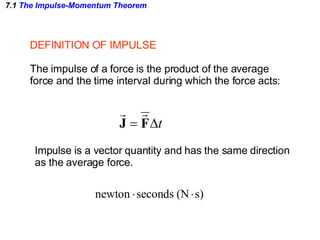
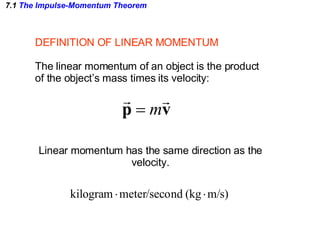
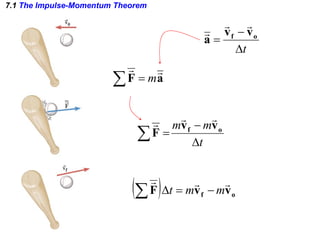
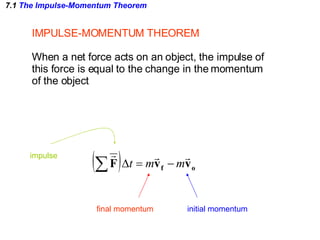
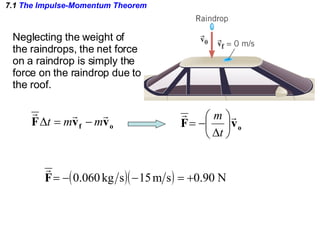
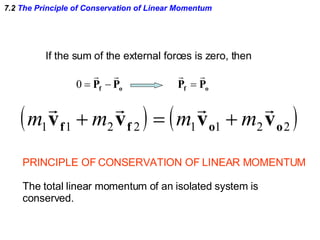
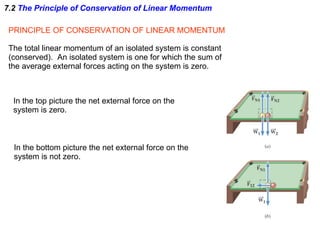
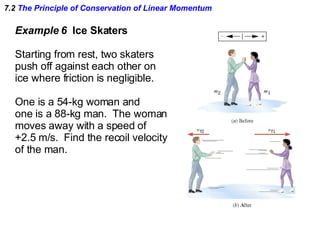
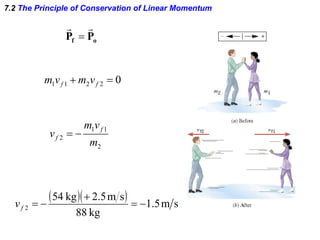
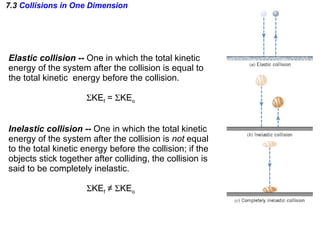
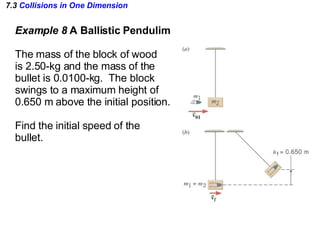
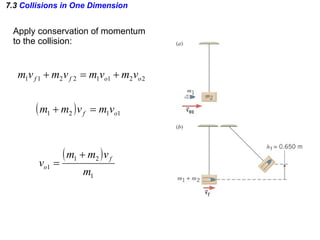
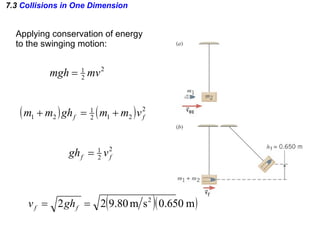
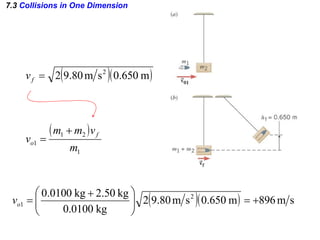
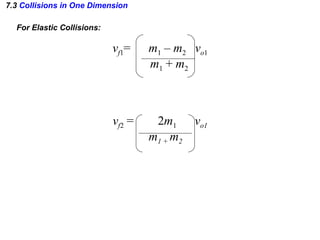
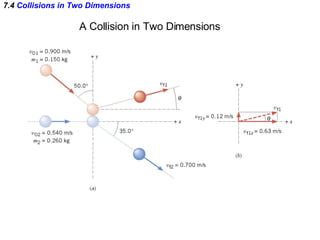
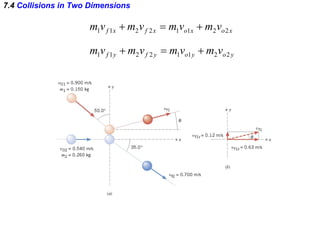
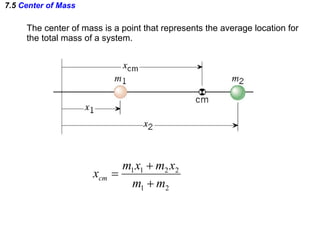
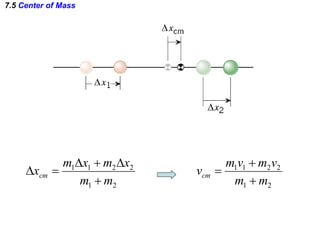
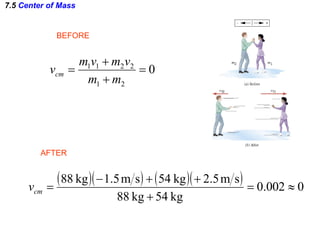
The document discusses impulse, momentum, and collisions. It defines impulse as the product of an average force and the time it acts, and momentum as the product of an object's mass and velocity. The impulse-momentum theorem states that impulse equals change in momentum when a net force acts. Conservation of momentum means the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant. Collisions can be elastic or inelastic, depending on whether kinetic energy is conserved.