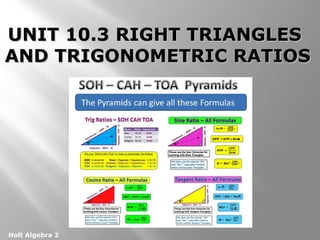
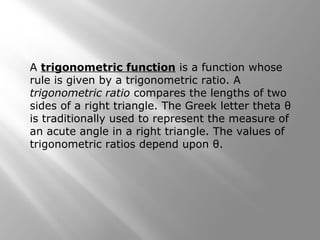
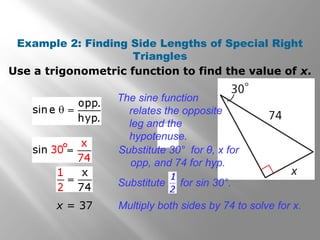
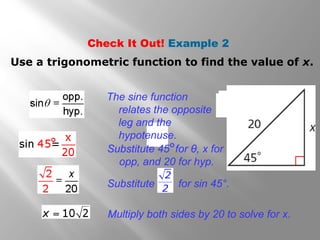
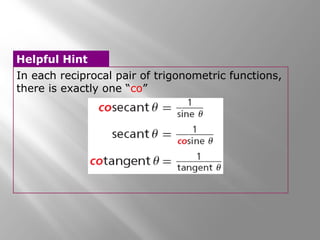
This document provides instruction on right triangles and trigonometric ratios. It begins with examples of finding missing angles and side lengths in right triangles using trigonometric functions like sine, cosine and tangent. Special right triangles involving 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 triangles are discussed. Real world applications include finding the height a skier leaves a ramp and the height of a tree using an angle of elevation. The document also covers cosecant, secant and cotangent functions and has practice problems for students.