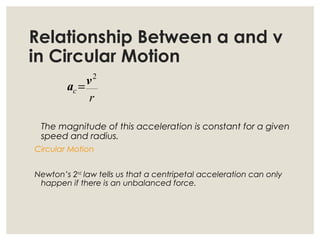
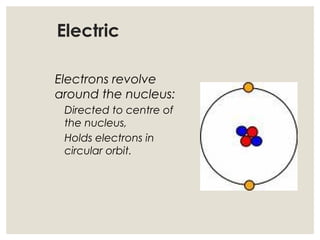
2. For an object in circular motion, there is an acceleration even when the speed is constant called centripetal acceleration which is directed towards the center of the circle. This acceleration requires a net force towards the center known as the centripetal force.
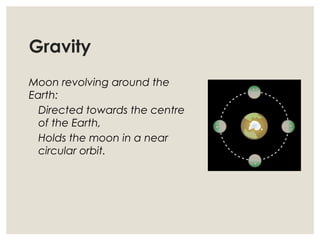
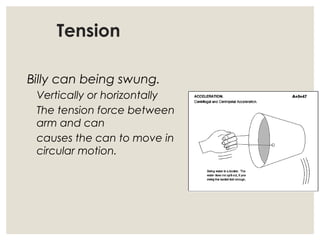
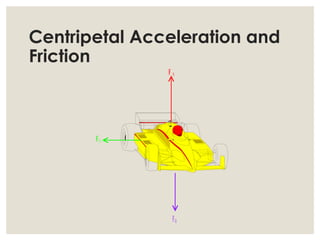
3. Common examples of centripetal force include gravity keeping planets in orbit, tension in a string keeping a rock whirling above one's head, and friction between tires and the road allowing cars to turn. The magnitude of centripetal acceleration depends on speed, radius of the