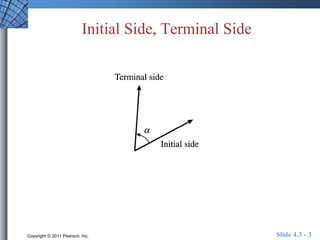
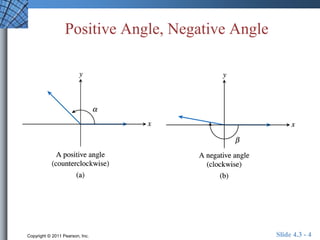
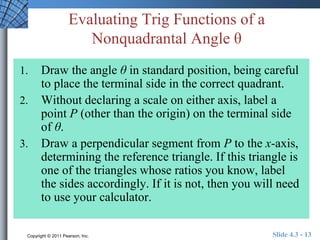
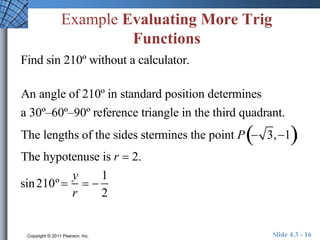
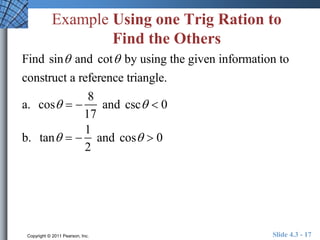
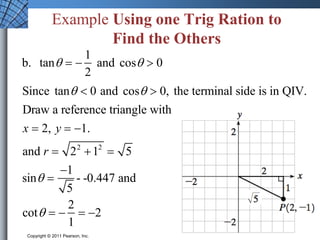
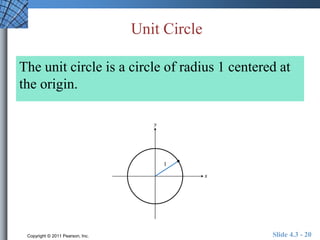
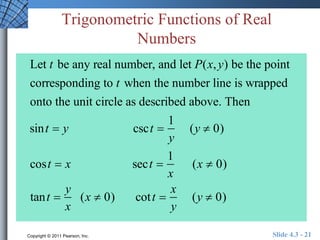
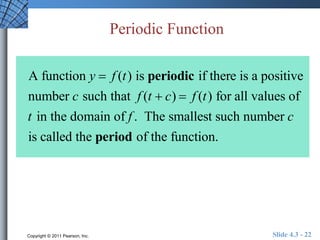
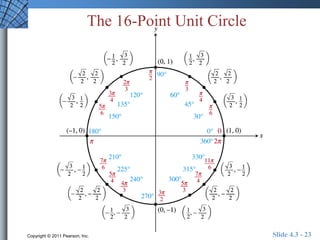
This document discusses extending trigonometric functions beyond right triangles. It introduces trig functions of any angle, coterminal angles, the unit circle, and periodic functions. Examples are provided on evaluating trig functions of angles in all quadrants using reference triangles. The key topics covered are trig functions of real numbers defined on the unit circle, and trig functions being periodic functions.