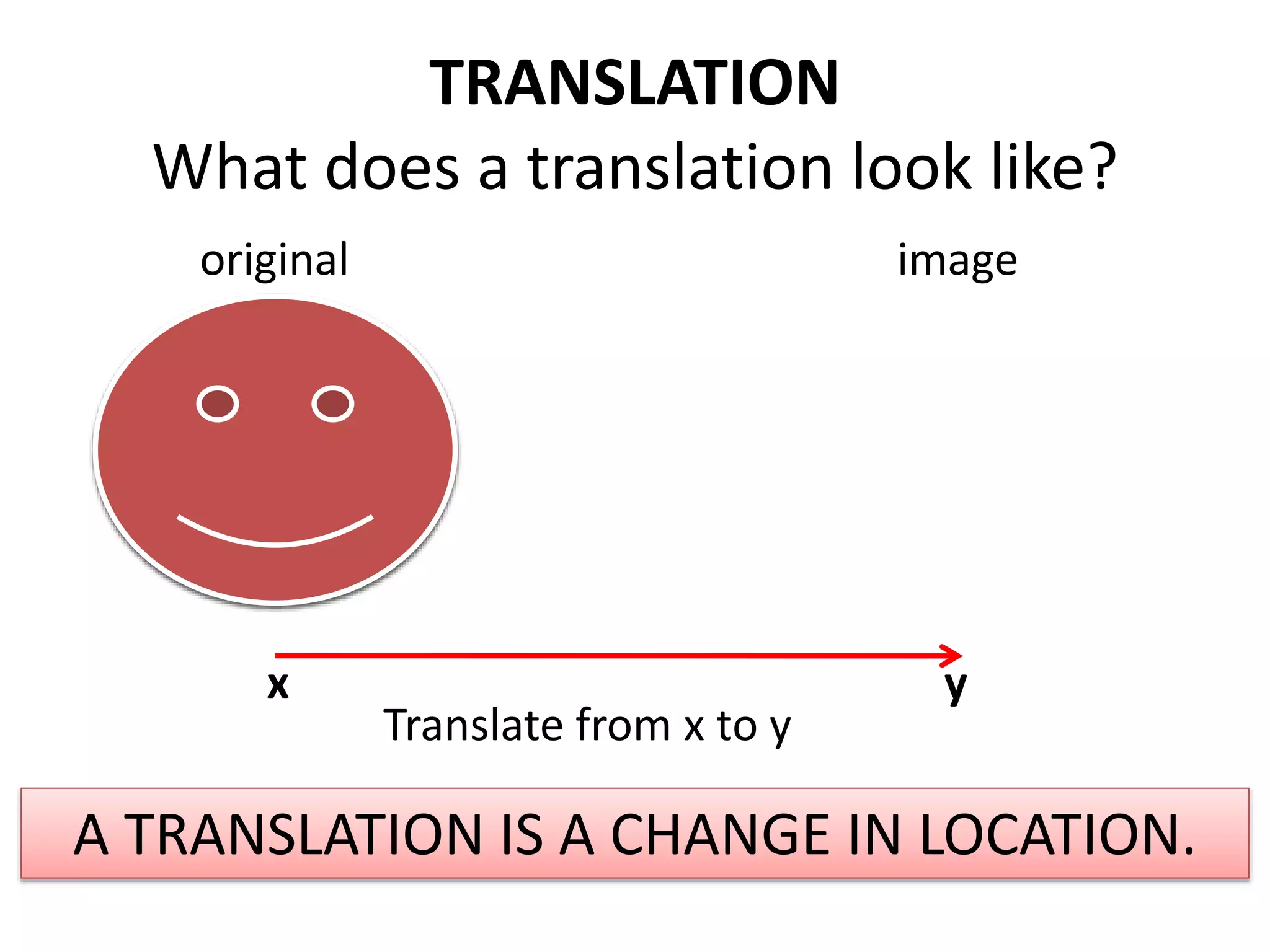
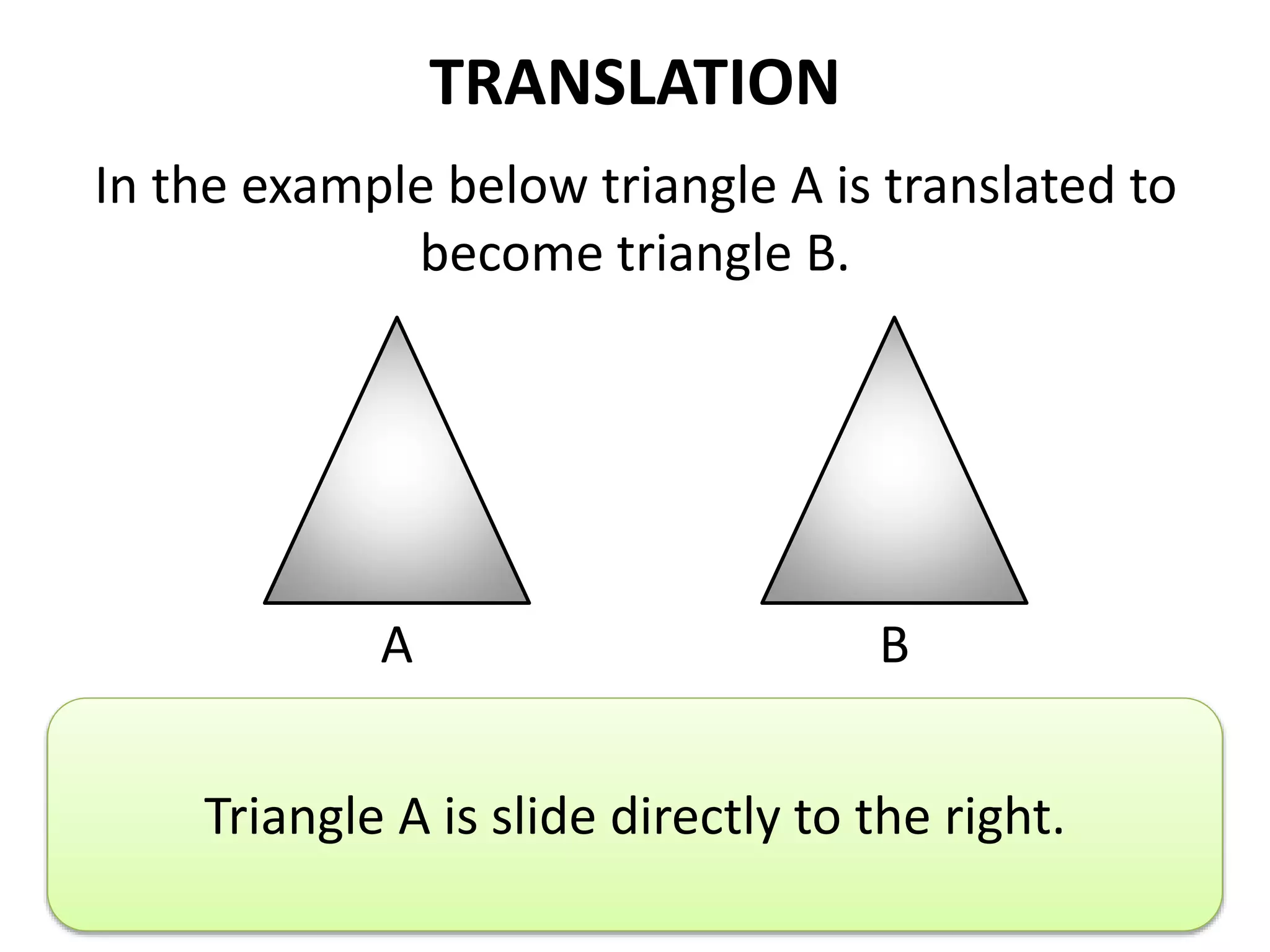
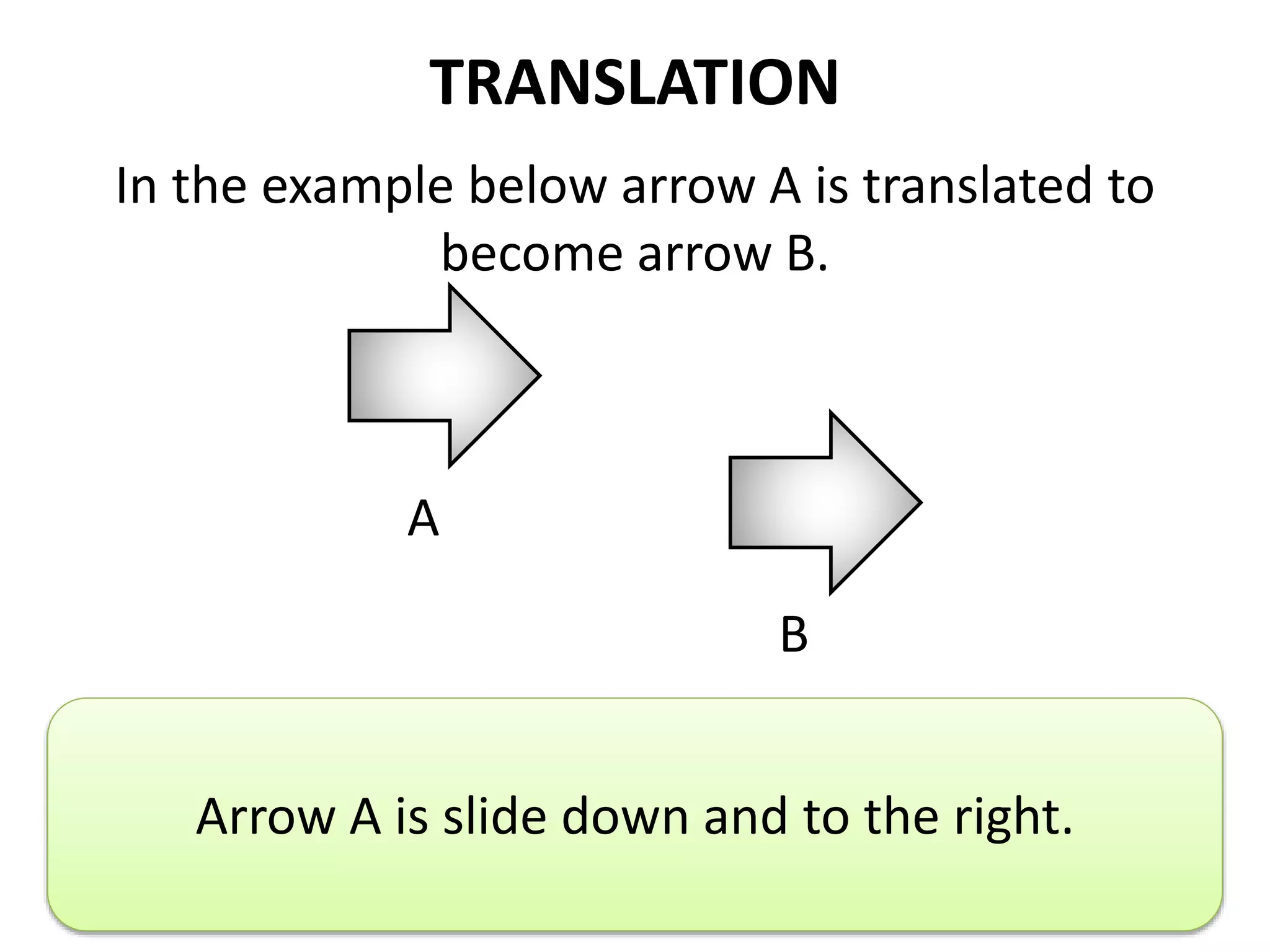
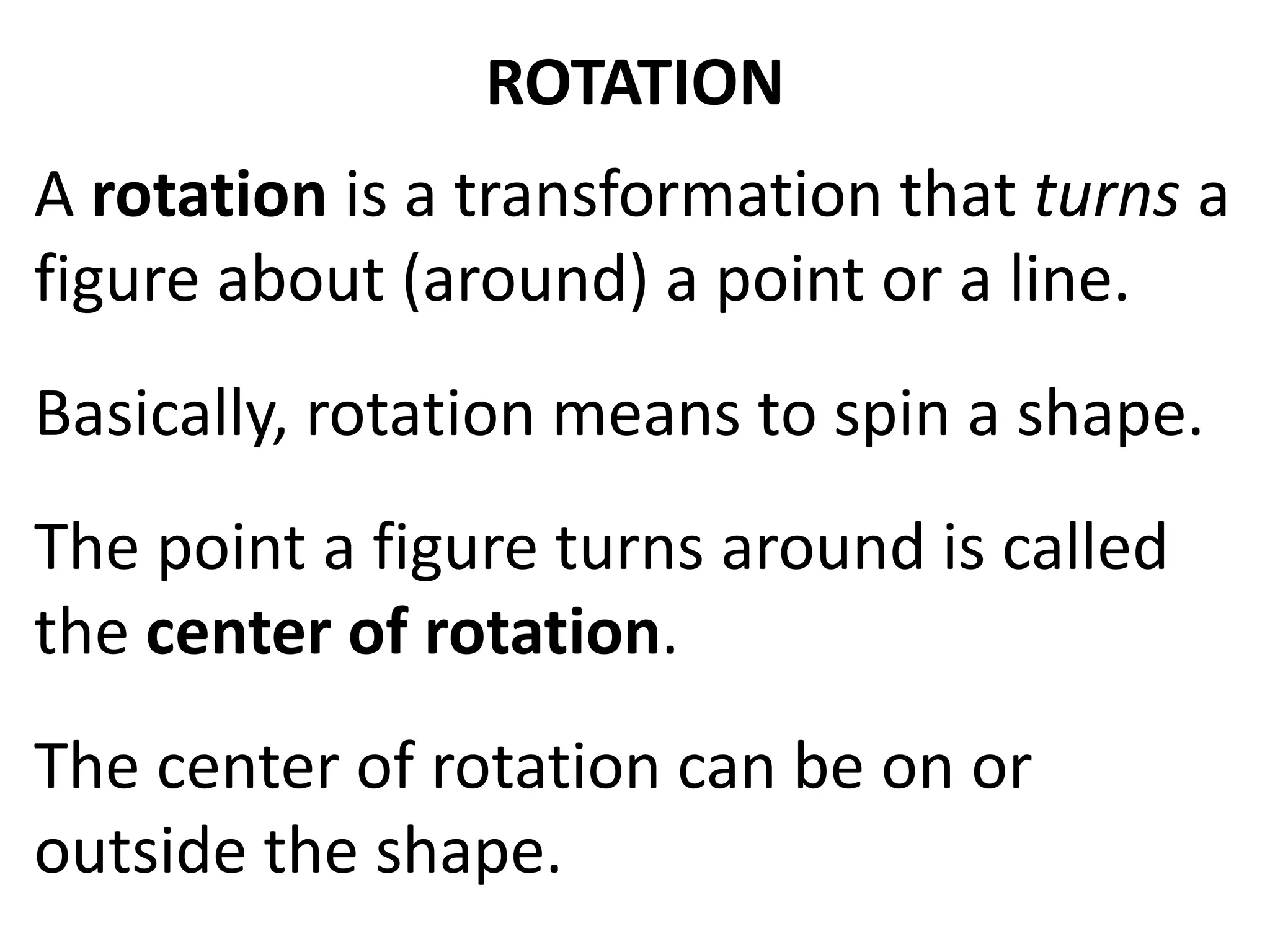
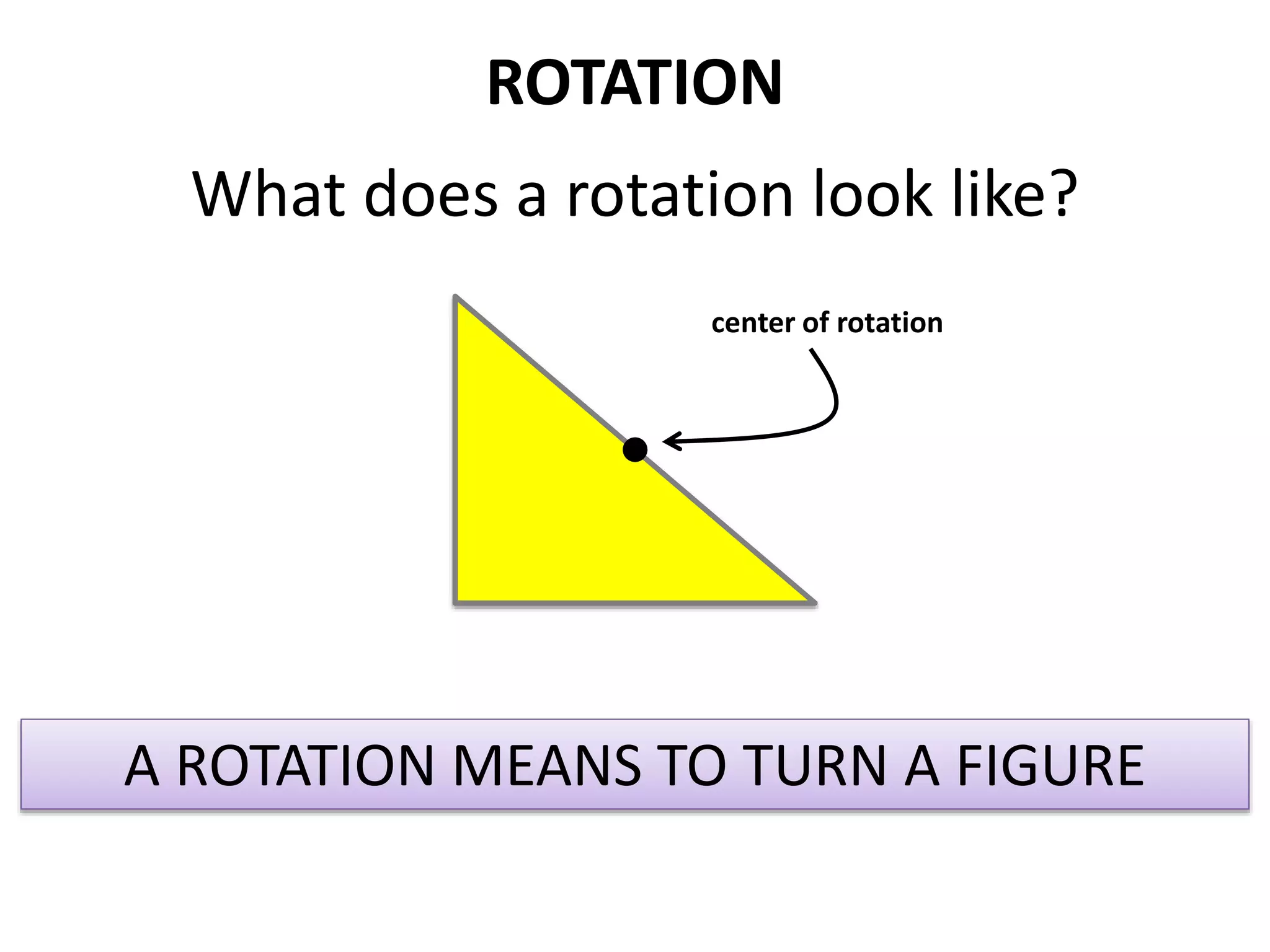
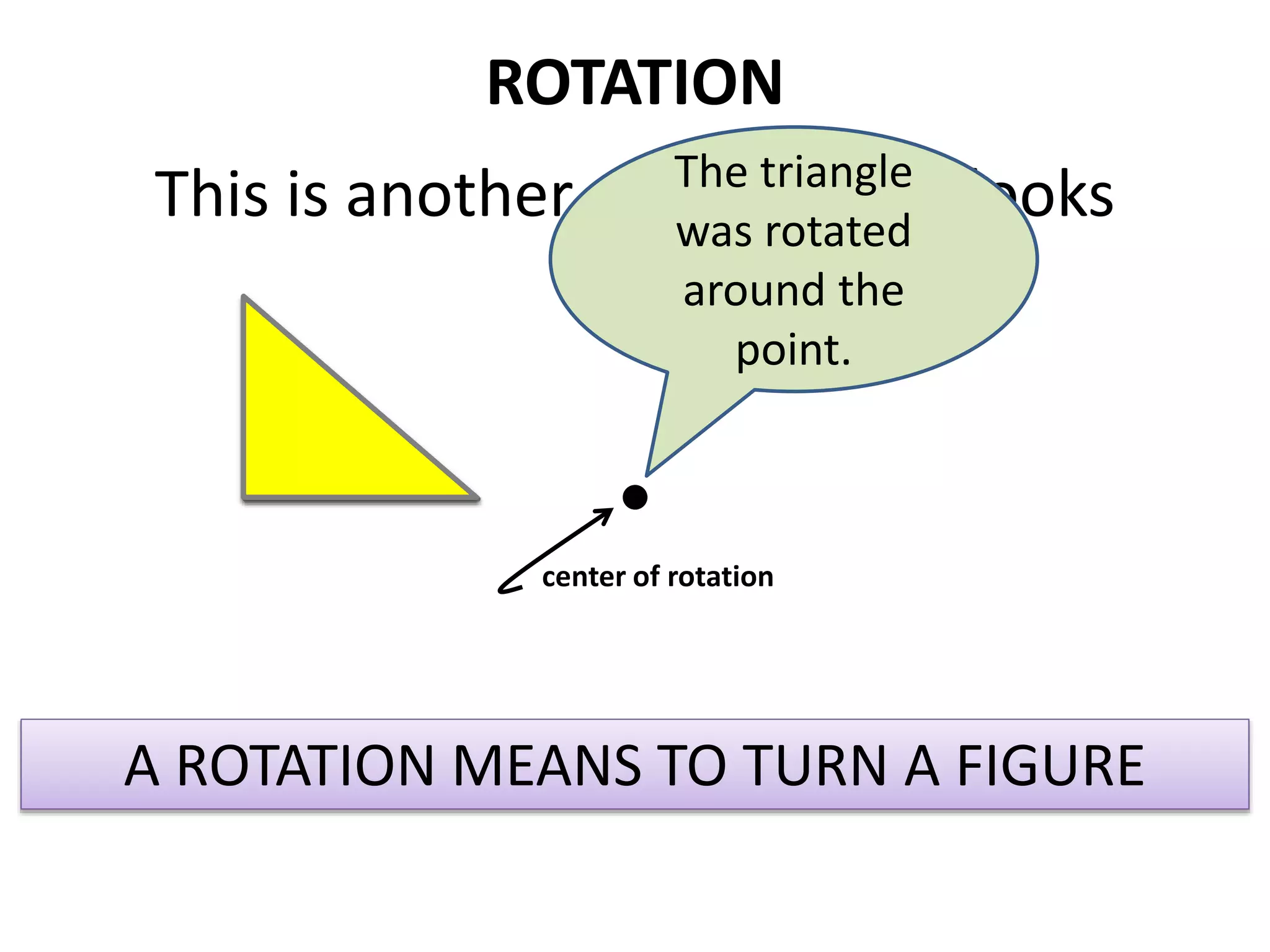
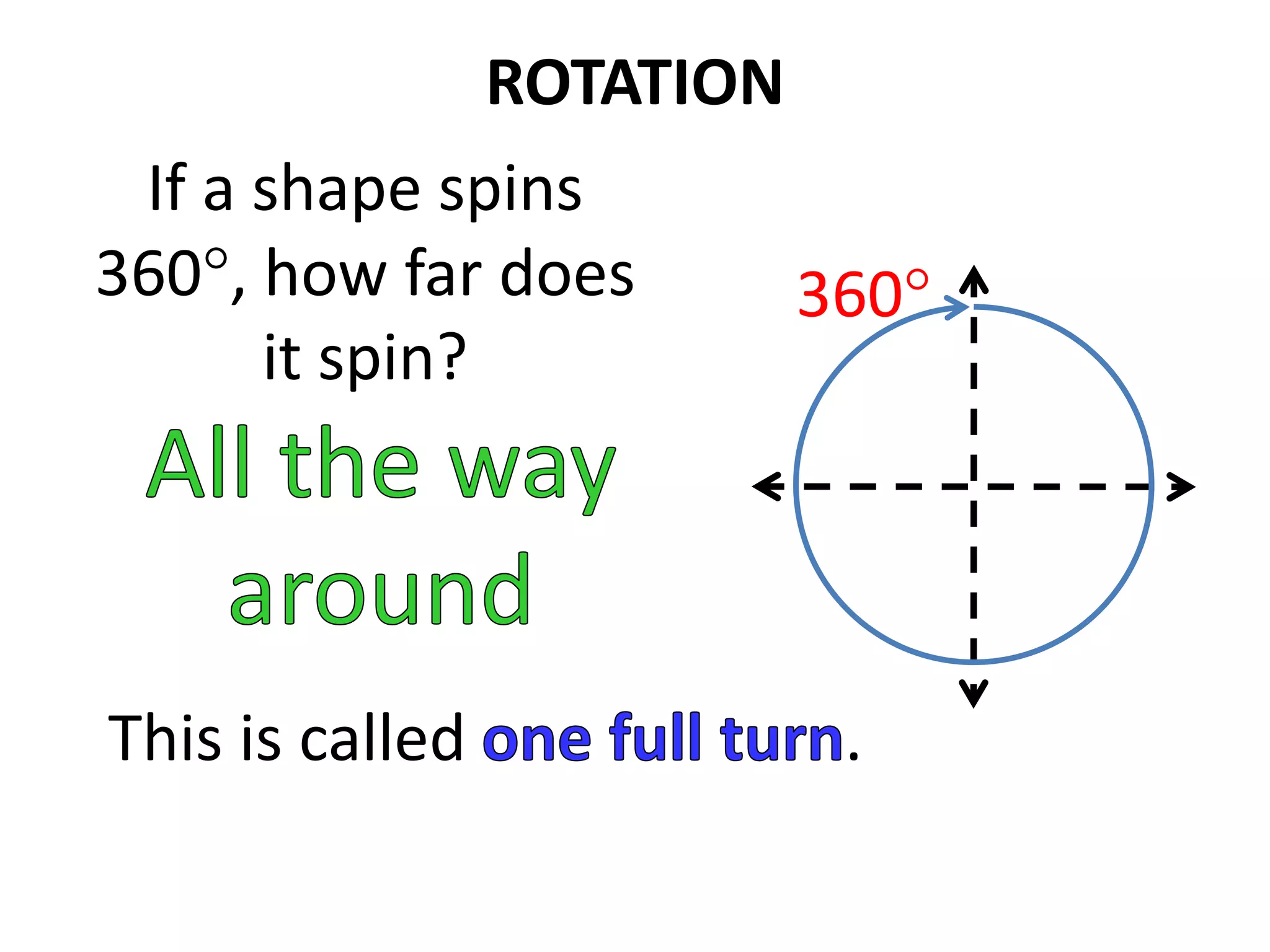
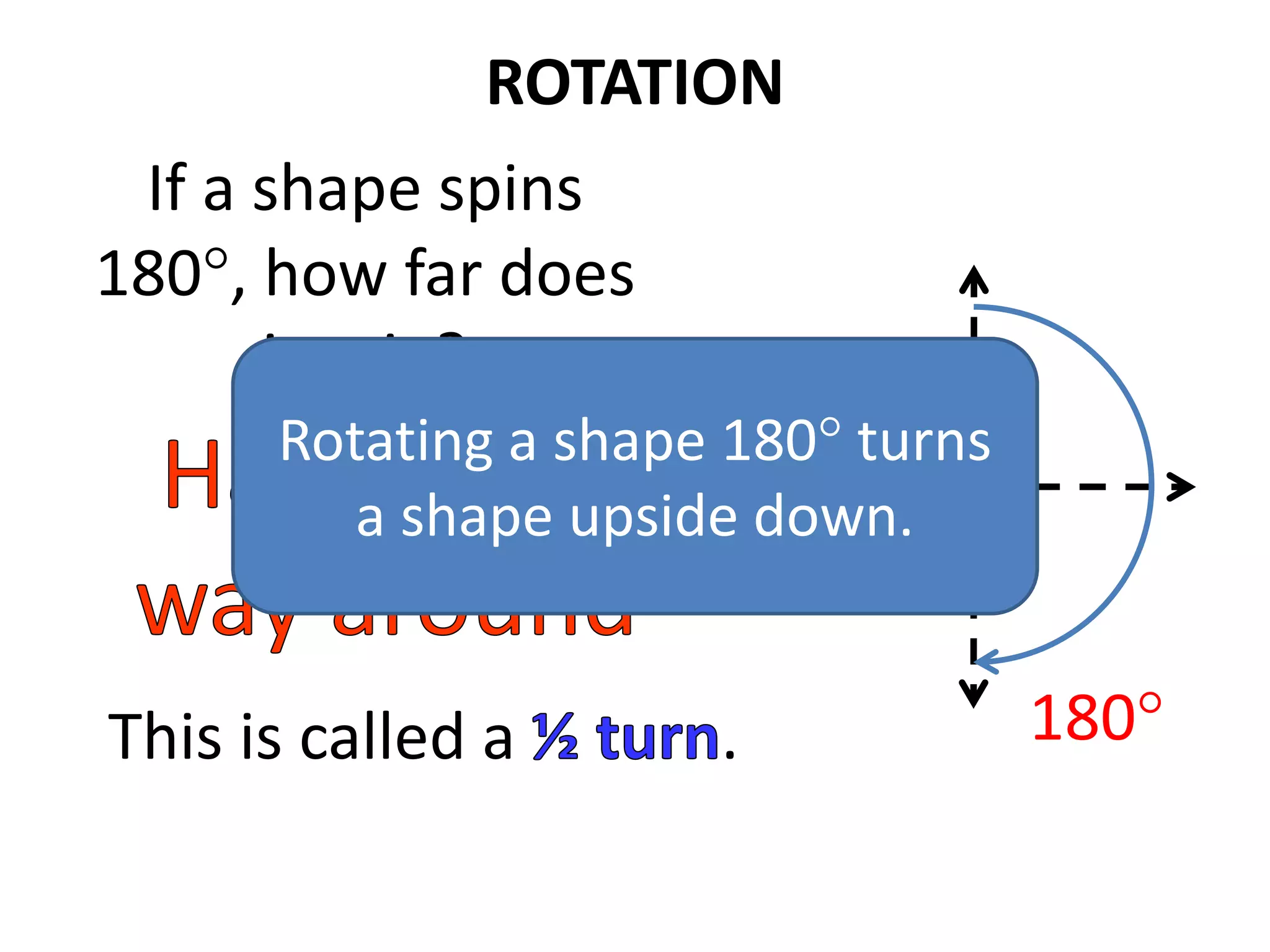
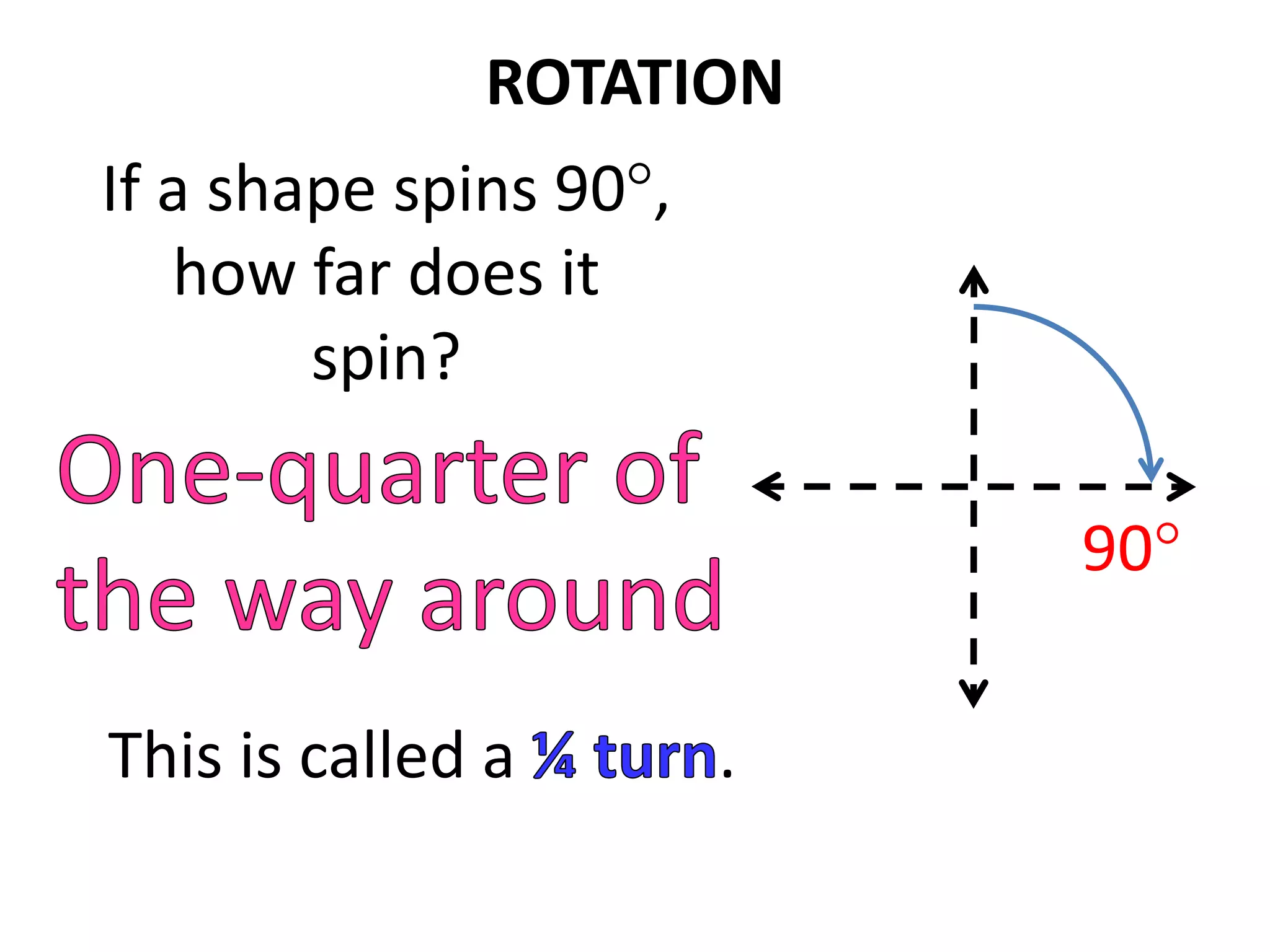
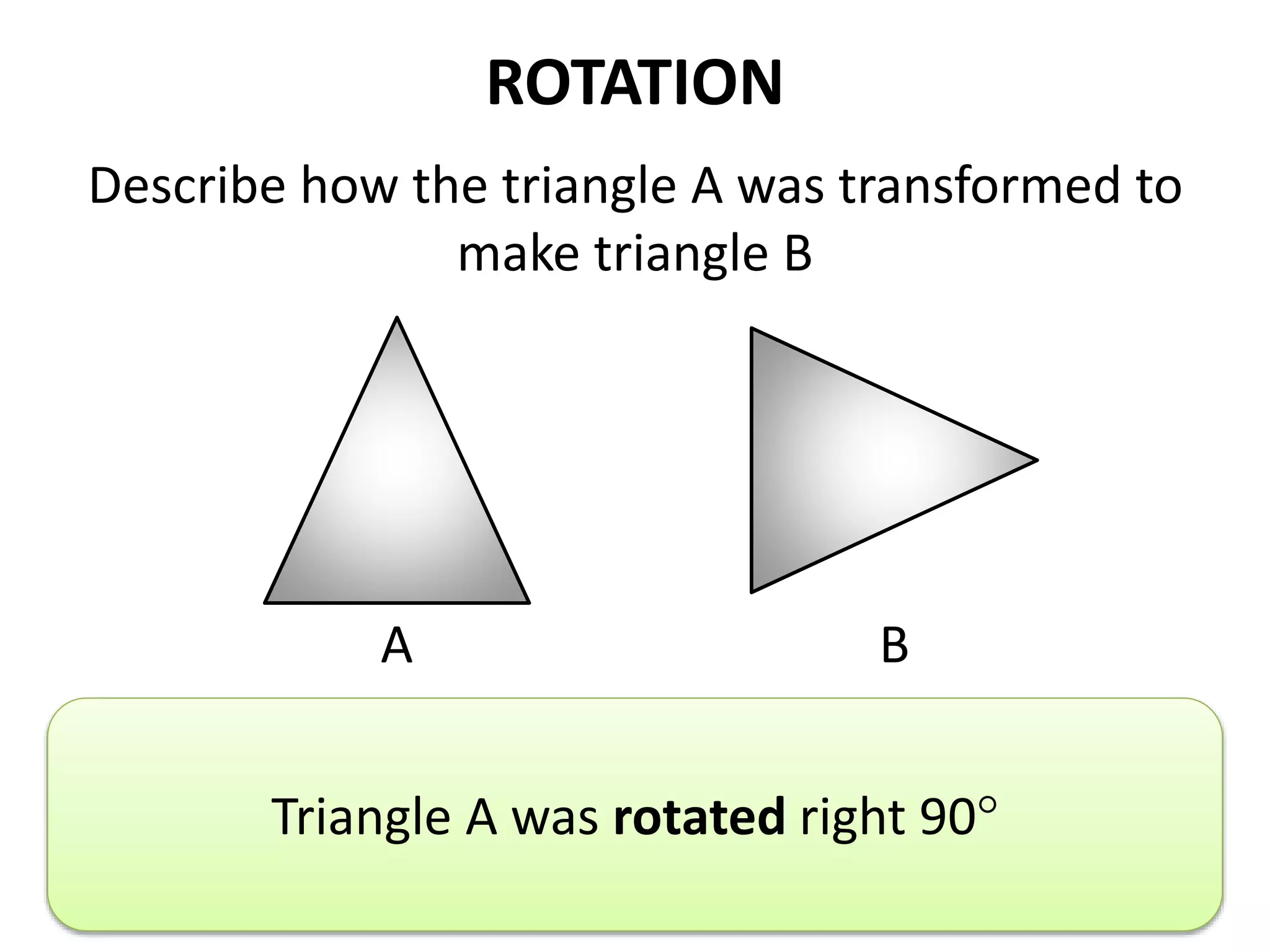
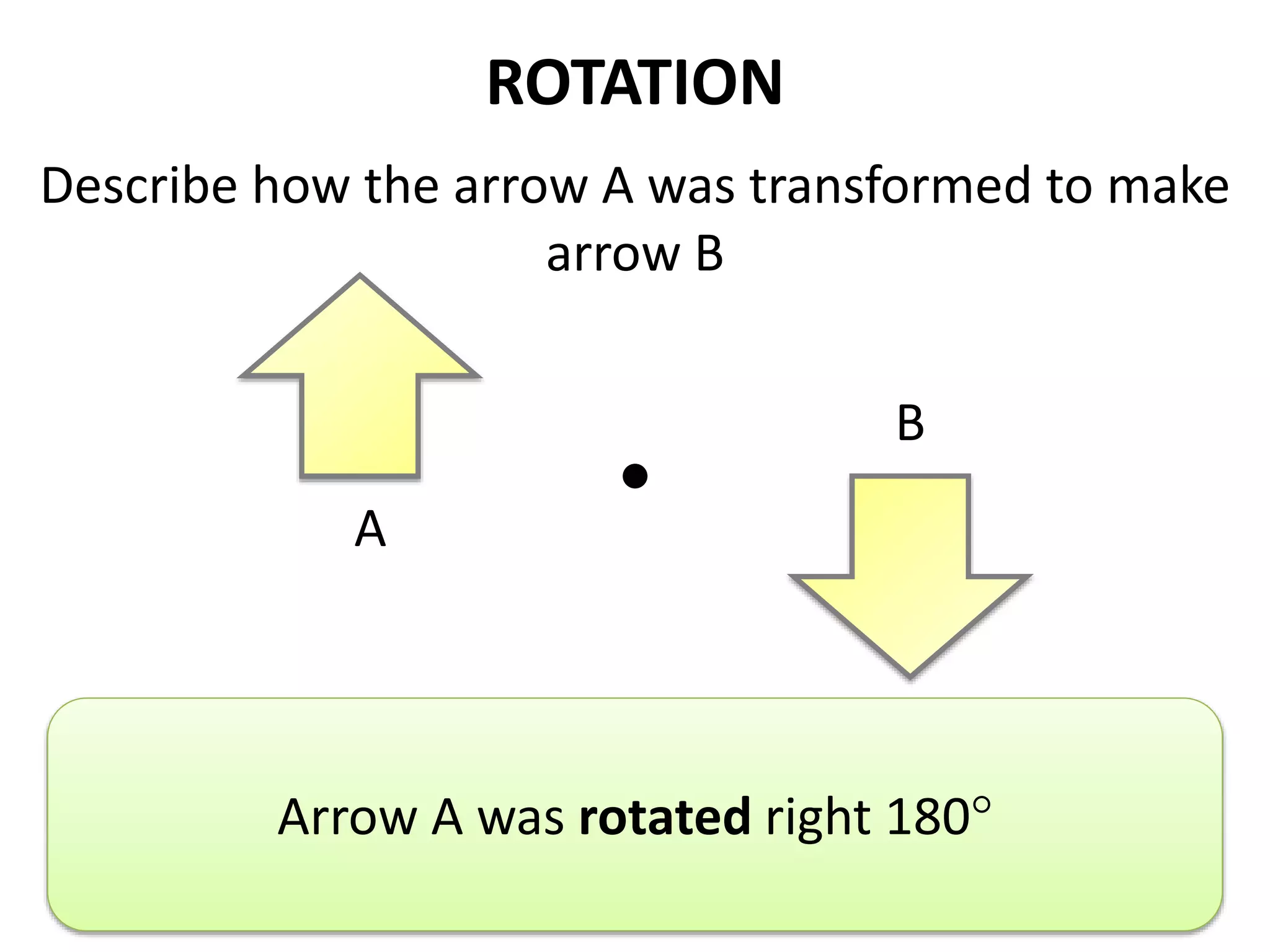
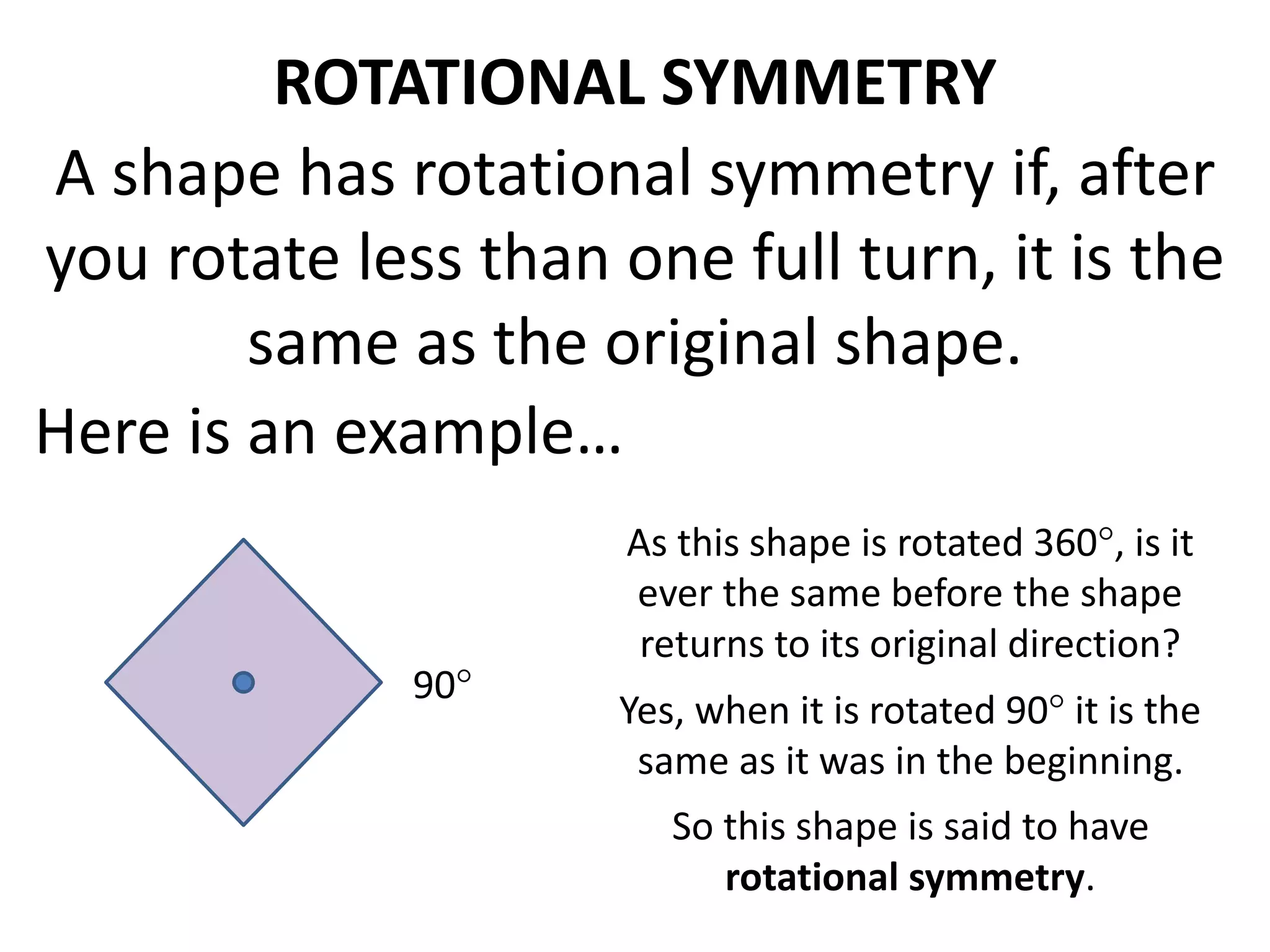
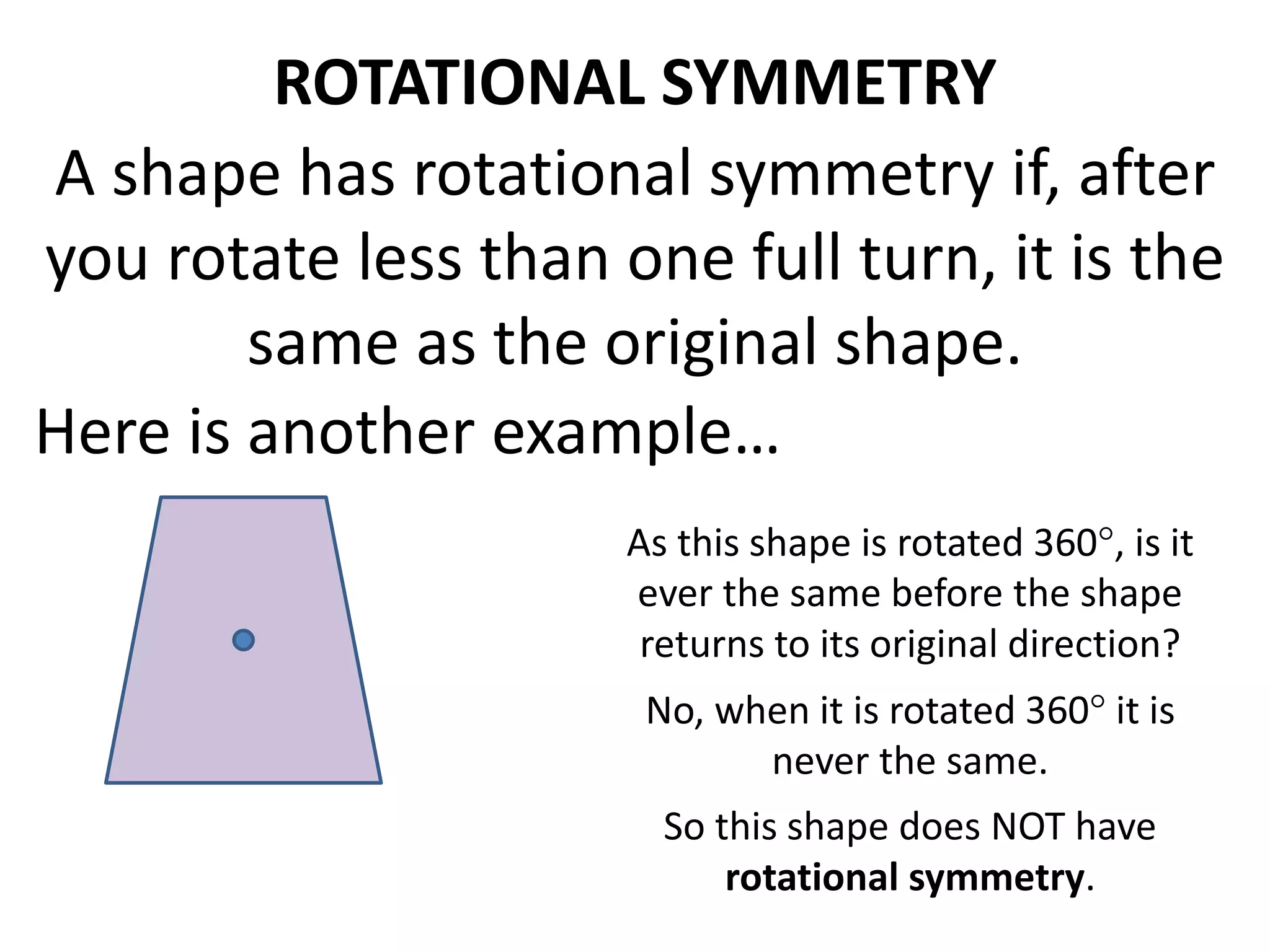
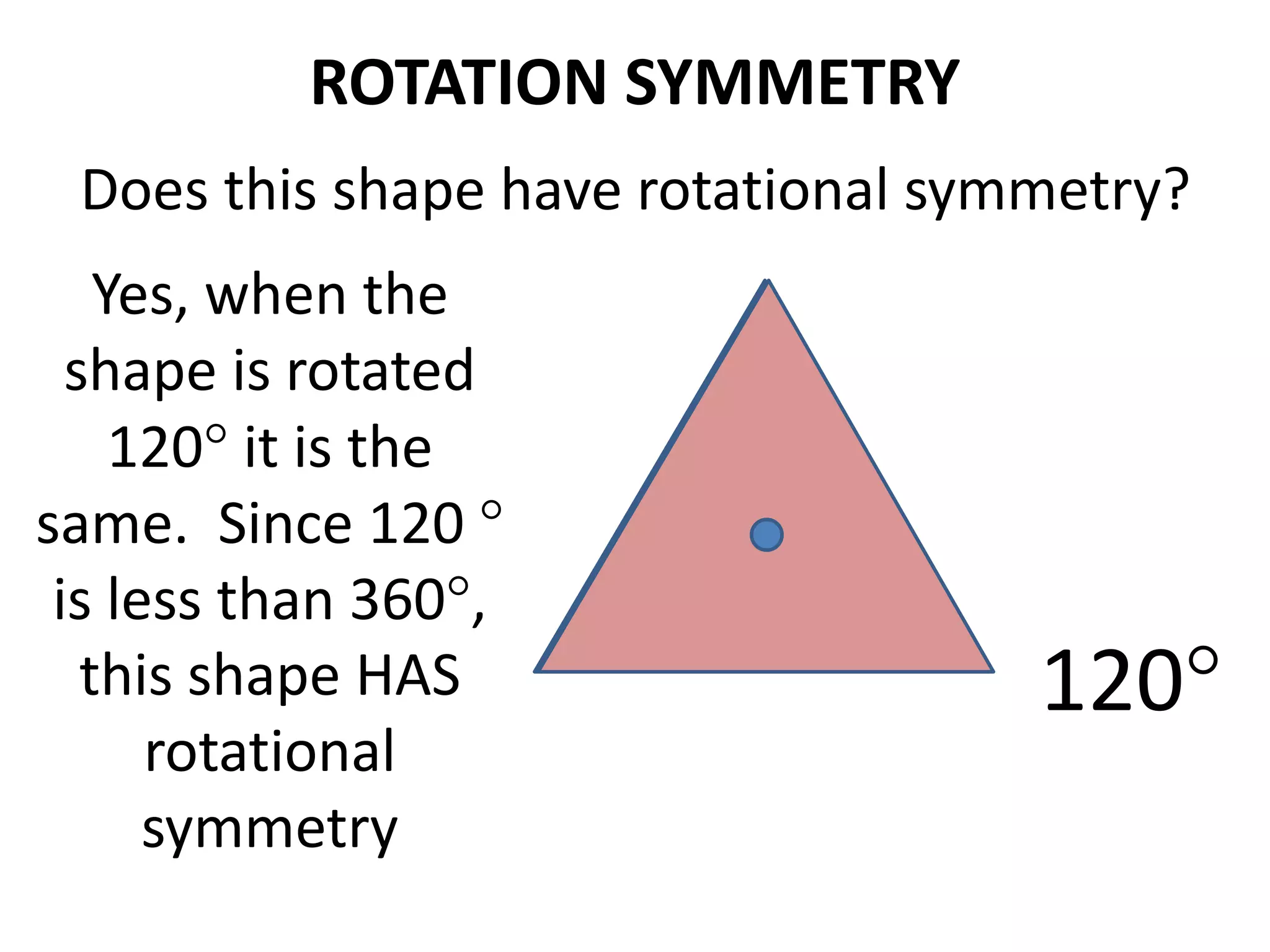
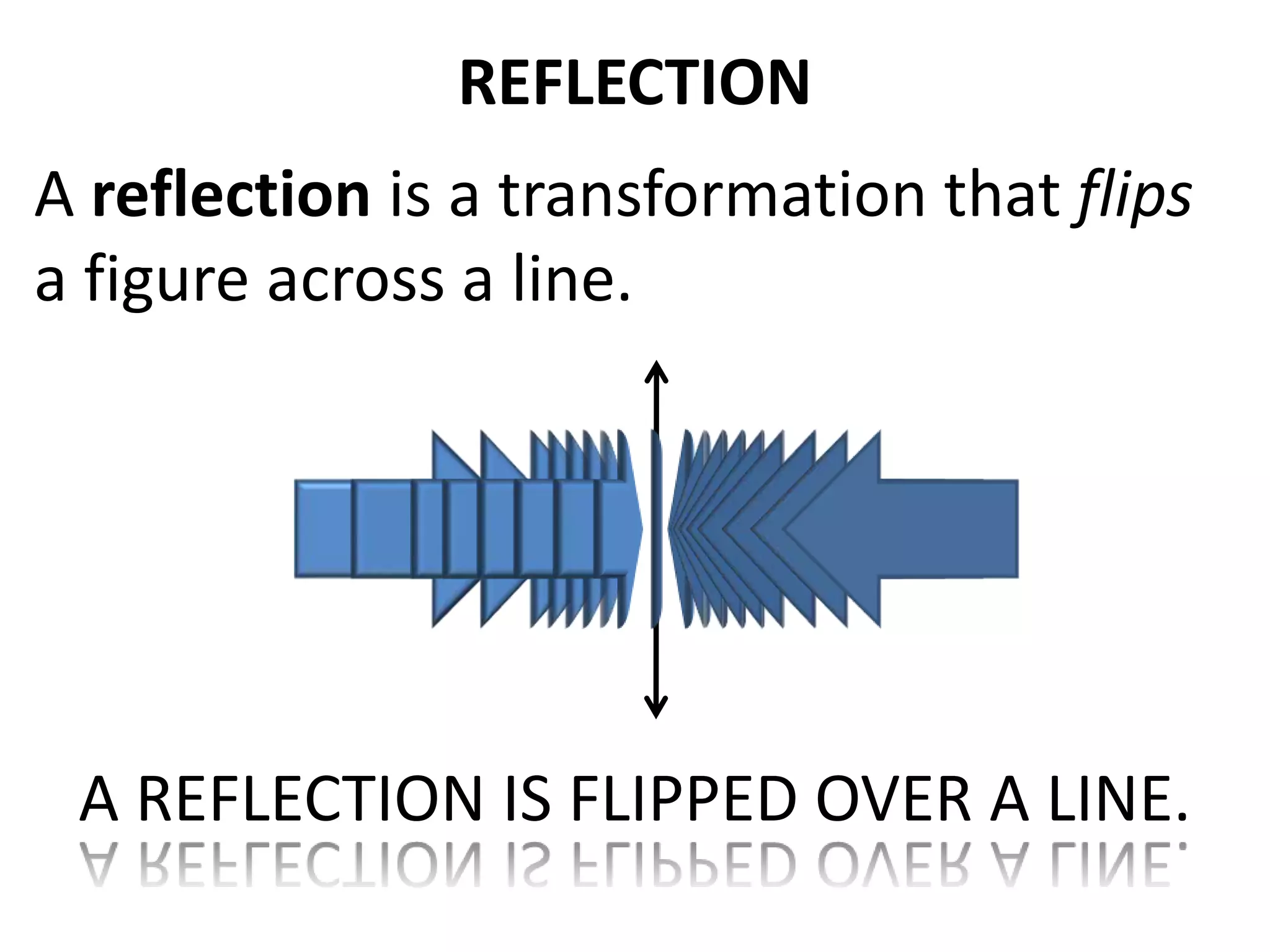
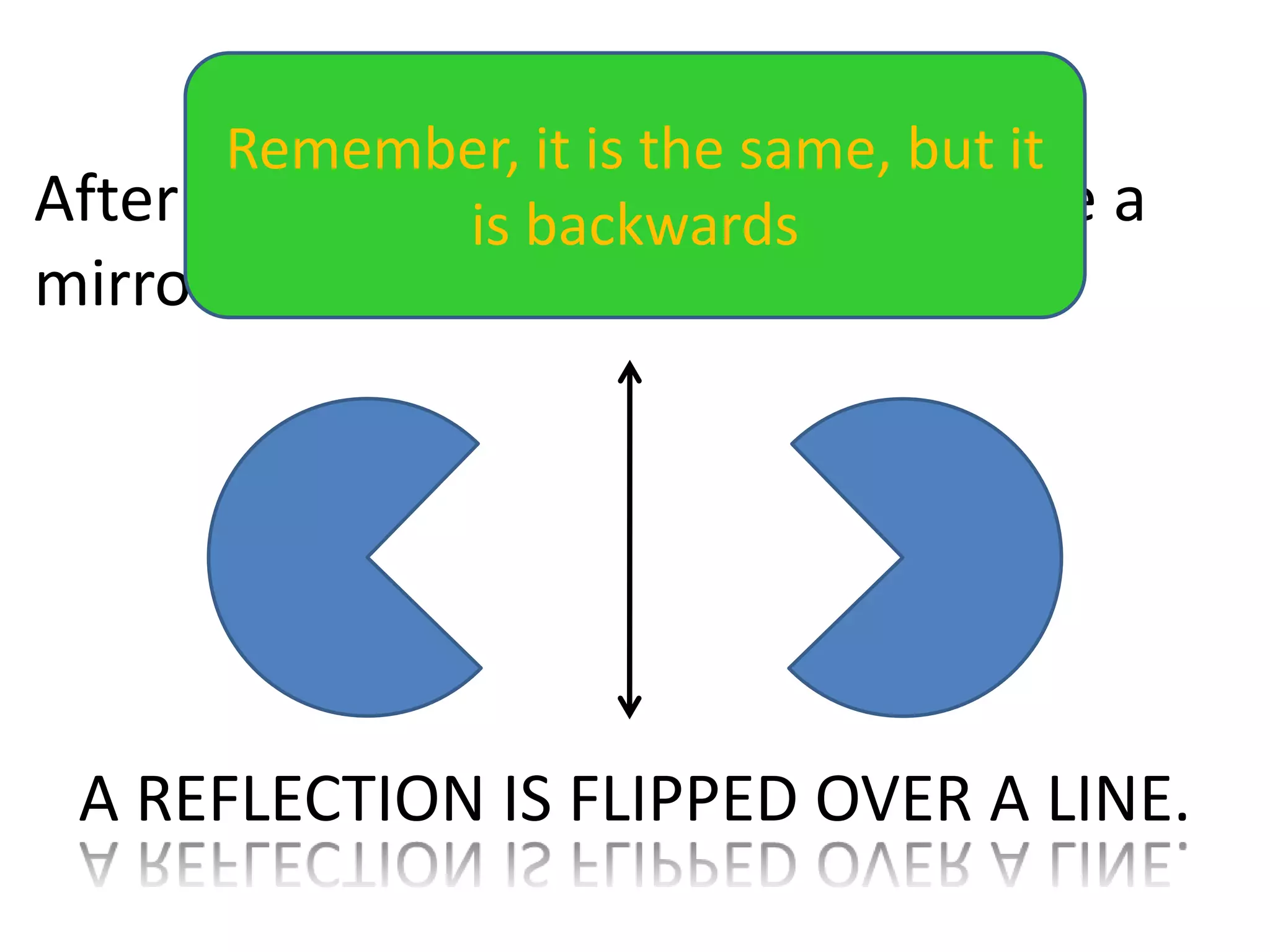
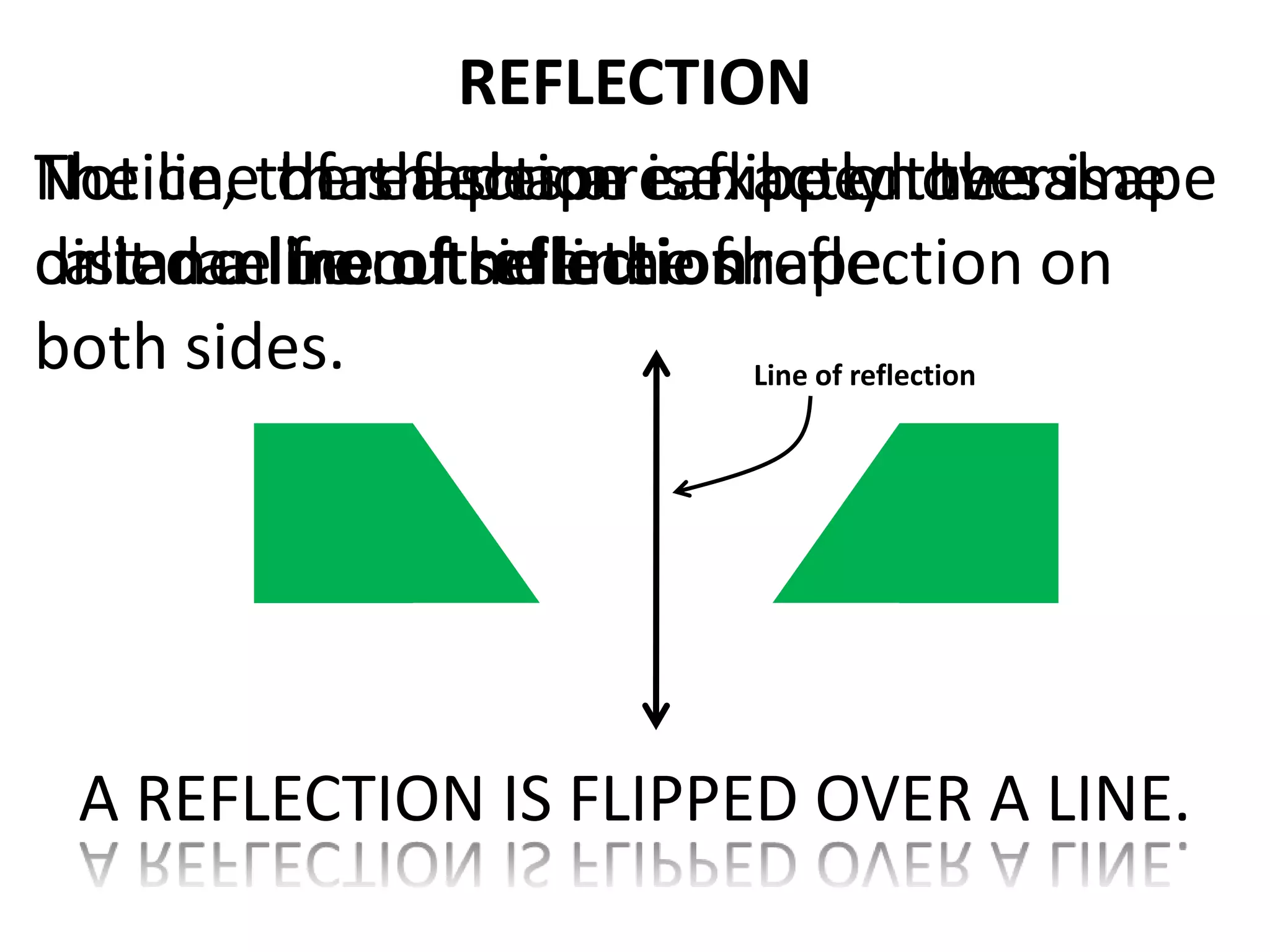
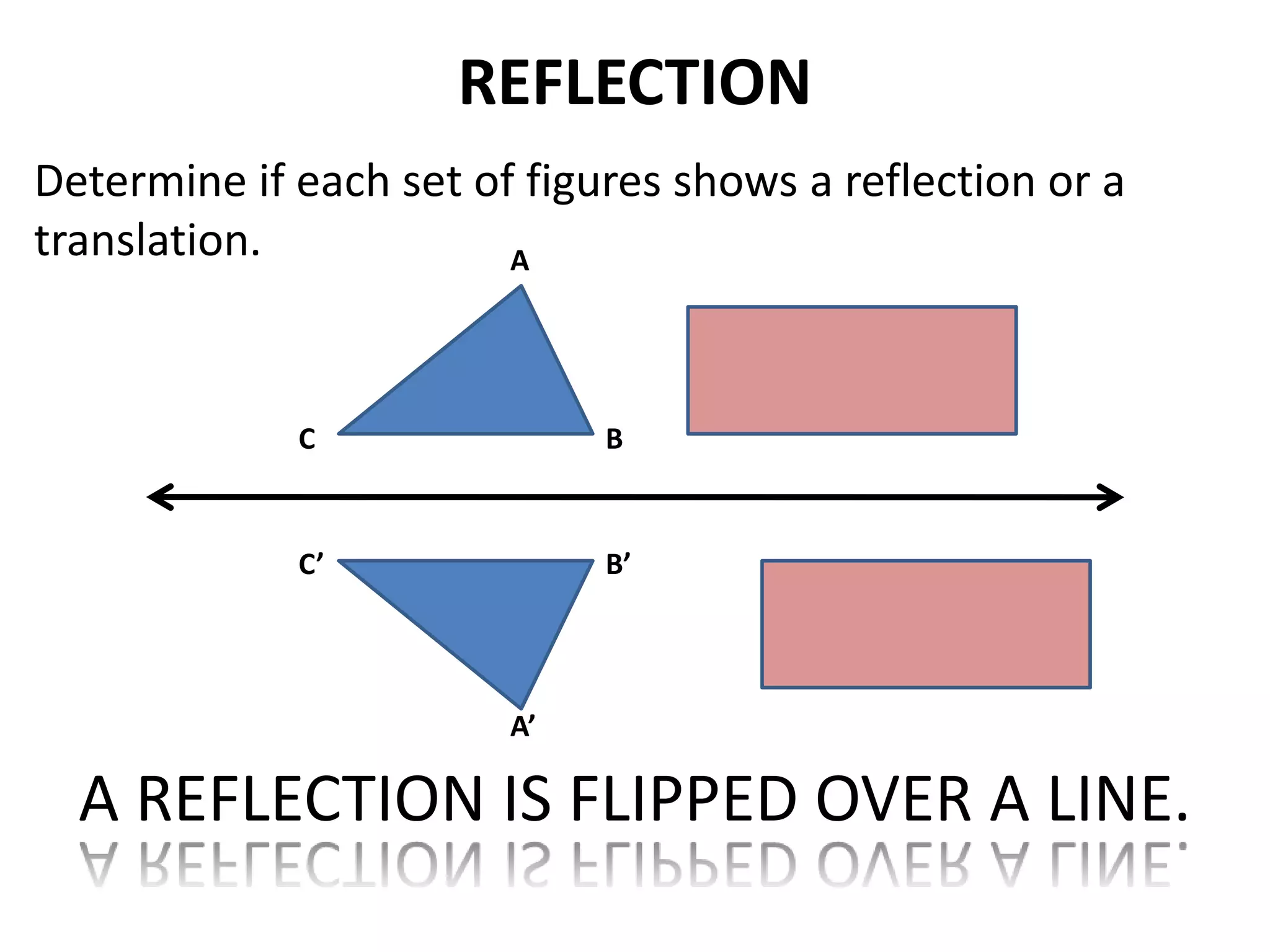
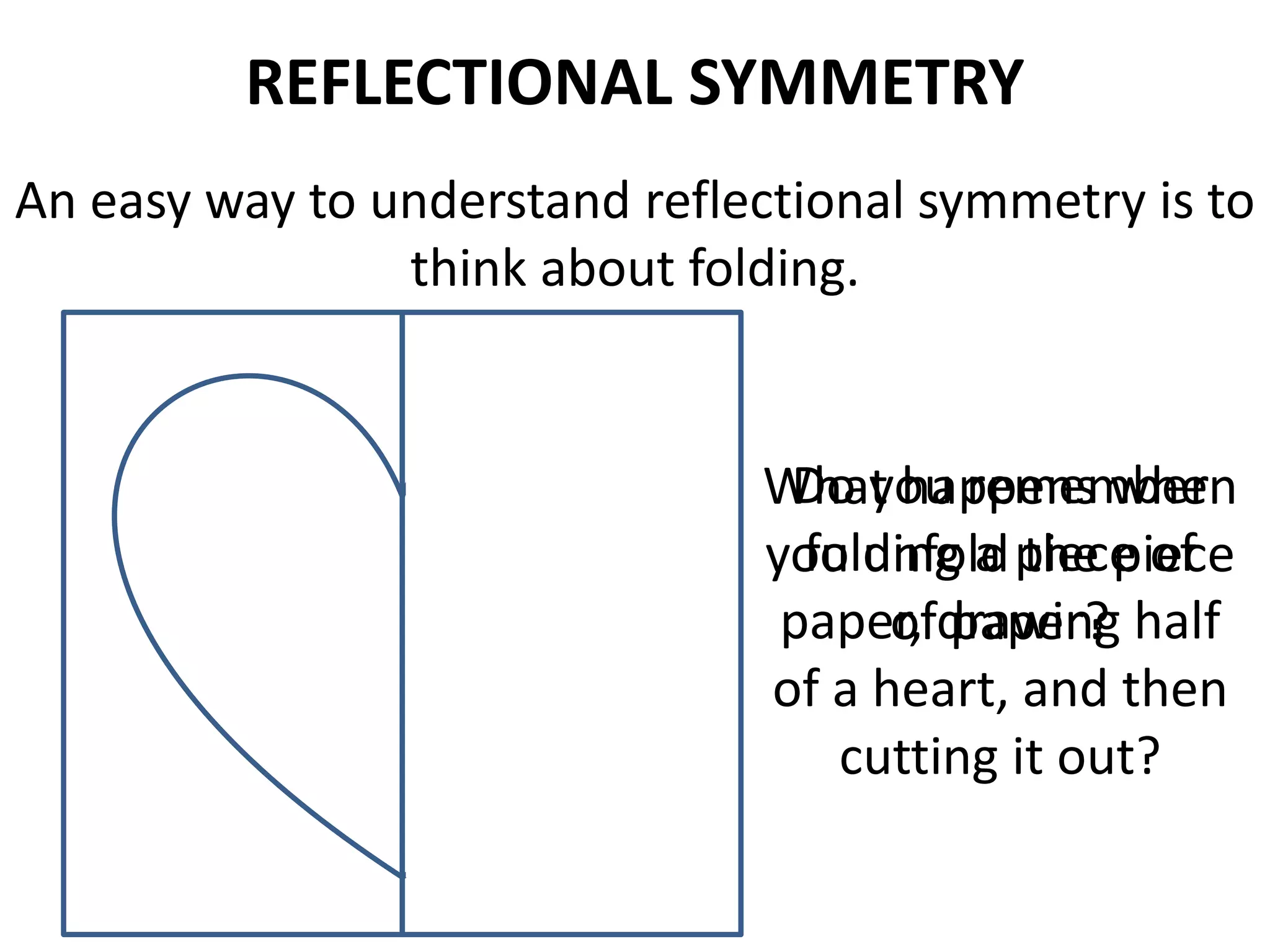
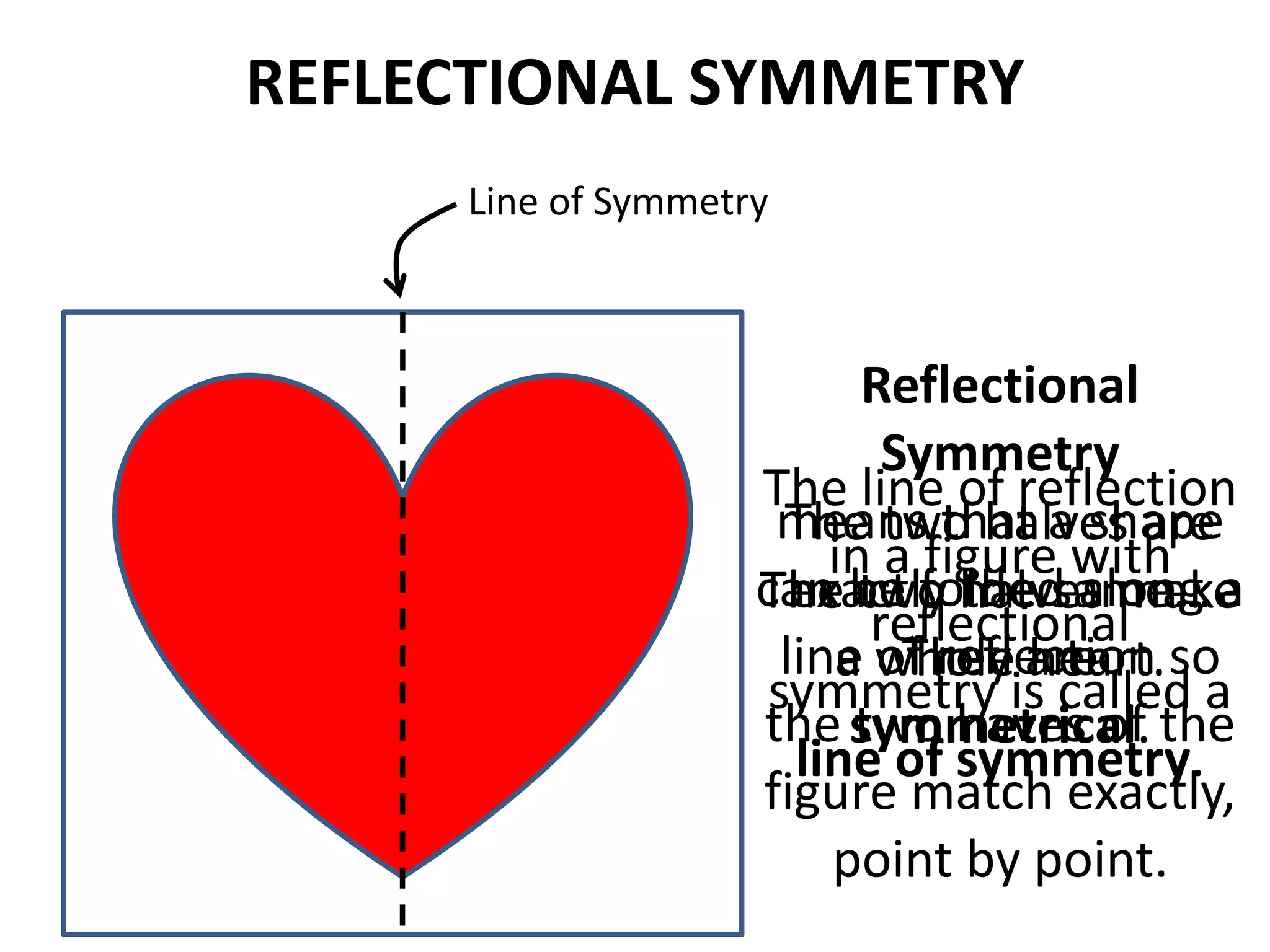
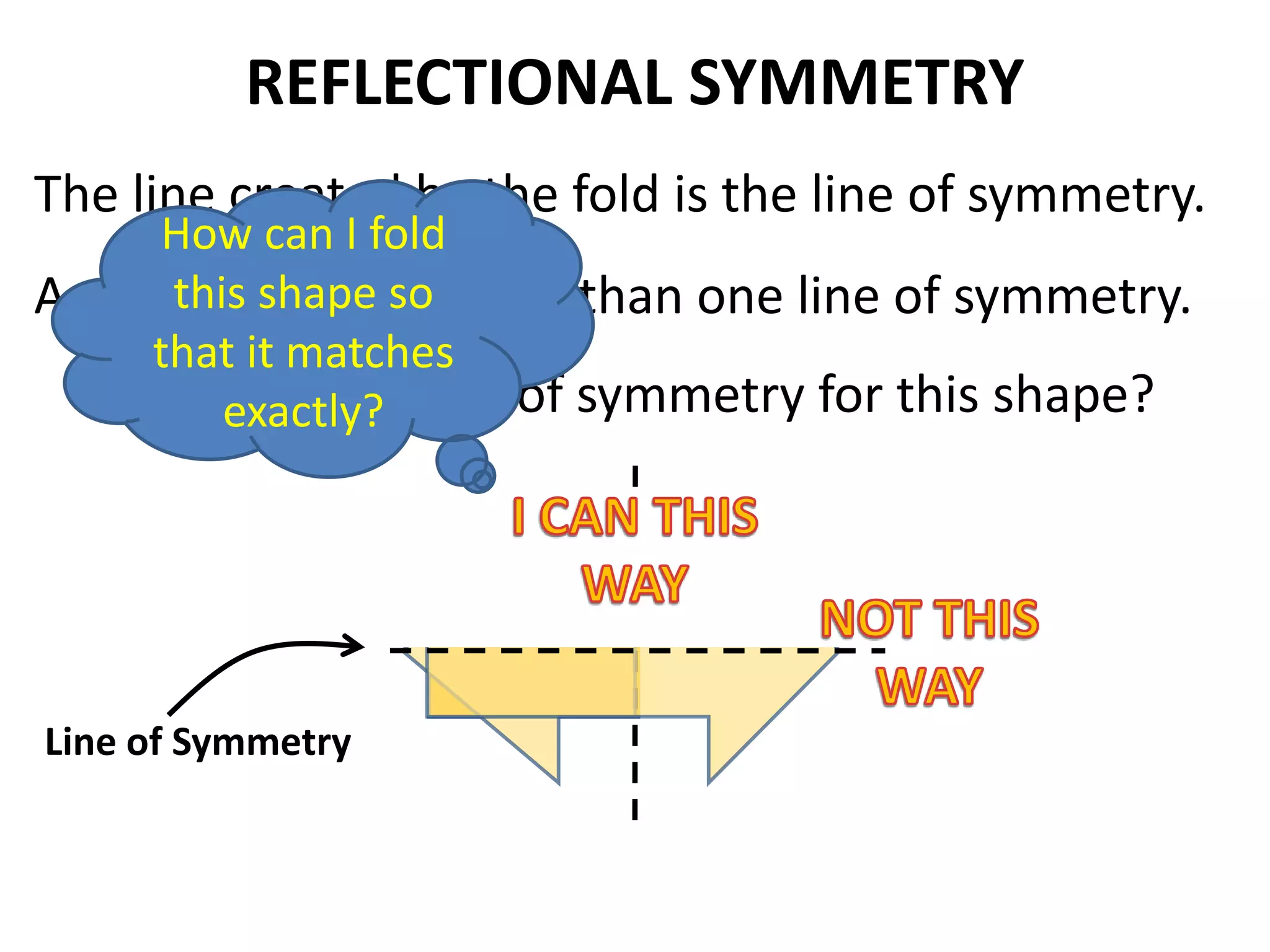
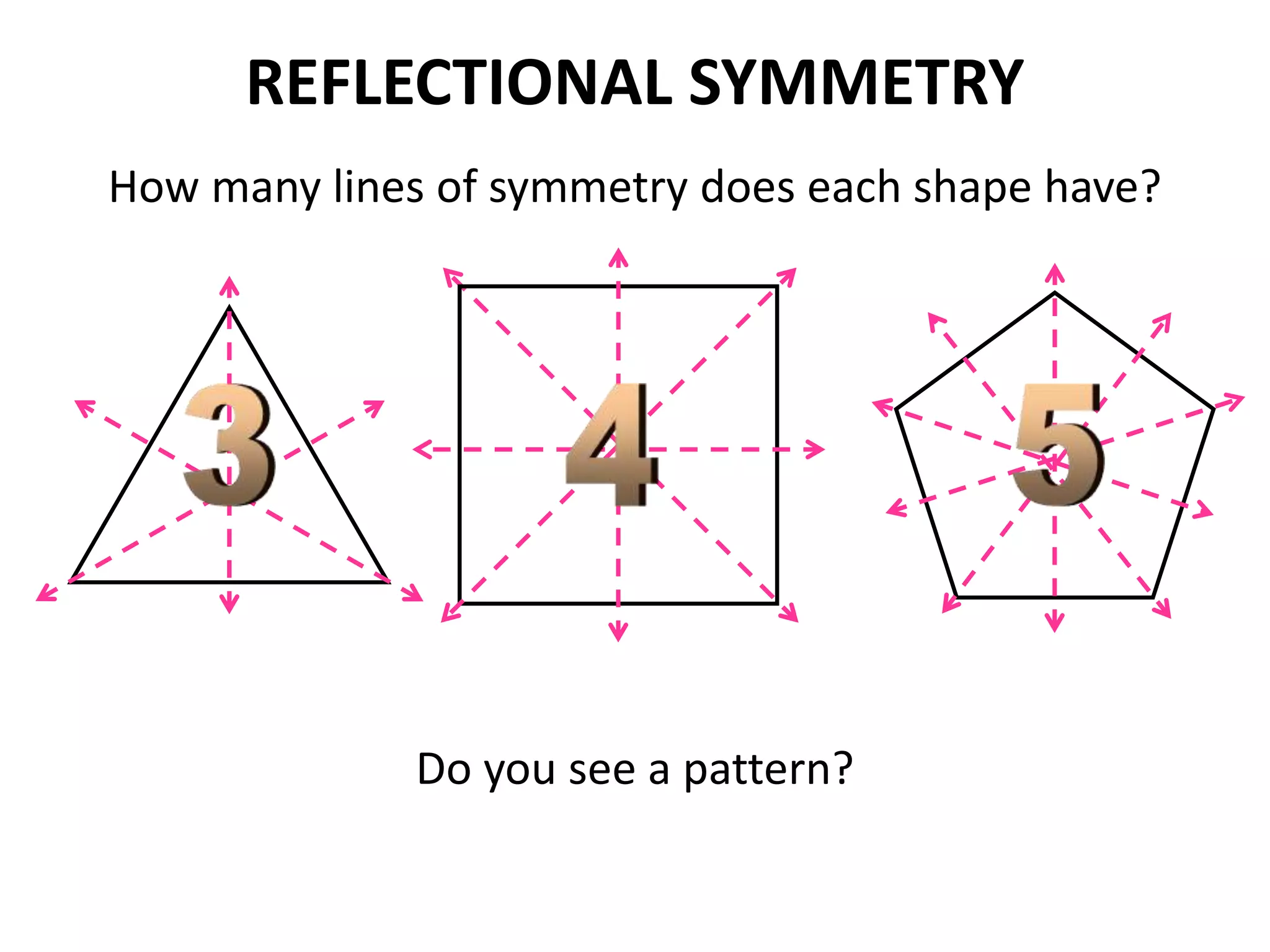
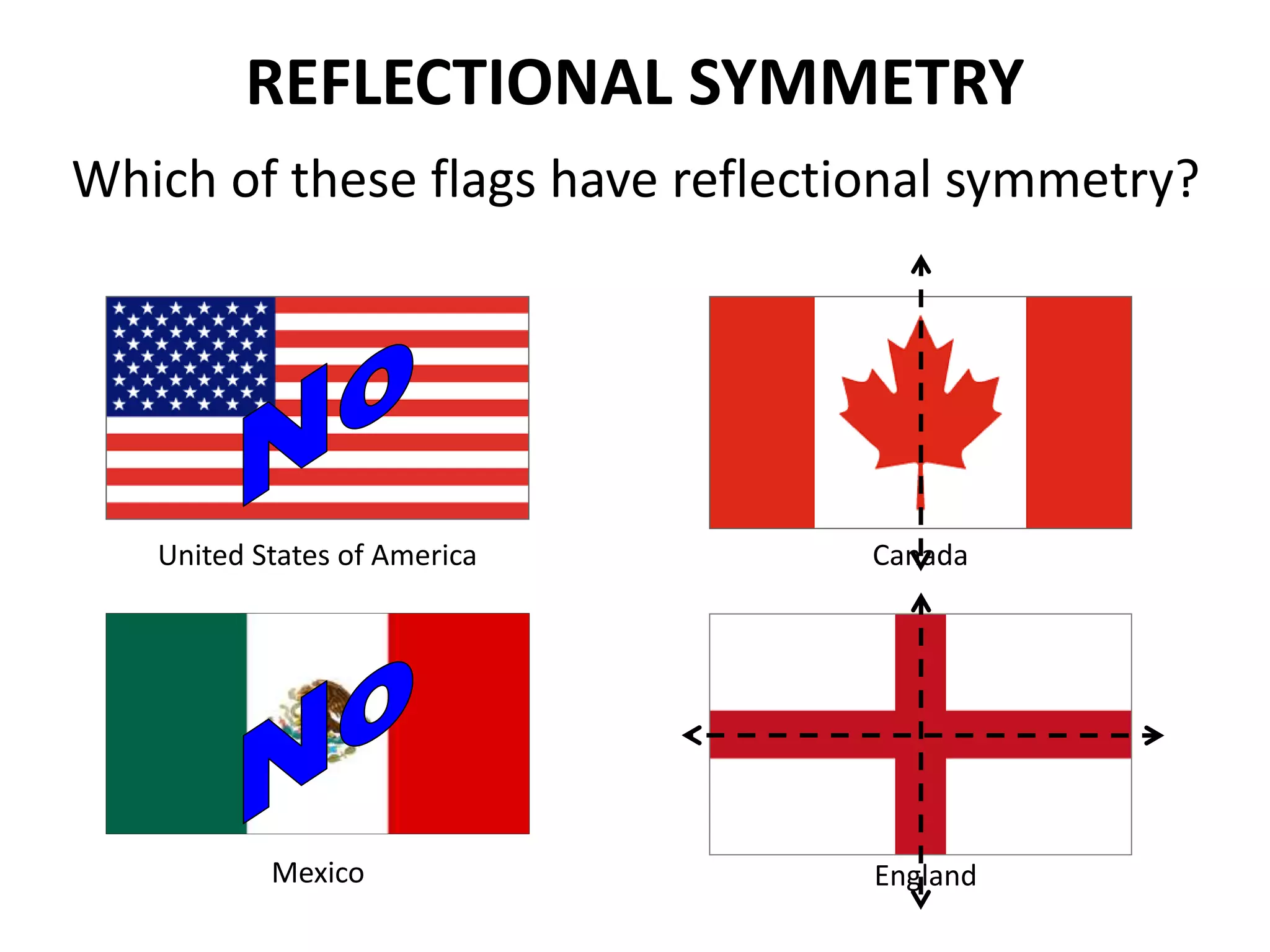
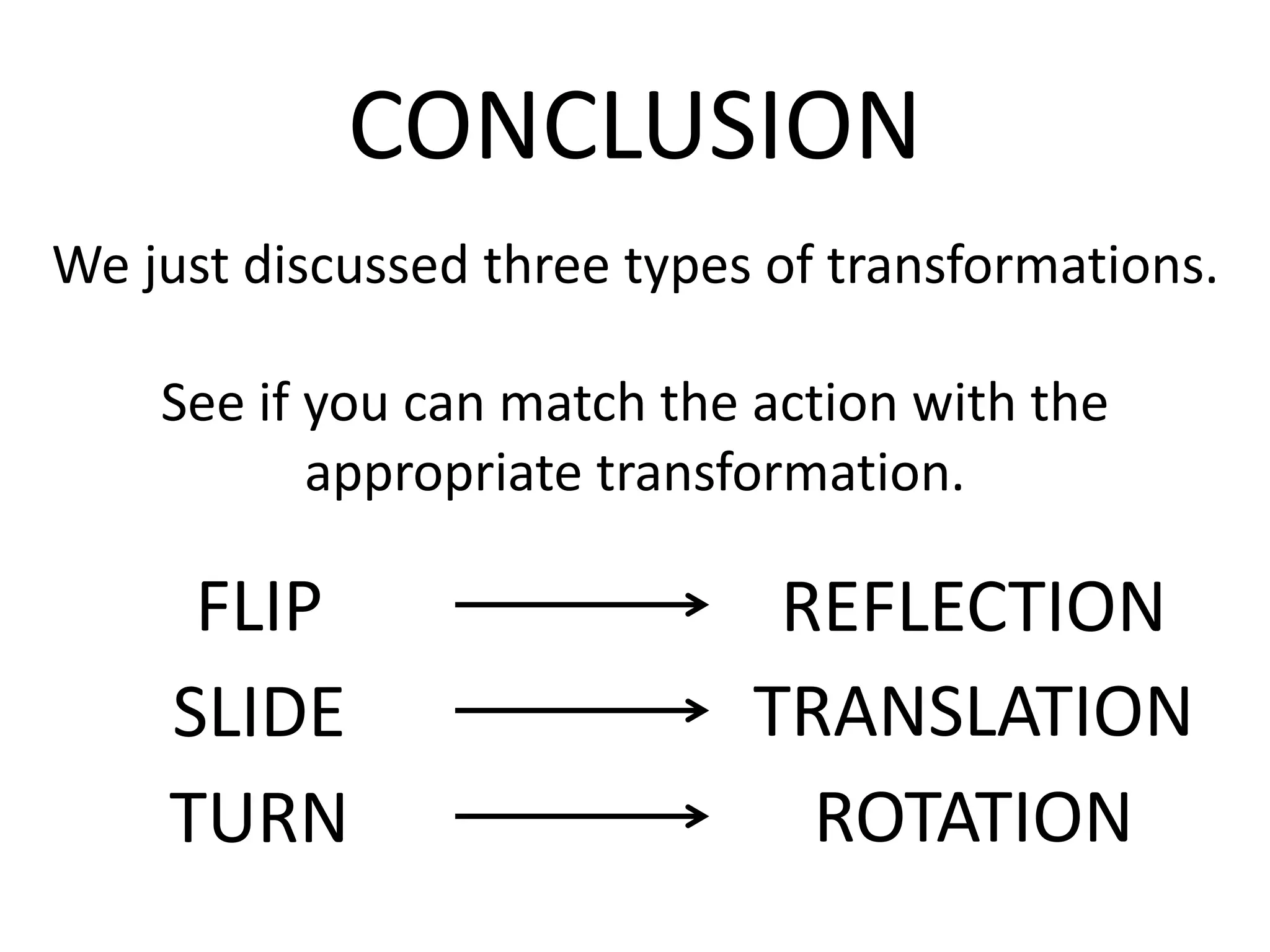
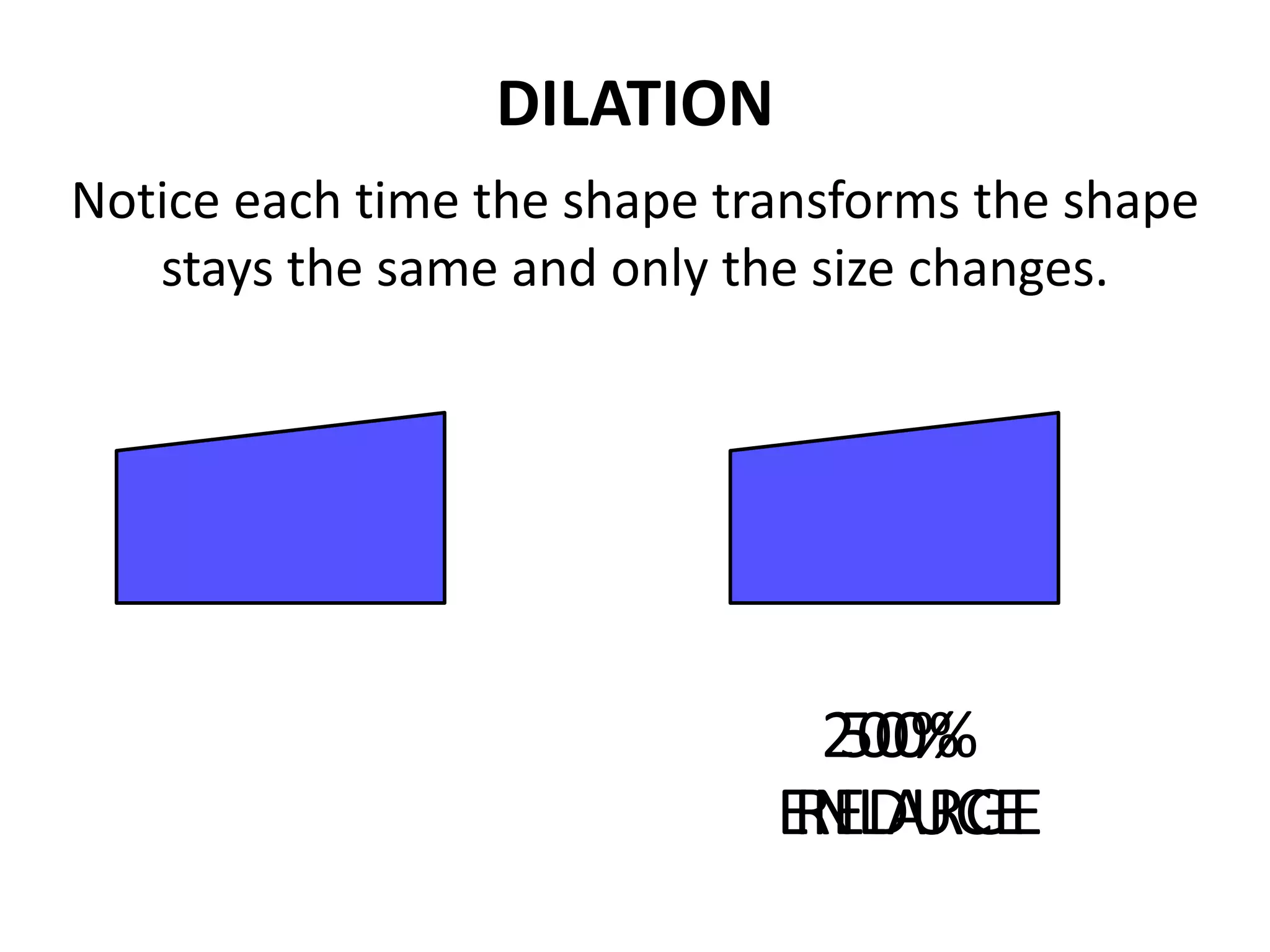
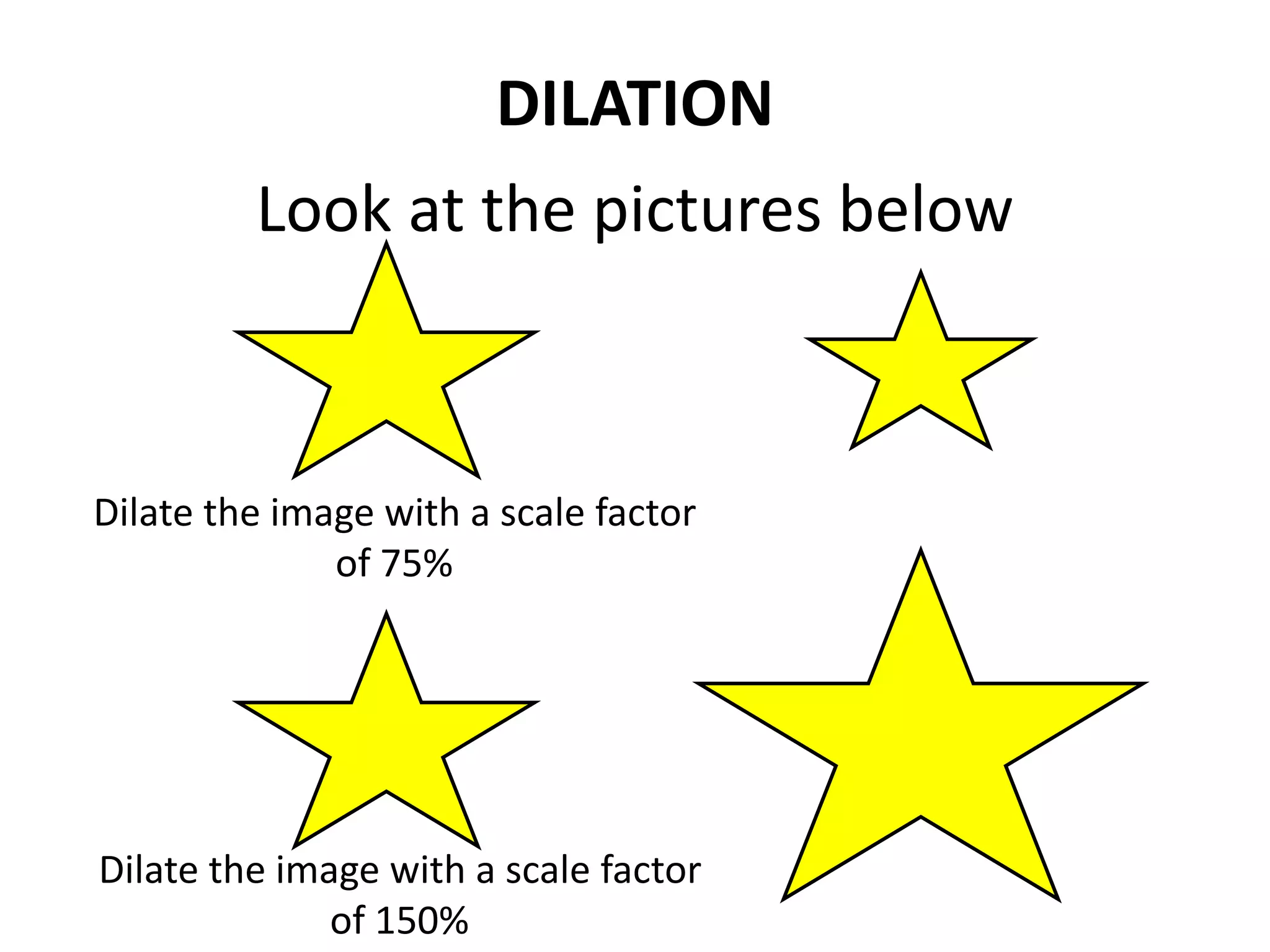
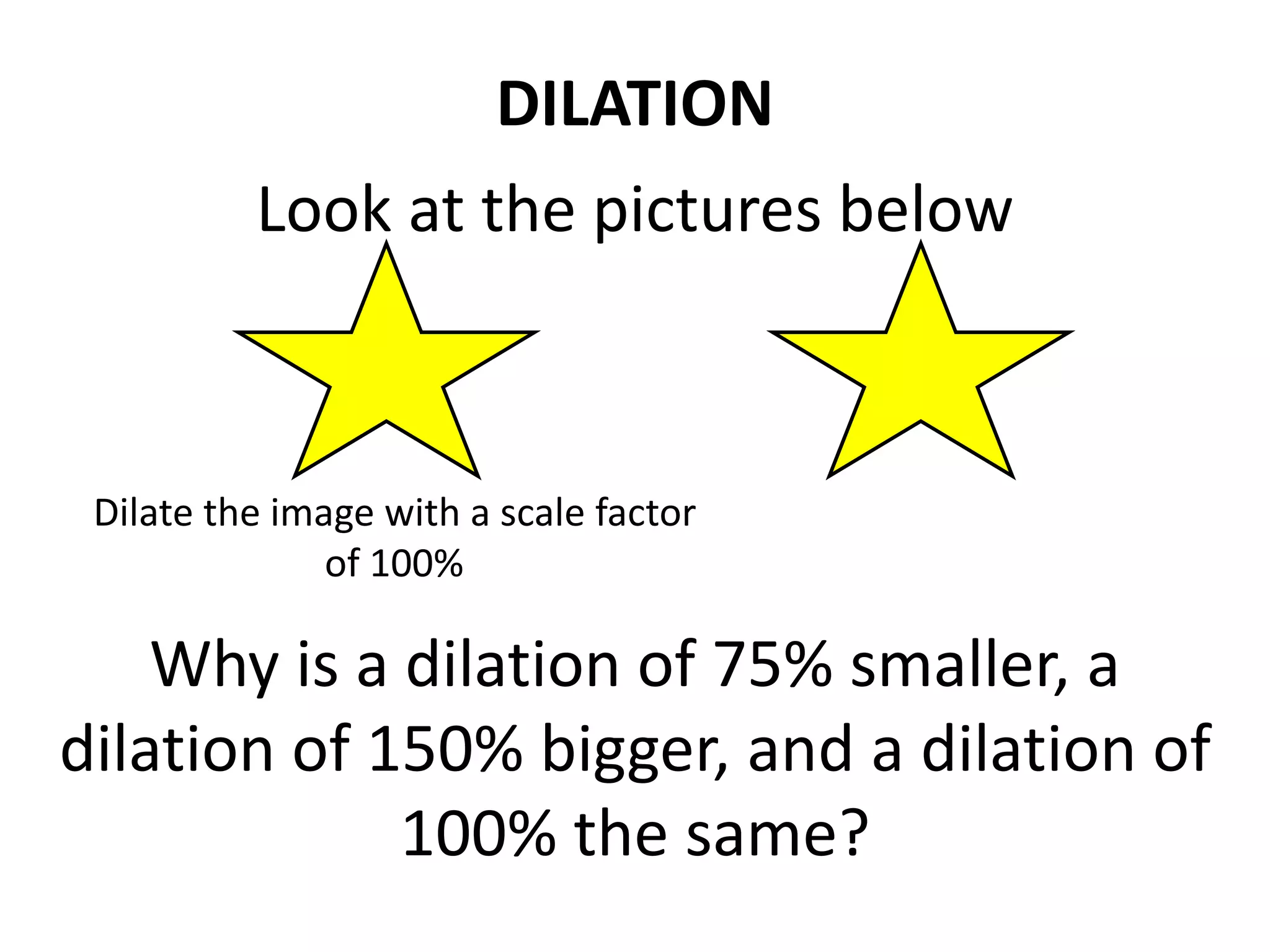
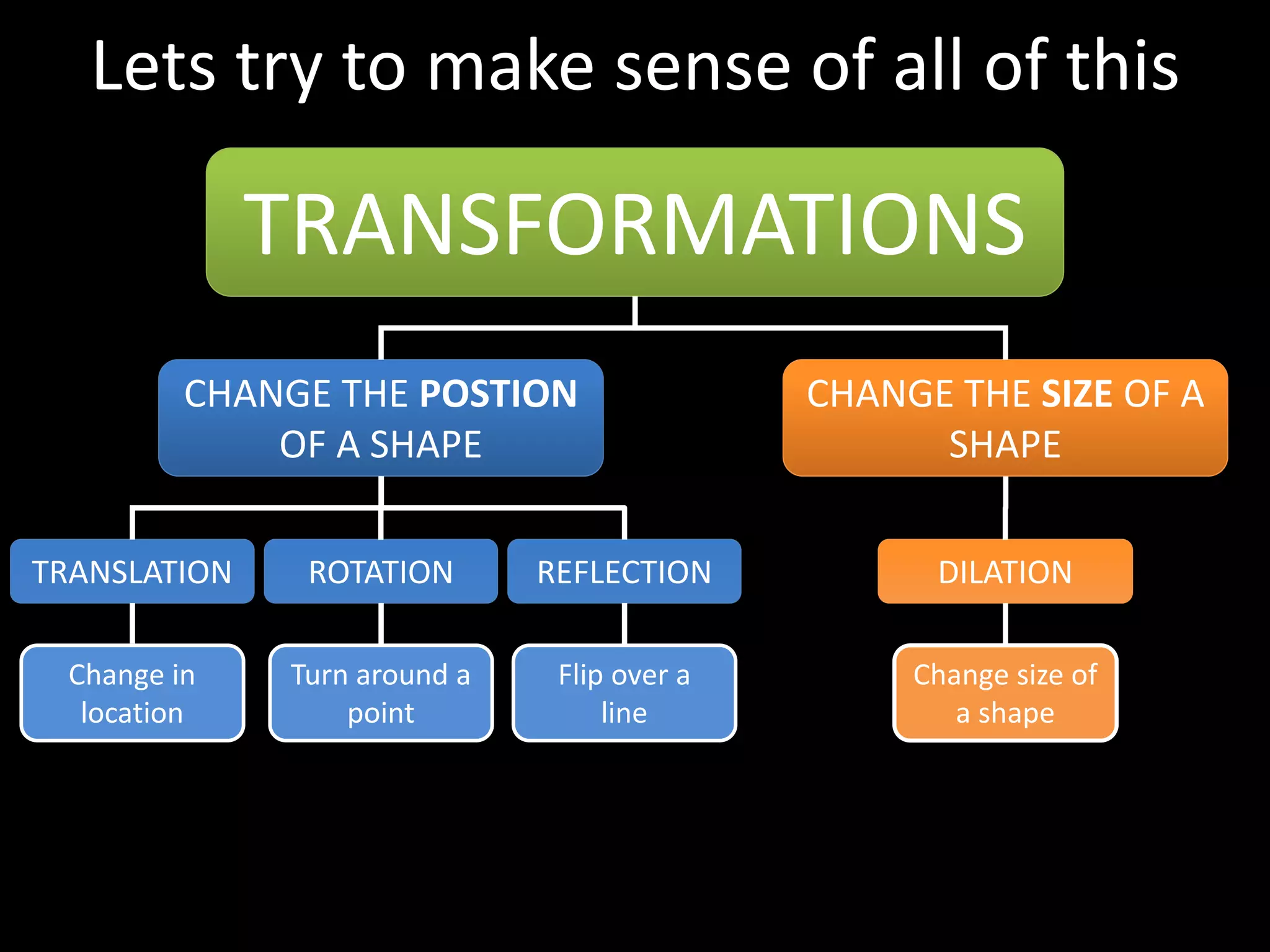
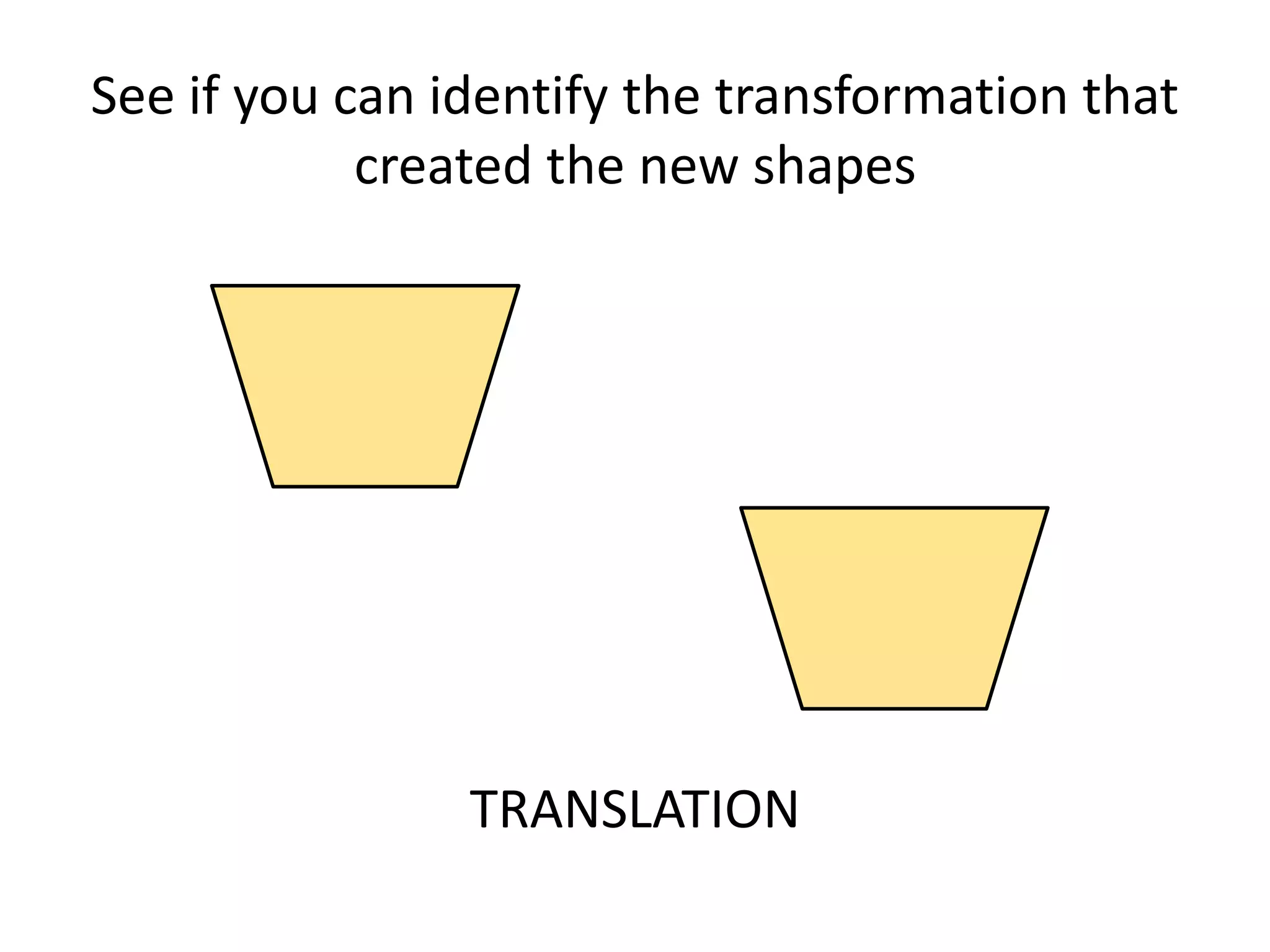
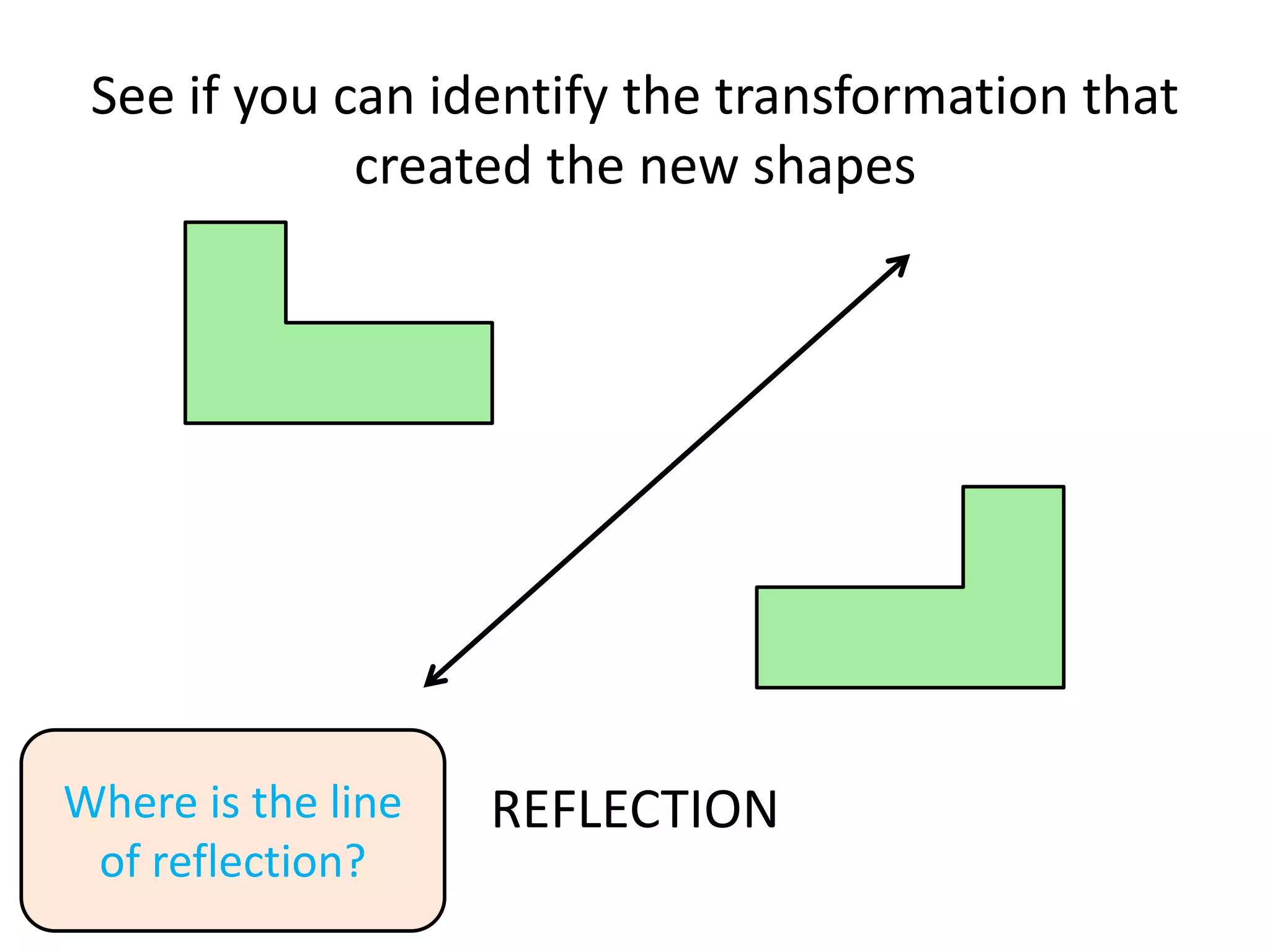
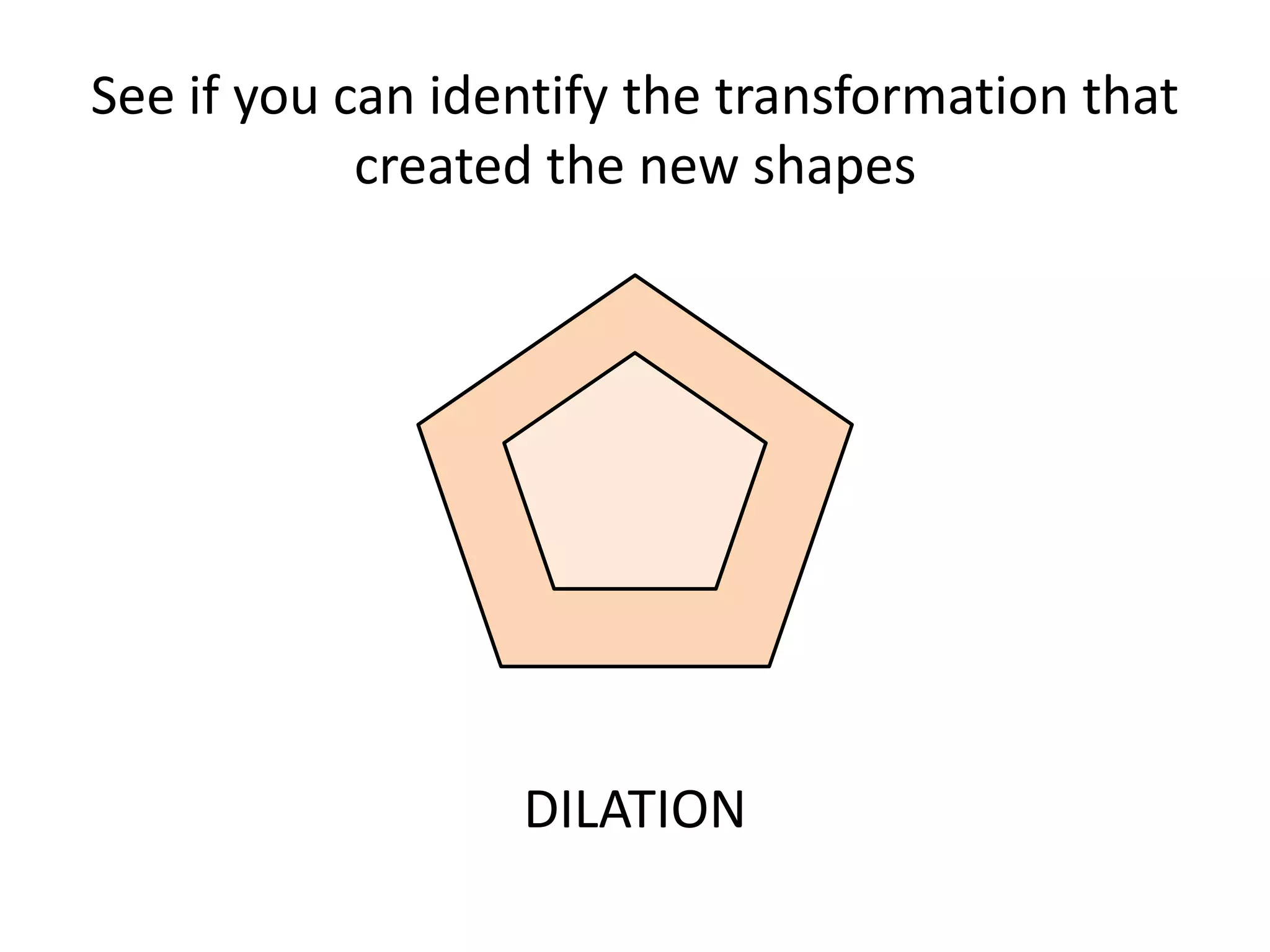
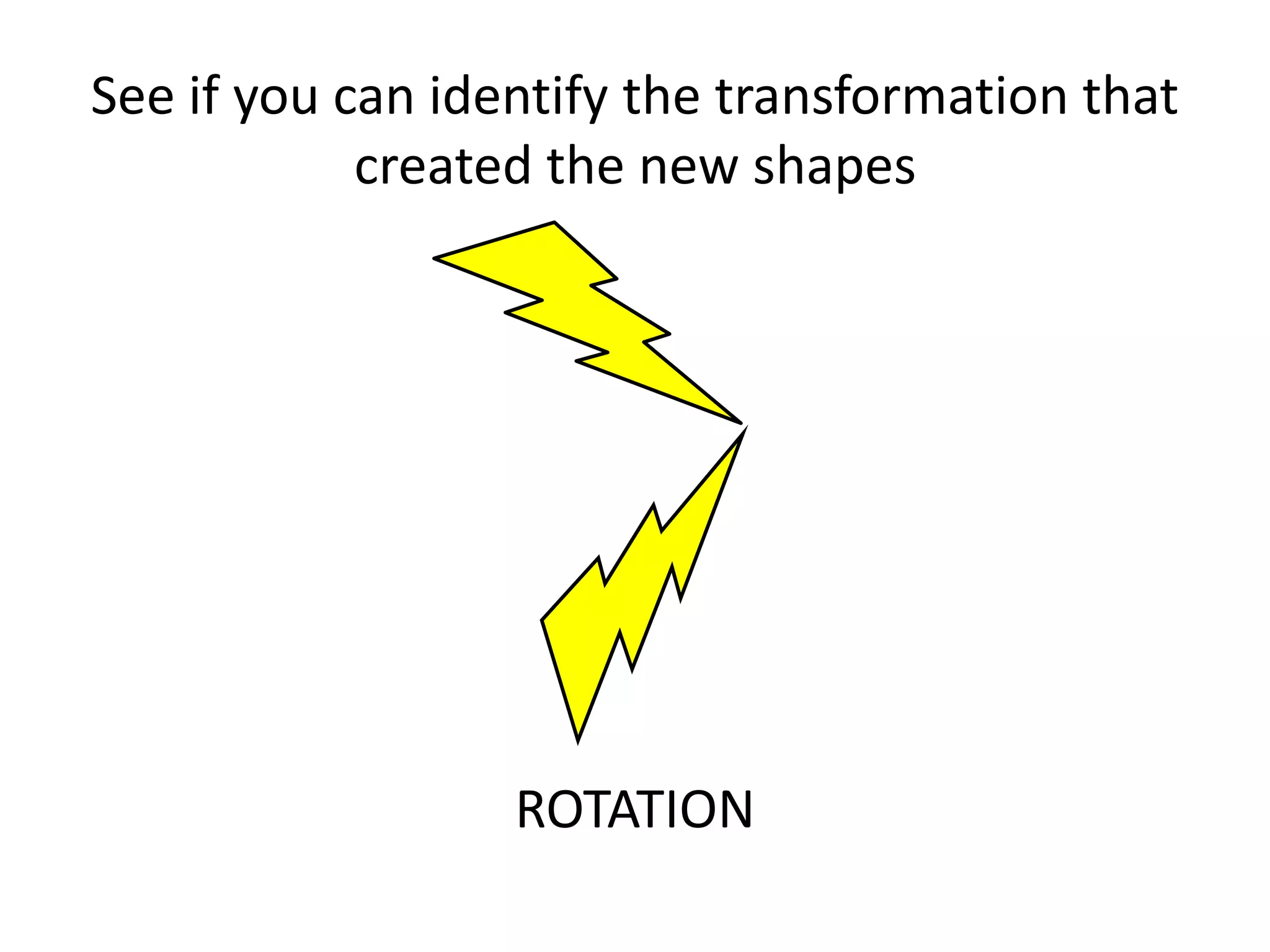
This document discusses different types of geometric transformations including translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. Translations move a figure across a plane without changing its size. Rotations turn a figure around a point or line. Reflections flip a figure across a line to create a mirror image. Dilation changes the size of a figure by enlarging or reducing it using a scale factor, while keeping the shape intact. The document provides examples and definitions of each transformation type.