Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX












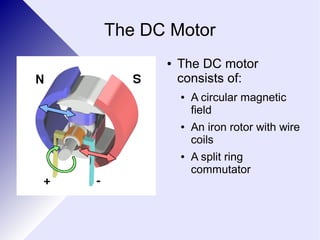








1. The document discusses the motor effect, which is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. It describes how the interaction between the magnetic field generated by the current and an external magnetic field produces a force. 2. Key factors that influence the magnitude of the motor effect force are outlined, including the strength of the magnetic field, current magnitude, length of the conductor in the field, and angle between the field and conductor. 3. Rules for determining the direction of the force are provided, such as the left hand motor rule. Parallel conductors experience attractive or repulsive forces depending on whether their currents are parallel or anti-parallel.




















