Embed presentation
Download to read offline
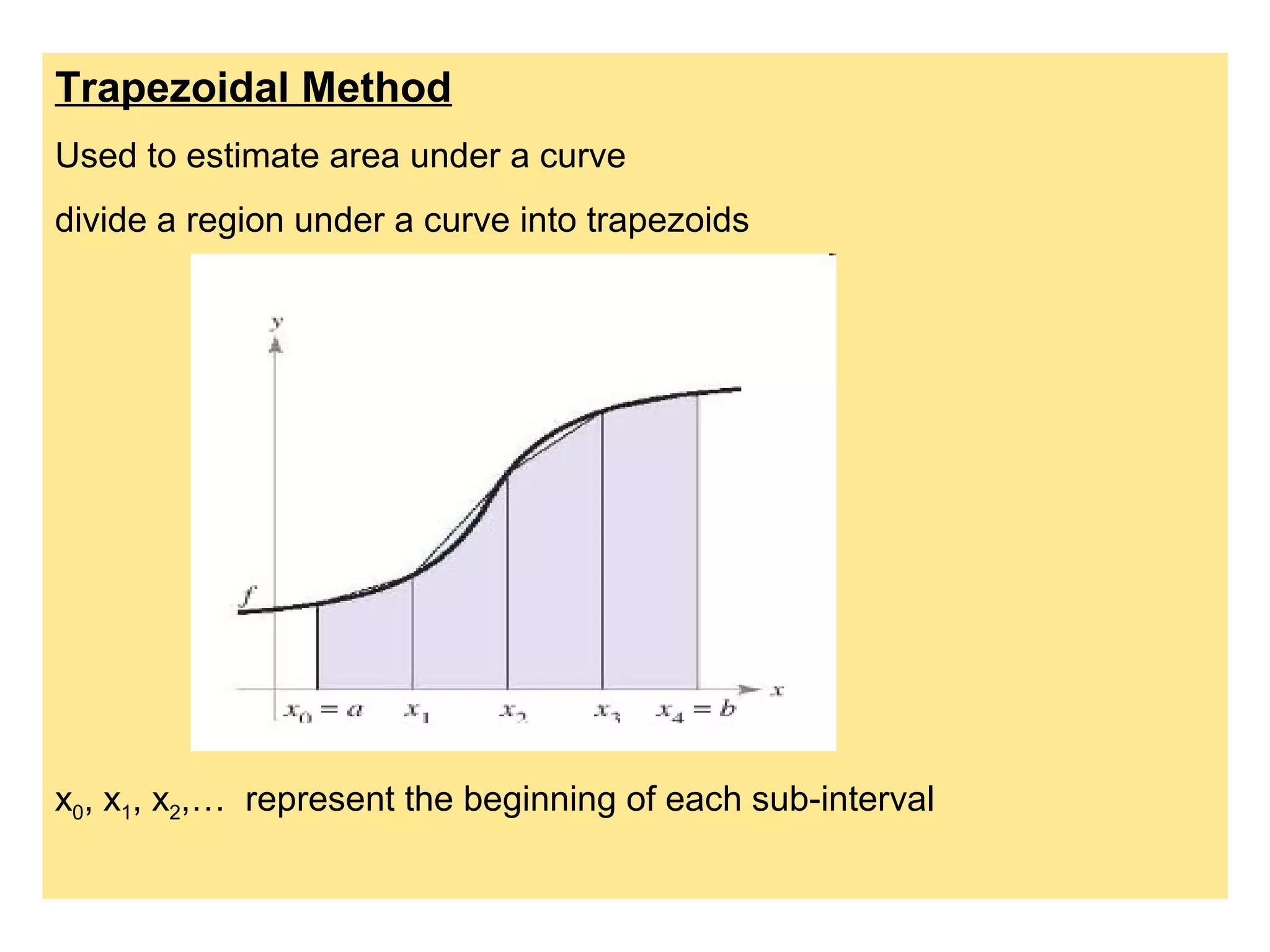
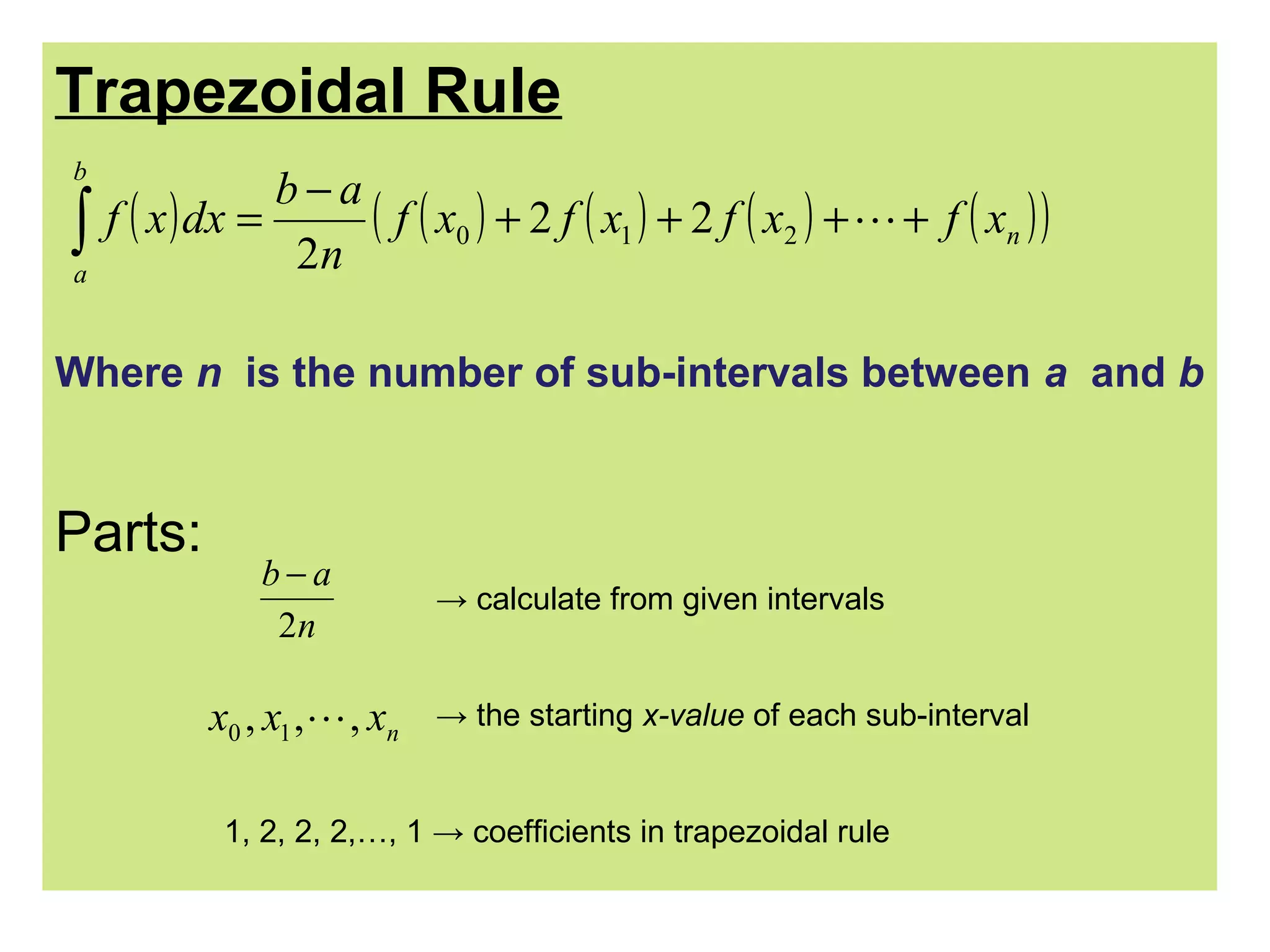
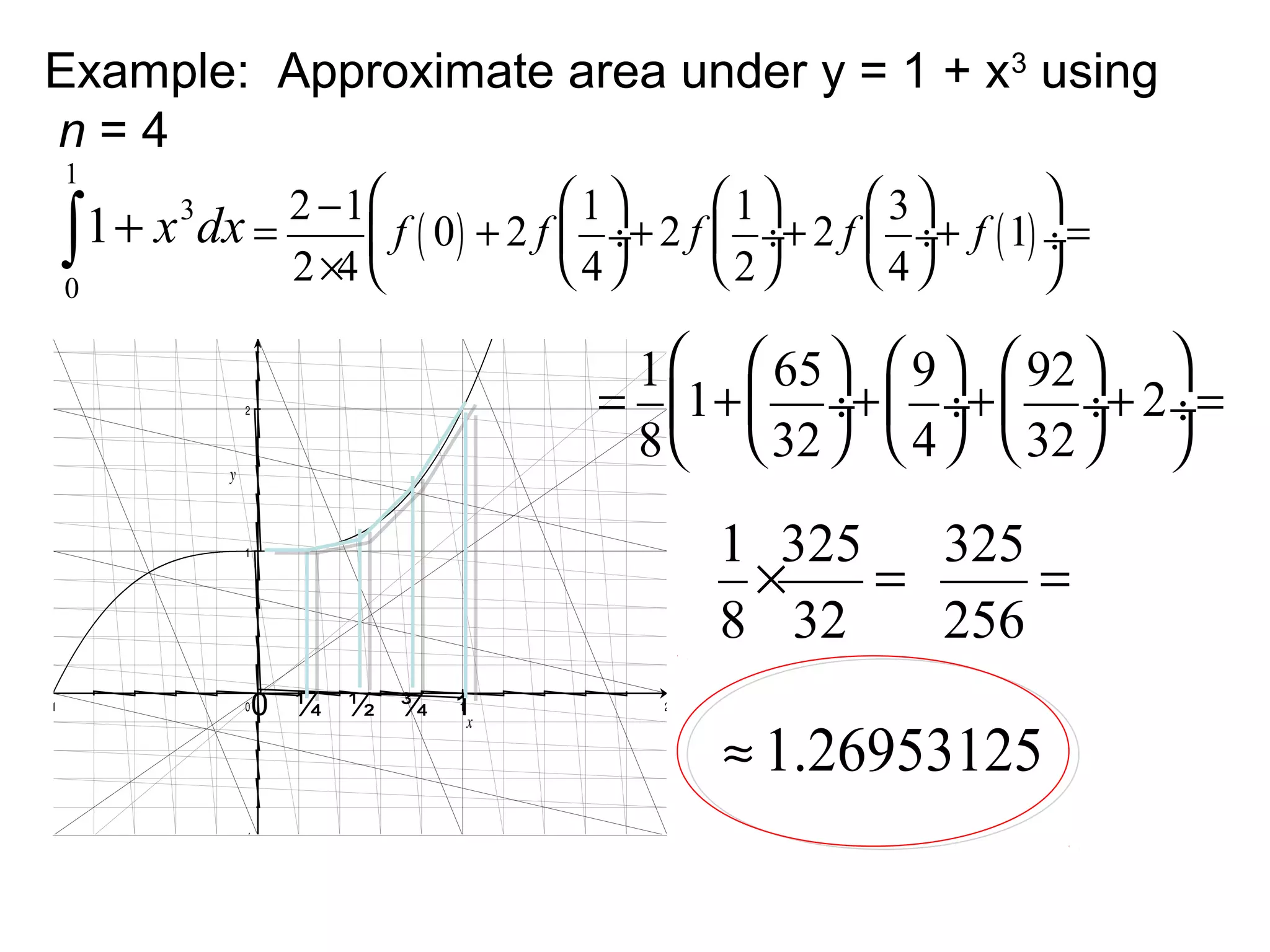
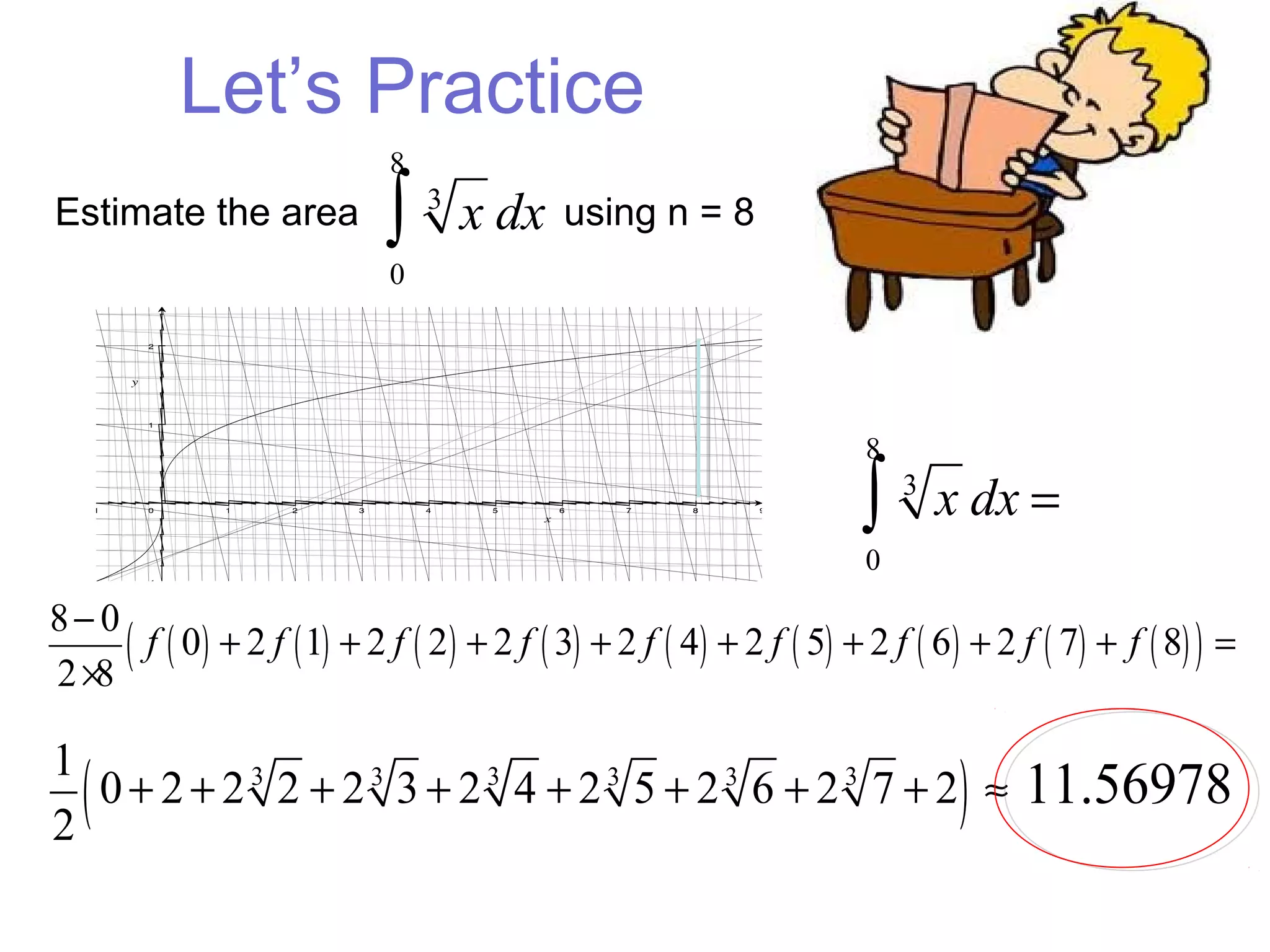
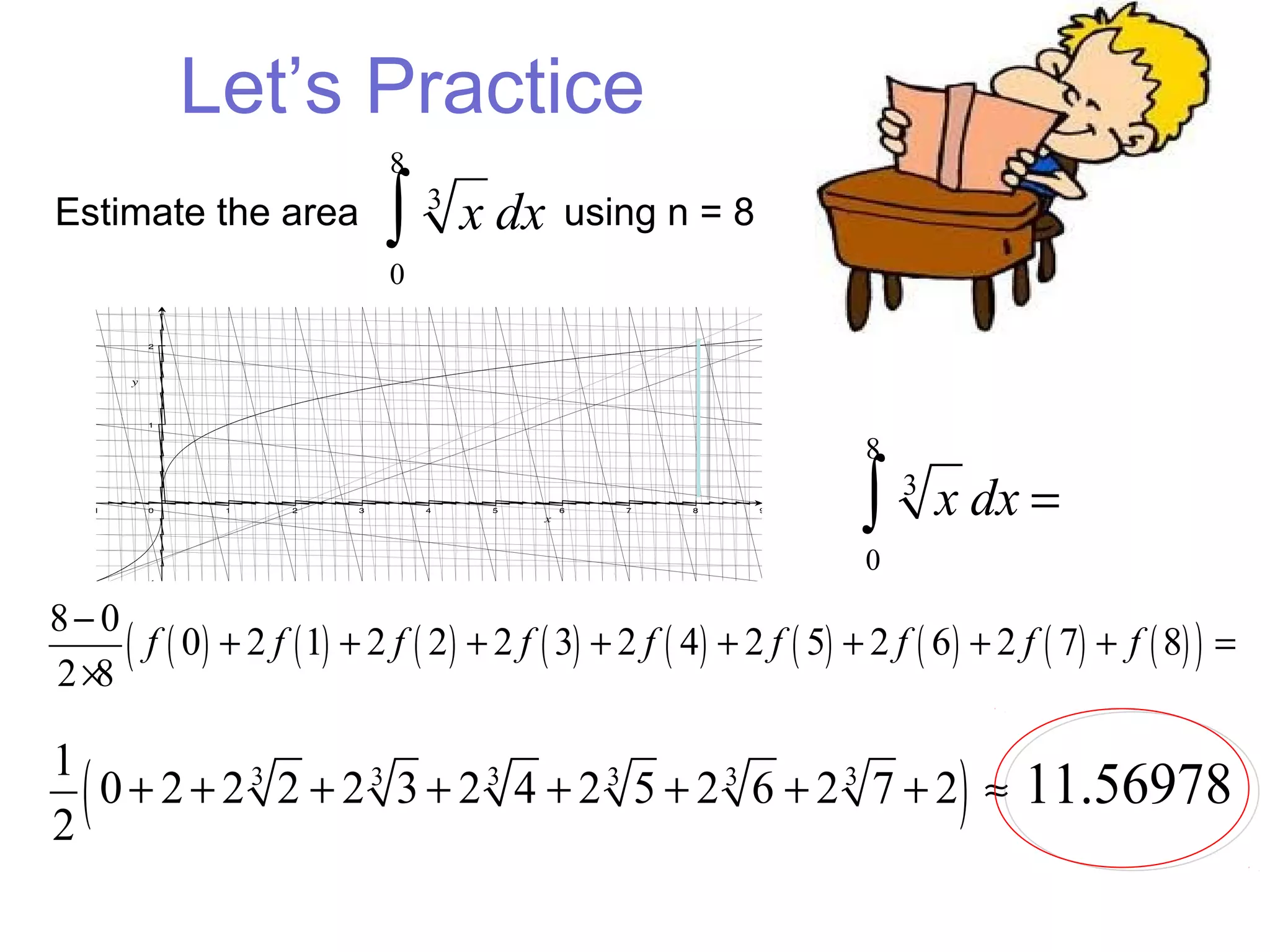
The trapezoidal rule is used to approximate the area under a curve by dividing it into trapezoids. It takes the average of the function values at the beginning and end of each sub-interval multiplied by the sub-interval width. The general formula sums these values over all sub-intervals divided by the number of intervals. An example calculates the area under y=1+x^3 from 0 to 1 using n=4 sub-intervals and gets an approximate value of 1.26953125.





