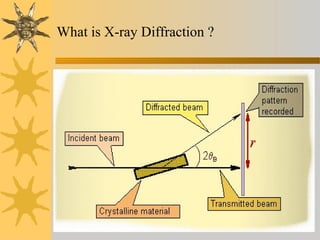
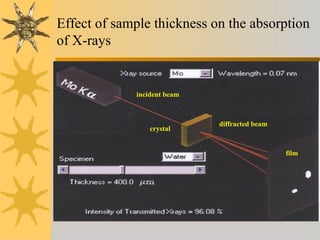
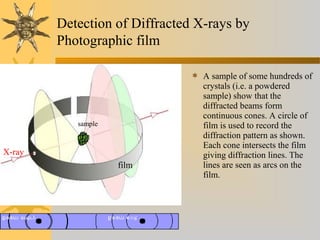
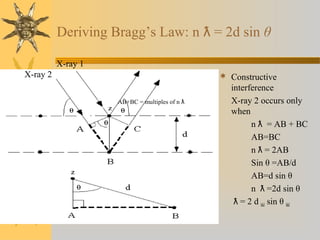
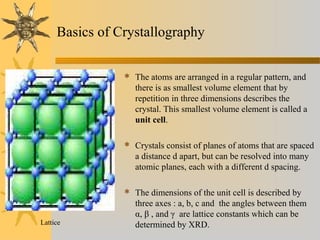
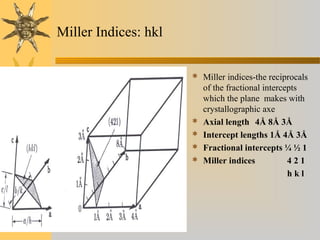
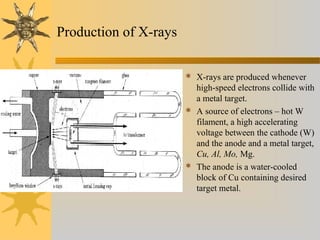
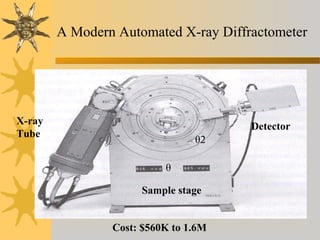
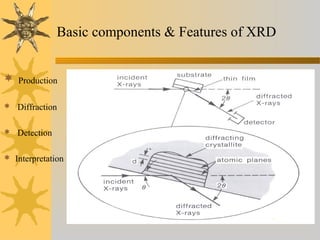
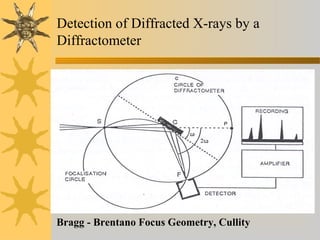
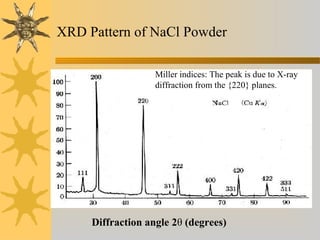
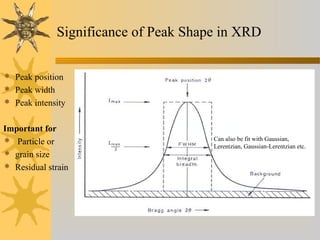
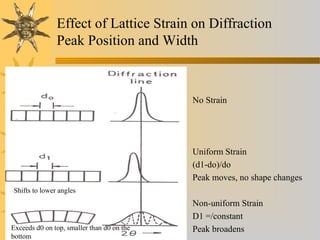
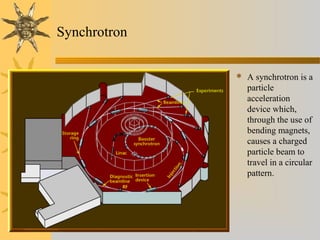
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing X-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the diffracted X-rays. This diffraction pattern acts as a "fingerprint" identifying the sample. Bragg's law describes how the diffraction pattern relates to the spacing of planes in the crystal lattice. XRD is used to determine properties like lattice parameters, grain size, strain, phase composition and crystal orientation. It has applications in fields like materials science, pharmaceuticals, and forensics.