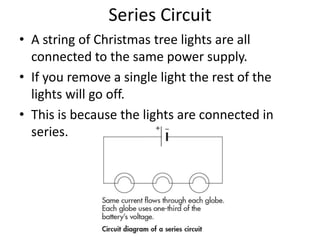
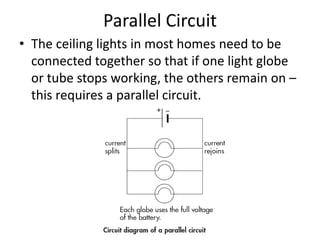
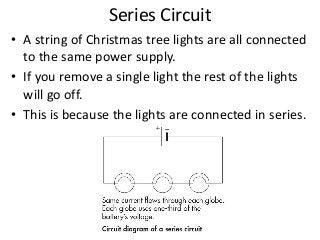
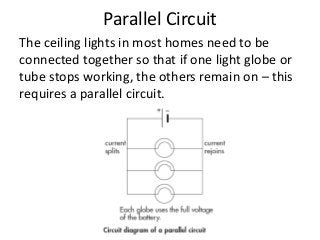
The document discusses key concepts about electrical energy including:
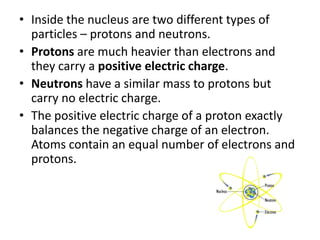
- Atoms are made up of a nucleus surrounded by electrons that carry a negative charge. Protons in the nucleus carry a positive charge while neutrons carry no charge.
- Static electricity occurs when surfaces rub against each other, transferring electrons between them and building up positive or negative charges.
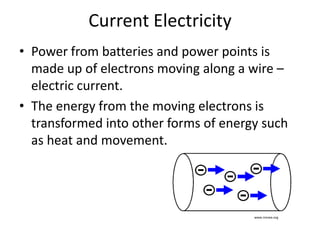
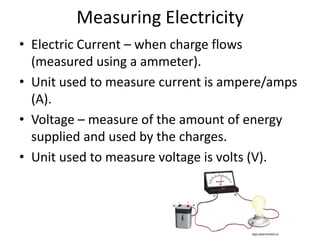
- Electric current involves the flow of electrons along a wire or conductor, which can be measured in amps. Voltage measures the energy supplied by these charges and is measured in volts.