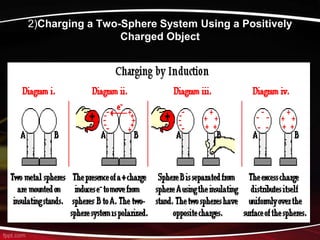
This document discusses electric charges and static electricity. It explains that atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The proton has a positive charge, the electron has a negative charge, and the neutron is neutral. It also discusses how charges behave, with like charges repelling and unlike charges attracting. Static electricity is generated through friction, such as when a polythene rod is rubbed with wool, transferring electrons from the wool to the rod. Conductors, insulators, and semiconductors are compared in terms of how they allow electrons to pass through. Earthing and electrostatic induction are also summarized.