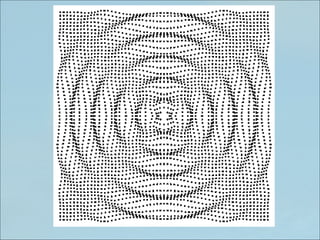
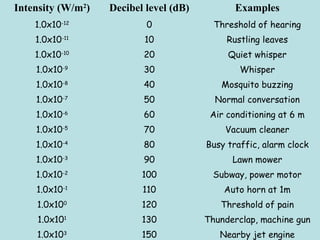
The document discusses sound waves and their characteristics including pitch, intensity, and frequency. It explains that sound is produced by vibrating objects like tuning forks and transmitted through compression and rarefaction waves. Pitch can be manipulated through effects like the Shepard tone which uses superposition of waves to create the illusion of a constantly increasing pitch. Intensity decreases with the inverse square of distance from the sound source and is measured in decibels on a logarithmic scale. The human range of hearing is from 20-20,000 Hz and our ears detect sound through the eardrum, hammer, anvil, stirrup, cochlea and auditory nerve.