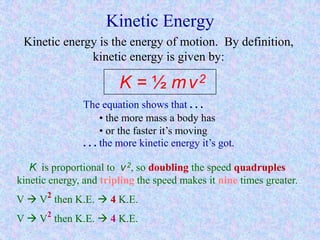
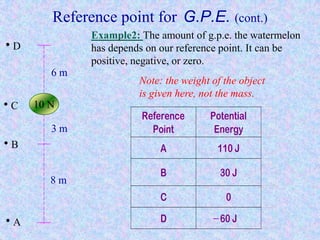
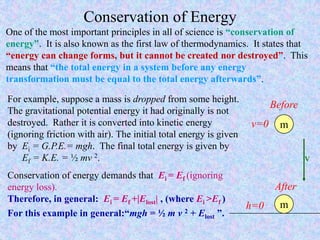
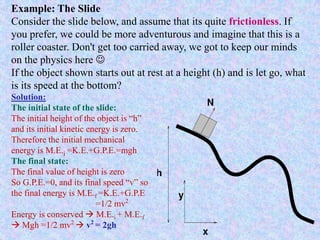
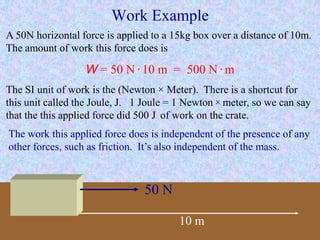
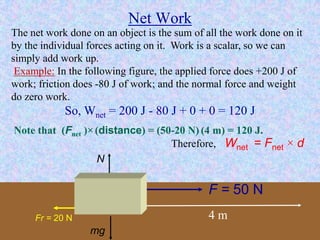
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is calculated as K = 1/2 mv^2, where m is mass and v is velocity. Doubling speed quadruples kinetic energy, and tripling speed multiplies it by nine. The SI unit for kinetic, potential, and all other types of energy is the Joule. Potential energy depends on mass, gravitational field strength, and height. The total energy before and after an energy transformation will be equal according to the law of conservation of energy. Work is the product of force and displacement and can be positive, negative, or zero depending on the direction of force relative to motion.