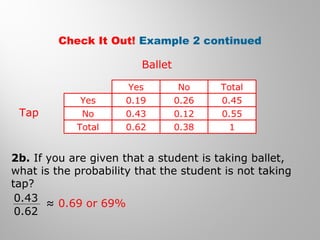
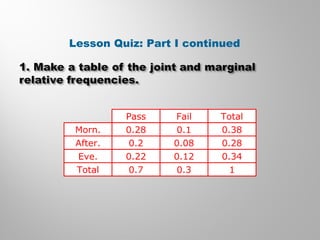
This document discusses conditional probability and how to calculate and interpret joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequencies using two-way frequency tables. It provides examples of finding conditional probabilities based on frequency tables of data involving variables like whether students are taking ballet or tap dancing classes. One example determines the probability a student is not taking tap dancing given they are taking ballet class is about 69%.