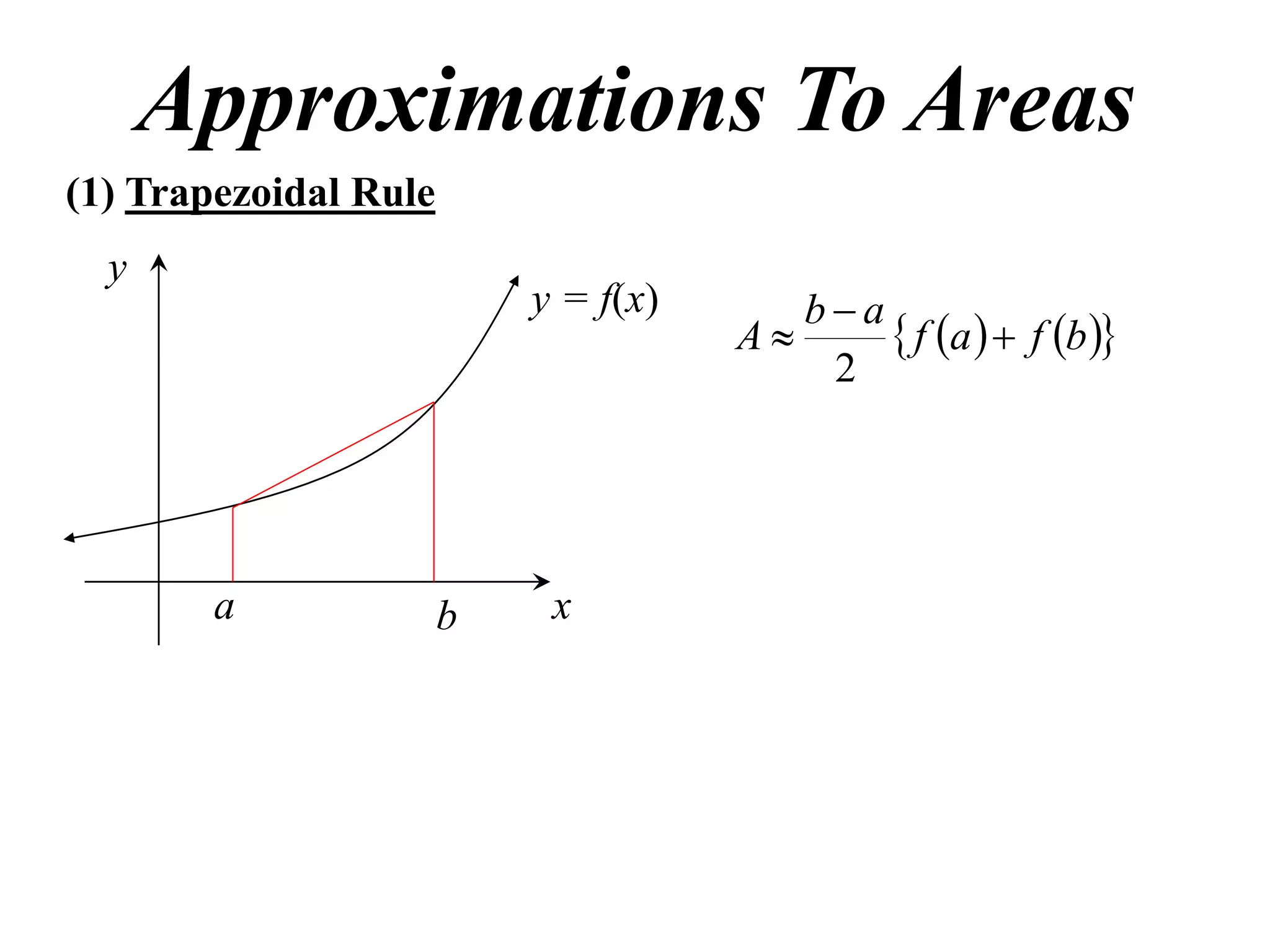
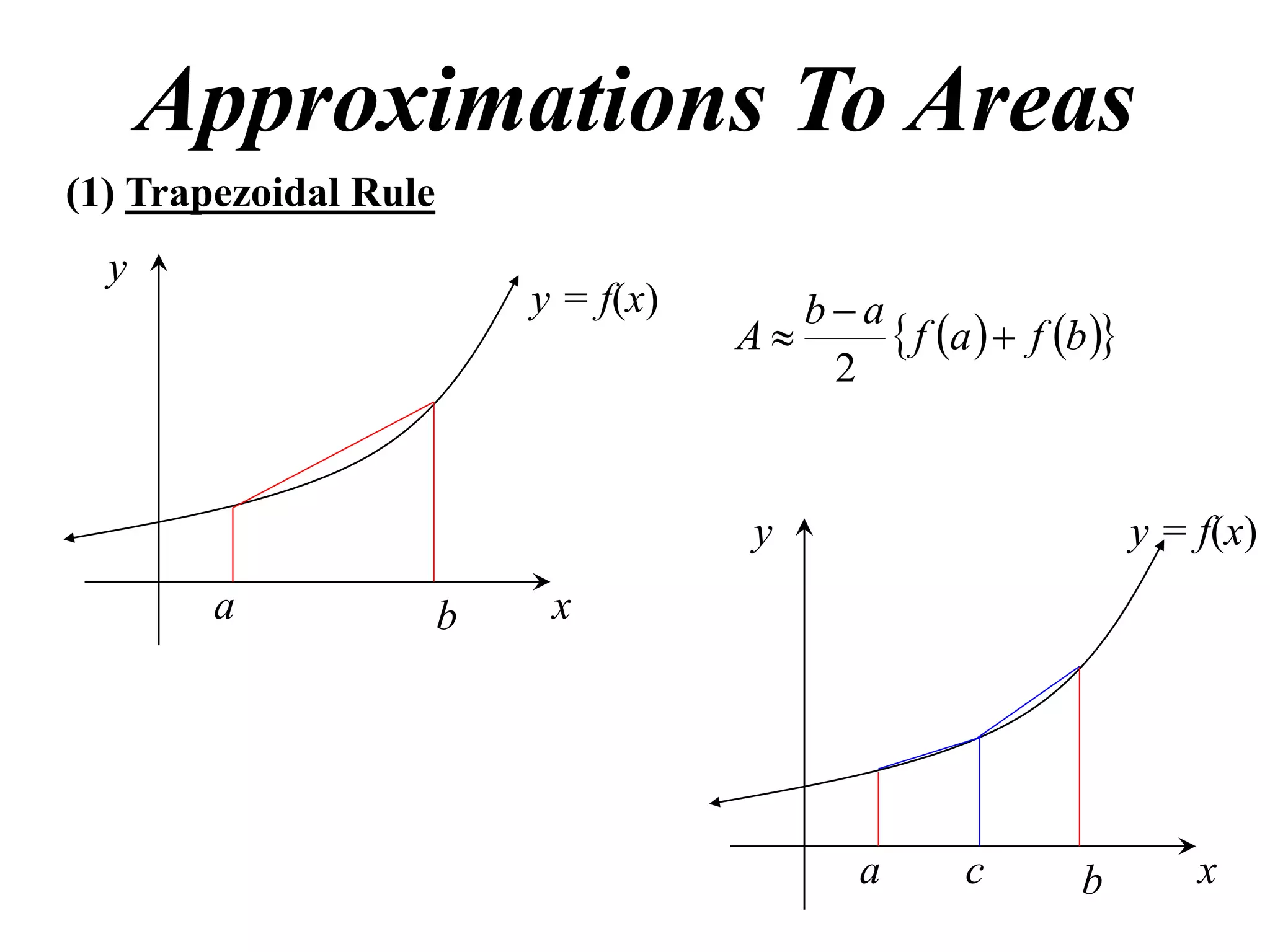
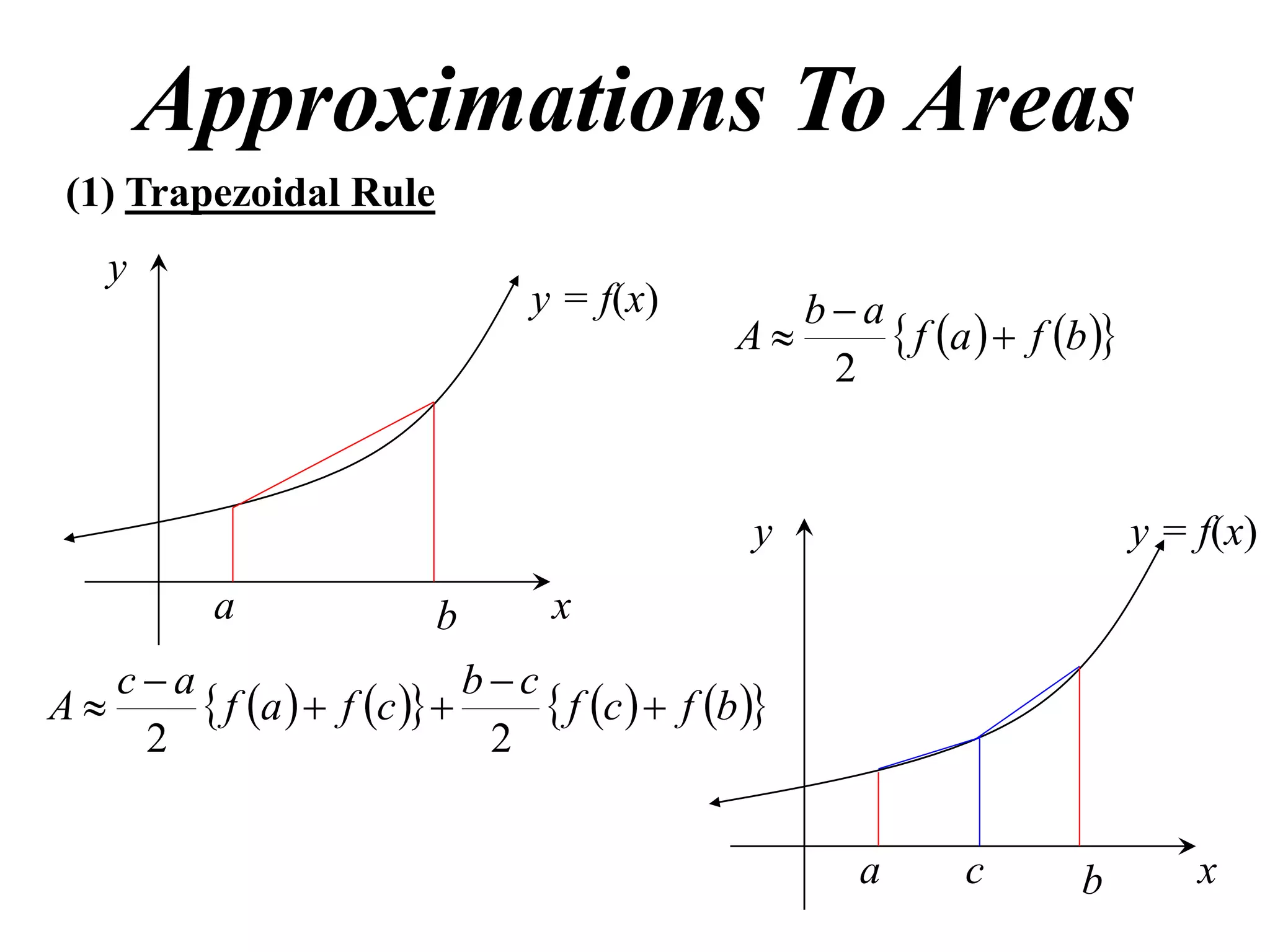
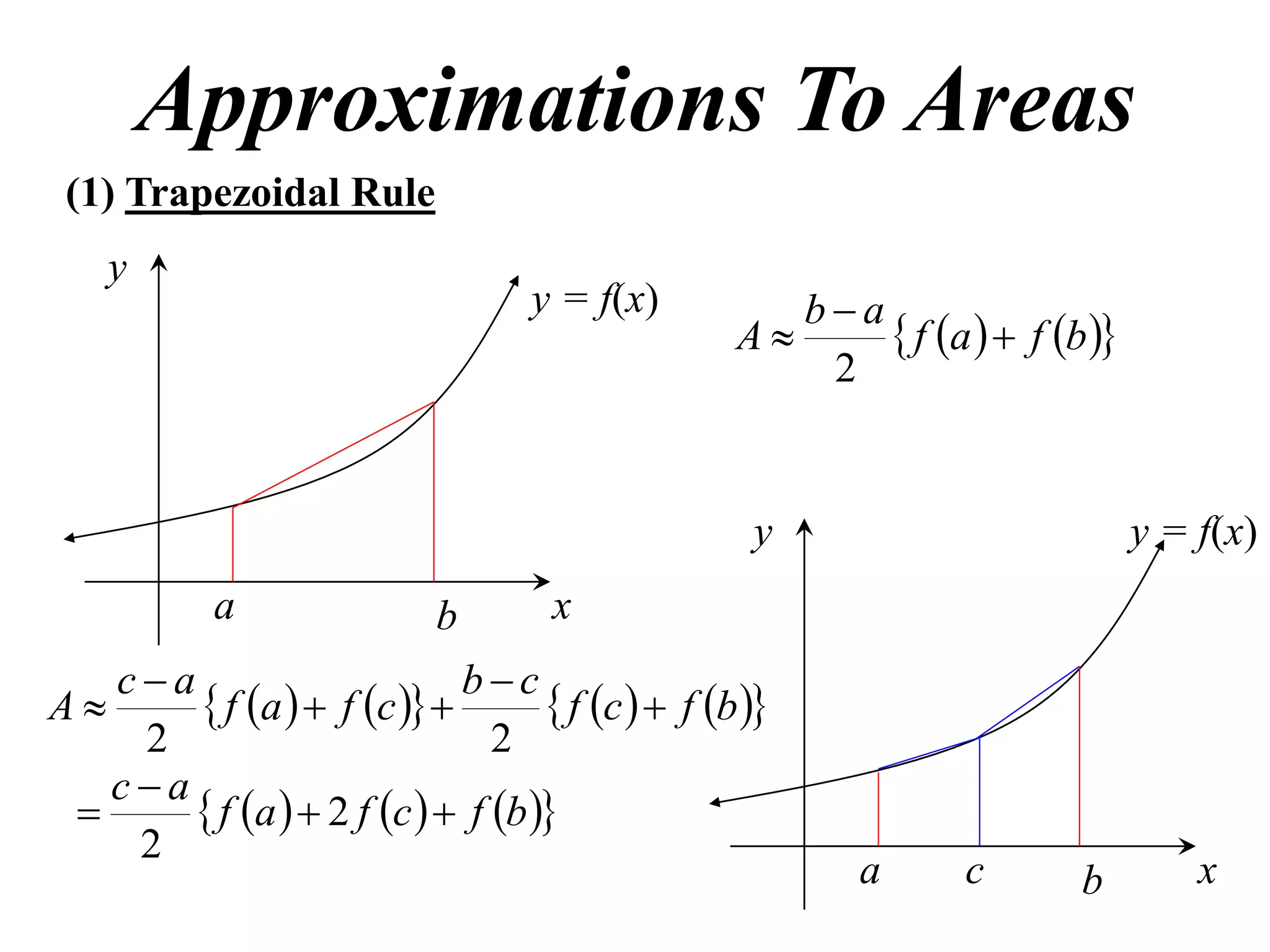
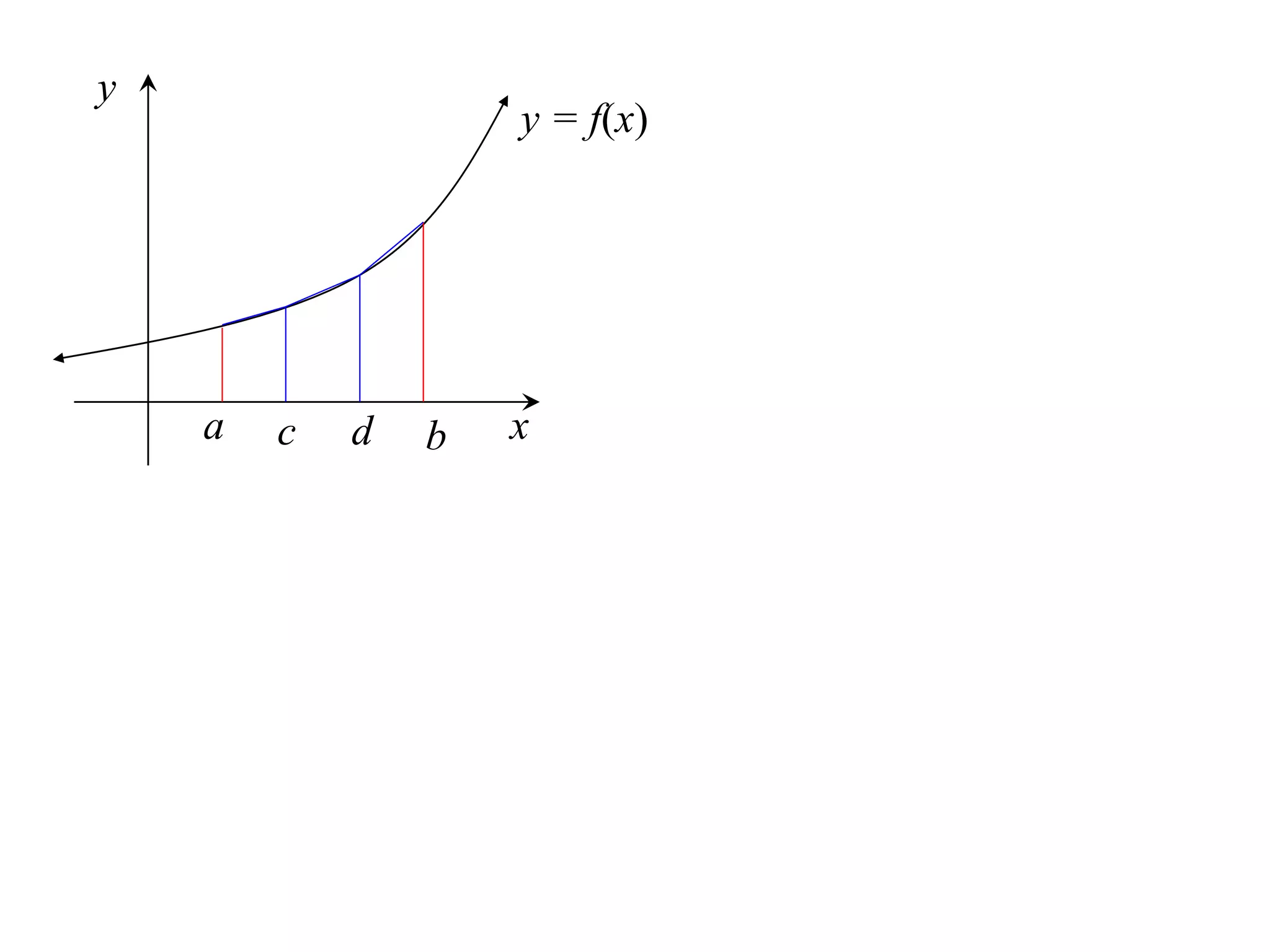
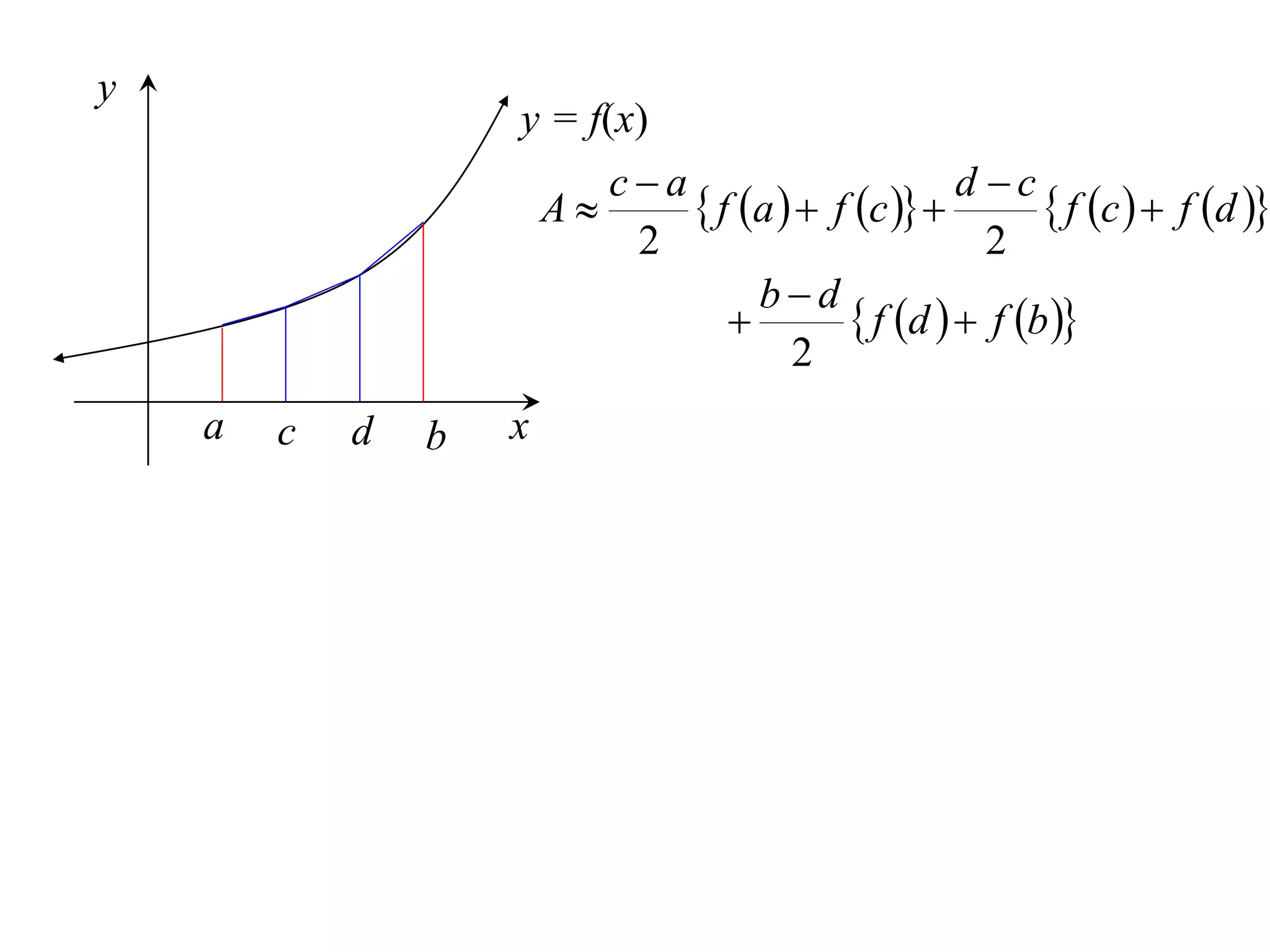
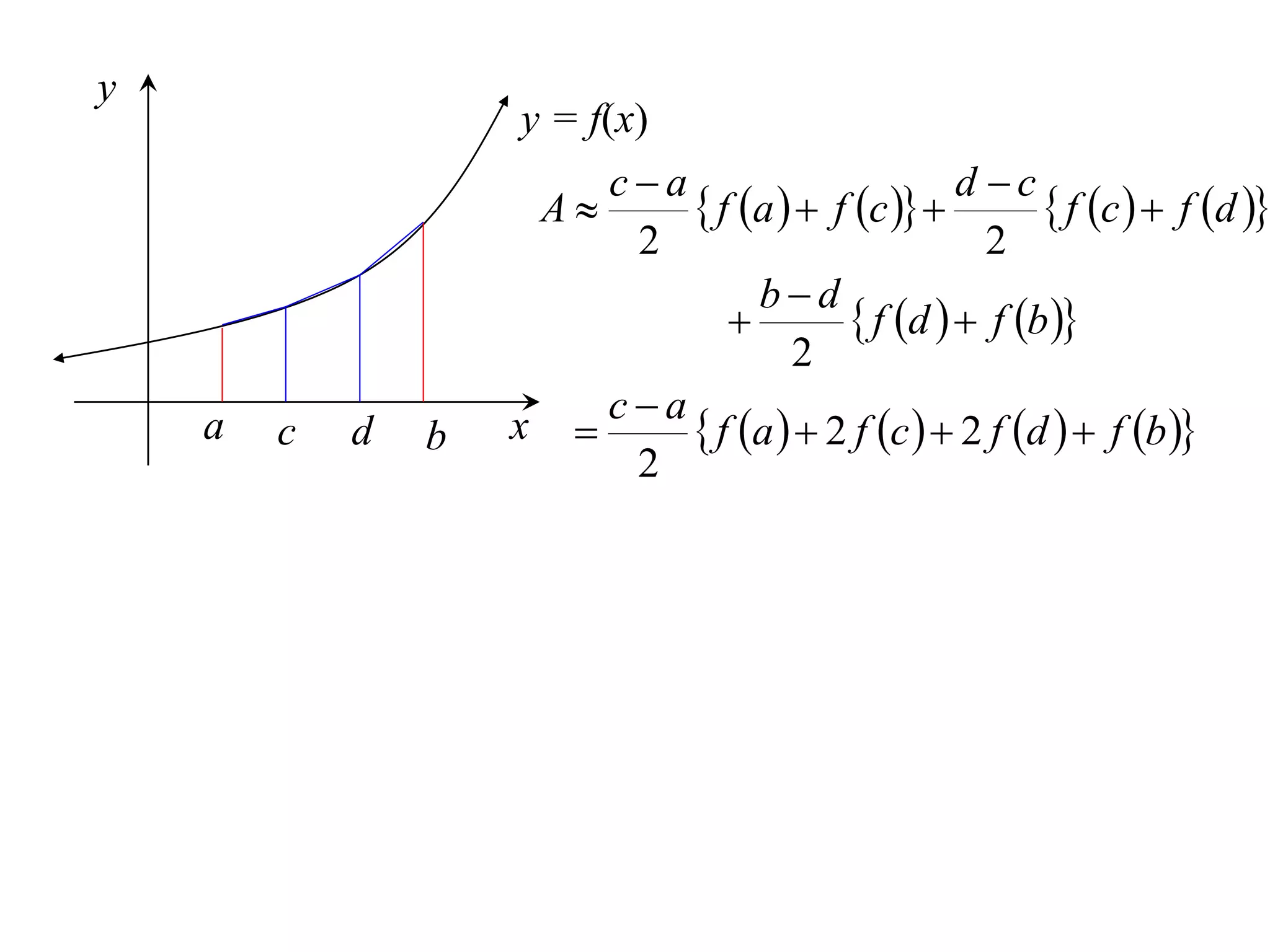
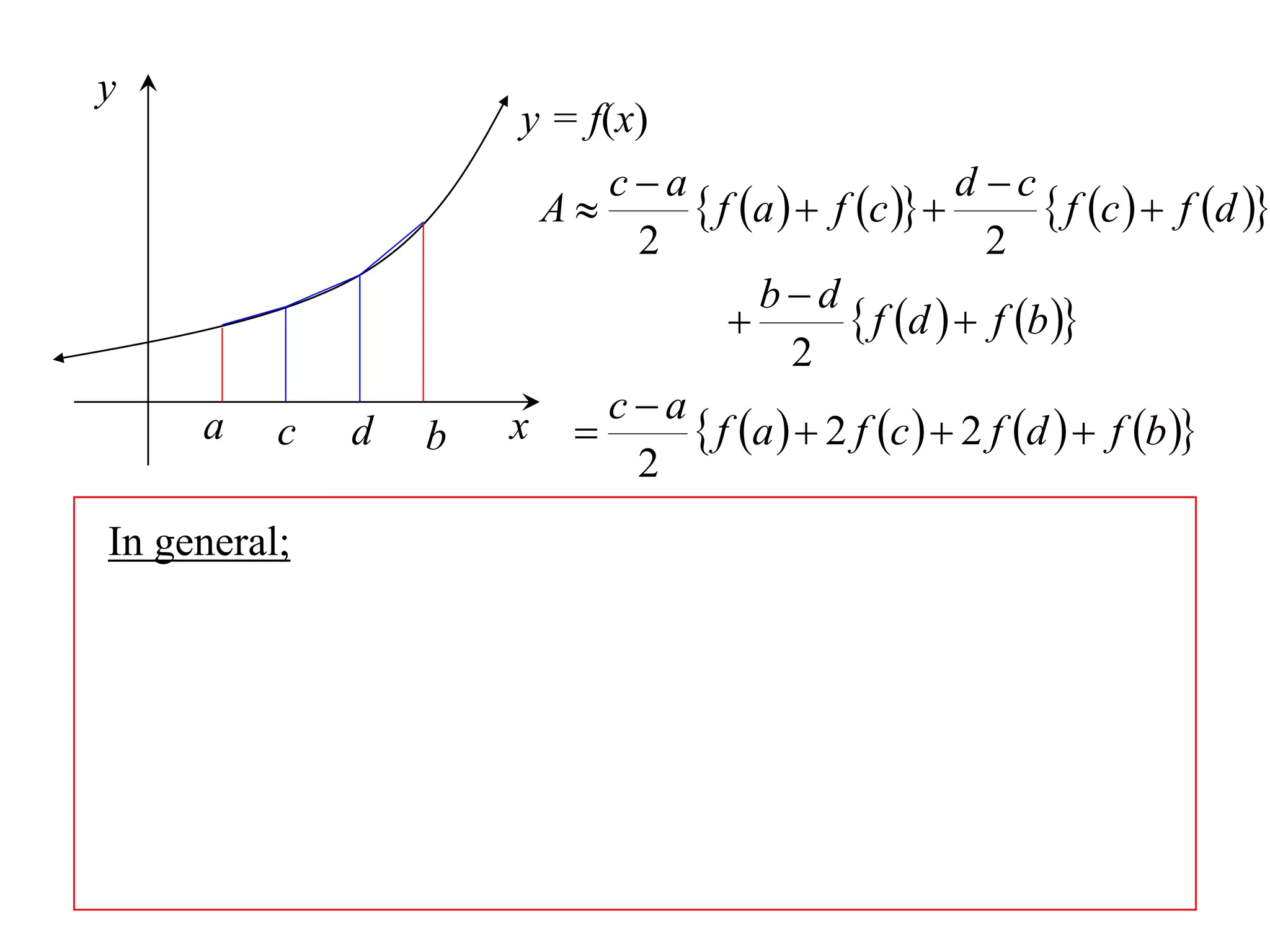
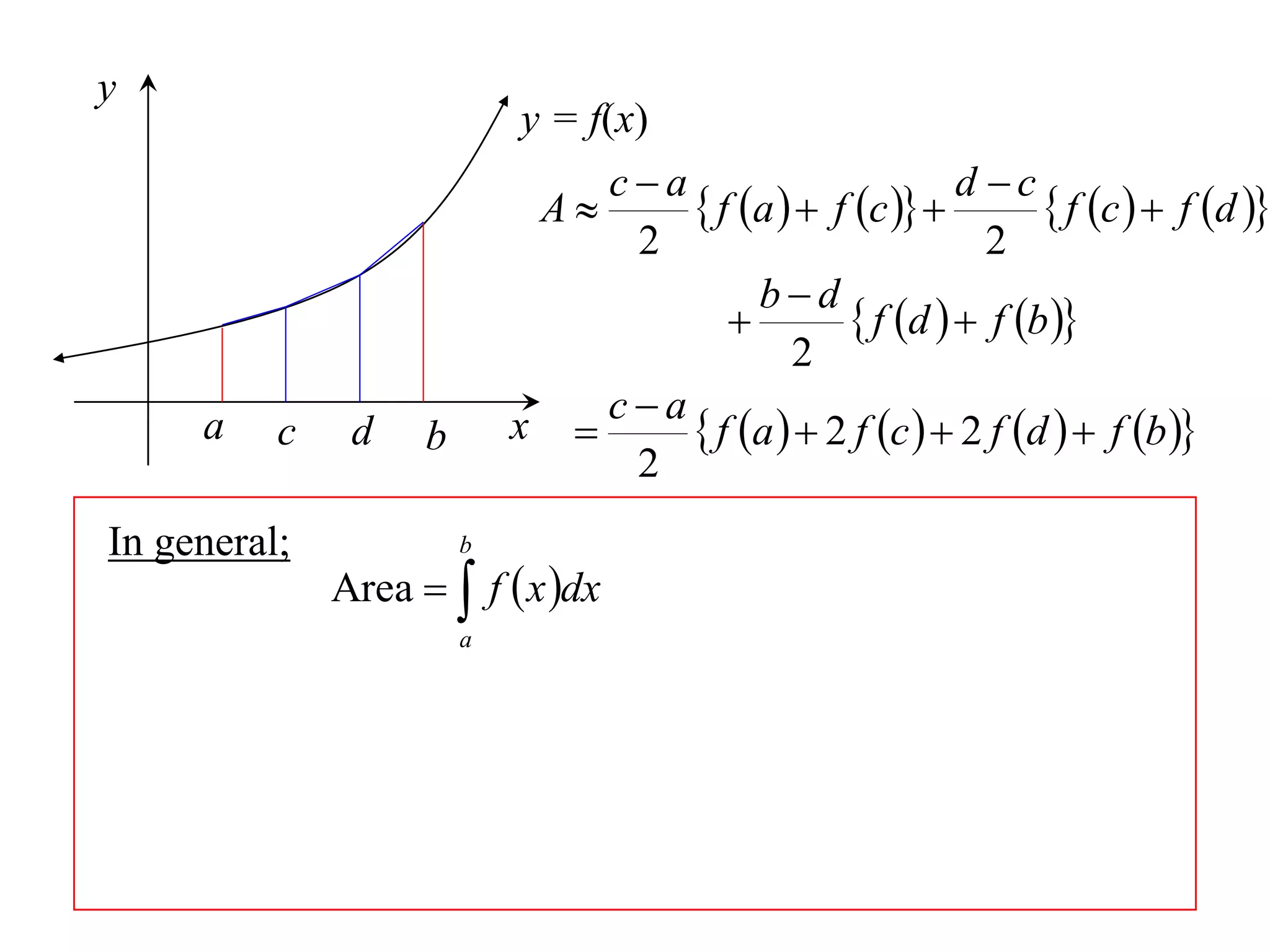
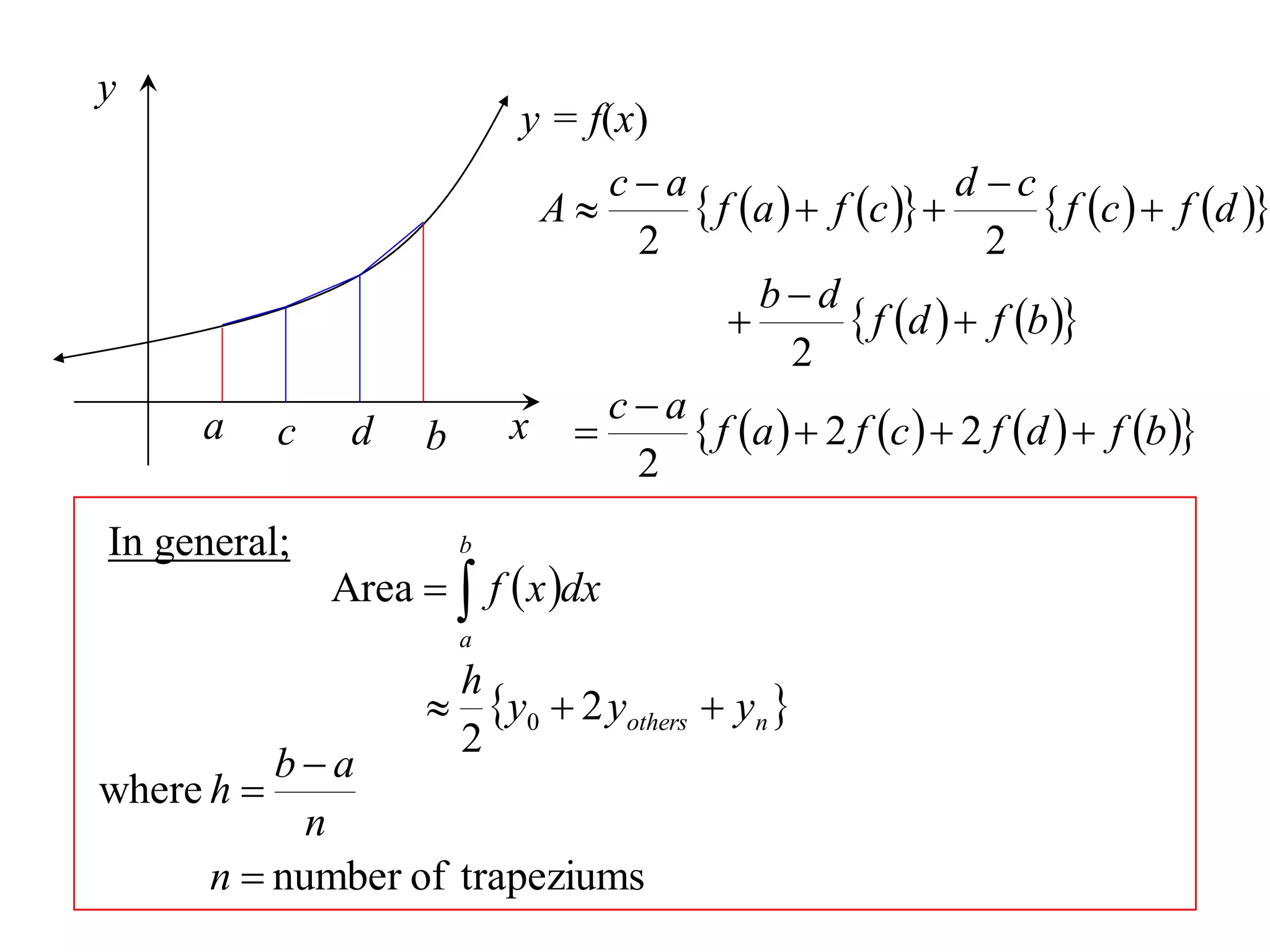
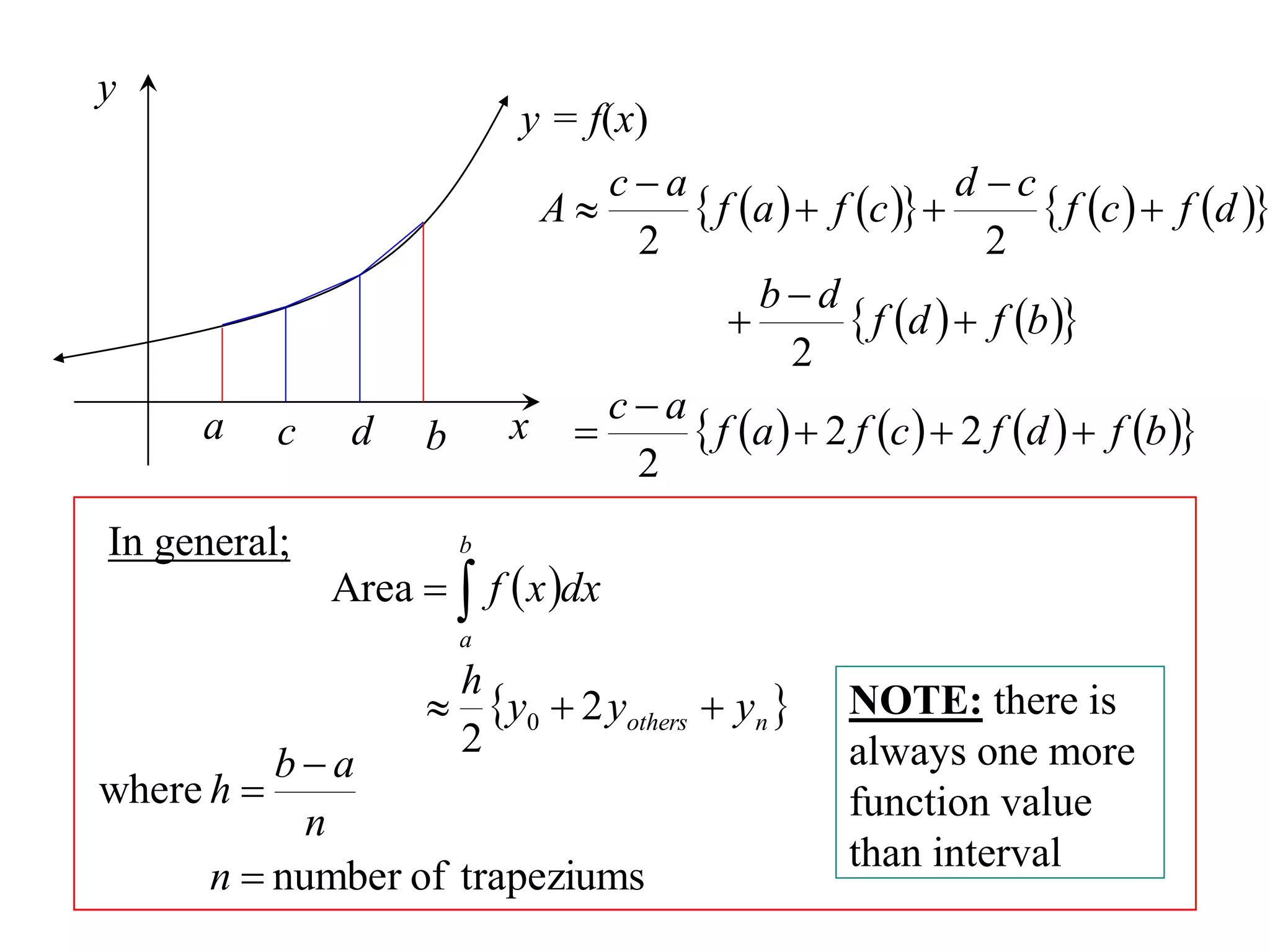
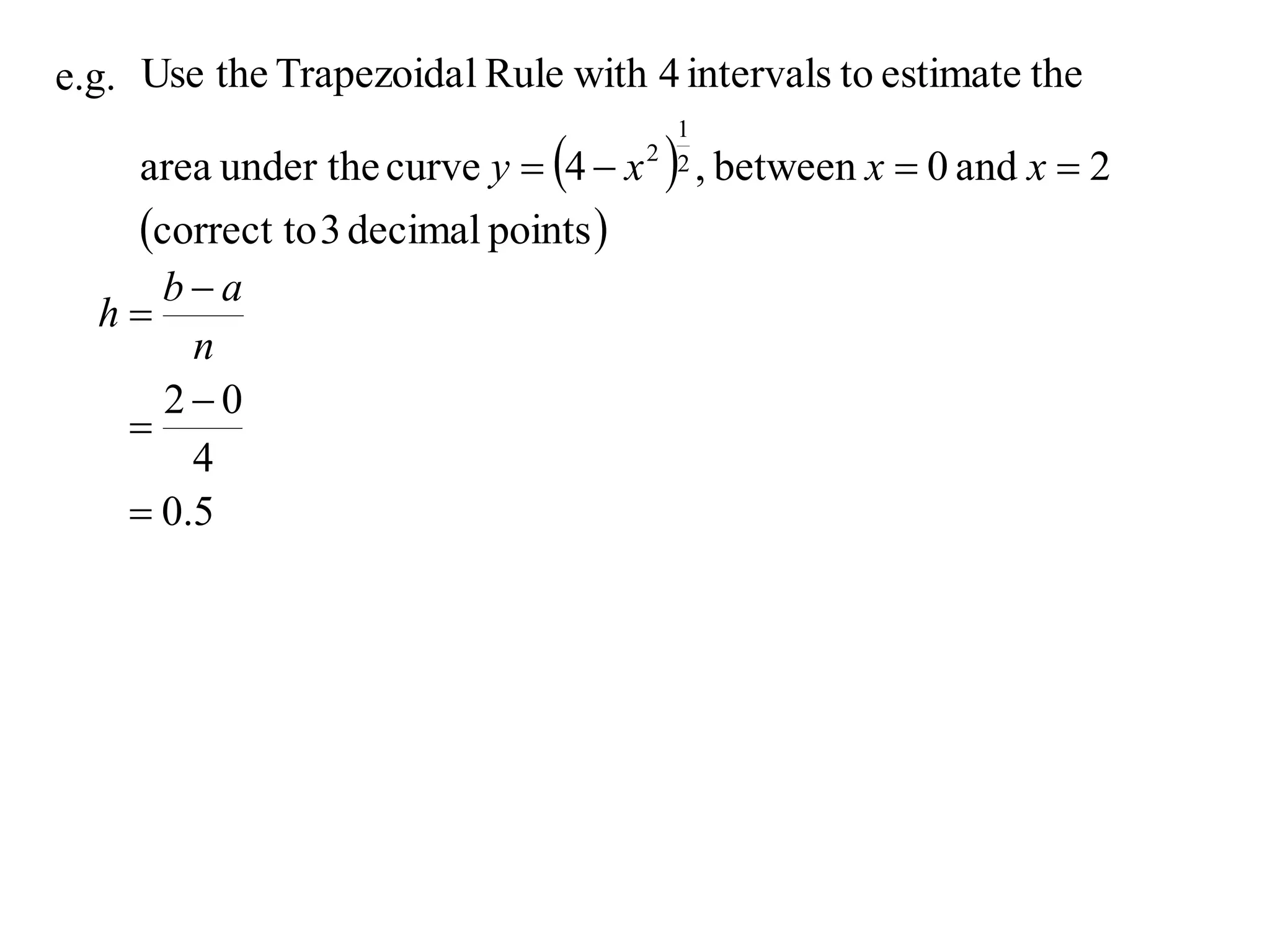
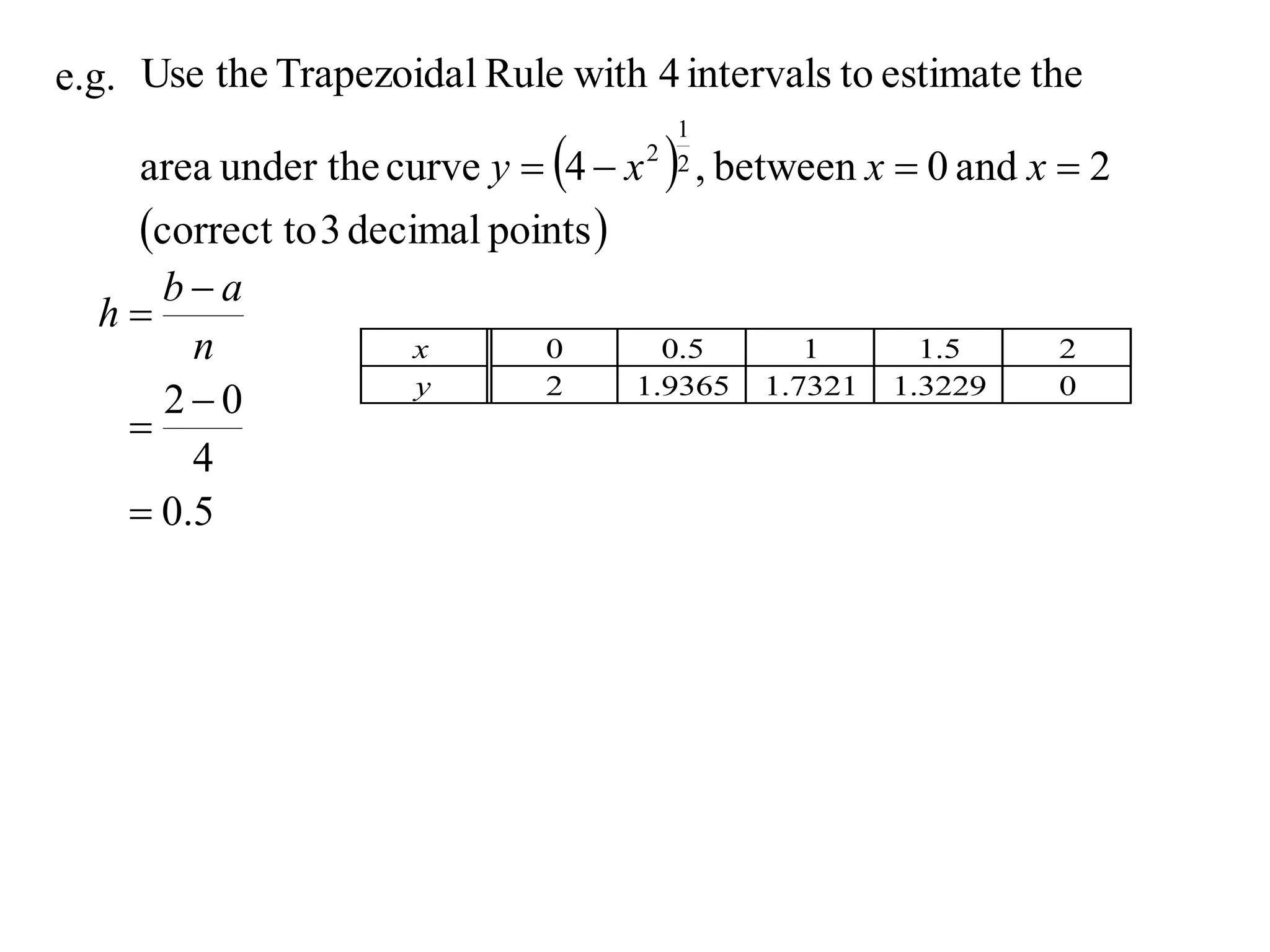
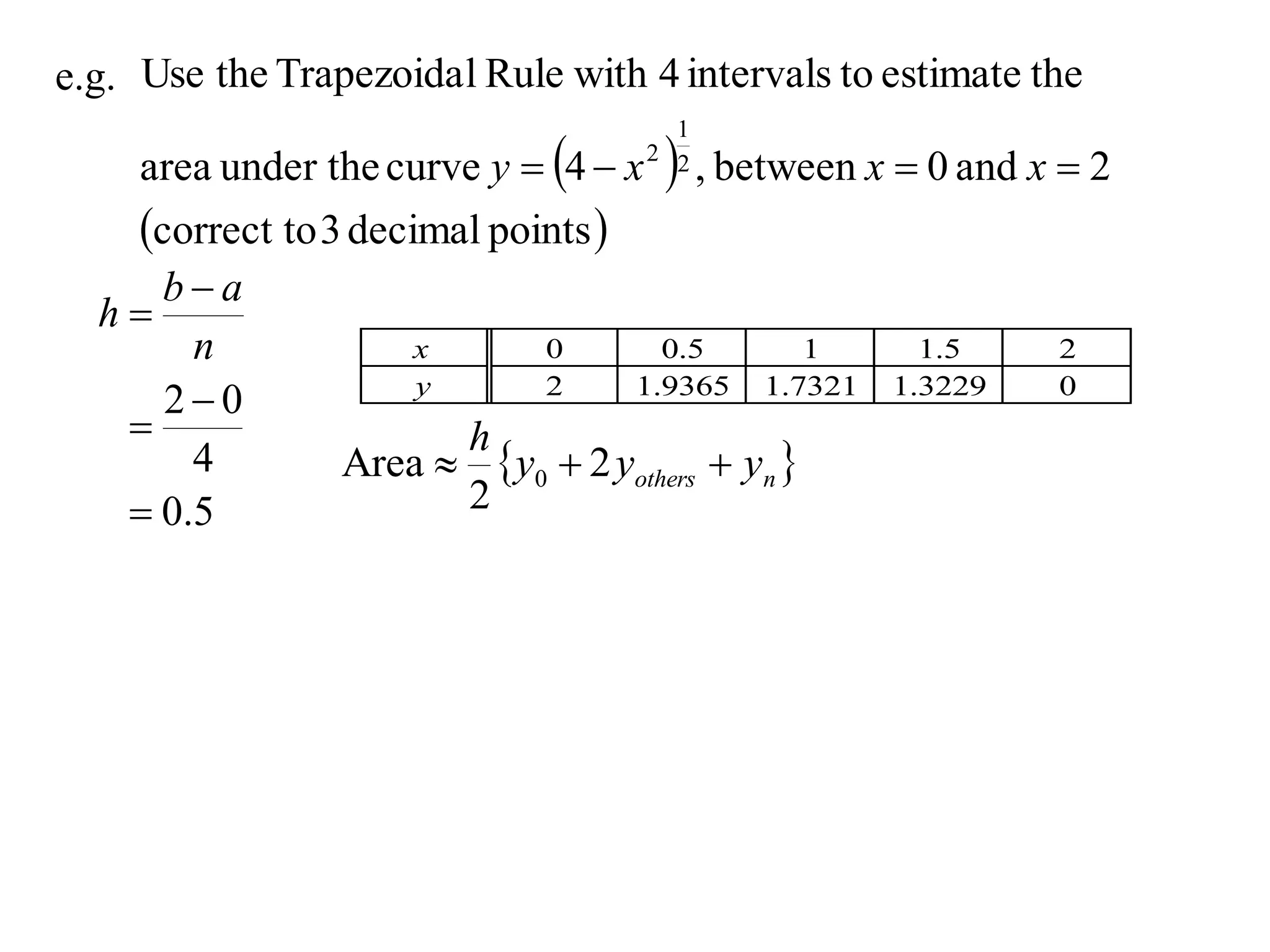
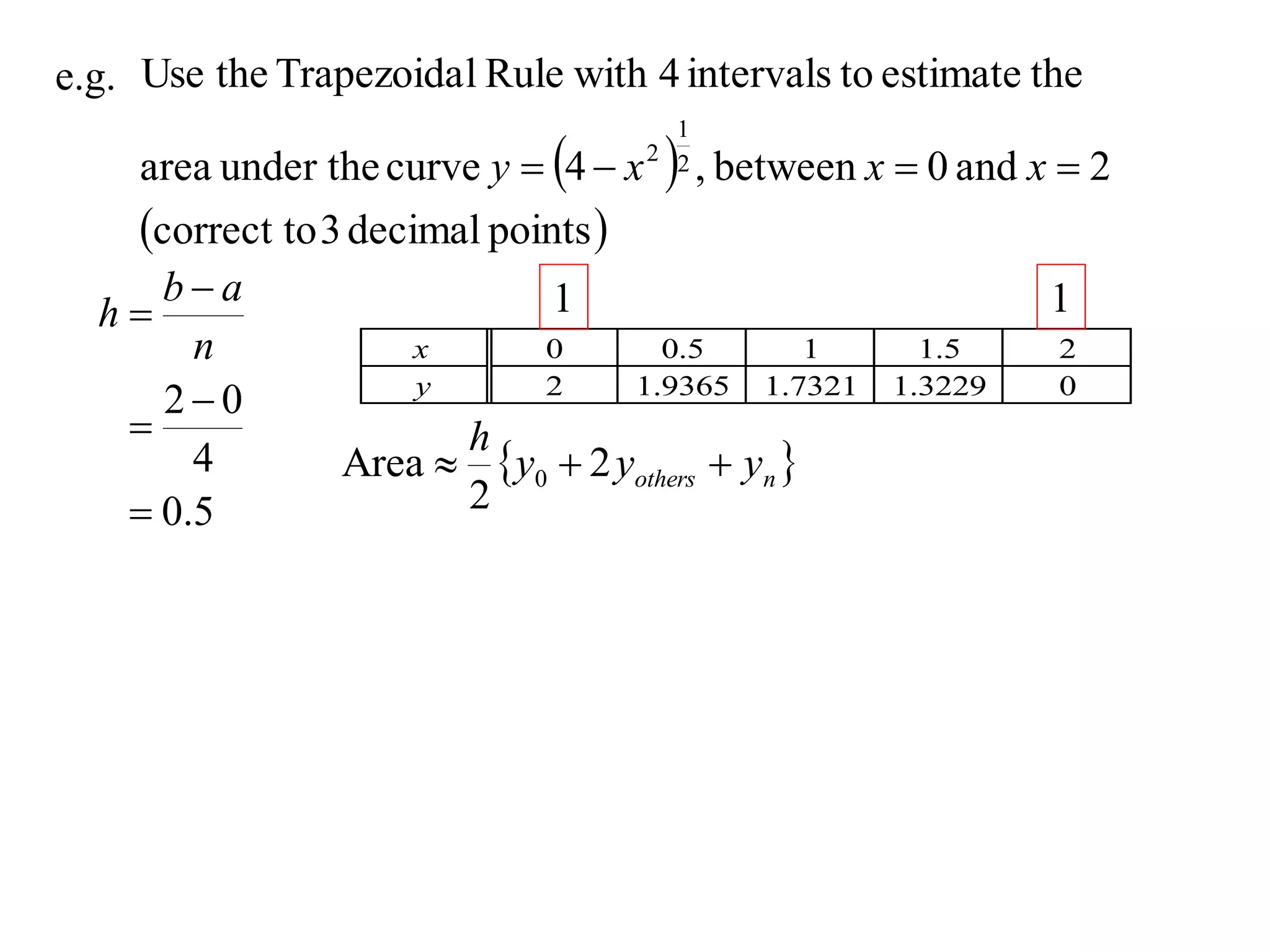
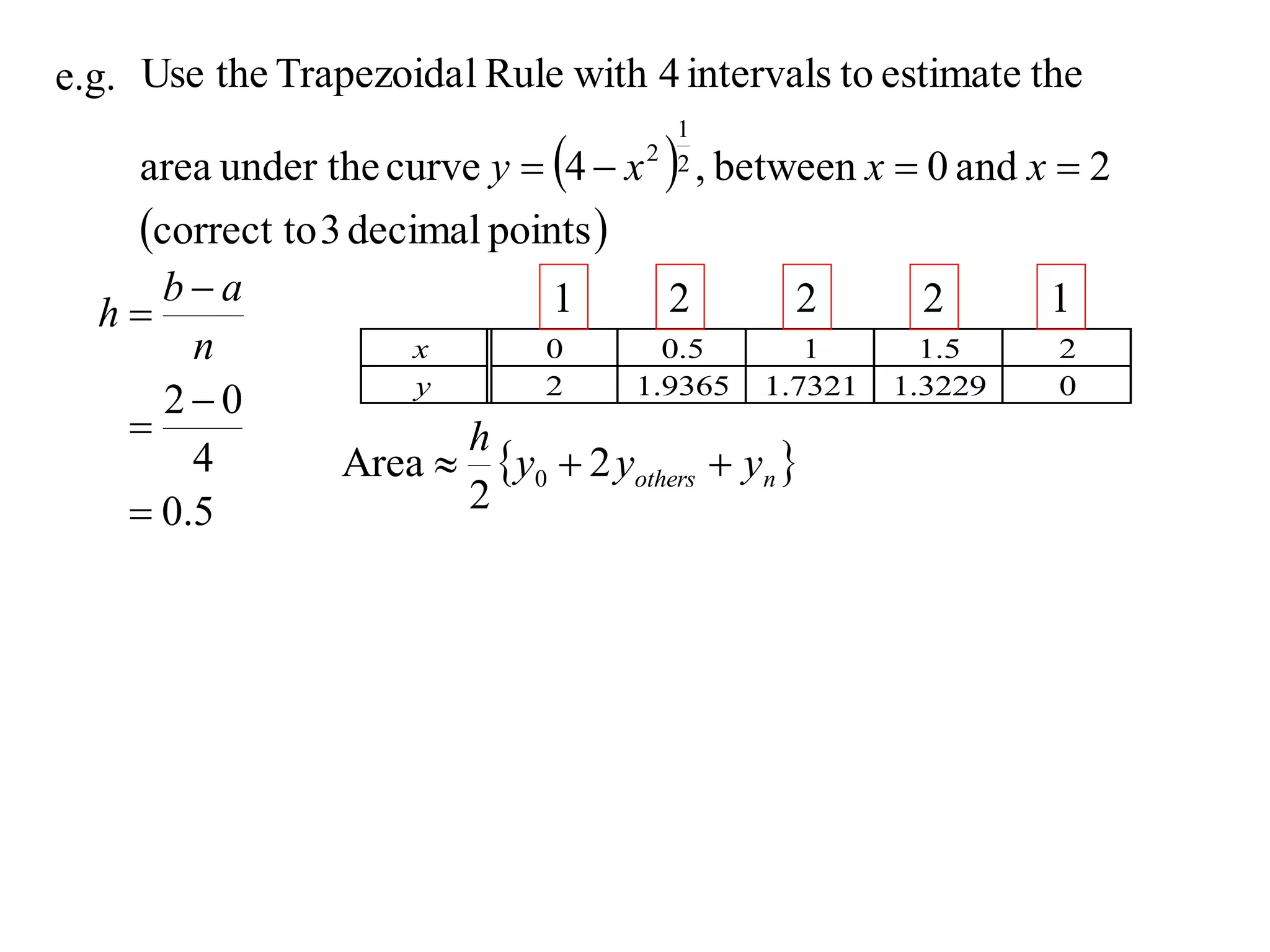
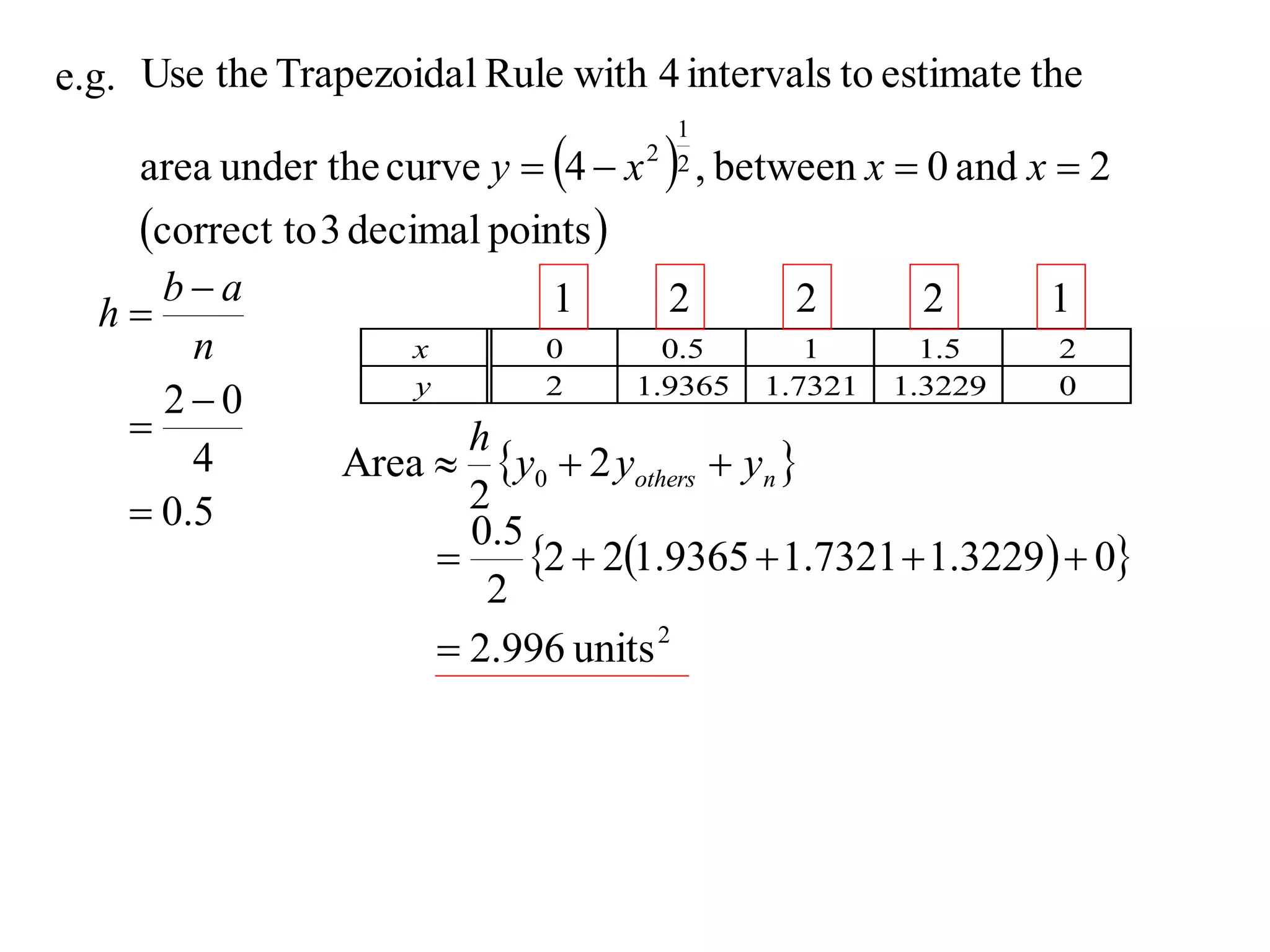
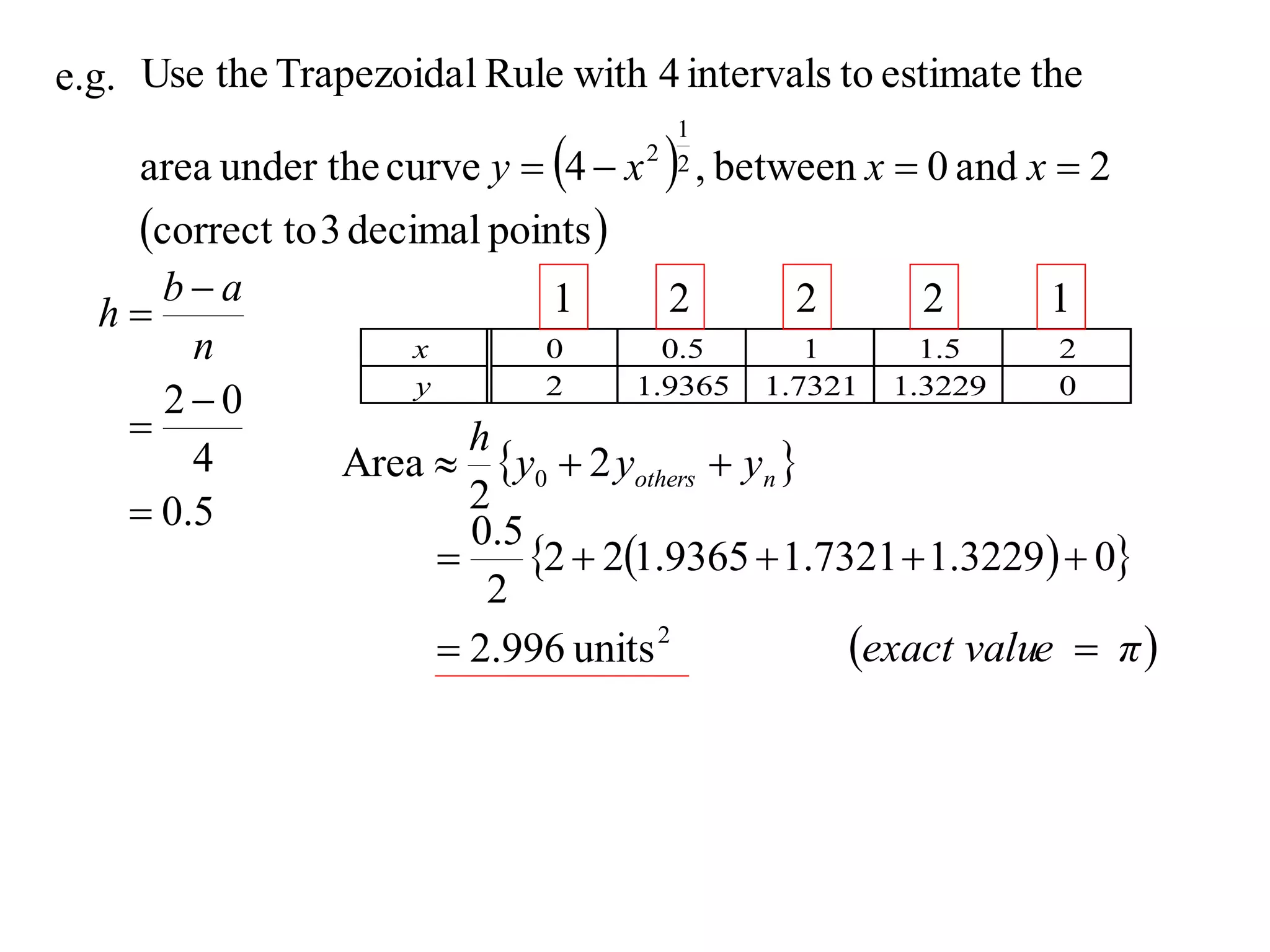
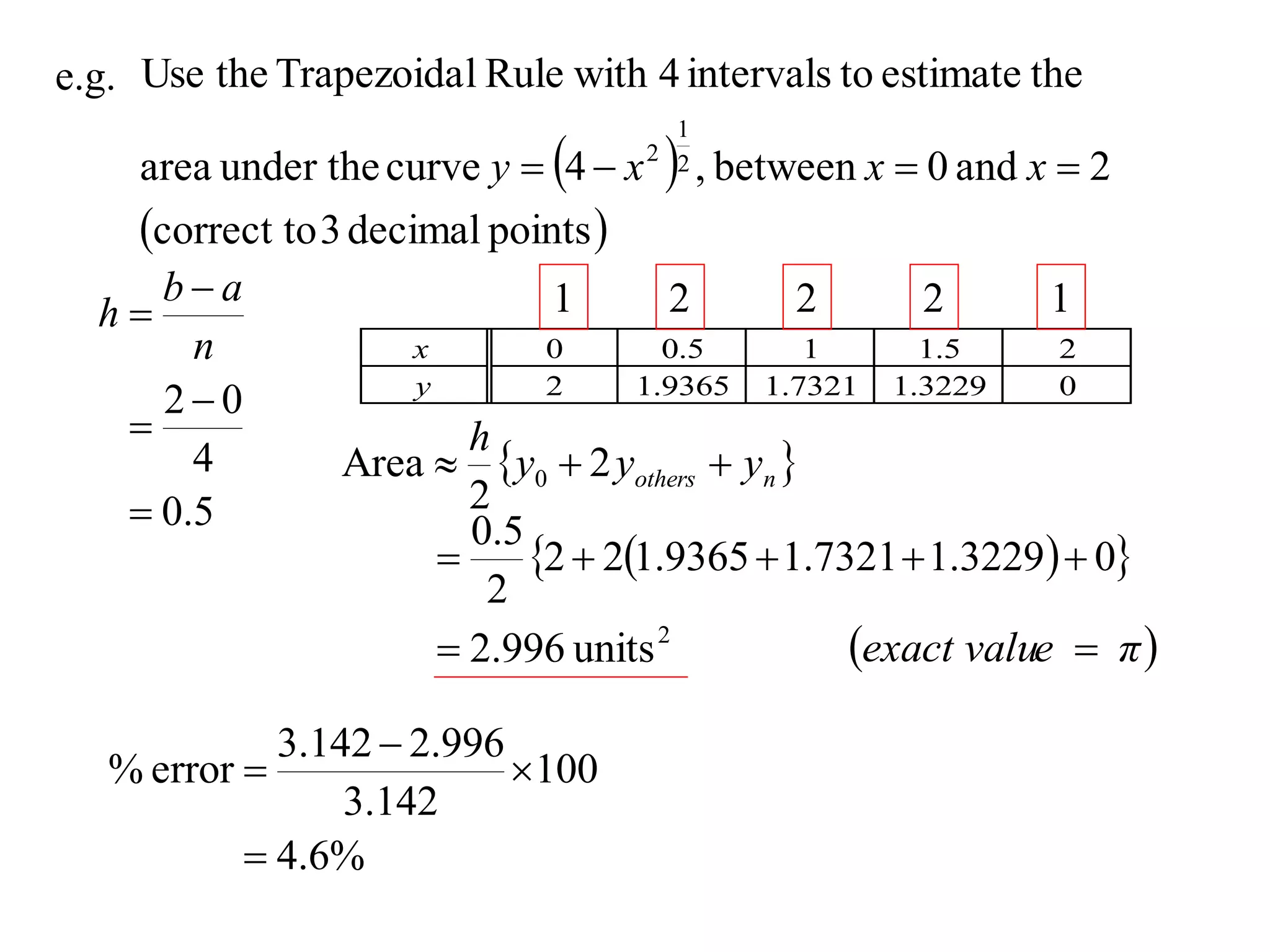
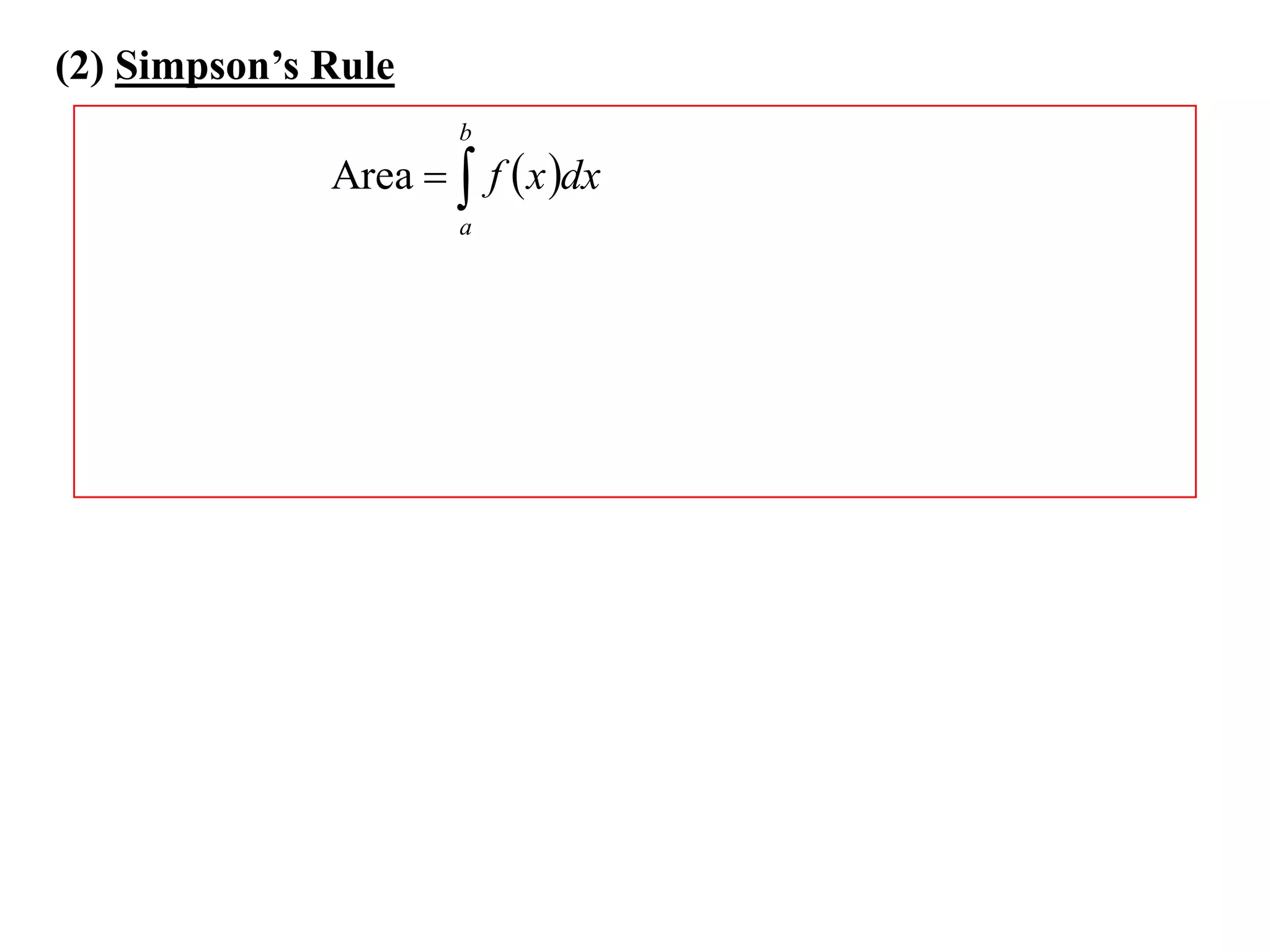
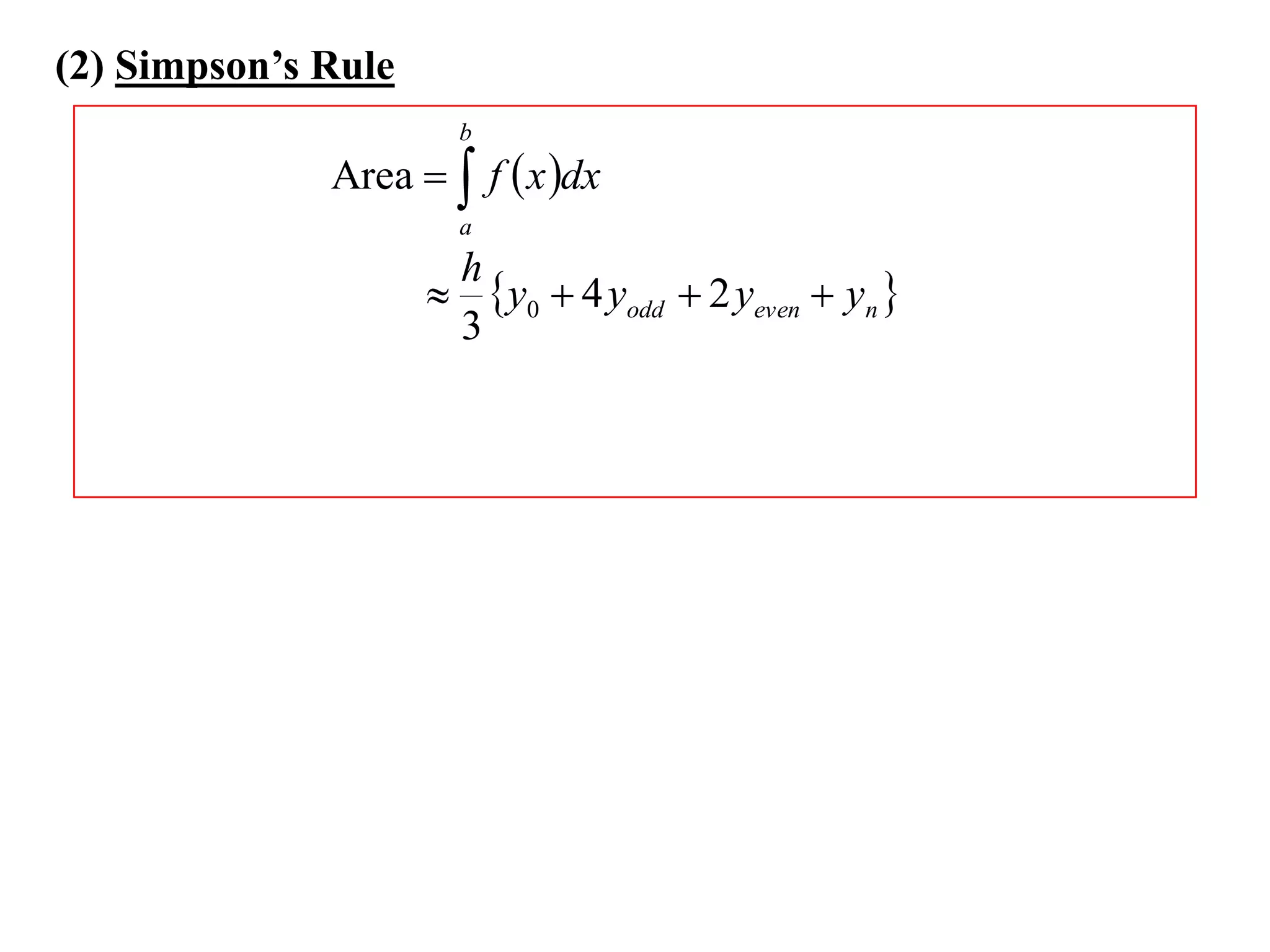
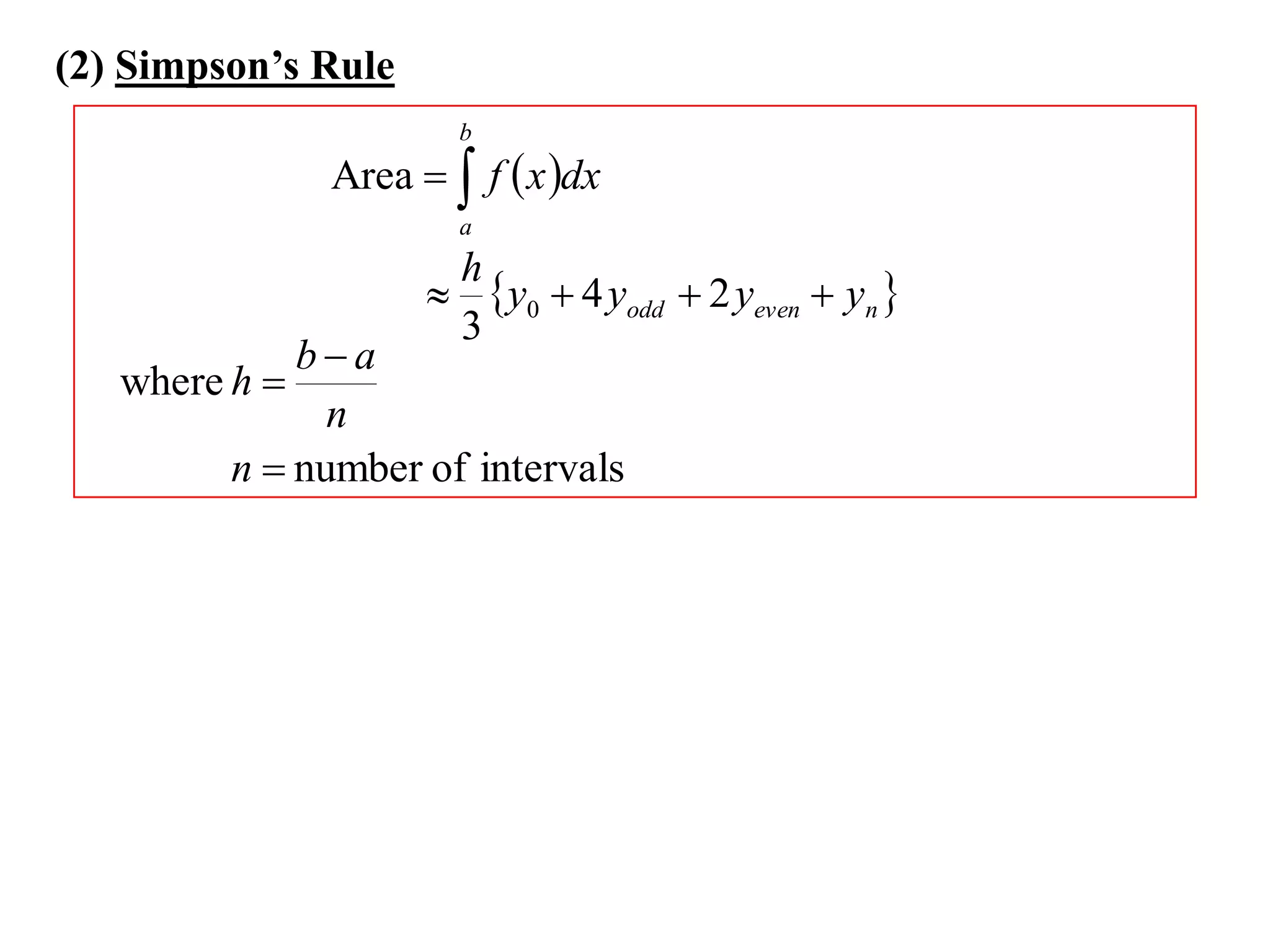
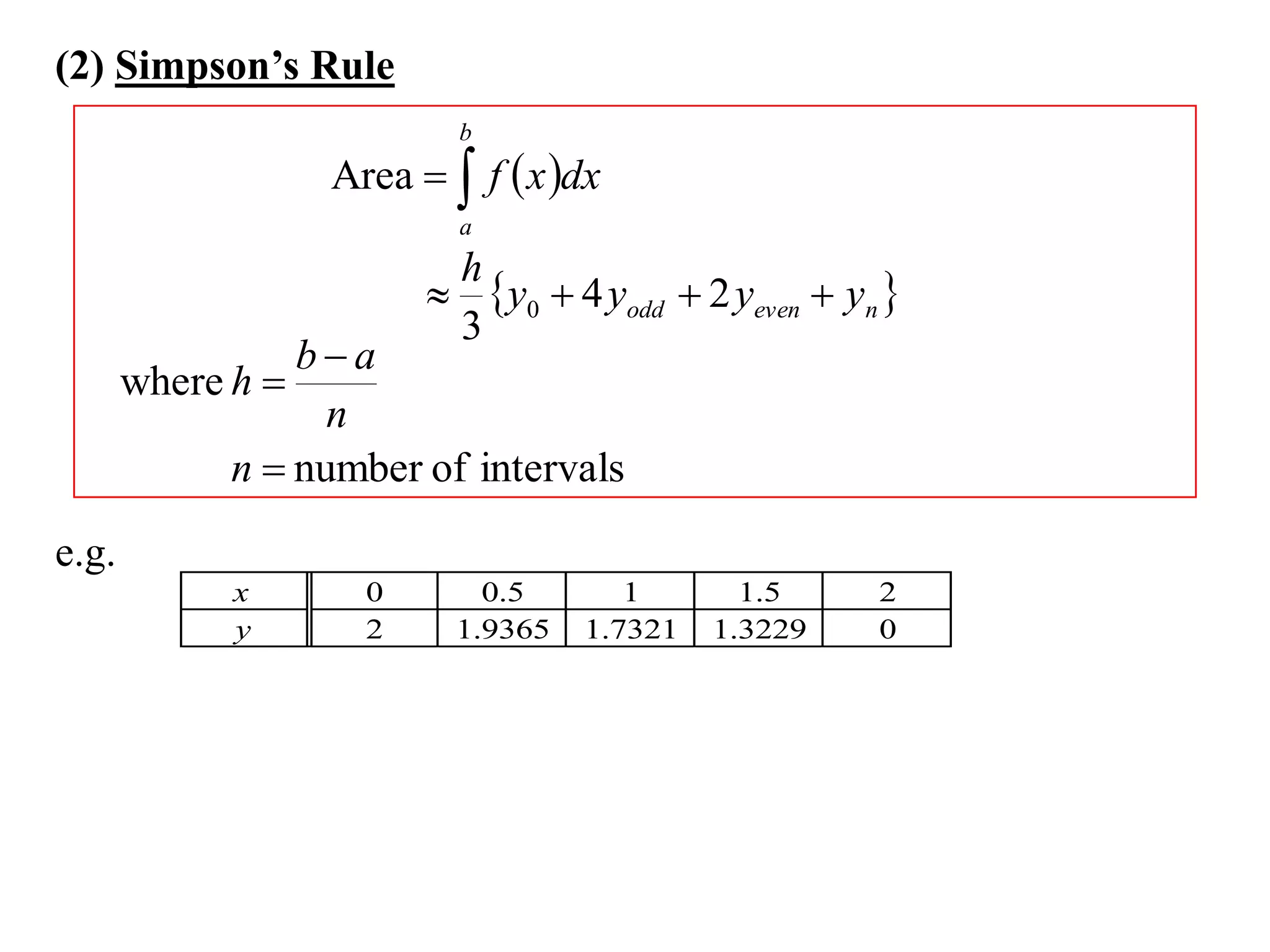
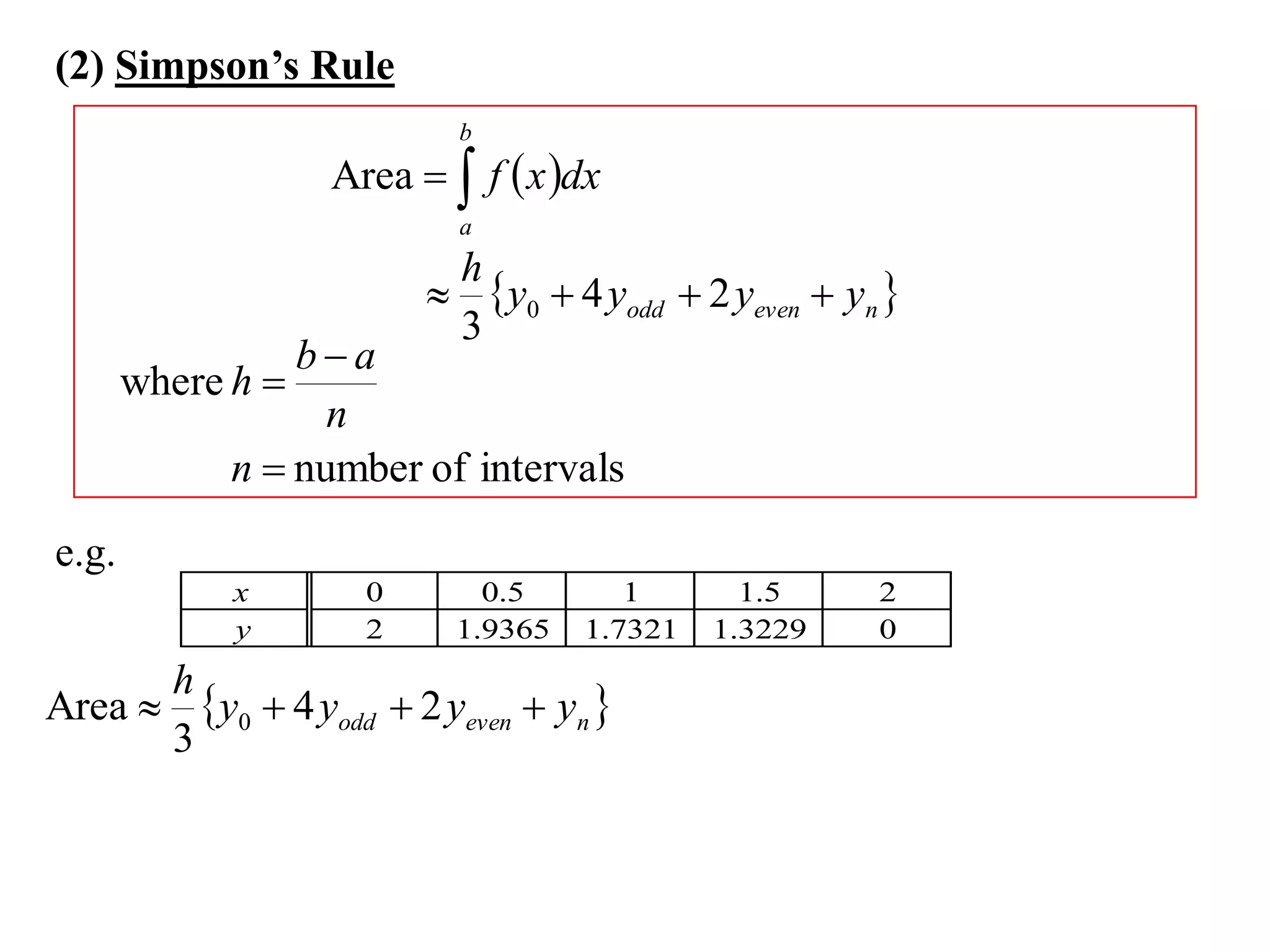
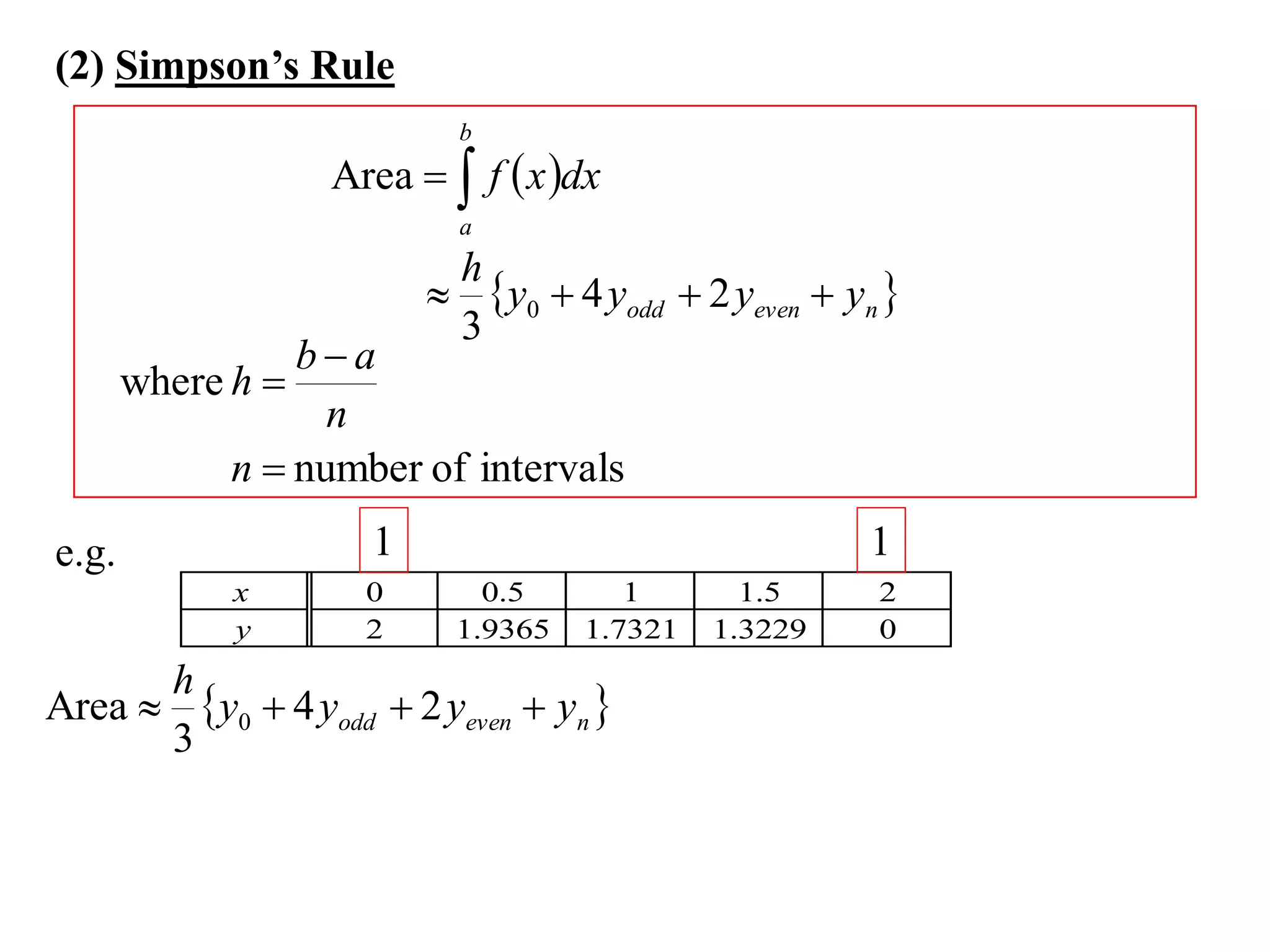
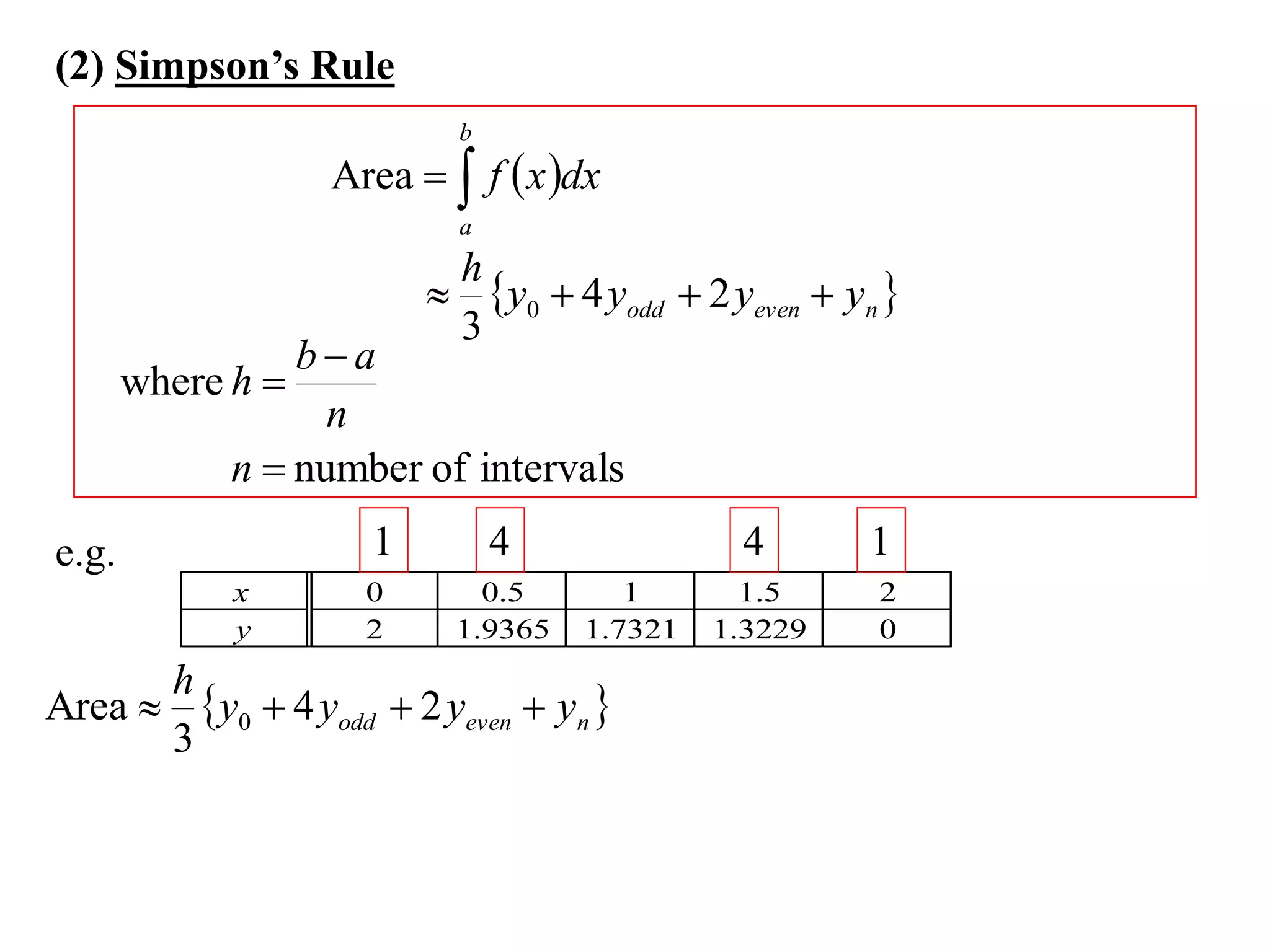
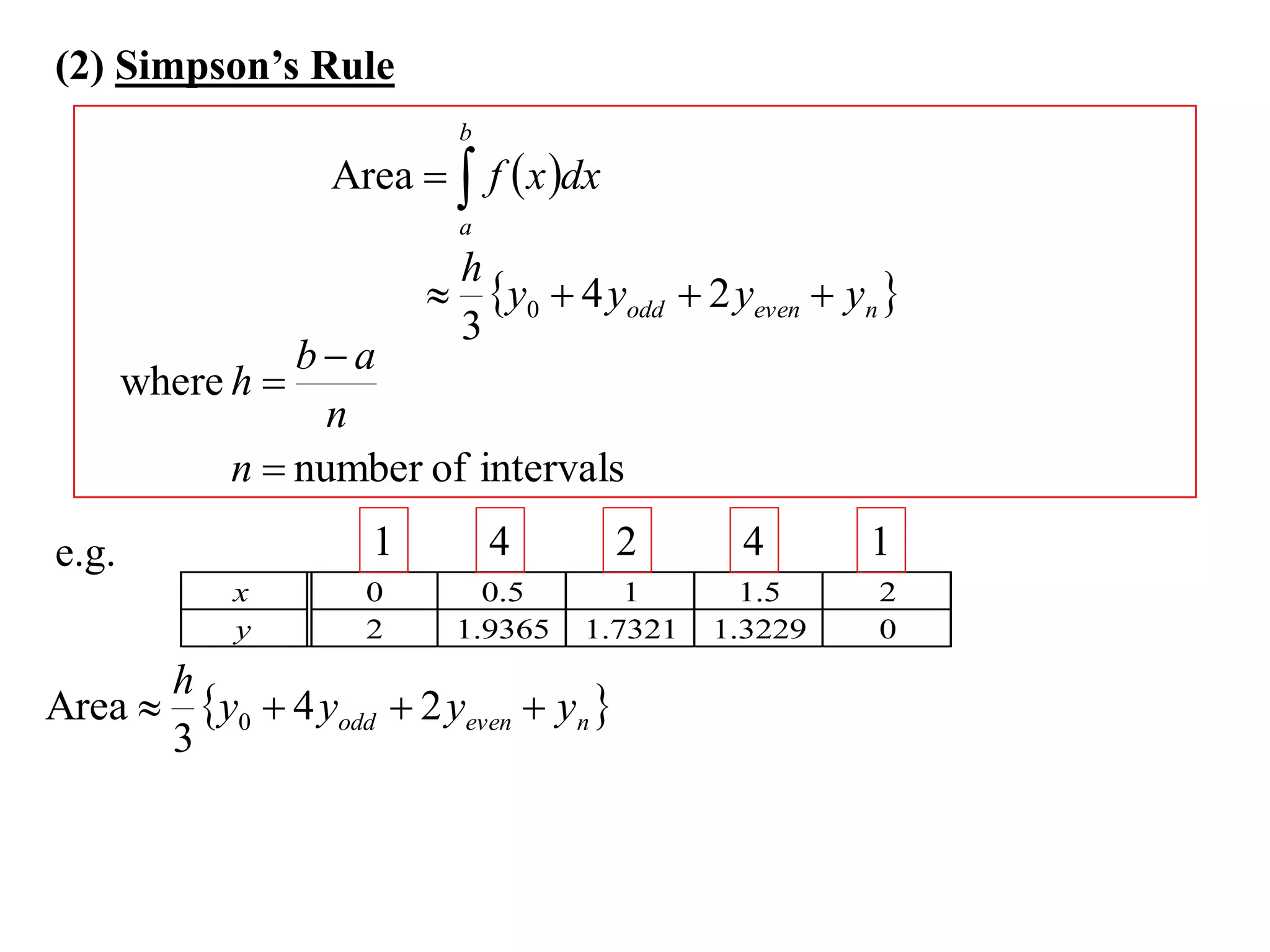
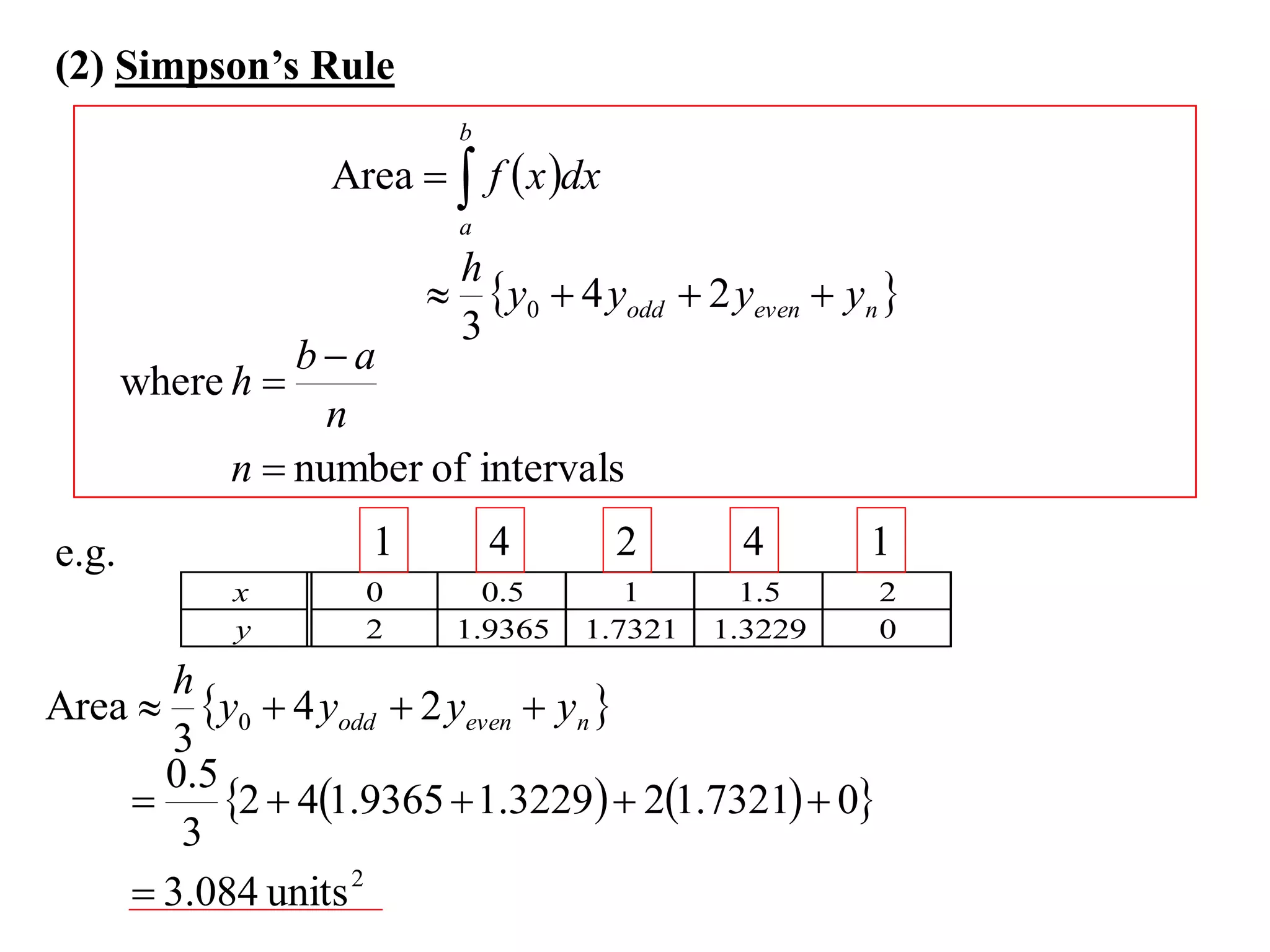
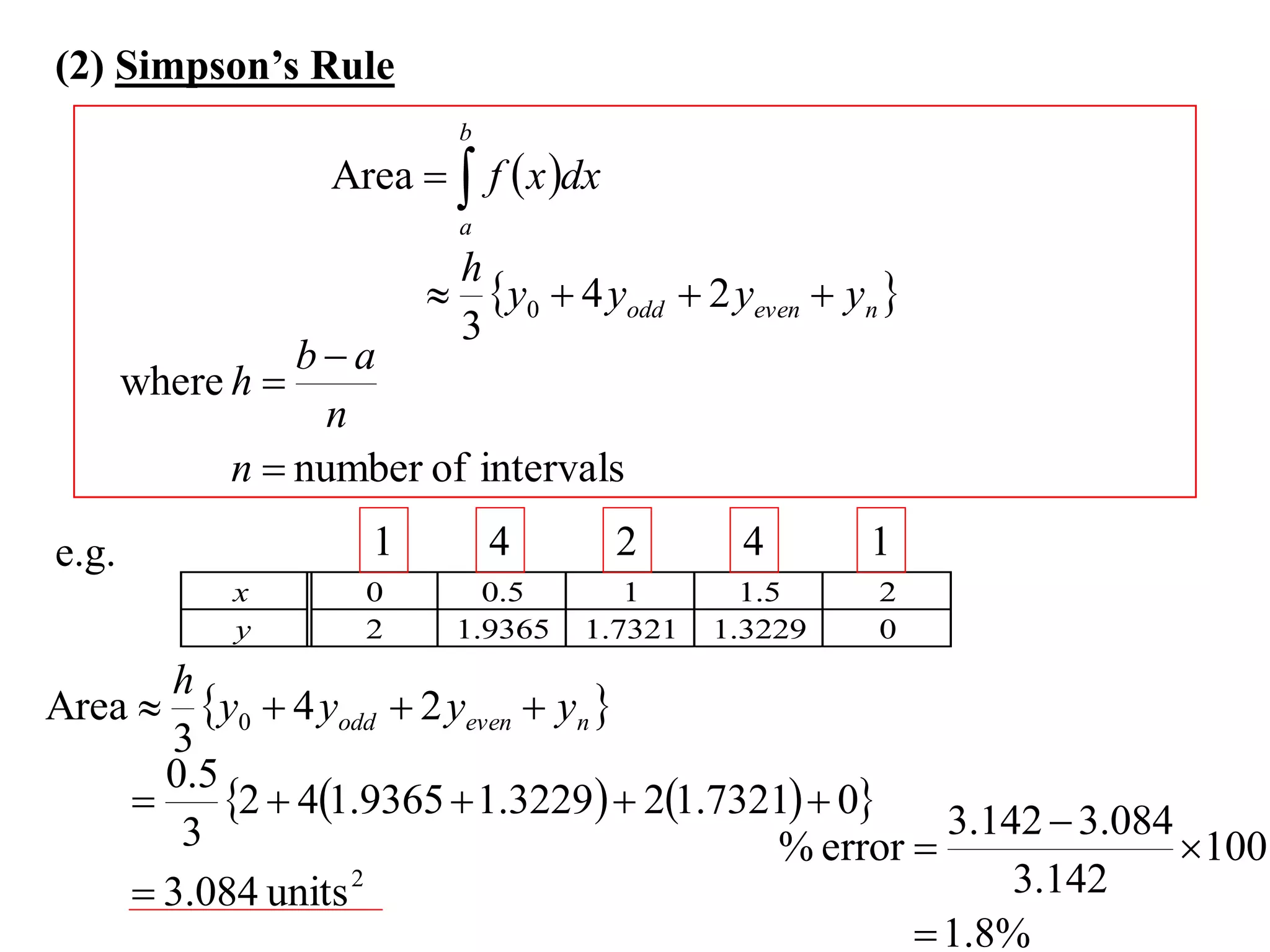
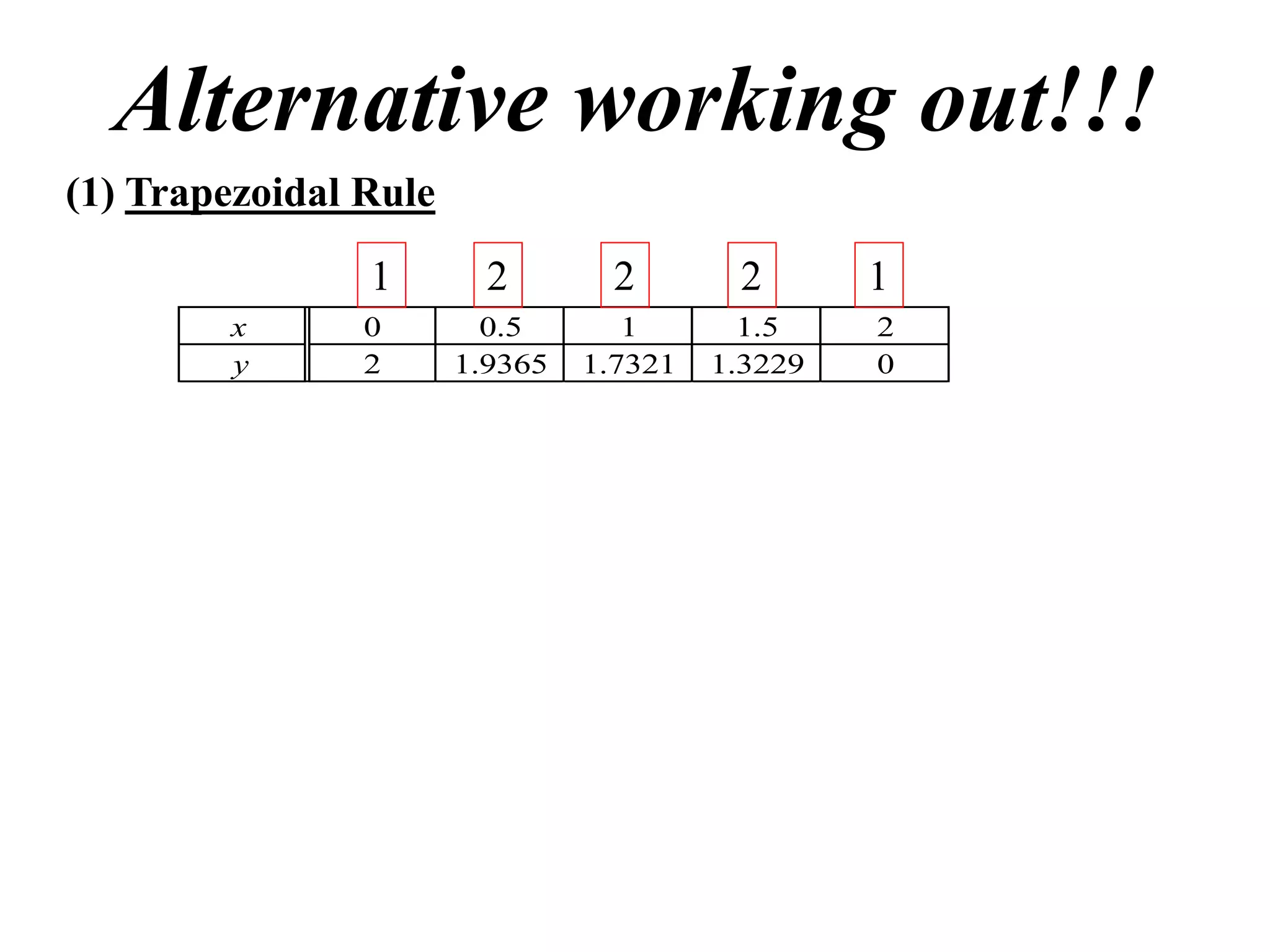
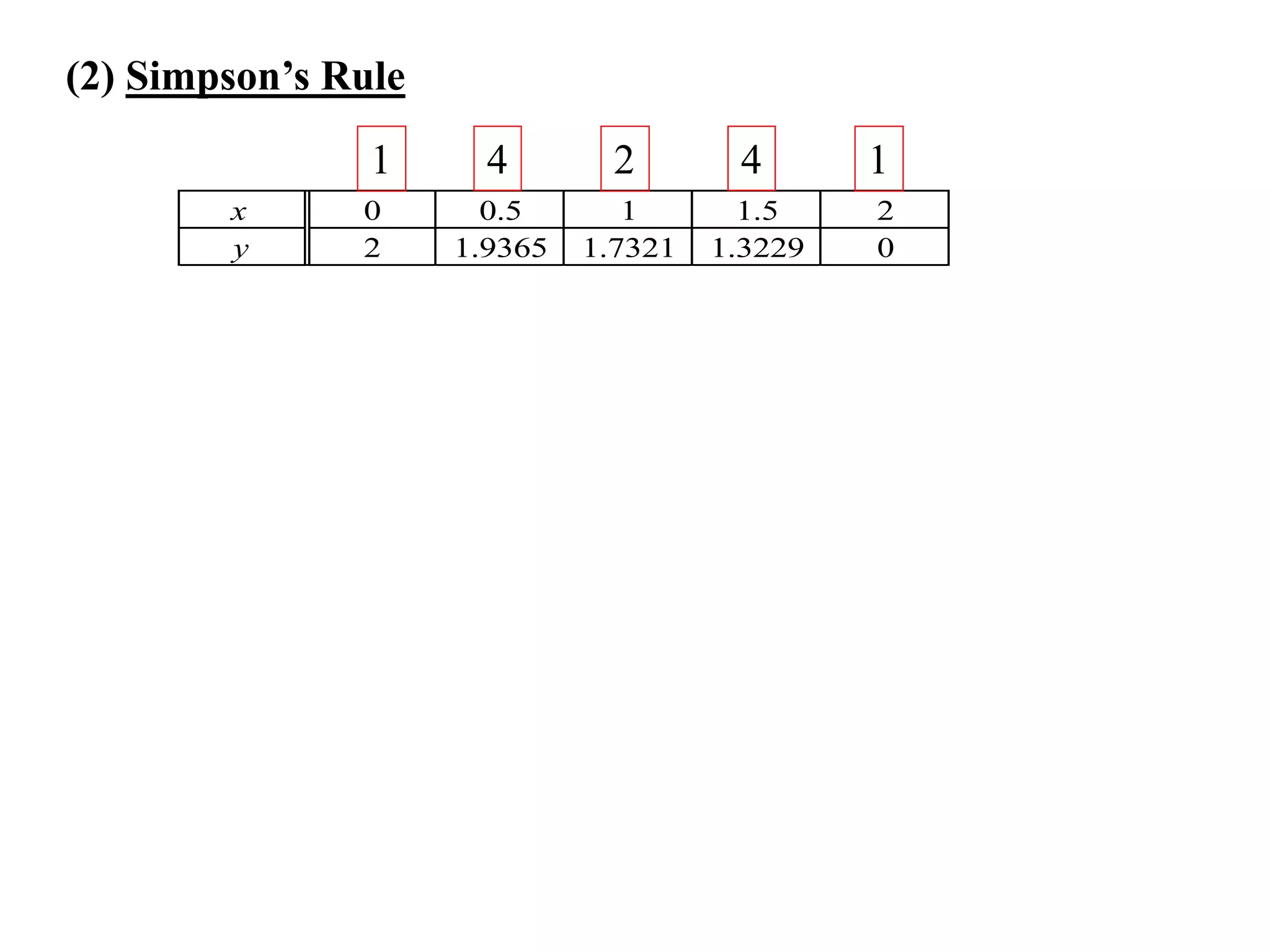
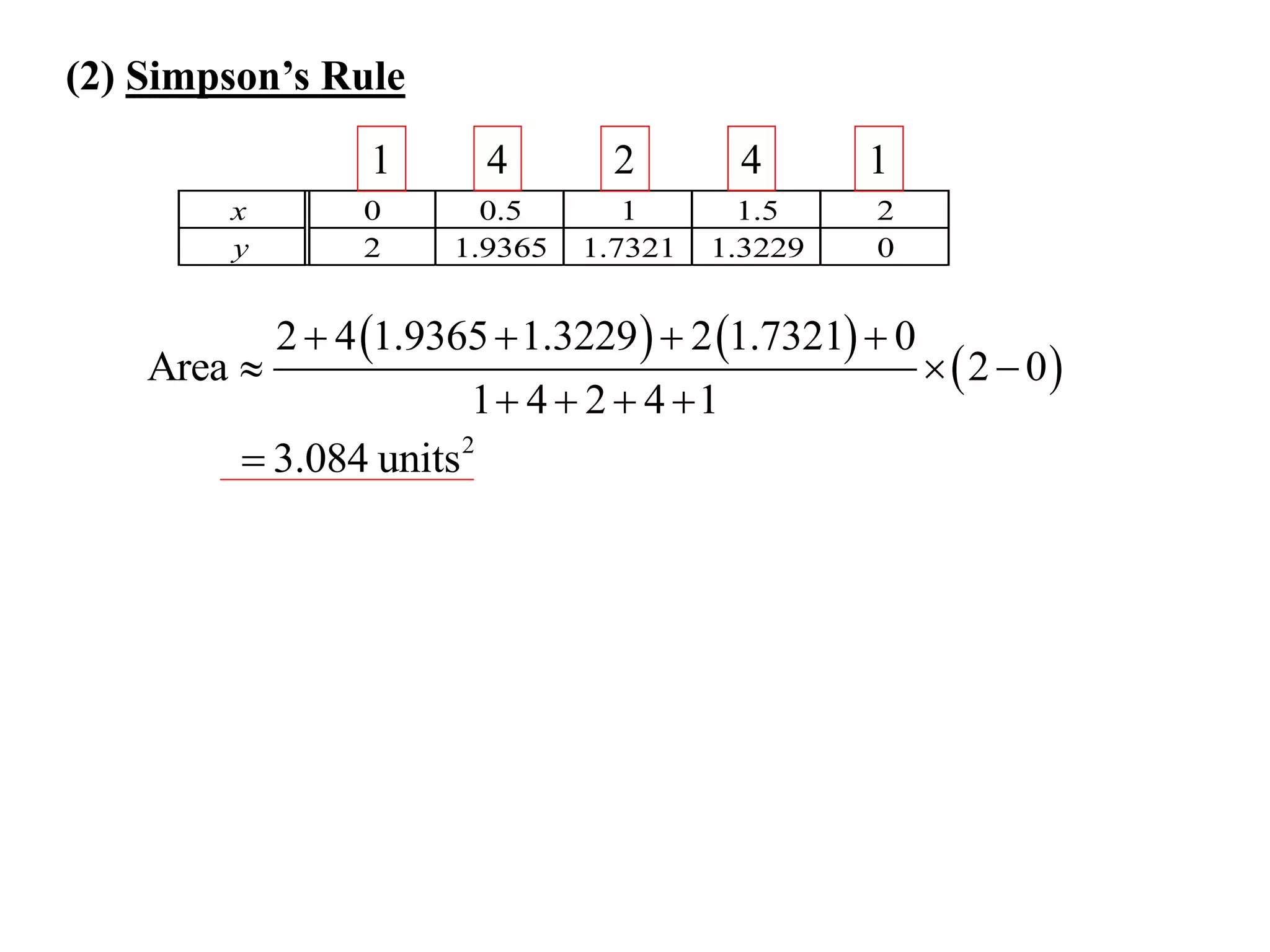
The document describes the Trapezoidal Rule for approximating the area under a curve between two points. It shows that the area A is estimated by dividing the region into trapezoids with height equal to the function values at the interval endpoints and bases equal to the intervals. In general, the area is approximated as the sum of the areas of each trapezoid, which is equal to the average of the endpoint function values multiplied by the interval length.