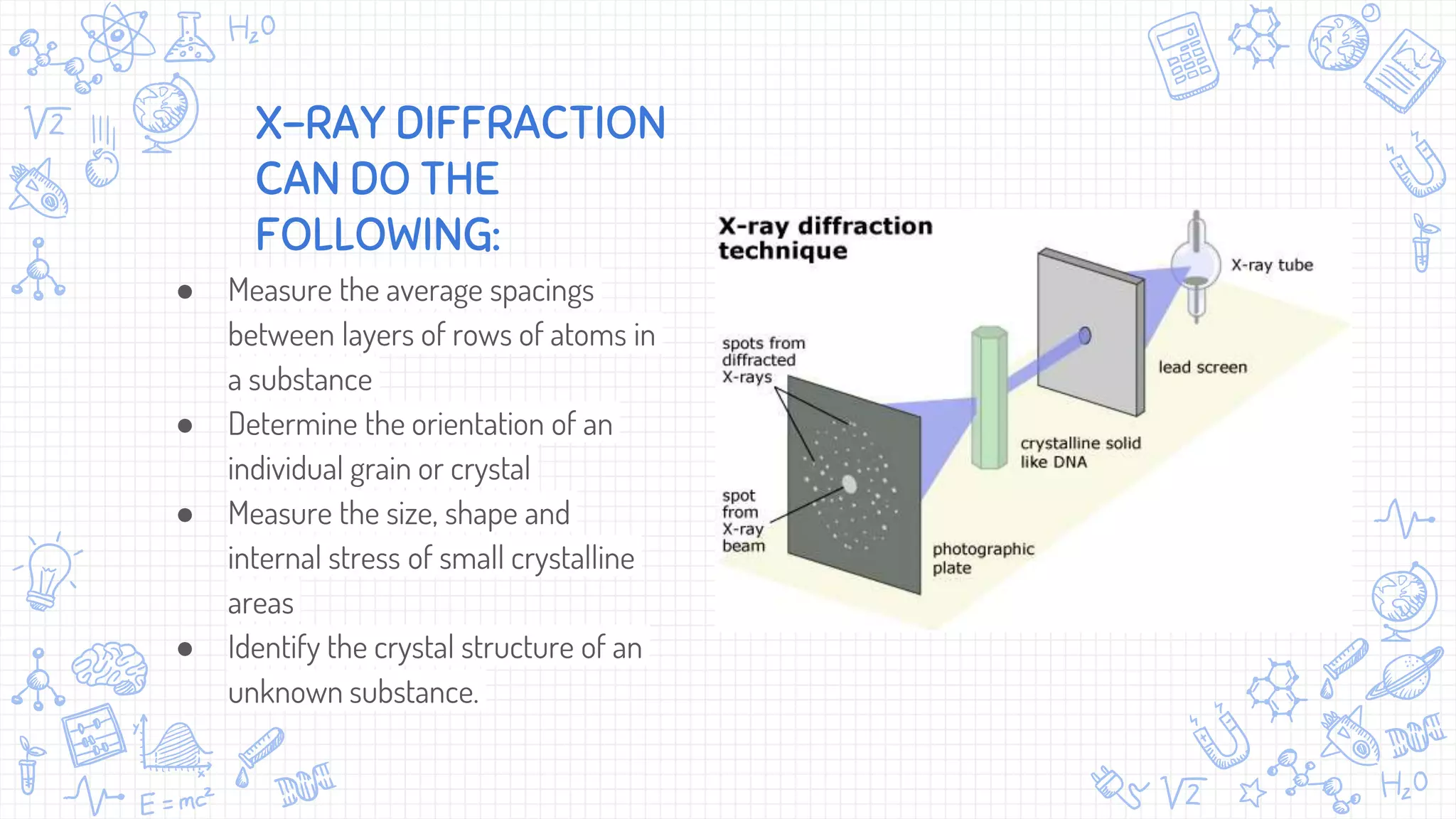
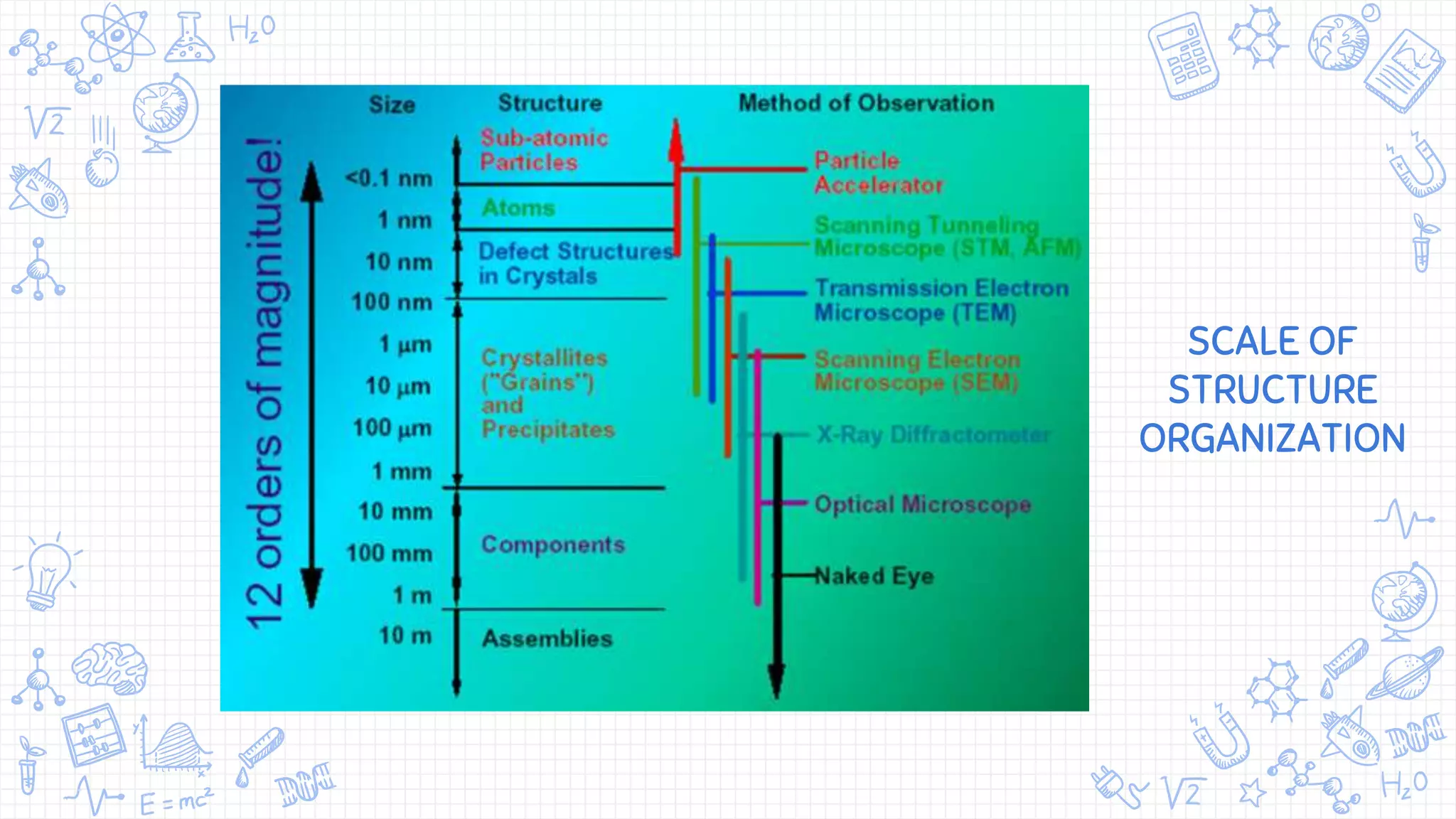
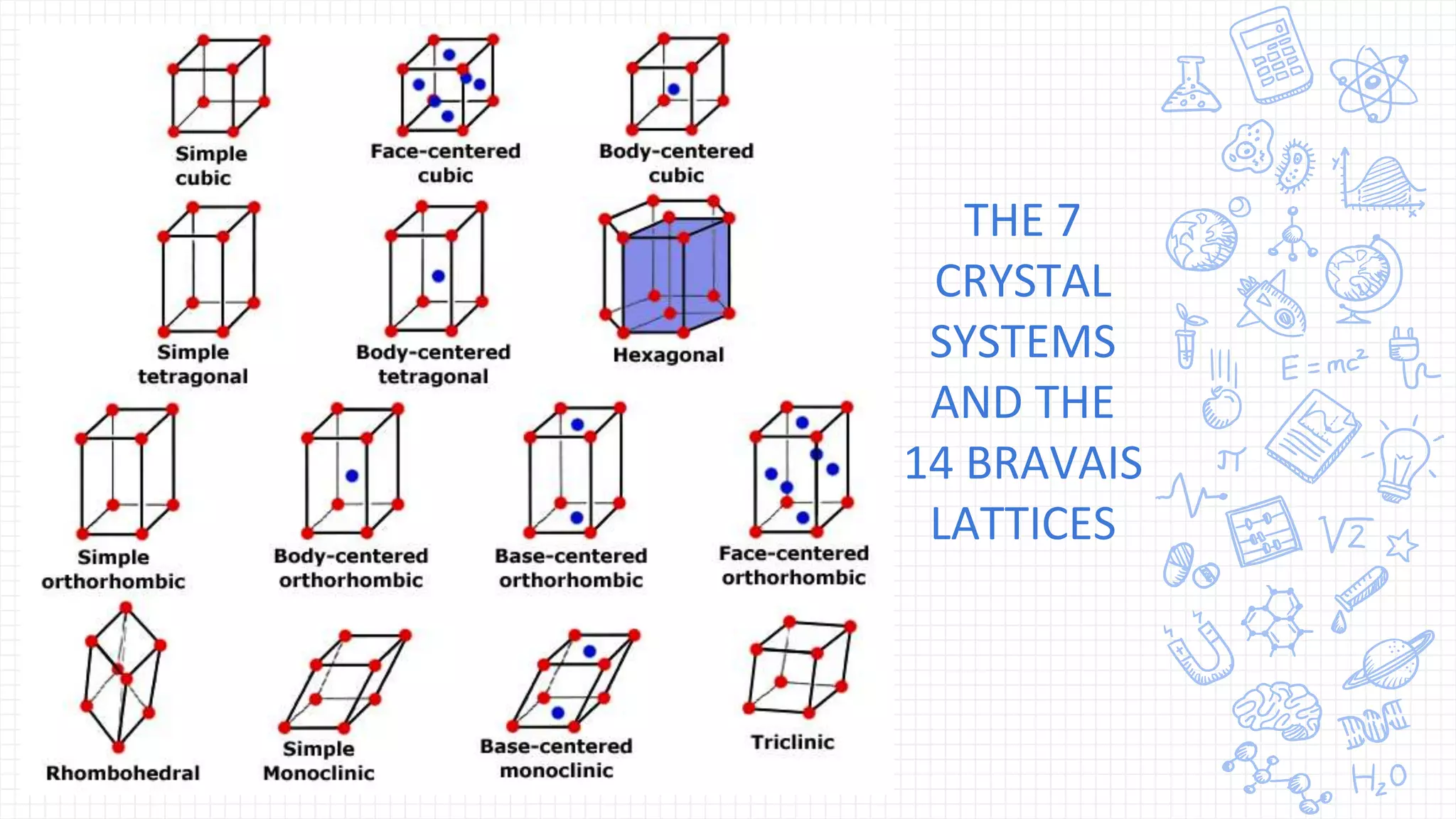
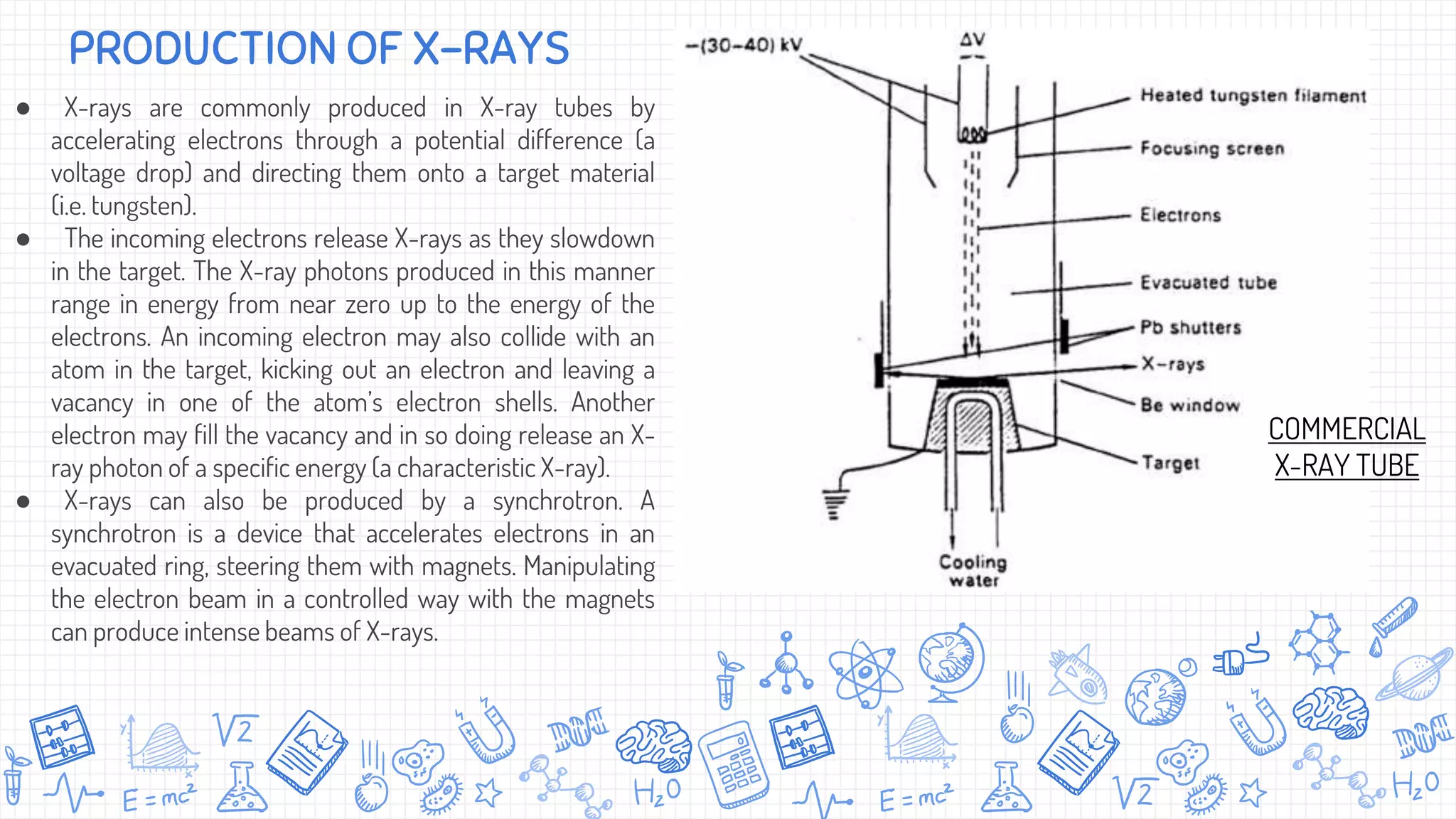
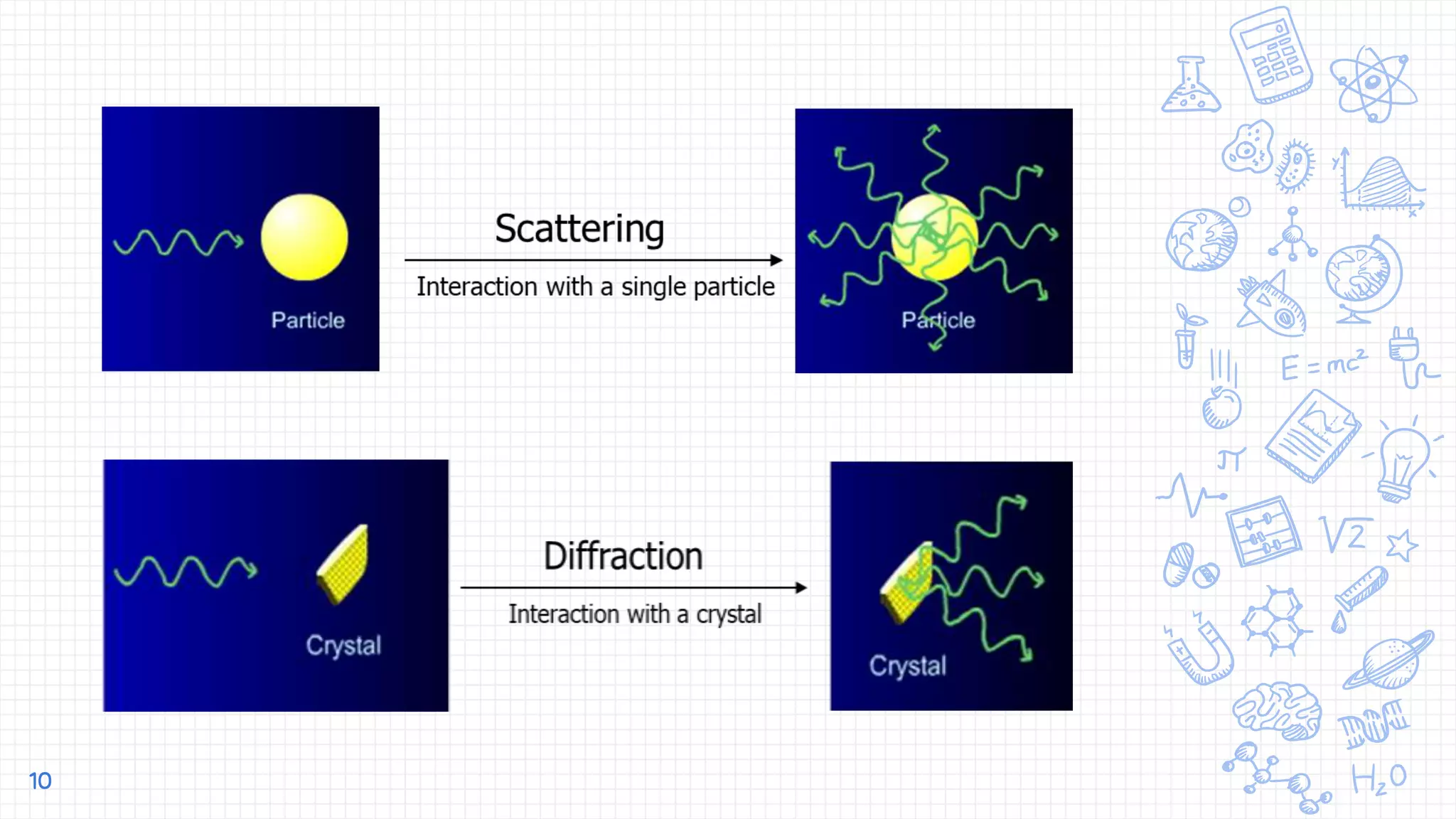
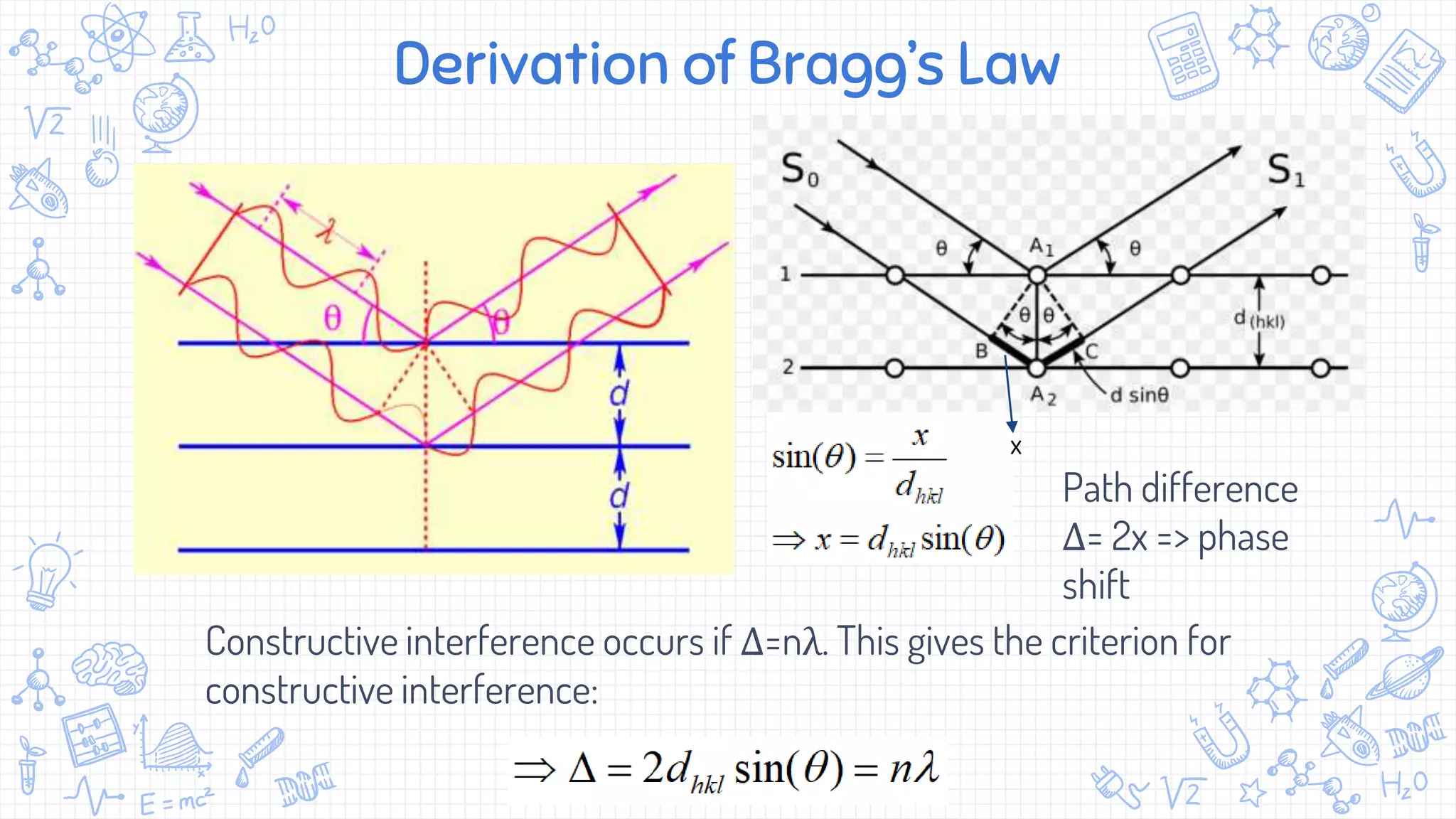
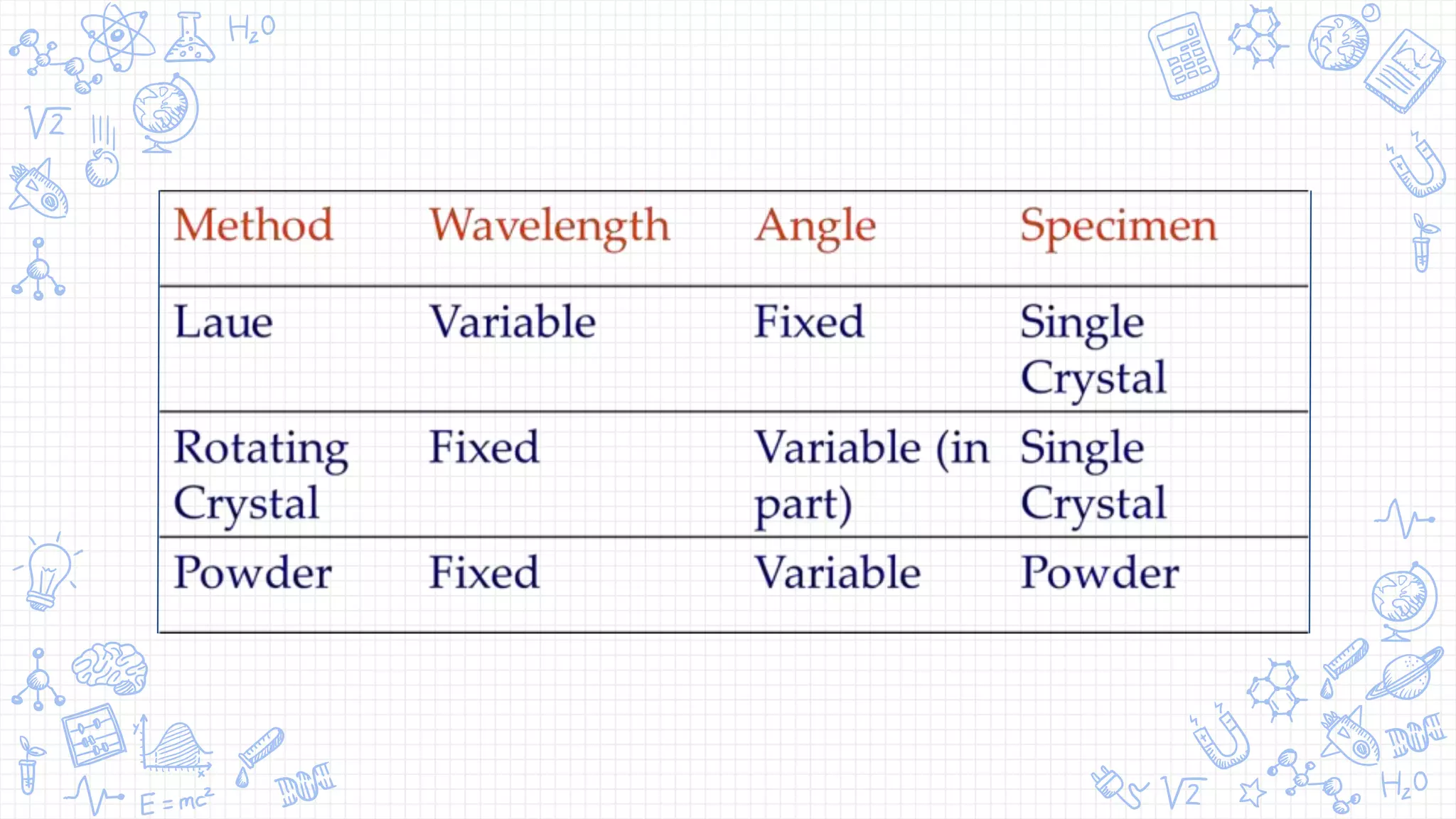
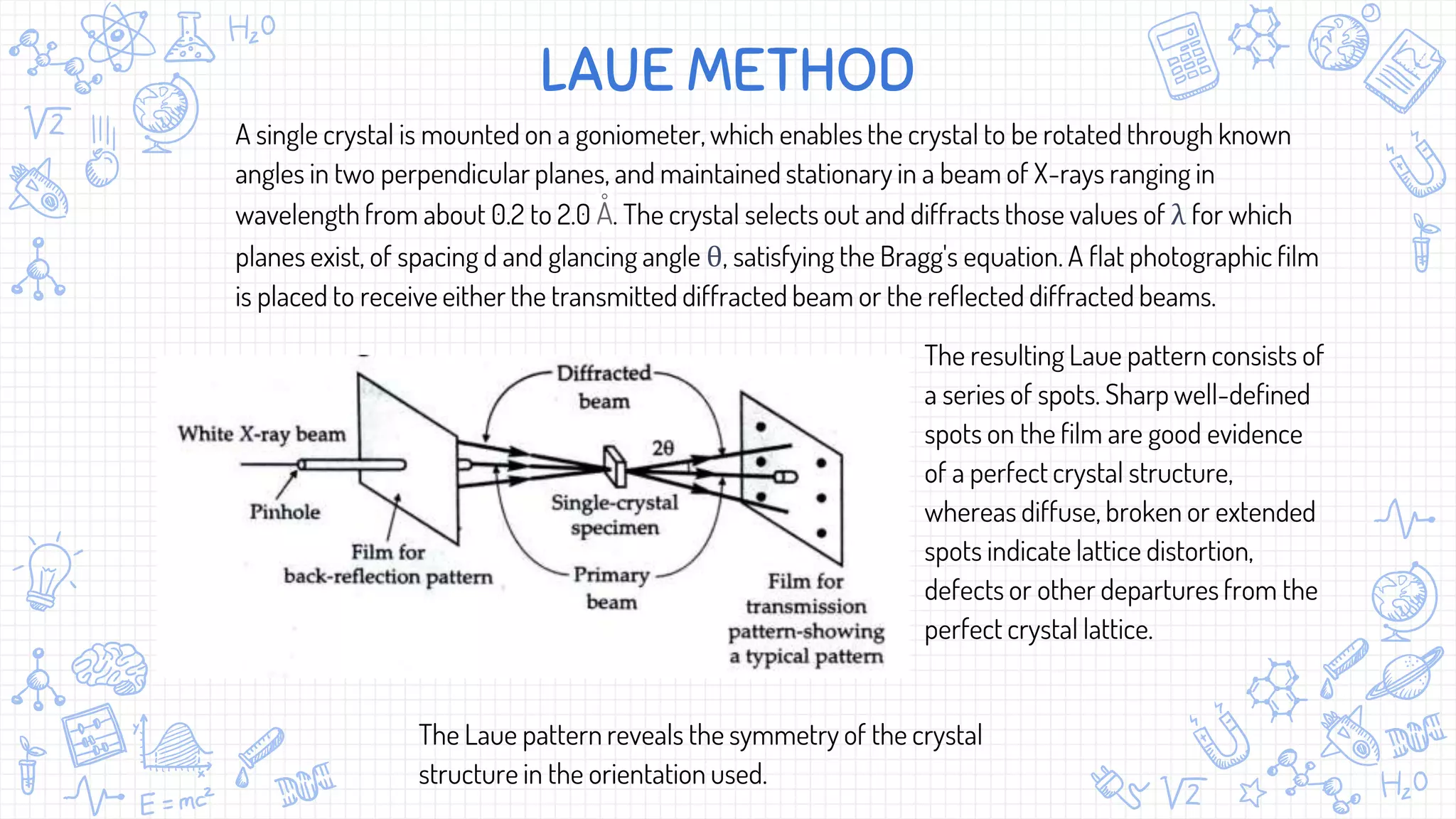
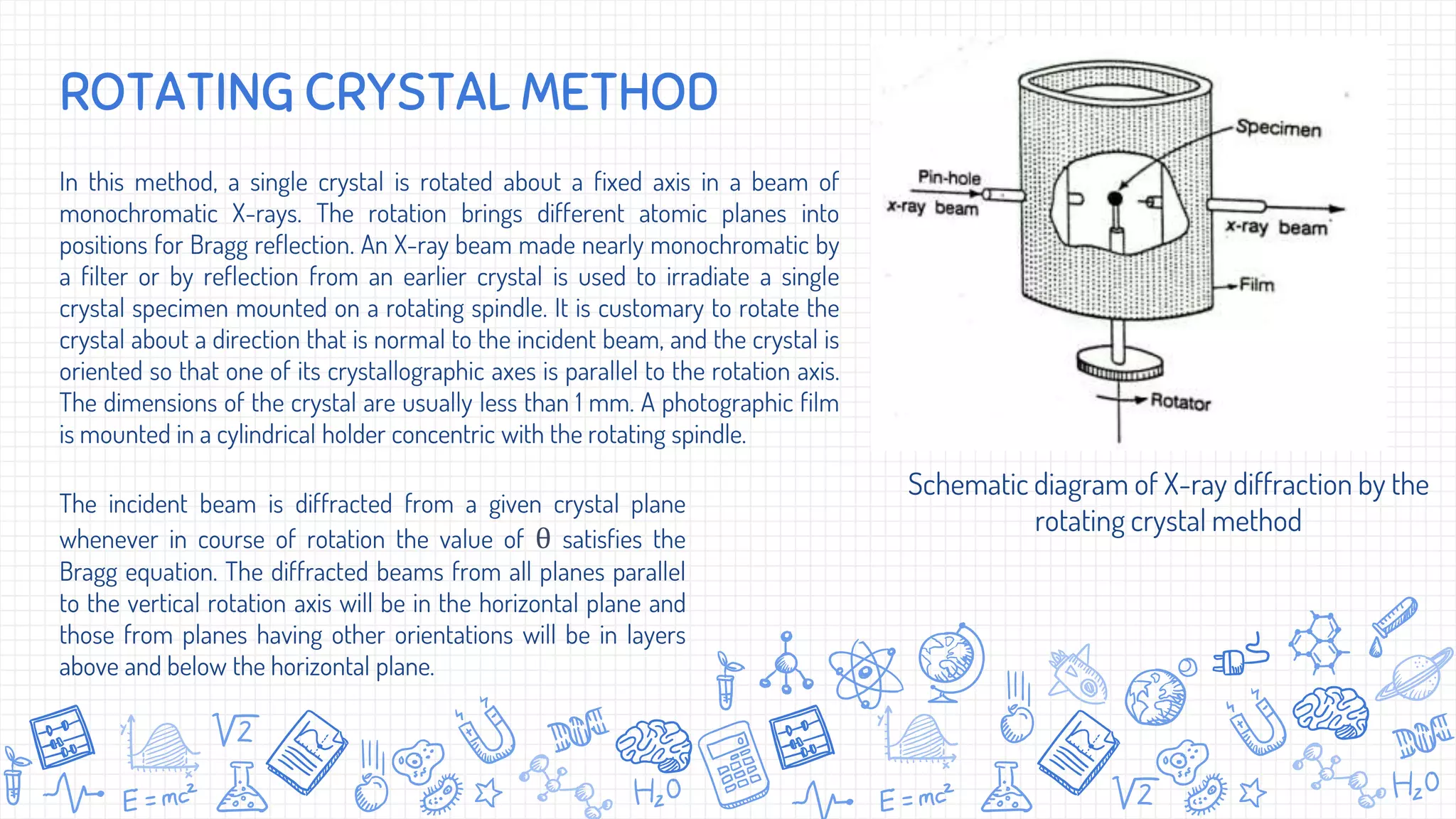
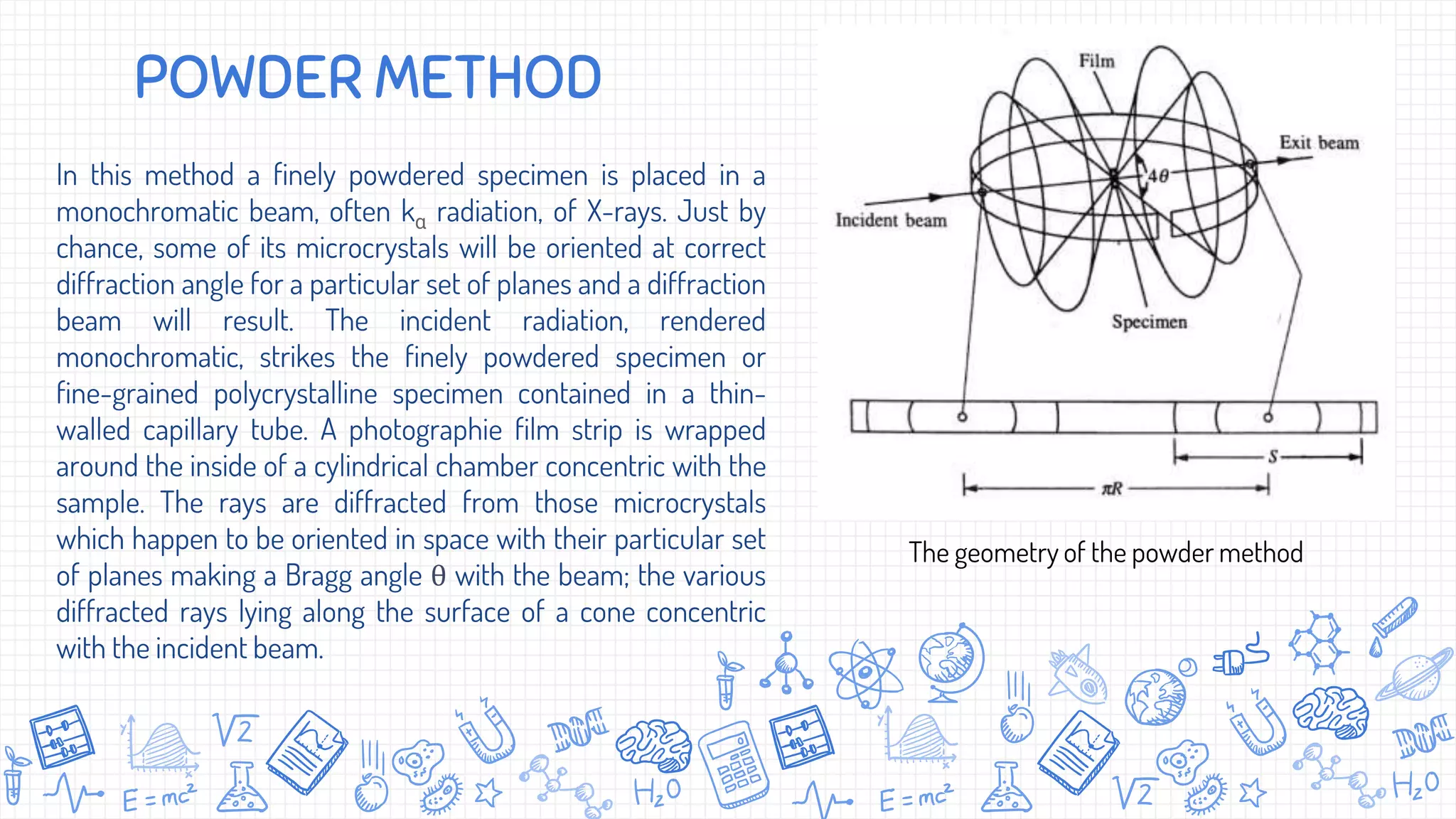
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to analyze the atomic and molecular structure of materials. It works by directing a beam of X-rays at a crystalline sample; the X-rays cause the atoms in the sample to diffract according to Bragg's law. This allows researchers to determine the sample's crystal structure, including properties like interplanar spacing. XRD is a common non-destructive characterization method in materials science, as it can identify unknown materials and analyze properties like grain size and stress levels. The document provides details on how XRD works, how X-rays are produced, Bragg's law, and experimental techniques like the Laue, rotating crystal, and powder methods.