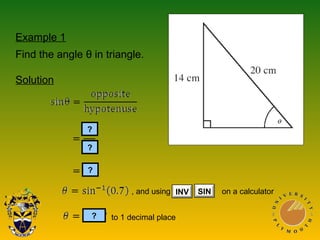
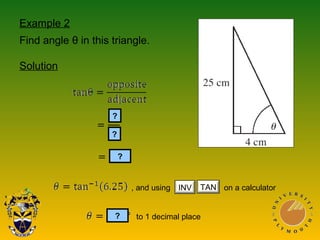
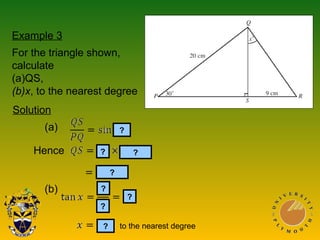
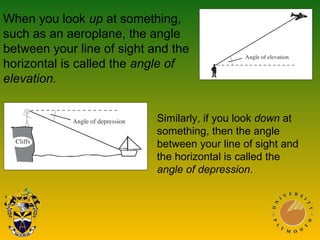
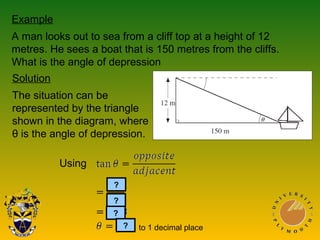
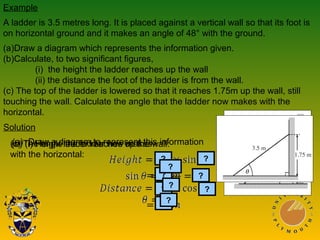
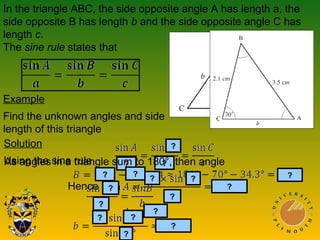
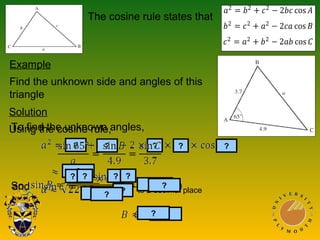
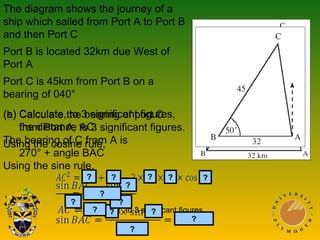
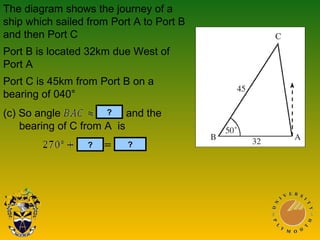
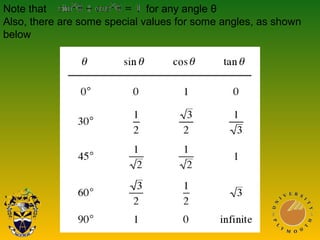
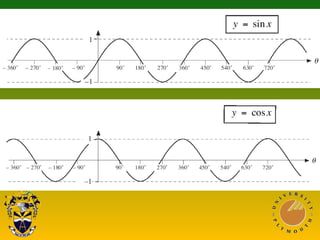
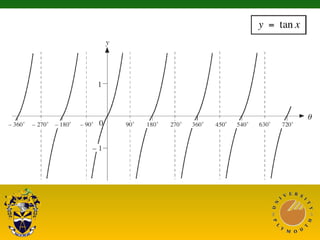
This document covers trigonometric concepts and problems involving right-angled triangles, bearings, and trigonometric functions. It includes 7 presentations on finding angles in right triangles using trig functions, problems using trigonometry including elevation and depression, the sine rule, cosine rule, problems with bearings, and trig functions. Examples are provided for each topic to demonstrate how to set up and solve various trigonometric problems.