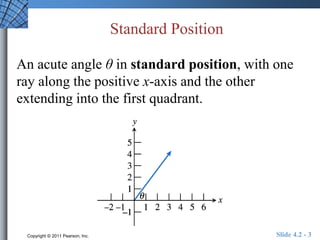
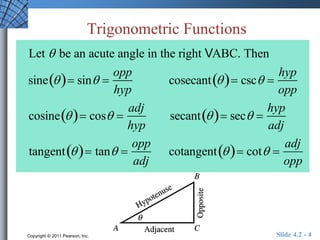
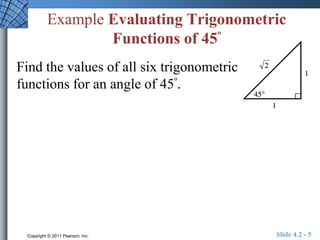
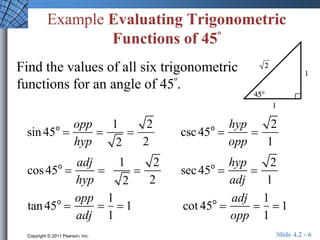
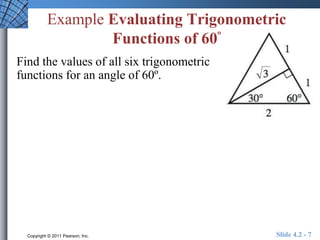
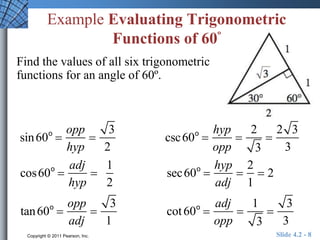
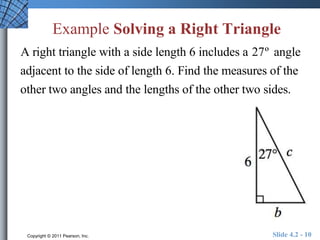
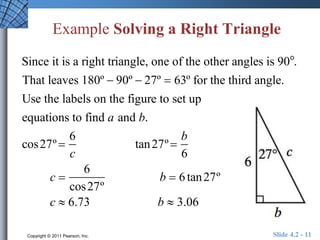
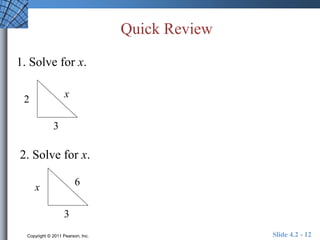
The document discusses trigonometric functions of acute angles. It defines the six trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant) using a right triangle. Examples are provided to evaluate the functions of 45 and 60 degree angles. Common calculator errors in evaluating trig functions are also discussed. The document concludes with an example problem solving a right triangle given side lengths and one interior angle measure.