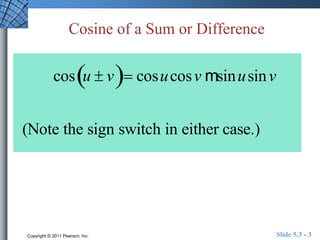
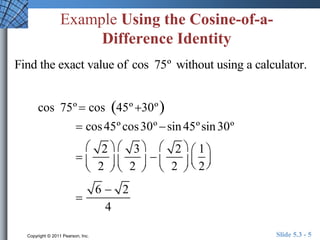
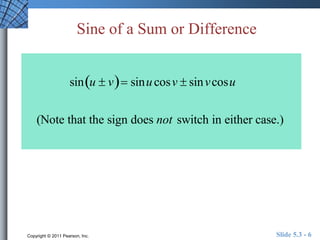
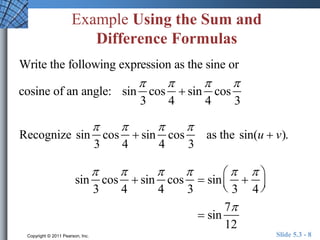
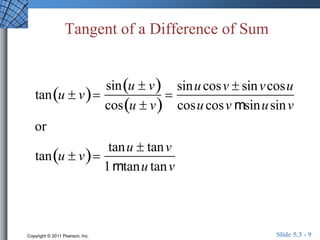
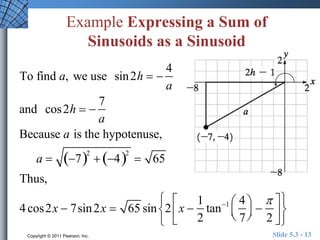
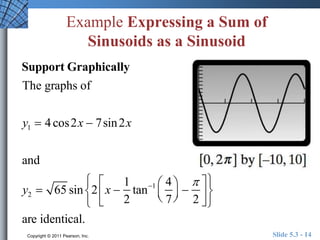
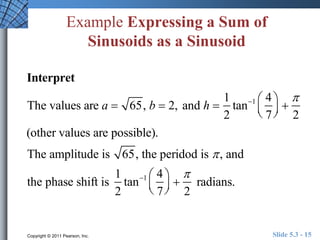
This document discusses trigonometric identities for sums and differences of angles. It provides examples of using identities for cosine, sine, and tangent of sums and differences to find exact trigonometric values without a calculator. One example expresses the sum of two sinusoids as a single sinusoid, finding the amplitude, frequency, and phase shift. In general, the identities allow decomposing compound angle expressions into combinations of basic trigonometric functions of the component angles.