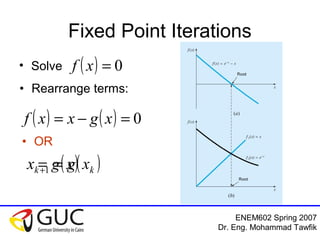
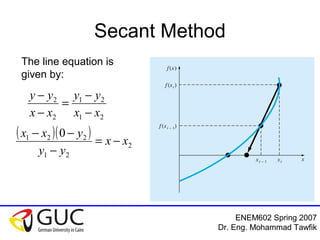
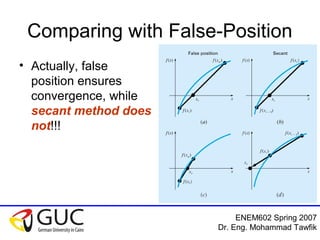
This document outlines numerical methods for finding roots of nonlinear equations presented by Dr. Eng. Mohammad Tawfik. It introduces the fixed point, Newton-Raphson, and secant methods. The fixed point method rearranges the equation to an iterative form where the next estimate is a function of the previous. Newton-Raphson linearizes the function to get faster convergence. The secant method does not require derivatives by using the slope between previous points. Convergence conditions and algorithms are provided for each method. Students are assigned homework problems from the textbook.