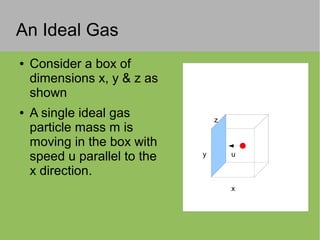
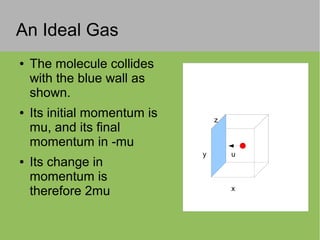
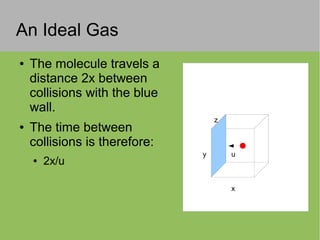
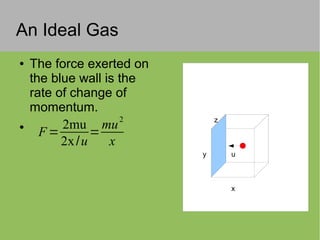
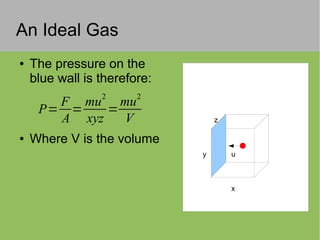
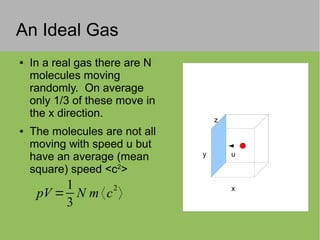
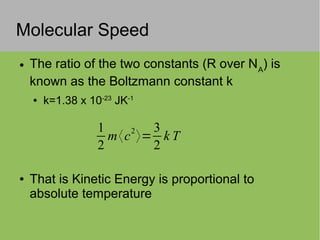
The document discusses the properties and behavior of ideal gases. It defines ideal gases as having point-like particles that exert no forces on each other except during elastic collisions. The document then derives the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) by considering the momentum transfer during particle collisions with the container walls and relating gas pressure to temperature via the kinetic energy and speeds of the particles. It concludes by noting that the ideal gas law can provide approximate descriptions of real gases.