Embed presentation
Downloaded 103 times


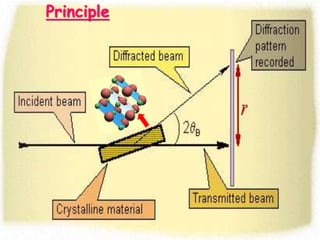
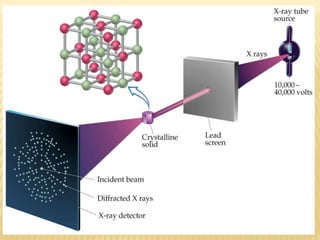
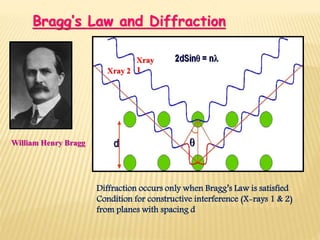
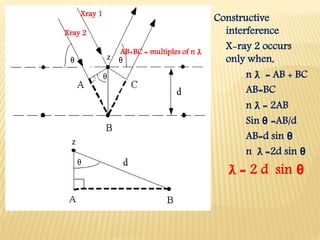



X-ray diffraction patterns provide a unique fingerprint for crystalline substances. When X-rays strike the planes of atoms within a crystal, they cause diffraction according to Bragg's law. Bragg's law states that constructive interference of X-rays occurs when the path length difference between X-rays reflected from successive planes is equal to an integer multiple of the wavelength. This relationship is expressed by the equation nλ = 2d sinθ, where d is the spacing between atomic planes, θ is the incident angle, n is an integer, and λ is the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. X-ray diffraction analysis can be used to determine properties of crystalline materials such as crystal structure, orientation, and stress.







