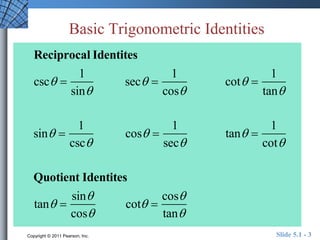
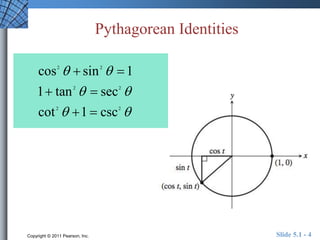
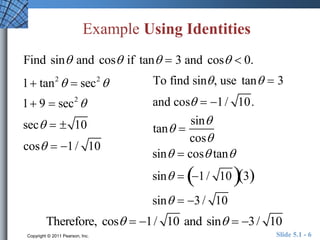
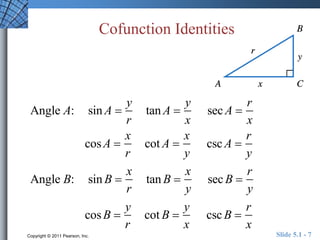
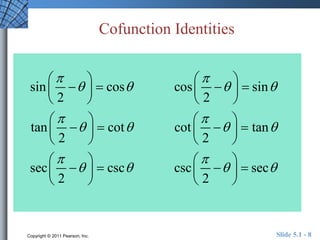
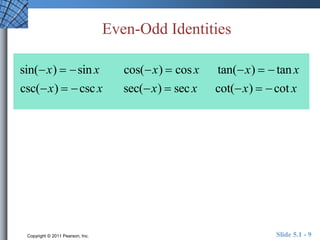
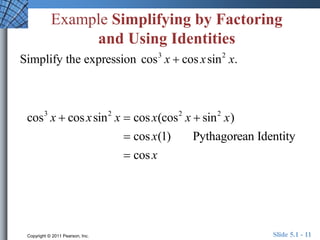
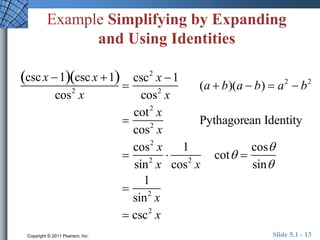
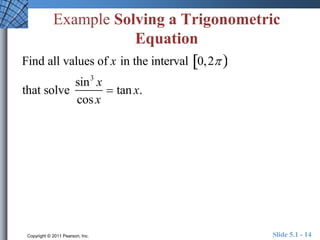
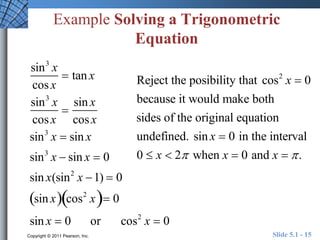
The document discusses trigonometric identities that are important for working with trigonometric functions in calculus. It covers basic identities like reciprocal, quotient, Pythagorean, cofunction, and odd-even identities. Examples are provided of using identities to simplify expressions and solve trigonometric equations.