This document provides an overview of key concepts in calculus including the definite integral, properties of definite integrals, the Mean Value Theorem for Integrals, the Average Value Theorem, the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus parts 1 and 2, and the Trapezoidal Rule for approximating definite integrals. It defines integrals, discusses how to evaluate them on a TI-84 calculator, and lists properties such as additivity, constant multiples, and order of integration. It also introduces concepts like finding the average value of a function over an interval using the integral, and relating the derivative of an integral to the original function.




![4.3 Properties of Definite Integrals:
a
b
f(x) dx
1. Order of Integration
f(x) dx
b
a
a
f(x) dx = 0
2. Zero
a
b
b
k f(x) dx
3. Constant Multiple
a
f(x) dx
a
b
4. Sum and Difference
k
b
[ f(x) g(x)] dx
a
b
5. Additivity
b
f(x) dx
a
c
a
c
f(x) dx + f(x) dx
a
b
g(x) dx
f(x) dx
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4review-140123061157-phpapp01/85/Definite-Integral-Review-5-320.jpg)
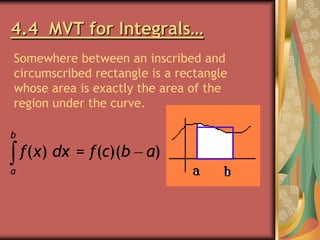
![4.4 Average Value Theorem
The value f(c) from the MVT is the
average value of f on [a,b]…
f(c)
1
b
(b a) a
f(x) dx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4review-140123061157-phpapp01/85/Definite-Integral-Review-7-320.jpg)

![4.4 Fund Thm of Calc: Part 2
x
d
[ f(t) dt] =f(x)
dx a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch4review-140123061157-phpapp01/85/Definite-Integral-Review-9-320.jpg)
