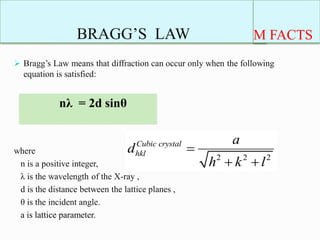
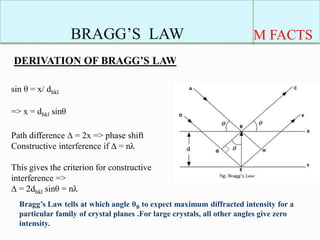
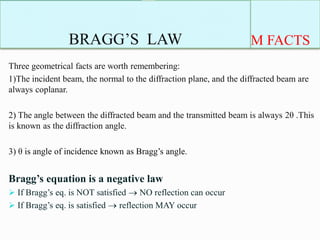
This document provides information about Bragg's law, which was introduced by Sir W. H. Bragg and his son Sir W. L. Bragg. Bragg's law correlates the X-ray wavelength, interplanar spacing of a crystal lattice, and reflection angle, stating that diffraction will occur when the path difference between reflected waves is equal to an integer multiple of the wavelength. The key equation is given as nλ = 2d sinθ, where n is a positive integer, λ is the X-ray wavelength, d is the distance between lattice planes, and θ is the incident angle. Examples are provided of how Bragg's law applies to cubic crystals.