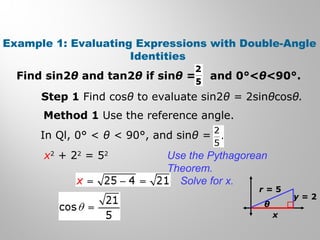
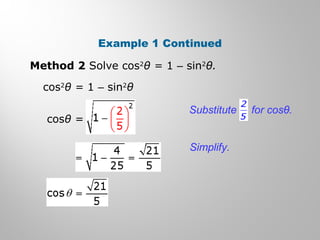
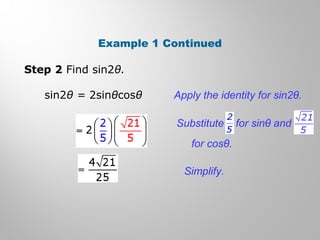
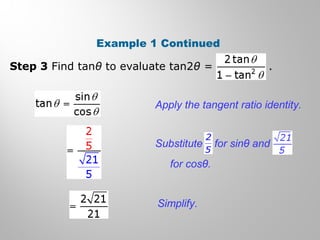
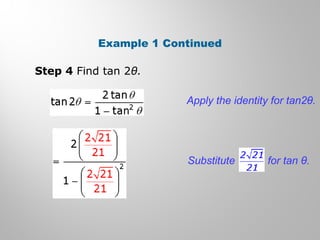
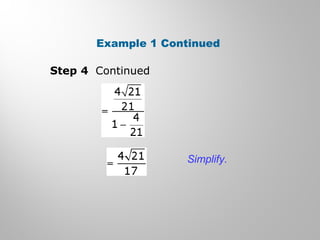
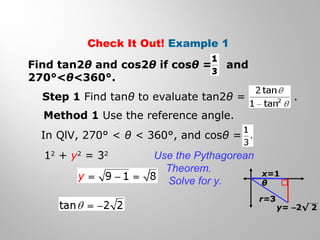
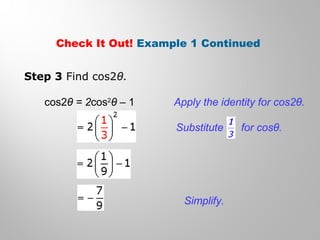
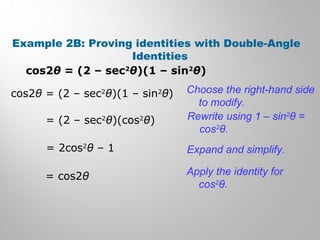
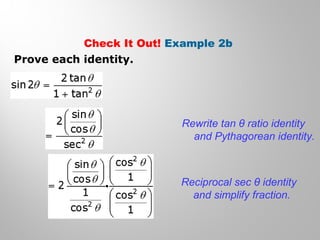
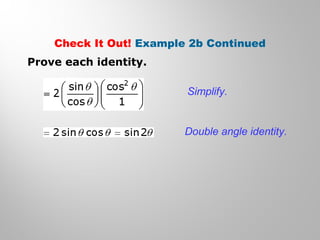
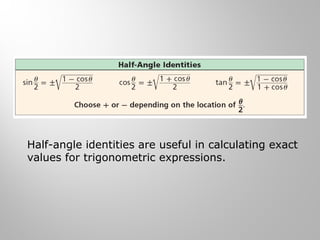
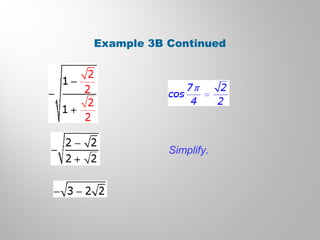
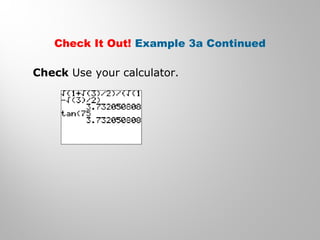
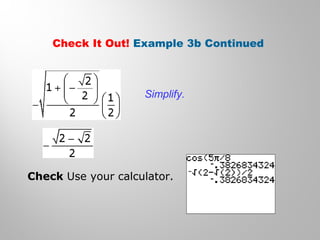
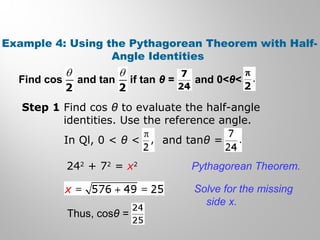
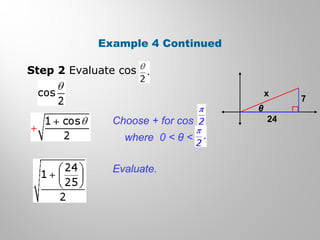
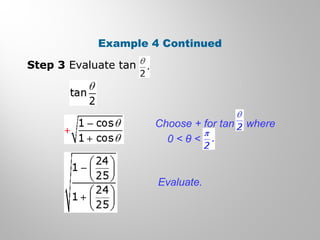
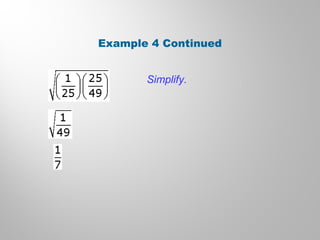
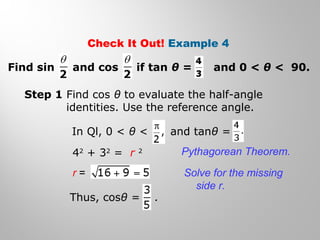
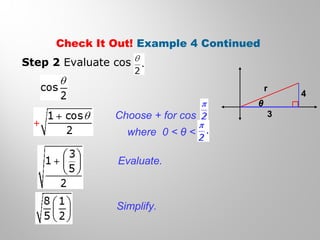
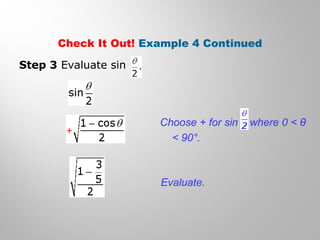
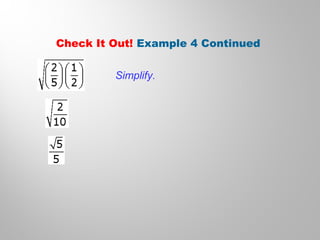
This document discusses double-angle and half-angle identities in trigonometry. It provides examples of using these identities to evaluate expressions and prove trigonometric identities. Key double-angle identities covered are sin(2θ), cos(2θ), and tan(2θ). The document also derives the half-angle identities and provides examples of using them to find exact trigonometric values.