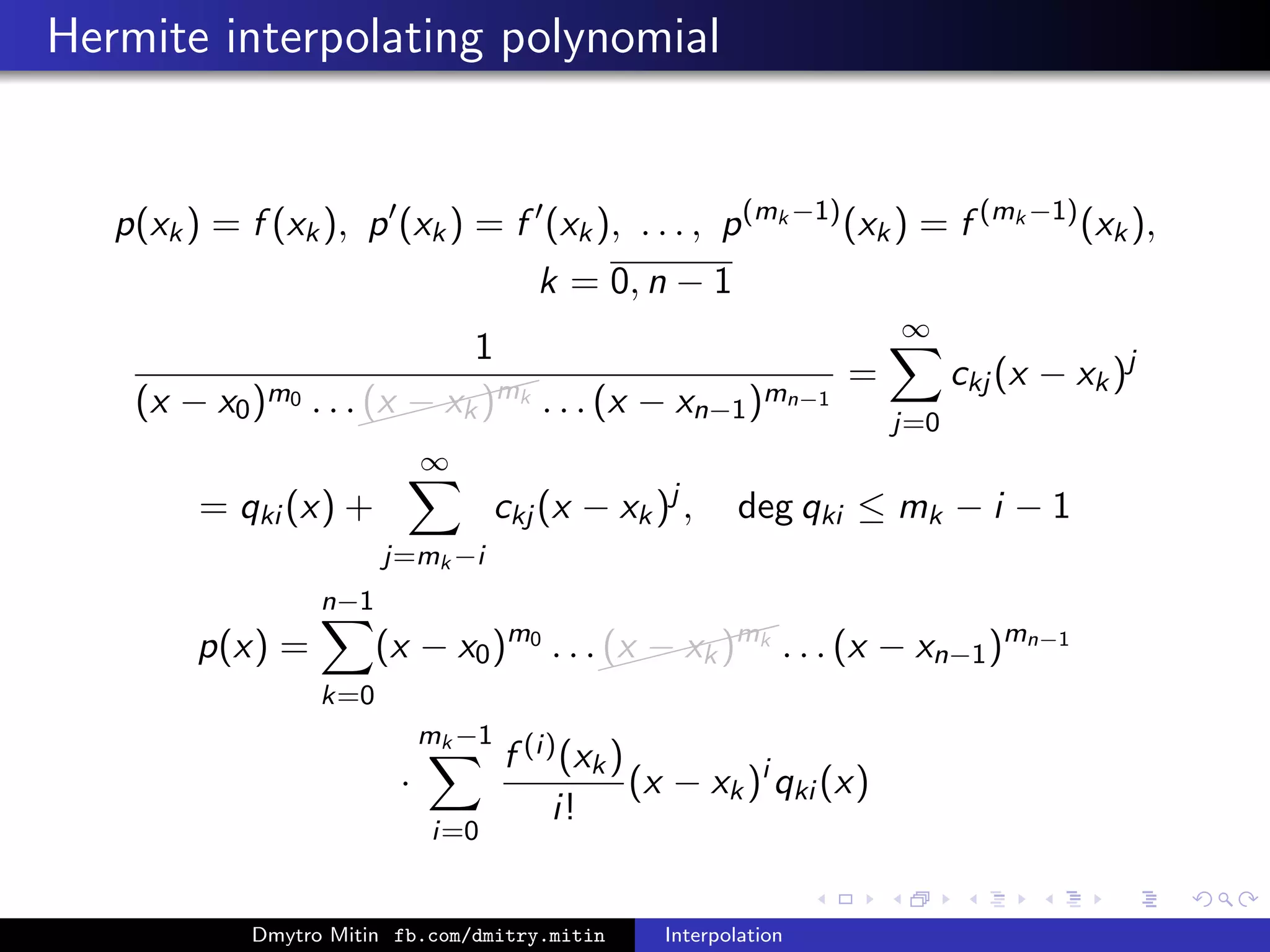
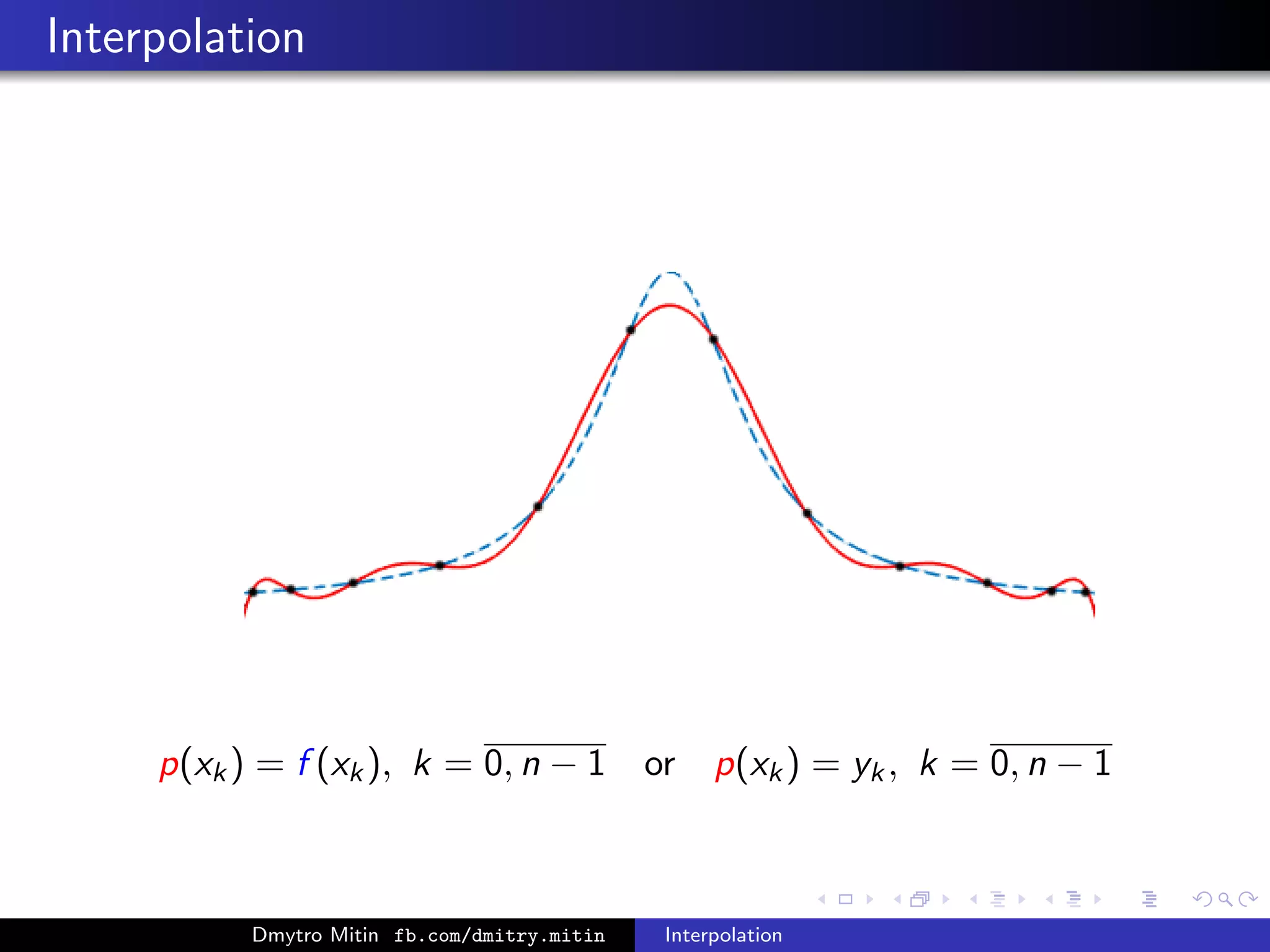
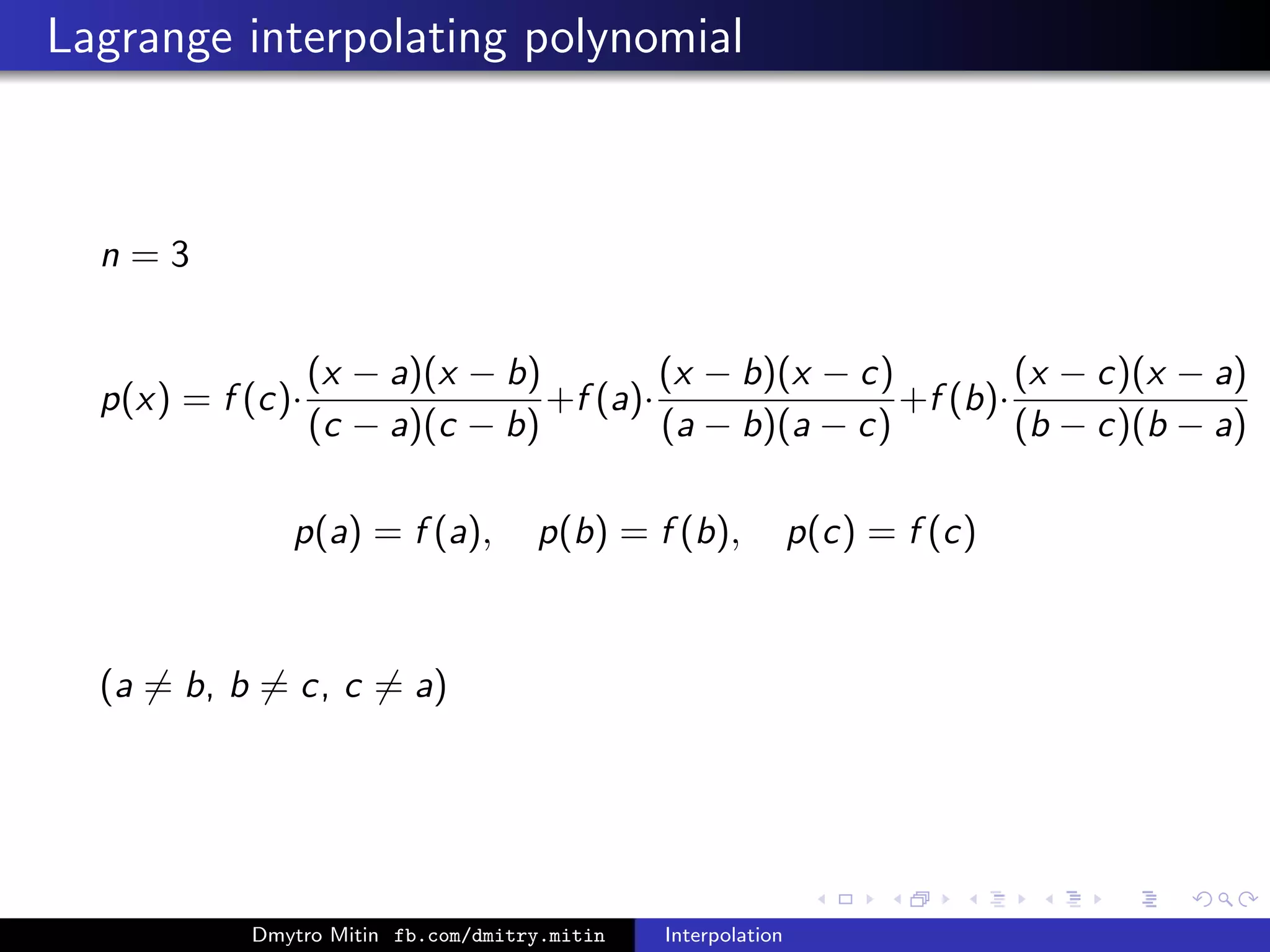
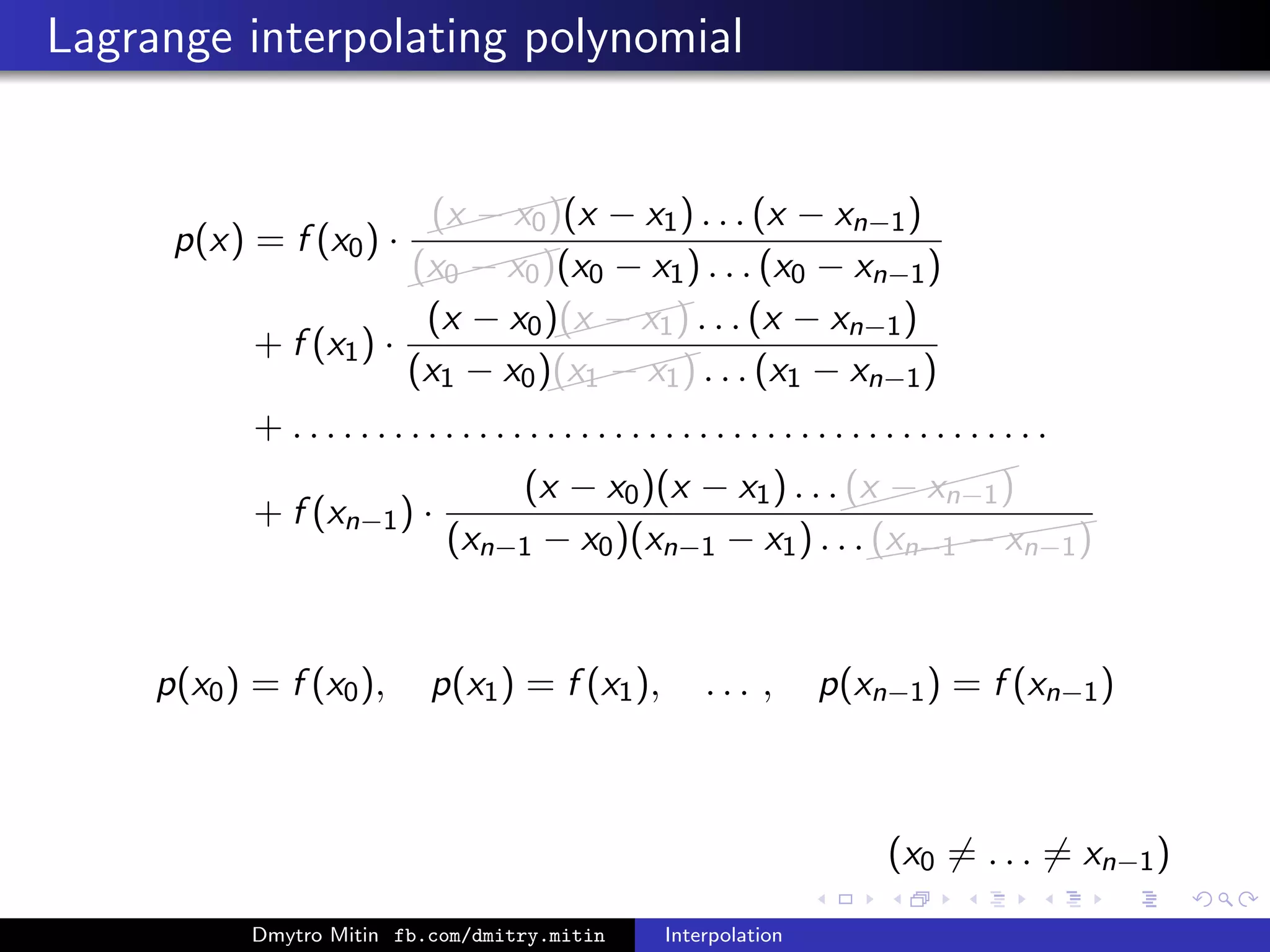
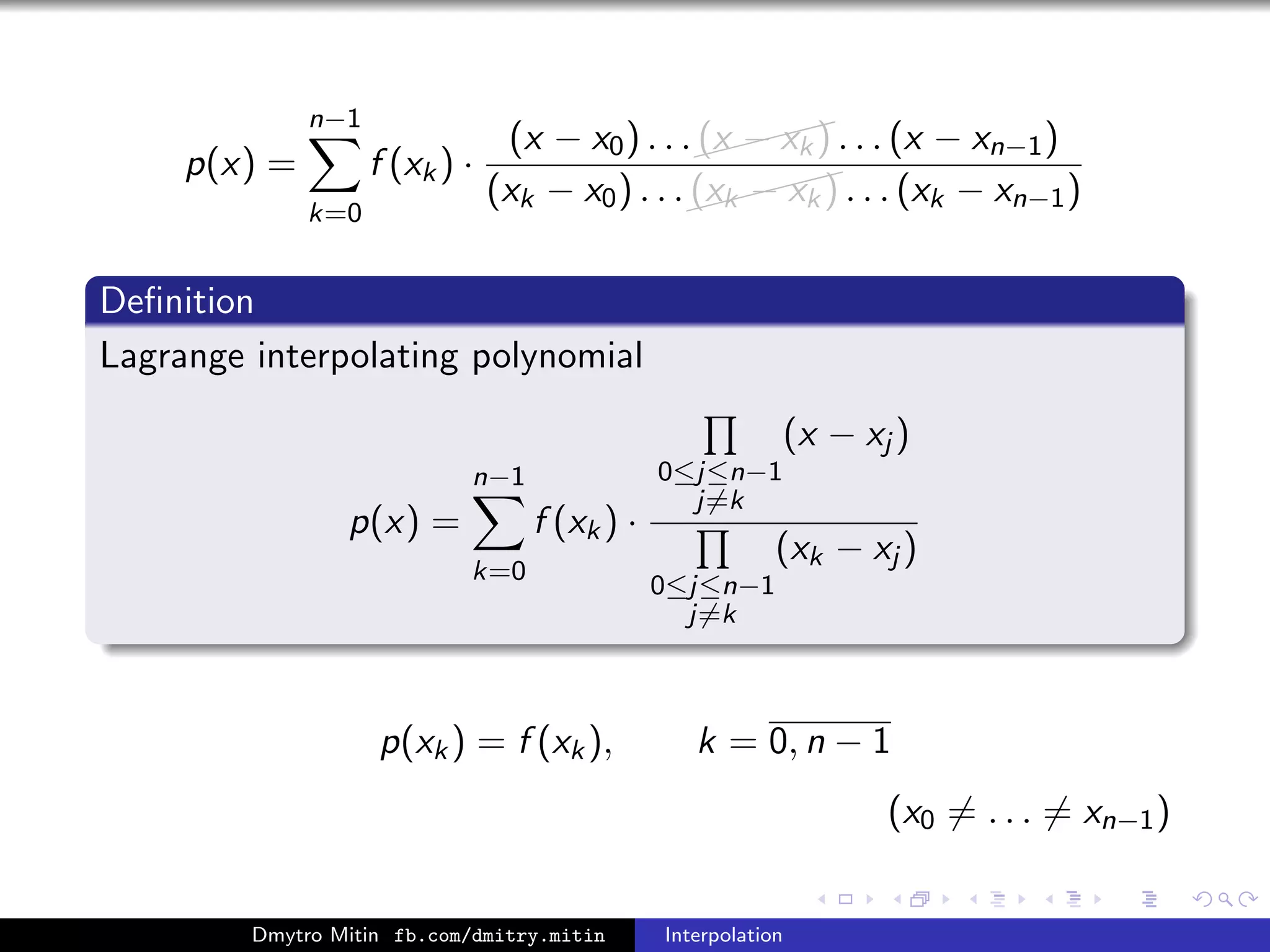
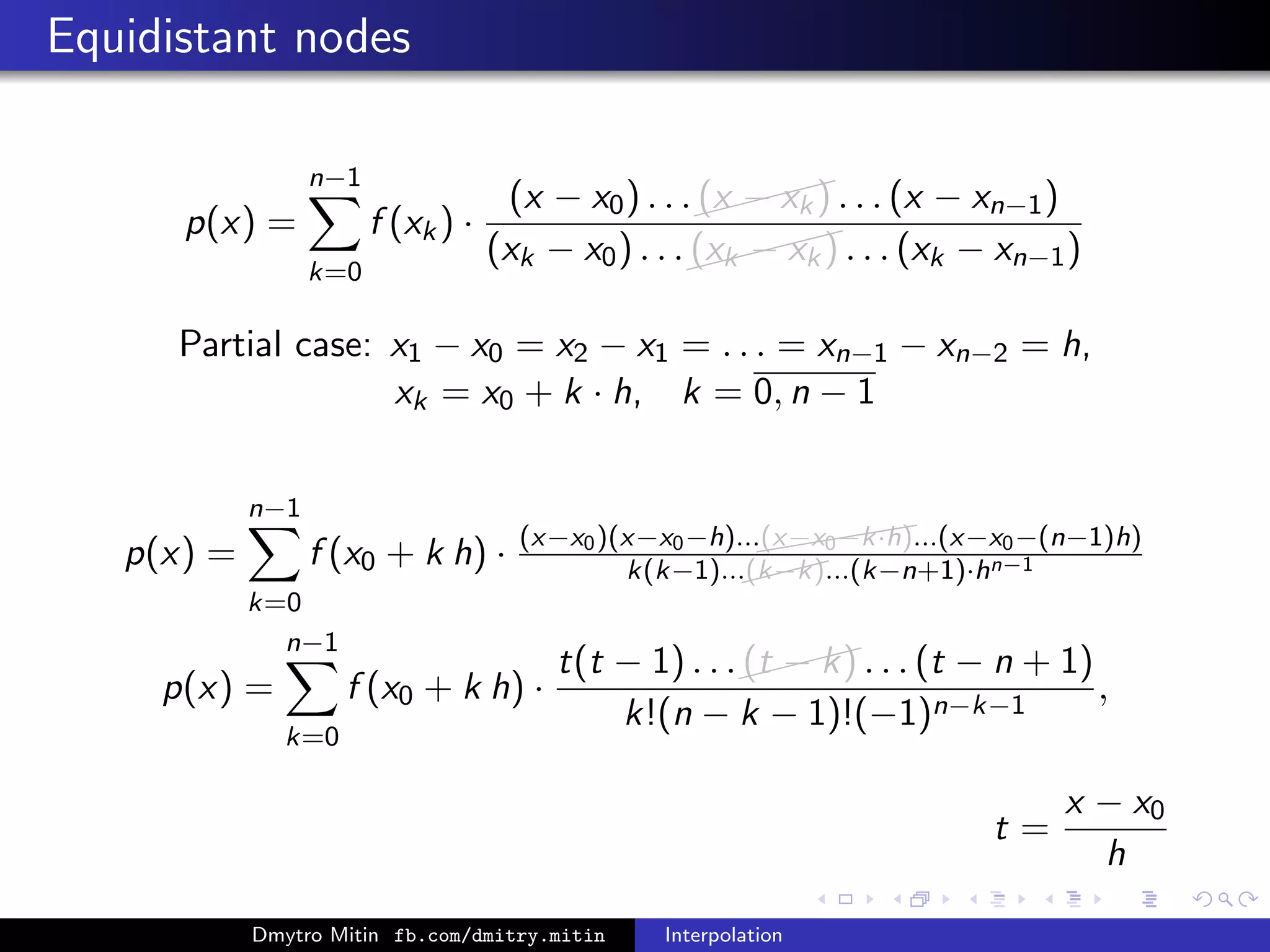
The document discusses various methods of interpolation, including Lagrange and Newton interpolation polynomials. Lagrange interpolation involves constructing a polynomial that passes through a set of n data points, represented by its values at the points. Newton interpolation similarly uses a polynomial but is based on divided differences. Both can be used to interpolate values within or extrapolate beyond the original data range. The complexity of calculating the interpolation polynomials is also addressed.




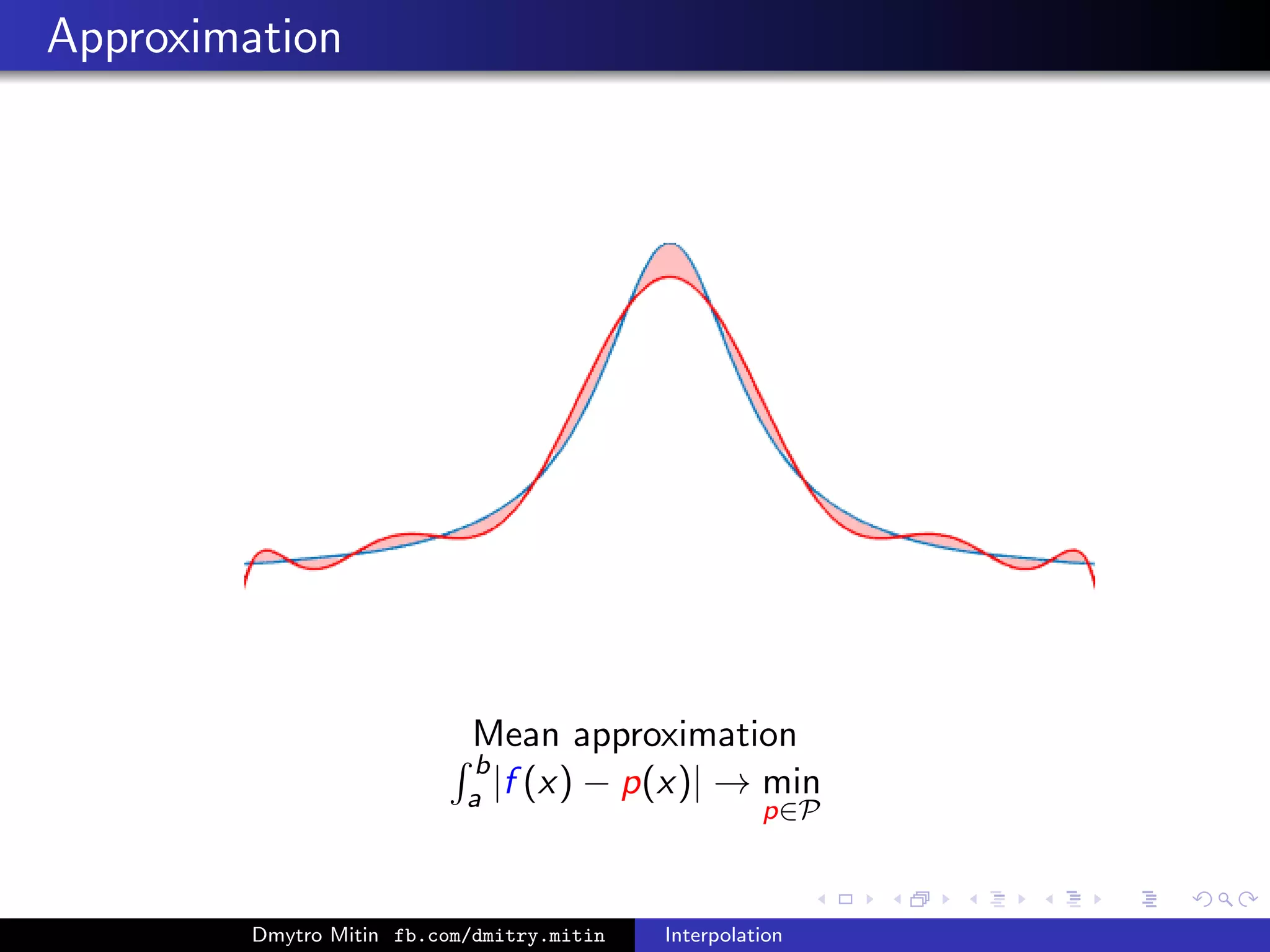
![Approximation
Uniform approximation
max
x∈[a,b]
|f (x) − p(x)| → min
p∈P
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-10-2048.jpg)




![Cj =
j
k=0
f (xk)
(xk − x0) . . .
(xk − xk) . . . (xk − xj )
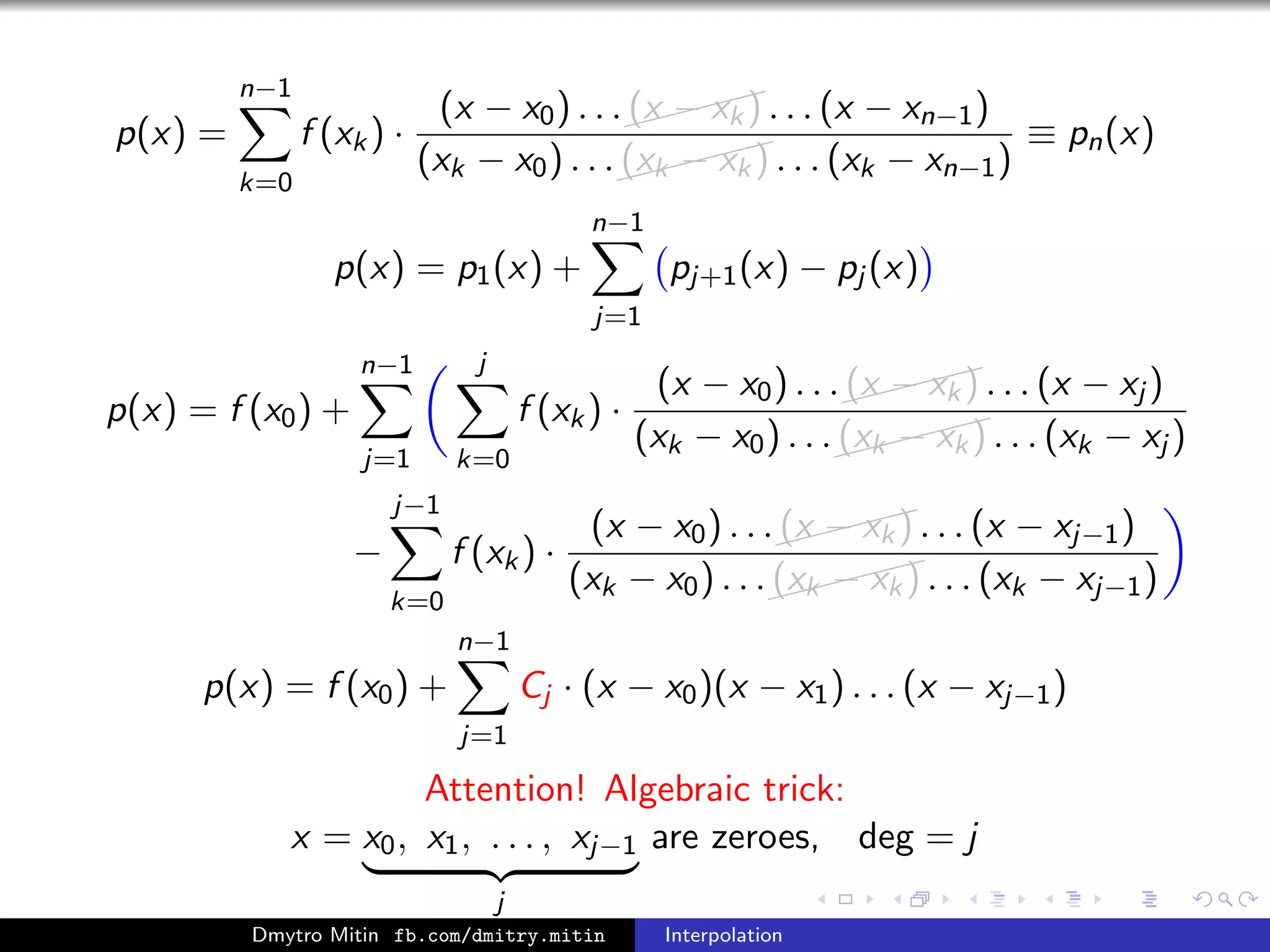
p(x) = f (x0) +
n−1
j=1
Cj · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
p(x) = f (x0) +
n−1
j=1
j
k=0
f (xk)
(xk − x0) . . .
(xk − xk) . . . (xk − xj )
·(x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
Definition
Newton interpolating polynomial
p(x) = f (x0) +
n−1
j=1
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ]
Divided differences
· (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-23-2048.jpg)
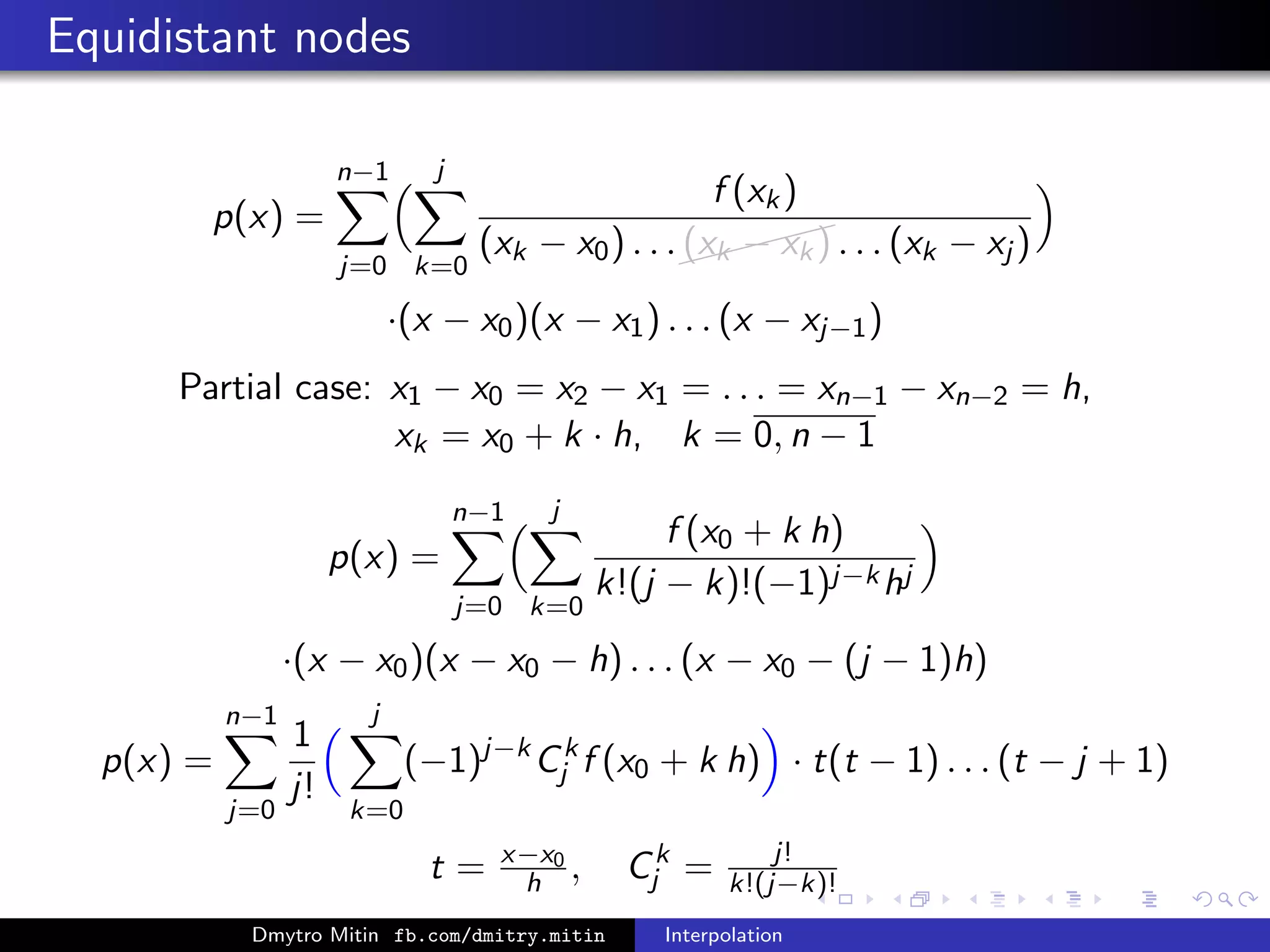


![Complexity
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
p(xk) = f (xk), k = 0, n − 1
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] =
j
k=0
f (xk)
(xk − x0) . . .
(xk − xk) . . . (xk − xj )
How to add new node?
What is complexity?
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-28-2048.jpg)
![Divided differences
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] =
j
k=0
f (xk)
(xk − x0) . . .
(xk − xk) . . . (xk − xj )
[f ; x0] = f (x0)
[f ; x0, x1] =
f (x0)
x0 − x1
+
f (x1)
x1 − x0
=
f (x0) − f (x1)
x0 − x1
[f ; x0, x1, x2] = f (x0)
(x0−x1)(x0−x2) + f (x1)
(x1−x0)(x1−x2) + f (x2)
(x2−x0)(x2−x1)
=
f (x0)−f (x1)
x0−x1
− f (x1)−f (x2)
x1−x2
x0 − x2
=
[f ; x0, x1] − [f ; x1, x2]
x0 − x2
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-29-2048.jpg)
![Divided differences
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] =
j
k=0
f (xk)
(xk − x0) . . .
(xk − xk) . . . (xk − xj )
Recurrence:
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ] =
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1] − [f ; x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ]
x0 − xj
, j ≥ 1
[f ; x0] = f (x0)
[f ; . . . , xr , . . . , xs, . . .] =
[f ; . . . , xr , . . . ,xs, . . .] − [f ; . . . ,xr , . . . , xs, . . .]
xr − xs
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-30-2048.jpg)
![Interpolation error
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
p(xk) = f (xk), k = 0, n − 1
q(x) =
n
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
= p(x) + [f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xn−1)
q(xk) = f (xk), k = 0, n
f (xn) = q(xn) = p(xn) + [f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn]
·(xn − x0)(xn − x1) . . . (xn − xn−1)
f (x) = p(x) + [f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn−1, x]
·(x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xn−1)
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-31-2048.jpg)
![Interpolation error
f (x) = p(x) + [f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn−1, x]
·(x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xn−1)
f (xk) − p(xk) = 0, k = 0, n − 1
f (n−1)
(ξ) − p(n−1)
(ξ) = 0, ξ ∈ [a, b] x0, . . . , xn−1
f (n−1)
(ξ) = p(n−1)
(ξ) = [f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn−1] · (n − 1)!
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xn−1] =
f (n−1)(ξ)
(n − 1)!
f (x) − p(x) =
f (n−1)(ξ)
(n − 1)!
· (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xn−1)
|f (x) − p(x)| ≤
1
(n − 1)!
max
[a,b]
|f (n−1)
| · (b − a)n
, x ∈ [a, b]
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-32-2048.jpg)
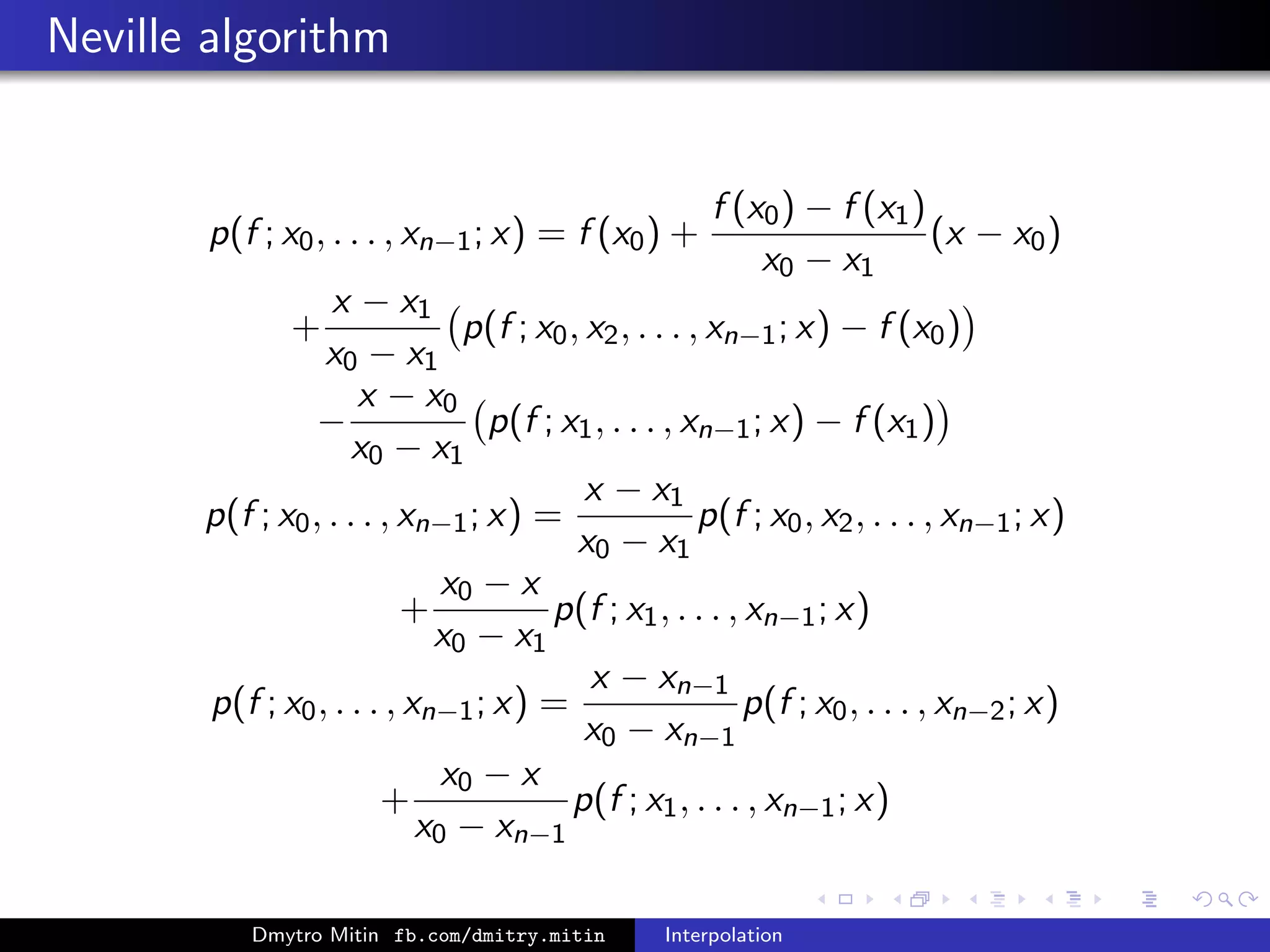
![Neville algorithm
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
= f (x0) + (x − x0) · [f ; x0, x1] + (x − x1) ·
. . . [f ; x0, . . . , xn−2] + (x − xn−1)[f ; x0, . . . , xn−1] . . .
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ] =
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1] − [f ; x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ]
x0 − xj
[f ; x0, . . . , xn−1]
[f ; x0, . . . , xn−2] [f ; x1, . . . , xn−1]
[f ; x0, . . . , xn−3] [f ; x1, . . . , xn−2] [f ; x2, . . . , xn−1]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
[f ; x0, x1] [f ; x1, x2] [f ; x2, x3] . . . . . . [f ; xn−3, xn−2] [f ; xn−2, xn−1]
f (x0) f (x1) f (x2) f (x3) . . . f (xn−3) f (xn−2) f (xn−1)
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-33-2048.jpg)

![Neville algorithm
p(x) =
n−1
j=0
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ] =
[f ; x0, x1, . . . , xj−1] − [f ; x1, . . . , xj−1, xj ]
x0 − xj
[f ; x0, x1, x2, . . . , xj ] =
[f ; x0, x2, . . . , xj ] − [f ; x1, x2, . . . , xj ]
x0 − x1
p(x) ≡ p(f ; x0, . . . , xn−1; x)
p(f ; x0, . . . , xn−1; x) = f (x0) +
f (x0) − f (x1)
x0 − x1
(x − x0)
+
x − x1
x0 − x1
n−1
j=2
[f ; x0, x2, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x2) . . . (x − xj−1)
−
x − x0
x0 − x1
n−1
j=2
[f ; x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-35-2048.jpg)
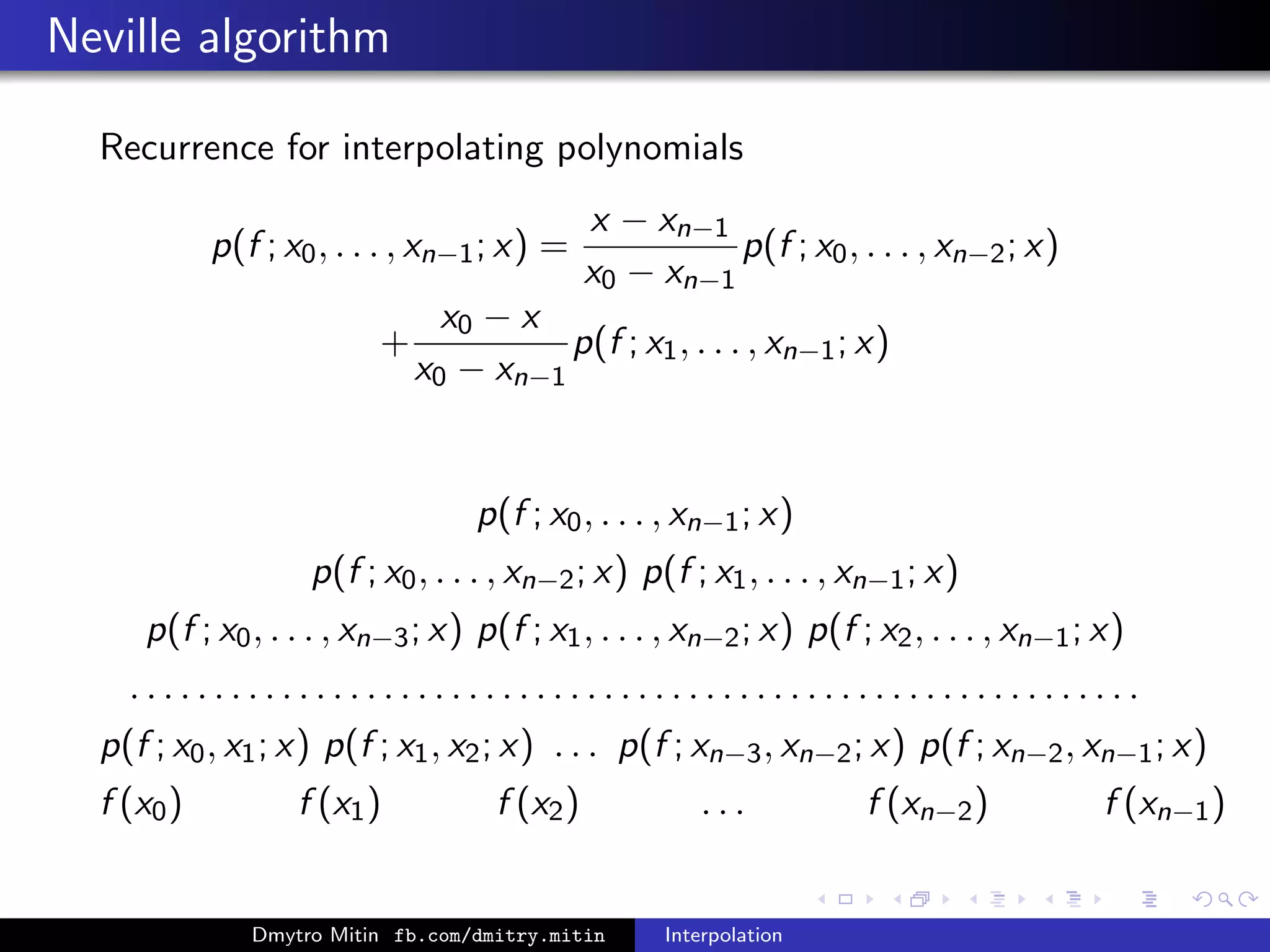
![Neville algorithm
p(f ; x0, . . . , xn−1; x) = f (x0) +
f (x0) − f (x1)
x0 − x1
(x − x0)
+
x − x1
x0 − x1
n−1
j=2
[f ; x0, x2, . . . , xj ] · (x − x0)(x − x2) . . . (x − xj−1)
−
x − x0
x0 − x1
n−1
j=2
[f ; x1, . . . , xj ] · (x − x1) . . . (x − xj−1)
p(f ; x0, . . . , xn−1; x) = f (x0) +
f (x0) − f (x1)
x0 − x1
(x − x0)
+
x − x1
x0 − x1
p(f ; x0, x2, . . . , xn−1; x) − f (x0)
−
x − x0
x0 − x1
p(f ; x1, . . . , xn−1; x) − f (x1)
Dmytro Mitin fb.com/dmitry.mitin Interpolation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpolation-151021143926-lva1-app6891/75/Interpolation-36-2048.jpg)