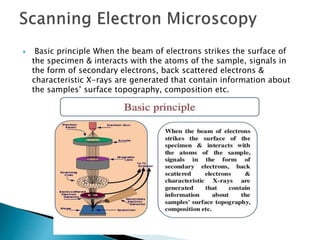
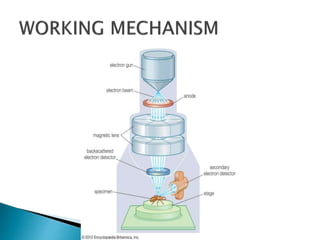
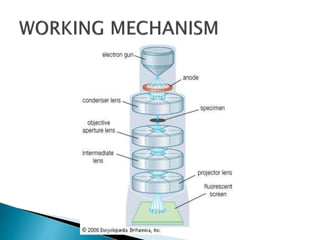
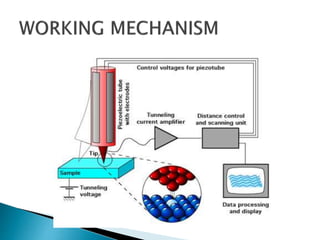
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used to characterize nanoparticles by examining their morphology, crystalline structure, and composition. SEM works by scanning a beam of electrons across a sample, detecting signals from interactions between the electrons and the sample's atoms. This allows examination of a sample's topography, texture, size and shape of particles, elemental composition, and crystalline arrangement at high resolution down to 1-5 nm.