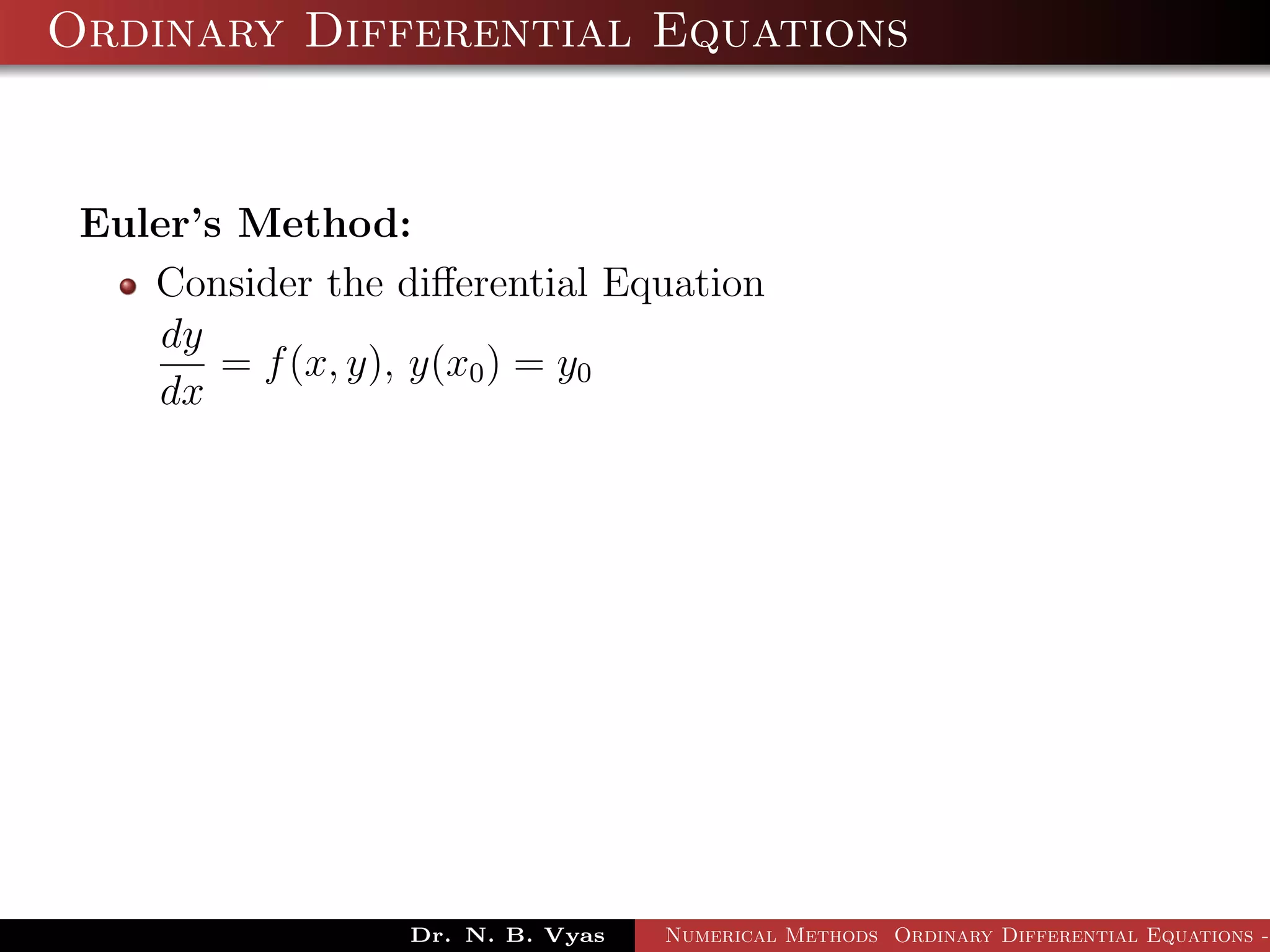
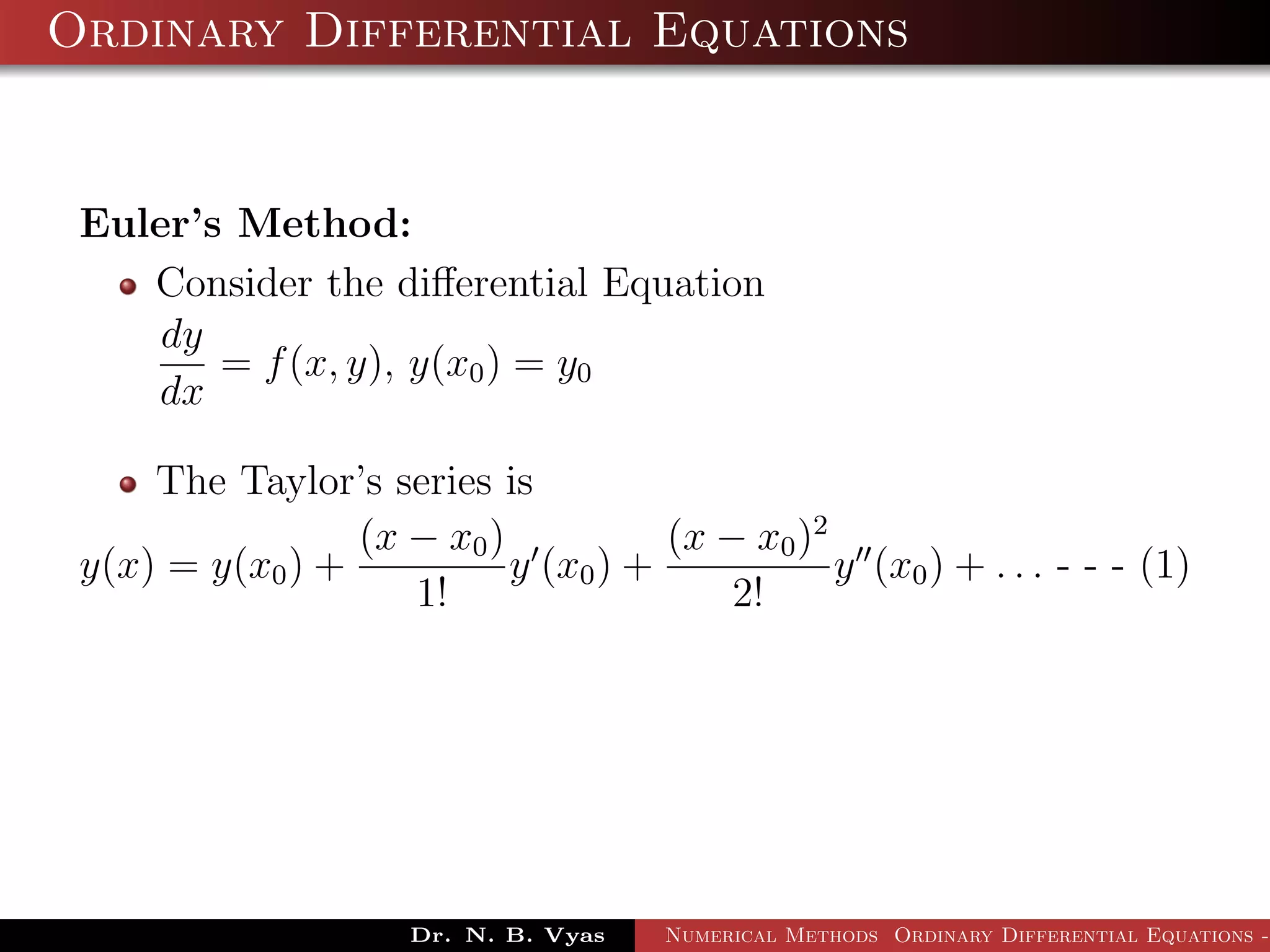
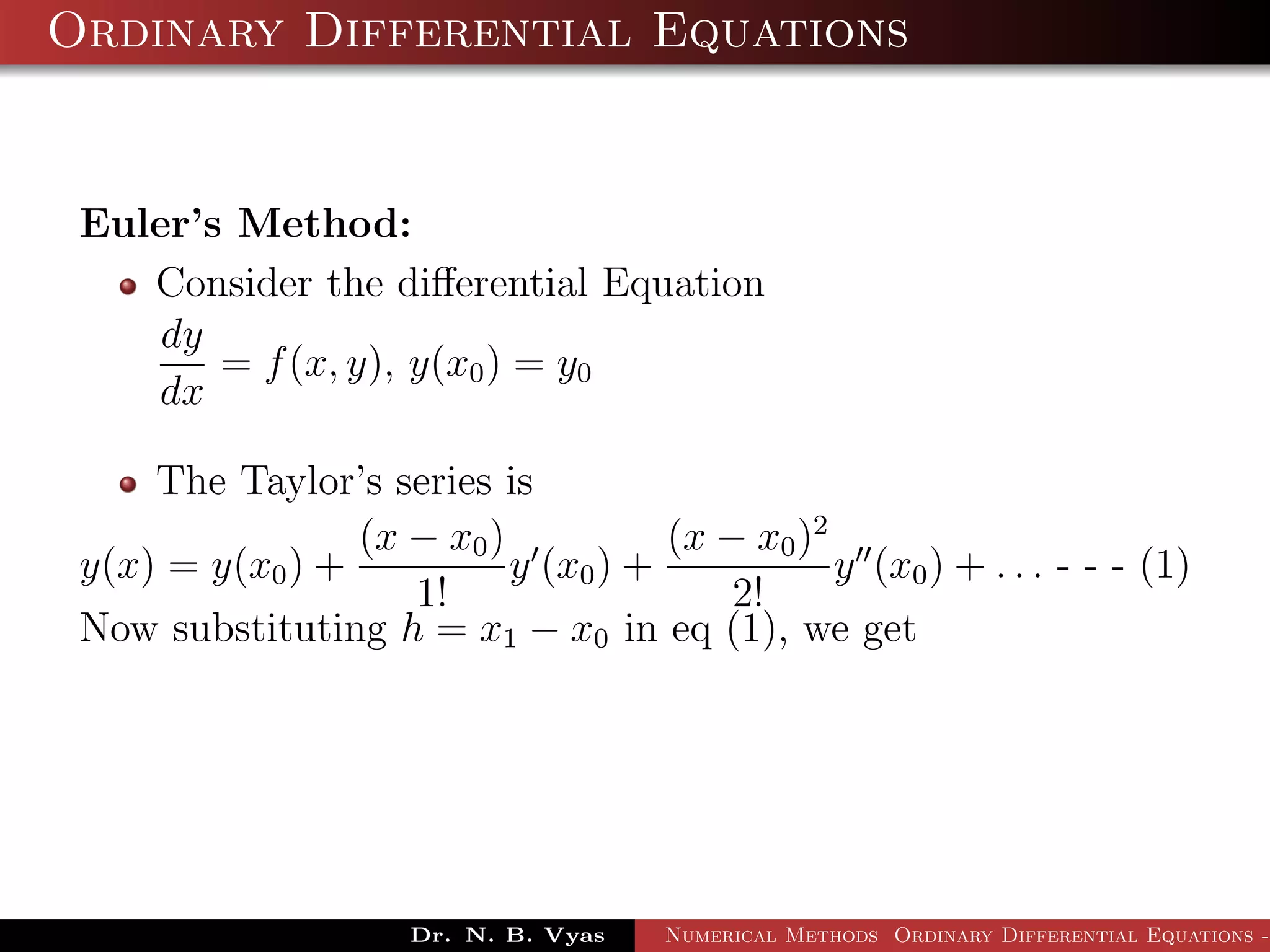
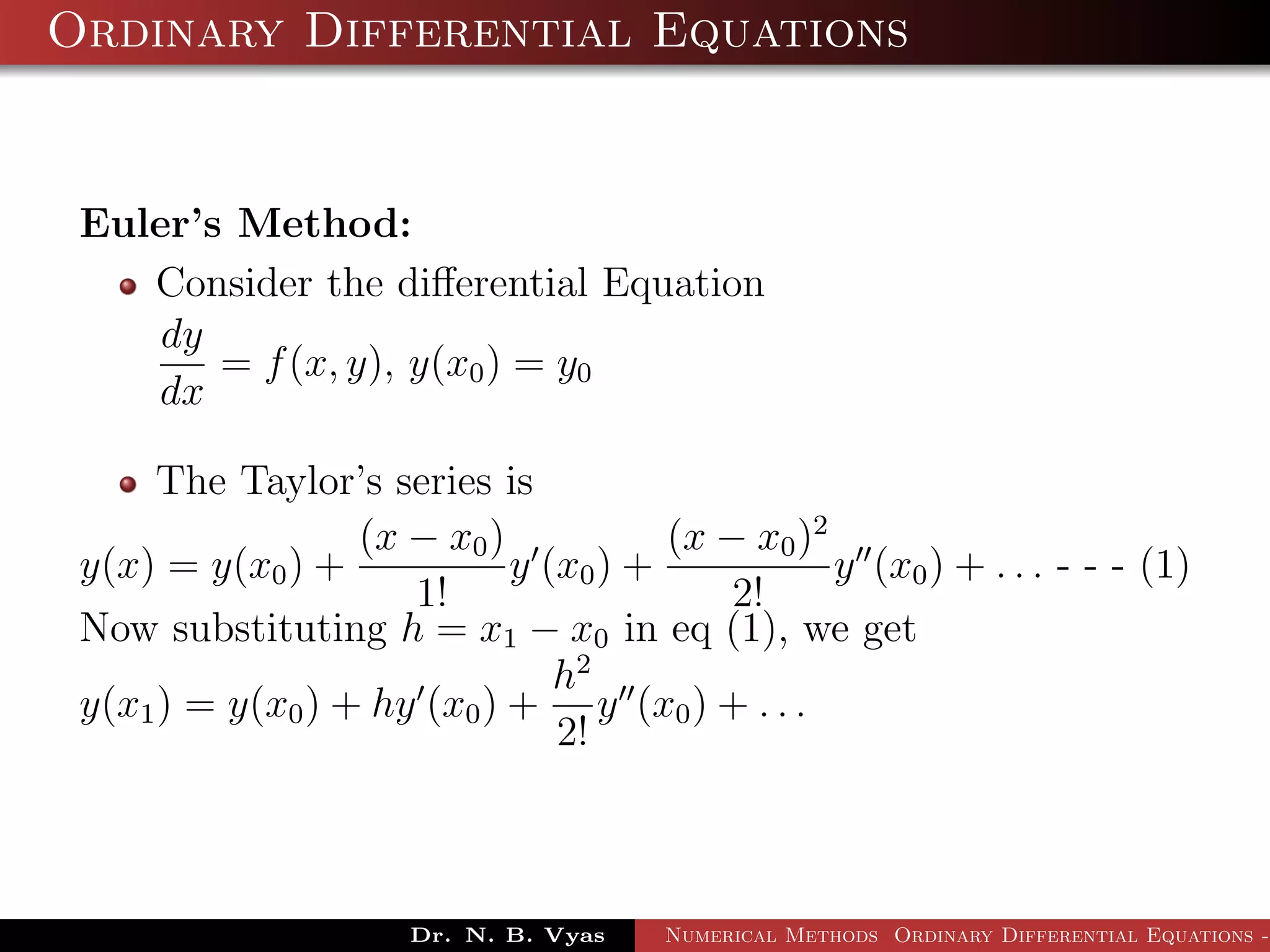
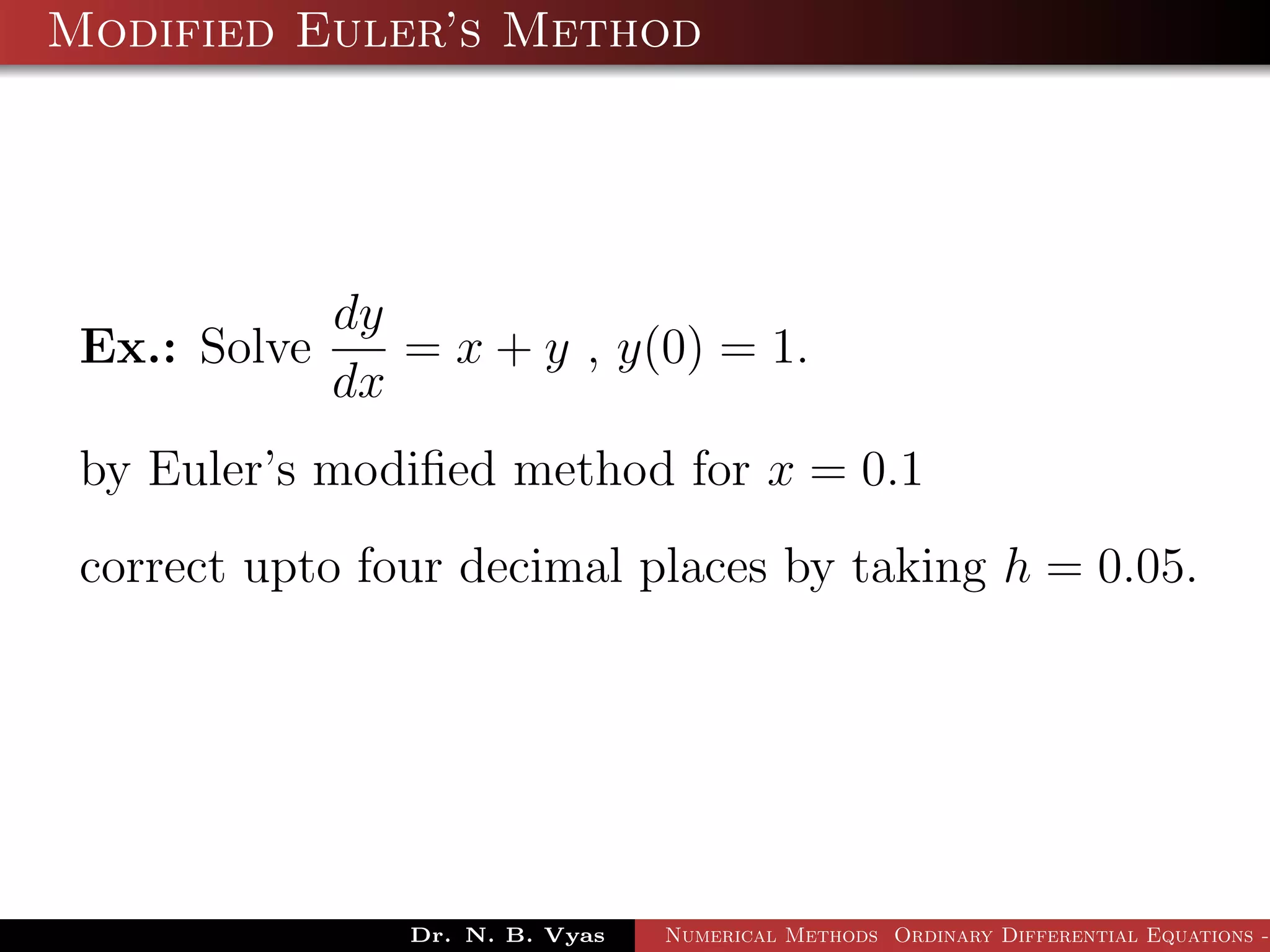
This document discusses Euler's method for solving ordinary differential equations numerically. It begins by considering the differential equation dy/dx = f(x,y), along with the initial condition y(x0) = y0. It then derives Euler's method by approximating the differential equation using the Taylor series expansion and neglecting higher order terms. The general step of Euler's method is given as yi+1 = yi + h*f(xi, yi), where h is the step size. Several examples are worked out applying Euler's method to solve initial value problems.































































































![Ordinary Differential Equations
Modified Euler’s Method:
By Euler’s method
y1 = y0 + hf(x0, y0)
For better approximation y
(1)
1 of y1, we take
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-100-2048.jpg)
![Ordinary Differential Equations
Modified Euler’s Method:
By Euler’s method
y1 = y0 + hf(x0, y0)
For better approximation y
(1)
1 of y1, we take
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
where x1 = x0 + h
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-101-2048.jpg)
![Ordinary Differential Equations
Modified Euler’s Method:
By Euler’s method
y1 = y0 + hf(x0, y0)
For better approximation y
(1)
1 of y1, we take
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
where x1 = x0 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
1 of y1,
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-102-2048.jpg)
![Ordinary Differential Equations
Modified Euler’s Method:
By Euler’s method
y1 = y0 + hf(x0, y0)
For better approximation y
(1)
1 of y1, we take
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
where x1 = x0 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
1 of y1,
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-103-2048.jpg)
![Ordinary Differential Equations
Modified Euler’s Method:
By Euler’s method
y1 = y0 + hf(x0, y0)
For better approximation y
(1)
1 of y1, we take
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
where x1 = x0 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
1 of y1,
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
we repeat this process till two consecutive values
of y agree.
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-104-2048.jpg)



![Modified Euler’s Method
Once y1 is obtained to desired degree of accuracy,
we find y2
y2 = y1 + hf(x1, y1)
For better approximation y
(1)
2 of y2, we take
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
where x2 = x1 + h
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-108-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
Once y1 is obtained to desired degree of accuracy,
we find y2
y2 = y1 + hf(x1, y1)
For better approximation y
(1)
2 of y2, we take
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
where x2 = x1 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
2 of y2,
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-109-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
Once y1 is obtained to desired degree of accuracy,
we find y2
y2 = y1 + hf(x1, y1)
For better approximation y
(1)
2 of y2, we take
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
where x2 = x1 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
2 of y2,
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(2)
2 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-110-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
Once y1 is obtained to desired degree of accuracy,
we find y2
y2 = y1 + hf(x1, y1)
For better approximation y
(1)
2 of y2, we take
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
where x2 = x1 + h
For still better approximation y
(2)
2 of y2,
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(2)
2 )
we repeat this step until y2 becomes stationary.
Then we proceed to calculate y3 in the same way
as above.
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-111-2048.jpg)






![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-119-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-120-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] = 1.0525
2nd approximation:
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-121-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] = 1.0525
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) +
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-122-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] = 1.0525
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-123-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] = 1.0525
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.0525)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-124-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.05)] = 1.0525
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
= 1 + 0.05
2 [(0 + 1) + (0.05 + 1.0525)] = 1.05256
∴ y1 = 1.05256 correct up to 4 decimal places.
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-125-2048.jpg)




![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-130-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
=
1.05256 + 0.05
2 [(0.05 + 1.05256) + (0.1 + 1.10769)]
=
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(1)
2 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-131-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
=
1.05256 + 0.05
2 [(0.05 + 1.05256) + (0.1 + 1.10769)]
=
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(1)
2 )
∴ y2 = .... correct up to 4 decimal places.
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-132-2048.jpg)






![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-139-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.2)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-140-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.2)] = 0.24214
2nd approximation:
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-141-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.2)] = 0.24214
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-142-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.2)] = 0.24214
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24214)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-143-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
1 = y0 +
h
2
[f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y1)]
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.2)] = 0.24214
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(1)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24214)] = 0.24635
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-144-2048.jpg)


![Modified Euler’s Method
3rd approximation:
y
(3)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24635)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-147-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
3rd approximation:
y
(3)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24635)] = 0.24678
4th approximation:
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-148-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
3rd approximation:
y
(3)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24635)] = 0.24678
4th approximation:
y
(4)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(3)
1 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-149-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
3rd approximation:
y
(3)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24635)] = 0.24678
4th approximation:
y
(4)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(3)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24678)] =
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-150-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
3rd approximation:
y
(3)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(2)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24635)] = 0.24678
4th approximation:
y
(4)
1 = y0 +
h
2
f(x0, y0) + f(x1, y
(3)
1 )
= 0 + 0.2
2 [f(0, 0) + f(0.2, 0.24678)] = 0.24681
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-151-2048.jpg)








![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-160-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
= 0.59687
2nd approximation:
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-161-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
= 0.59687
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(1)
2 )
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-162-2048.jpg)
![Modified Euler’s Method
1st approximation:
y
(1)
2 = y1 +
h
2
[f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y2)]
= 0.59687
2nd approximation:
y
(2)
2 = y1 +
h
2
f(x1, y1) + f(x2, y
(1)
2 )
=0.60251
Dr. N. B. Vyas Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmode2-160210054831/75/Numerical-Methods-Oridnary-Differential-Equations-2-163-2048.jpg)






