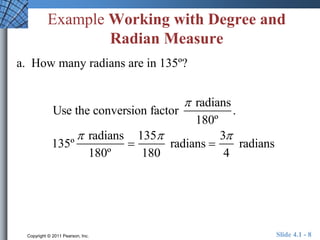
This document discusses angles and their measurement. It explains that angles are measured in degrees, with a full circle being 360 degrees, or radians, where the radian measure is based on arc length. It provides examples of converting between degrees and radians. It also discusses measuring angular motion in revolutions per minute versus linear motion in miles per hour or feet per second. Circumference and arc length formulas are presented using both degree and radian measures.