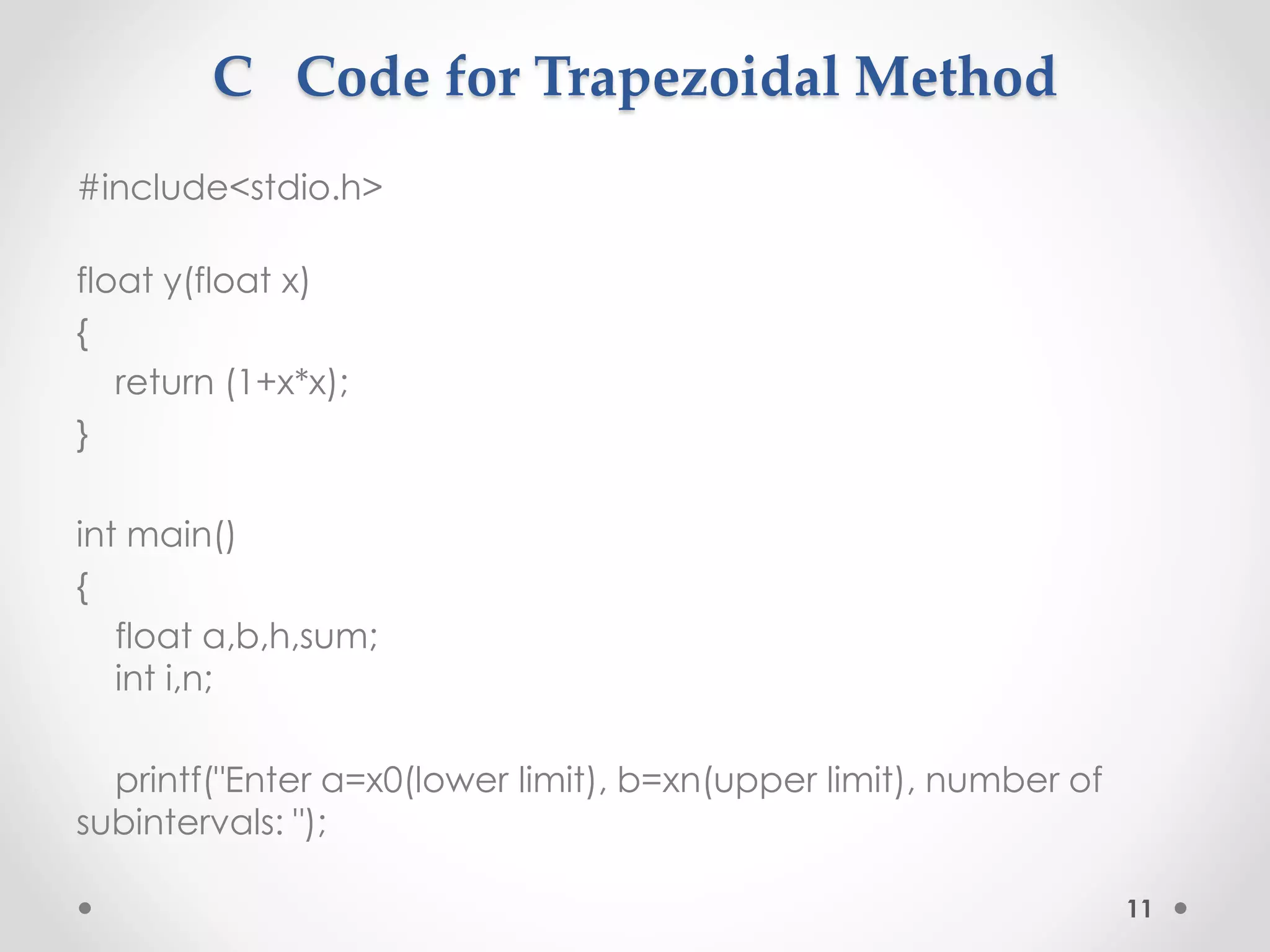
The document discusses the trapezoidal method, which is a technique for approximating definite integrals. It provides the general formula for the trapezoidal rule, explains how it works by approximating the area under a function as a trapezoid, and discusses its history, advantages of being easy to use and having powerful convergence properties. An example application of the trapezoidal rule is shown, along with pseudocode and a C code implementation. The document concludes the trapezoidal rule can accurately integrate non-periodic and periodic functions.





![General Formula of Integration
In general Integration formula when n=1 its
Trapezoidal rule.
I=h[n푦0+
푛2
2
Δ푦0+
2푛3−3푛2
12
Δ2푦0+
푛4−4푛3+4푛2
24
Δ3푦0 + ⋯ ]
After putting n=1,
Trapezoidal Rule =
ℎ
2
[푦0 + 푦푛 + 2(푦1 + 푦2 + 푦3 + ⋯ . 푦푛−1)]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonnumericalmethodpowerpointfinal-141213041412-conversion-gate02/75/Presentation-on-Numerical-Method-Trapezoidal-Method-6-2048.jpg)

![The trapezoidal rule works
by approximating the region
under the graph of the
function as a trapezoid and
calculating its area in limit.
It follows that,
푏
f(x) dx ≈
푎
(b−a)
2
[f(a) +f(b)]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonnumericalmethodpowerpointfinal-141213041412-conversion-gate02/75/Presentation-on-Numerical-Method-Trapezoidal-Method-8-2048.jpg)




![Example:
푥1 푥2 푥3
=2 =3 =4
=1 =5
5
1 + 푥2 푑푥
1
h =
5−1
4
=1
Trapezoidal Rule =
1
2
[ 푓(1) + 푓(5) + 2(푓(2) + 푓(3) + 푓(4)]
=
1
2
[ (1 + 12) + (1 + 52) + 2((1 + 22) + (1 + 32) + (1 + 42)]
=
1
2
× 92
= 46 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonnumericalmethodpowerpointfinal-141213041412-conversion-gate02/75/Presentation-on-Numerical-Method-Trapezoidal-Method-13-2048.jpg)